Finance
How To Teach Budgeting
Published: October 11, 2023
Learn how to teach budgeting and financial management skills with our comprehensive guide. Discover effective strategies and resources to empower individuals to take control of their finances.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Learning how to budget is a crucial life skill that can have a significant impact on our financial wellbeing. Yet, many people struggle with managing their finances effectively. The key to teaching budgeting lies in providing individuals with the knowledge and tools they need to make informed financial decisions.
Budgeting involves understanding and tracking income and expenses, setting financial goals, prioritizing expenses, saving and investing, and regularly reviewing and adjusting budgets. By teaching budgeting skills, we empower individuals to take control of their financial lives, reduce debt, and work towards achieving their financial goals.
In this article, we will explore a step-by-step approach to teaching budgeting that can be used by educators, parents, or anyone interested in helping others develop healthy financial habits. Each step will focus on a specific aspect of budgeting and provide practical tips and strategies for implementation.
By following this comprehensive guide, you can equip individuals with the necessary tools to make sound financial decisions, manage their money effectively, and work towards a more secure financial future.
Step 1: Setting Financial Goals
The first step in teaching budgeting is helping individuals define and set their financial goals. Setting clear and realistic goals provides a sense of purpose and motivation for managing money effectively. By having specific objectives in mind, individuals are more likely to stay committed and focused on their financial journey.
To assist individuals in setting financial goals, start by encouraging them to think about their short-term, medium-term, and long-term aspirations. Short-term goals may include paying off credit card debt, while medium-term goals could involve saving for a down payment on a house. Long-term goals might include saving for retirement or a child’s education.
Once the goals are identified, it’s essential to help individuals set specific and measurable targets. For example, instead of simply aiming to save money, the goal could be to save $500 per month or to pay off $5,000 in debt within a year. Specific goals make it easier to track progress and evaluate success.
Furthermore, it’s crucial to emphasize the importance of creating realistic goals. Setting unattainable targets can lead to frustration and demotivation. Encourage individuals to consider their current financial situation and capabilities when establishing goals.
Lastly, it can be beneficial to discuss the why behind each goal. Understanding the underlying reasons can provide individuals with a stronger sense of purpose and determination. For example, someone might want to save for a dream vacation as a way to reward themselves for their hard work and financial discipline.
Teaching individuals to set financial goals lays the foundation for effective budgeting. By helping them define their aspirations, make them measurable, keep them realistic, and understand their motivations, we empower them to take control of their financial future.
Step 2: Tracking Income and Expenses
One of the key elements of successful budgeting is understanding where money comes from and where it goes. Teaching individuals to track their income and expenses is essential for gaining clarity and control over their finances.
Start by explaining the importance of tracking income. Income is not only limited to regular paychecks but can also include side hustles, freelance work, dividends, or any other sources of income. Encourage individuals to keep a record of all their income sources, whether it’s through a spreadsheet, budgeting app, or a dedicated notebook.
Next, move on to tracking expenses. Explain that expenses encompass all the money spent on various categories such as housing, transportation, groceries, entertainment, and more. Discuss the importance of keeping receipts or using digital tools like expense tracking apps to record every expense accurately.
Teaching individuals to track their income and expenses offers several benefits. Firstly, it provides an accurate picture of their financial habits and spending patterns. By analyzing this information, individuals can identify areas where they may be overspending or areas where they can make adjustments to save more.
Tracking income and expenses also helps individuals identify recurring expenses, such as subscriptions or monthly bills, which can sometimes be overlooked. This awareness allows for better planning and decision-making when it comes to budgeting.
Furthermore, tracking income and expenses facilitates tracking progress towards financial goals. By comparing income and expenses to the established targets, individuals can determine whether they’re on track and make necessary adjustments if needed.
Encourage individuals to make tracking income and expenses a regular habit. Suggest setting aside time each week or month to review and update the records. Consistency is key to maintaining an accurate and up-to-date financial snapshot.
By teaching individuals to track their income and expenses, we equip them with the tools to gain control over their financial situation. This step is crucial for creating a foundation of knowledge and understanding that will support effective budgeting and decision-making.
Step 3: Creating a Budget
A budget is a financial roadmap that helps individuals allocate their money wisely and prioritize their expenses. Teaching individuals how to create a budget is an essential step in effective financial management.
Start by explaining the purpose of a budget – to plan and allocate income in a way that aligns with financial goals. Emphasize the importance of tracking income and expenses from the previous step to ensure accuracy and completeness in the budgeting process.
When teaching individuals to create a budget, encourage them to start with their income. Have them list all sources of income and their corresponding amounts. This provides a clear picture of their total available funds.
Next, move on to expenses. Help individuals list and categorize their expenses, such as housing, transportation, groceries, utilities, debt payments, and discretionary spending. It’s important to ensure that all expenses are included and accounted for.
