Home>Finance>When Does The Budgeting Phase Of The Budget Cycle Begin

Finance
When Does The Budgeting Phase Of The Budget Cycle Begin
Published: October 10, 2023
Learn when the budgeting phase of the budget cycle begins and gain insights into financial planning and management. Explore finance topics and strategies.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of budgeting and the budget cycle! In the realm of finance, effective budgeting is a critical process that allows organizations and individuals to plan, allocate resources, and achieve financial goals. The budget cycle is a systematic approach that encompasses various phases, each serving a specific purpose in the financial planning and control process.
Through careful analysis and forecasting, the budget cycle helps in determining how financial resources should be allocated, enabling organizations to make informed decisions about spending and revenue generation. One essential phase of this cycle is the budgeting phase, which marks the beginning of the budget cycle.
During the budgeting phase, organizations engage in comprehensive planning and preparation, setting the stage for the development of an effective budget. It is a crucial step that lays the foundation for financial success and guides decision-making processes throughout the budget cycle.
This article will delve into the intricacies of the budgeting phase, exploring its significance, key initiatives, typical timeline, and challenges faced. By understanding the nuances of this phase and the factors that influence its start, individuals and organizations can navigate the budget cycle with confidence and precision.
Definition of the Budget Cycle