Once the income and expenses are identified, guide individuals in comparing the two to determine whether there is a surplus or a deficit. If there is a surplus, discuss the importance of allocating funds towards financial goals, such as saving or investing. If there is a deficit, help individuals identify areas where they can cut back or make adjustments to balance their budget.
It’s important to note that creating a budget is not about deprivation or restricting spending. Rather, it’s about making intentional choices with money and ensuring that expenses align with financial priorities.
Encourage individuals to review and adjust their budget regularly. Life circumstances and financial goals may change, requiring modifications to the budget. Consistent monitoring and evaluation are essential for maintaining a budget that reflects current needs and aspirations.
Lastly, provide resources and tools that can assist individuals in creating and managing their budget. These may include budgeting apps, spreadsheets, or templates that simplify the process and offer automation and visualization of financial data.
Teaching individuals to create a budget empowers them to take control of their financial resources and make conscious decisions about how to allocate them. It sets the stage for effective financial planning and allows individuals to make progress towards their financial goals.
Step 4: Prioritizing Expenses
Prioritizing expenses is a crucial step in budgeting that helps individuals allocate their limited financial resources effectively. By determining which expenses are most important, individuals can ensure they are using their money in a way that aligns with their financial goals and values.
When teaching individuals to prioritize expenses, emphasize the importance of identifying needs versus wants. Needs are essential expenses required for basic living, such as housing, utilities, food, and healthcare. Wants, on the other hand, are discretionary expenses that are not essential for survival, such as entertainment, vacations, and luxury items.
Make it clear to individuals that satisfying needs should be the top priority when budgeting. Encourage them to allocate enough funds to cover these essential expenses first before moving on to discretionary expenses.
Once needs are addressed, guide individuals in prioritizing their wants. Help them identify which wants are most important and align with their values and long-term financial goals. For example, saving for a down payment on a house or investing in education might take precedence over dining out or purchasing new gadgets.
Teaching individuals to prioritize expenses also involves discussing trade-offs. Help them understand that by choosing to spend money on one thing, they may have to forego spending on something else. This encourages individuals to make conscious decisions and think about the long-term impact of their spending choices.
Encourage individuals to periodically reassess their priorities as their circumstances and goals change. Flexibility is key in ensuring that expenses remain aligned with their ever-evolving financial situation.
Additionally, provide guidance on strategies to manage and reduce expenses. This could include tips for negotiating bills, comparison shopping, or finding ways to cut back on discretionary spending.
By teaching individuals to prioritize expenses, we empower them to make intentional and informed decisions about how they allocate their financial resources. This step ensures that their money is being used in a way that supports their financial goals and values, leading to a more secure and fulfilling financial future.
Step 5: Saving and Investing
Saving and investing are vital components of a well-rounded financial plan. Teaching individuals how to save and invest their money effectively is essential for building wealth, achieving financial goals, and preparing for the future.
Start by discussing the importance of saving. Explain that saving involves setting aside a portion of income for future use. Emphasize the benefits of having an emergency fund, which serves as a financial safety net for unexpected expenses or income disruptions.
Encourage individuals to determine a specific amount or percentage of their income to save each month. This could range from 10% to 20%, depending on their financial situation and goals. Discuss the concept of “paying yourself first,” where individuals prioritize saving by automatically transferring money to a dedicated savings account or investment vehicle before spending on other expenses.
Teach individuals about different types of savings accounts and investment options. Explain the benefits of high-yield savings accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs), or other low-risk vehicles for short-term savings goals. Introduce the concept of compound interest and the potential for higher returns associated with long-term investments such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, or retirement accounts like IRAs or 401(k)s.
Guide individuals in deciding where to allocate their savings based on their risk tolerance, time horizon, and financial goals. Help them understand the importance of diversification and spreading investments across different asset classes to mitigate risk.
Furthermore, discuss the benefits of regularly reviewing and adjusting investment portfolios. Explain the concept of rebalancing and how it helps maintain a desired asset allocation over time.
Teaching individuals to save and invest also involves discussing the role of compound interest and the power of starting early. Help them understand that even small contributions made consistently over time can have a significant impact on long-term wealth accumulation.
Encourage individuals to seek professional advice, especially when it comes to complex investment decisions. Explain the importance of conducting research, understanding fees and costs associated with investments, and staying informed about market trends and economic indicators.
By teaching individuals to save and invest wisely, we empower them to grow their wealth, build financial security, and work towards achieving their long-term financial goals. This step is crucial for ensuring financial stability and preparing for a comfortable future.
Step 6: Teaching Money Management Techniques
Teaching individuals effective money management techniques is essential for developing good financial habits and ensuring long-term financial success. By equipping them with practical strategies and tools, we empower individuals to make informed decisions and take control of their financial lives.
Start by teaching the importance of budgeting and tracking expenses, as discussed in earlier steps. Emphasize the need to stay organized and regularly review financial records. Introduce various budgeting methods, such as the 50/30/20 rule (allocating 50% of income to needs, 30% to wants, and 20% to savings) or the envelope system (assigning cash to specific categories).
Introduce the concept of mindful spending and decision-making. Encourage individuals to pause and evaluate whether a purchase aligns with their values and financial goals before making it. Discuss strategies for avoiding impulse buying, such as implementing a waiting period or creating a spending plan for discretionary expenses.
Teach individuals about the importance of building and maintaining good credit. Explain how credit scores are calculated, the impact of credit on borrowing costs, and strategies for improving creditworthiness. Discuss the responsible use of credit cards, the importance of making timely payments, and monitoring credit reports for inaccuracies.
Introduce the concept of debt management. Teach individuals about different types of debt and the importance of distinguishing between good debt (such as a mortgage for a home) and bad debt (such as high-interest credit card debt). Discuss strategies for paying off debt, such as the debt avalanche method (paying off high-interest debt first) or the debt snowball method (paying off small balances first for a sense of achievement).
Encourage individuals to establish an emergency fund to prepare for unexpected expenses. Teach them the importance of saving three to six months’ worth of living expenses in a separate account that is easily accessible.
Discuss strategies for saving on everyday expenses. Teach individuals to compare prices, look for discounts and deals, and negotiate bills. Provide tips on energy-saving practices, meal planning, and reducing wasteful spending.
Lastly, encourage ongoing financial education. Recommend books, podcasts, and online resources that can help individuals expand their knowledge and stay informed about personal finance topics. Encourage them to continue learning and seeking guidance to adapt to changing economic conditions and new financial challenges.
By teaching individuals money management techniques, we provide them with the tools and knowledge needed to make informed financial decisions. These techniques form the basis for building a solid financial foundation and achieving long-term financial stability.
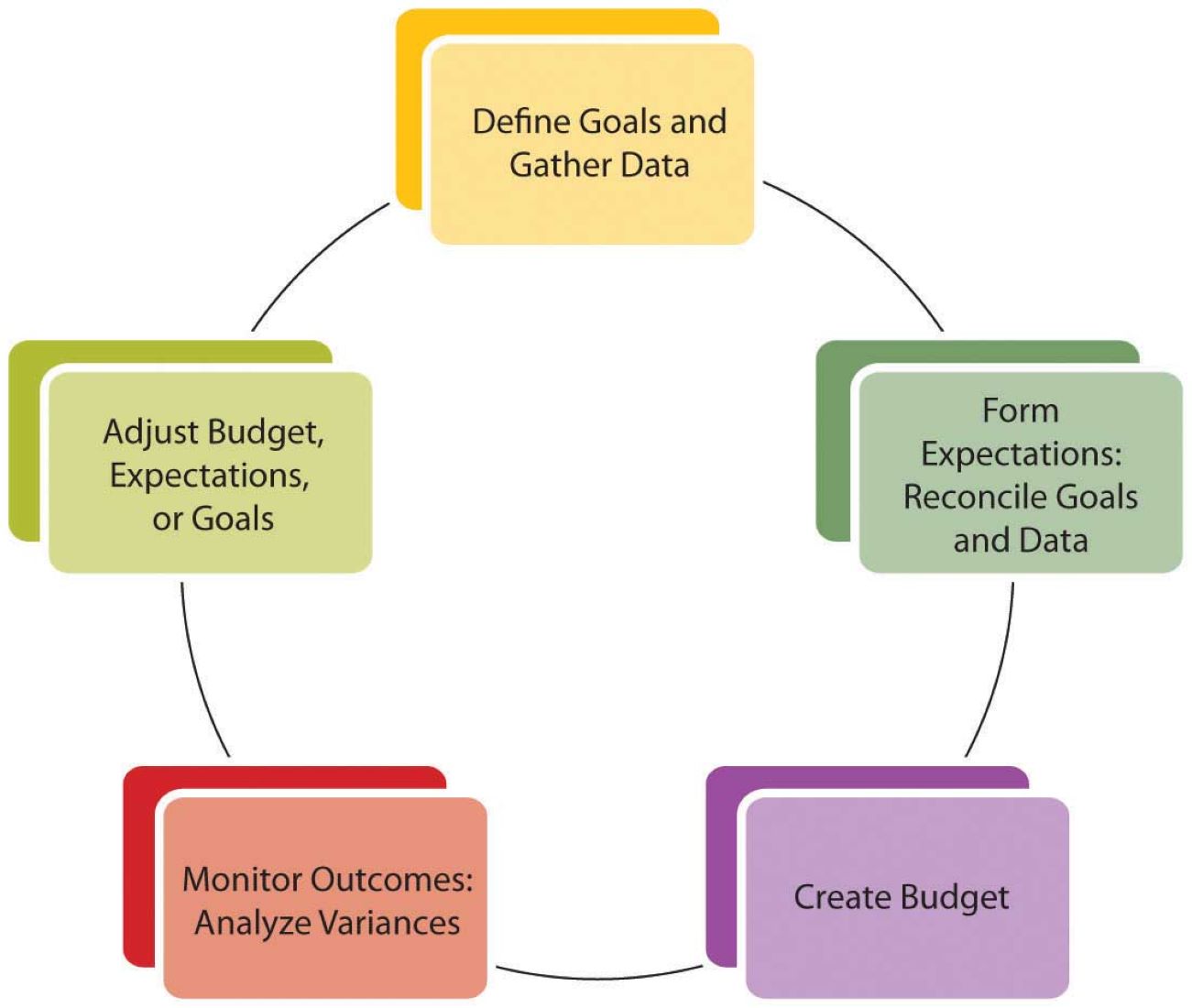
Step 7: Reviewing and Adjusting Budgets
Regularly reviewing and adjusting budgets is a critical step in the budgeting process. It ensures that individuals stay on track with their financial goals and make necessary changes based on evolving circumstances or priorities.
Emphasize the importance of conducting periodic budget reviews. Encourage individuals to set aside time at least once a month to evaluate their budget and financial progress. During this review, they should assess their income, expenses, and savings against their established targets and goals.
Guide individuals in analyzing their spending habits and identifying areas where adjustments may be necessary. This could involve cutting back on discretionary expenses, renegotiating bills or subscriptions, or finding creative ways to reduce costs.
Encourage individuals to assess whether their financial goals have changed or if they need to reprioritize their expenses. Life circumstances, such as a job change, the birth of a child, or an unexpected event, may require adjustments to the budget to accommodate new financial needs.
Teach individuals to be proactive in seeking opportunities to save or earn more money. This might involve exploring ways to increase income through side hustles, negotiation for salary raises, or seeking investment and passive income opportunities.
Reiterate the importance of tracking and recording expenses to ensure accuracy during budget reviews. Advise individuals to use budgeting apps, spreadsheets, or dedicated notebooks to maintain an easy-to-access record of their financial transactions.
Encourage individuals to celebrate their successes and motivation to continue their financial journey. Recognize achievements, such as reaching savings milestones or paying off debts, to provide a sense of accomplishment and reinforce positive financial behaviors.
Discuss the potential need to seek professional advice in certain situations. Individuals may benefit from consulting financial advisors, accountants, or experts in specific fields to get specialized guidance and support.
Finally, stress the importance of perseverance and resilience. Financial journeys can have ups and downs, and setbacks are part of the process. Encourage individuals to learn from mistakes, adjust their strategies, and stay committed to their financial goals.
By teaching individuals to regularly review and adjust their budgets, we empower them to adapt to changing circumstances and stay on the path to financial success. This step ensures that their financial plans remain relevant, effective, and aligned with their evolving needs and goals.
Conclusion
Teaching budgeting is a vital skill that empowers individuals to take control of their financial lives and work towards their financial goals. By following the step-by-step approach outlined in this guide, individuals can develop healthy financial habits and make informed decisions with their money.
Setting financial goals forms the foundation of effective budgeting. By defining specific objectives and understanding the motivations behind them, individuals gain purpose and direction in their financial journey.
Tracking income and expenses provides a clear picture of where money is coming from and where it is being spent. This awareness helps individuals make informed decisions, identify areas for improvement, and stay on top of their financial situation.
Creating a budget is a crucial step in allocating funds according to priorities. By establishing a plan for income and expenses, individuals can ensure that their money is being used in a way that aligns with their financial goals and values.
Prioritizing expenses involves distinguishing between needs and wants, making conscious choices, and understanding trade-offs. This step helps individuals focus their financial resources on what matters most and avoid unnecessary or impulsive spending.
Saving and investing are key components of building wealth and securing a strong financial future. By teaching individuals about different saving options and investment strategies, we equip them with the tools to make their money work for them.
Teaching money management techniques provides individuals with practical strategies and habits to effectively manage their finances. By instilling good financial practices, such as budgeting, mindful spending, and debt management, individuals can make wise financial decisions and navigate through various financial challenges.
Finally, regularly reviewing and adjusting budgets ensures that financial plans remain relevant and effective. By adapting to changing circumstances and priorities, individuals can stay on track towards their financial goals and make necessary changes to their spending and savings patterns.
Overall, teaching budgeting is about providing individuals with the knowledge, skills, and confidence to take control of their financial future. By incorporating these steps into your teachings, you can empower individuals to make informed financial decisions, reduce financial stress, and work towards a more secure and prosperous future.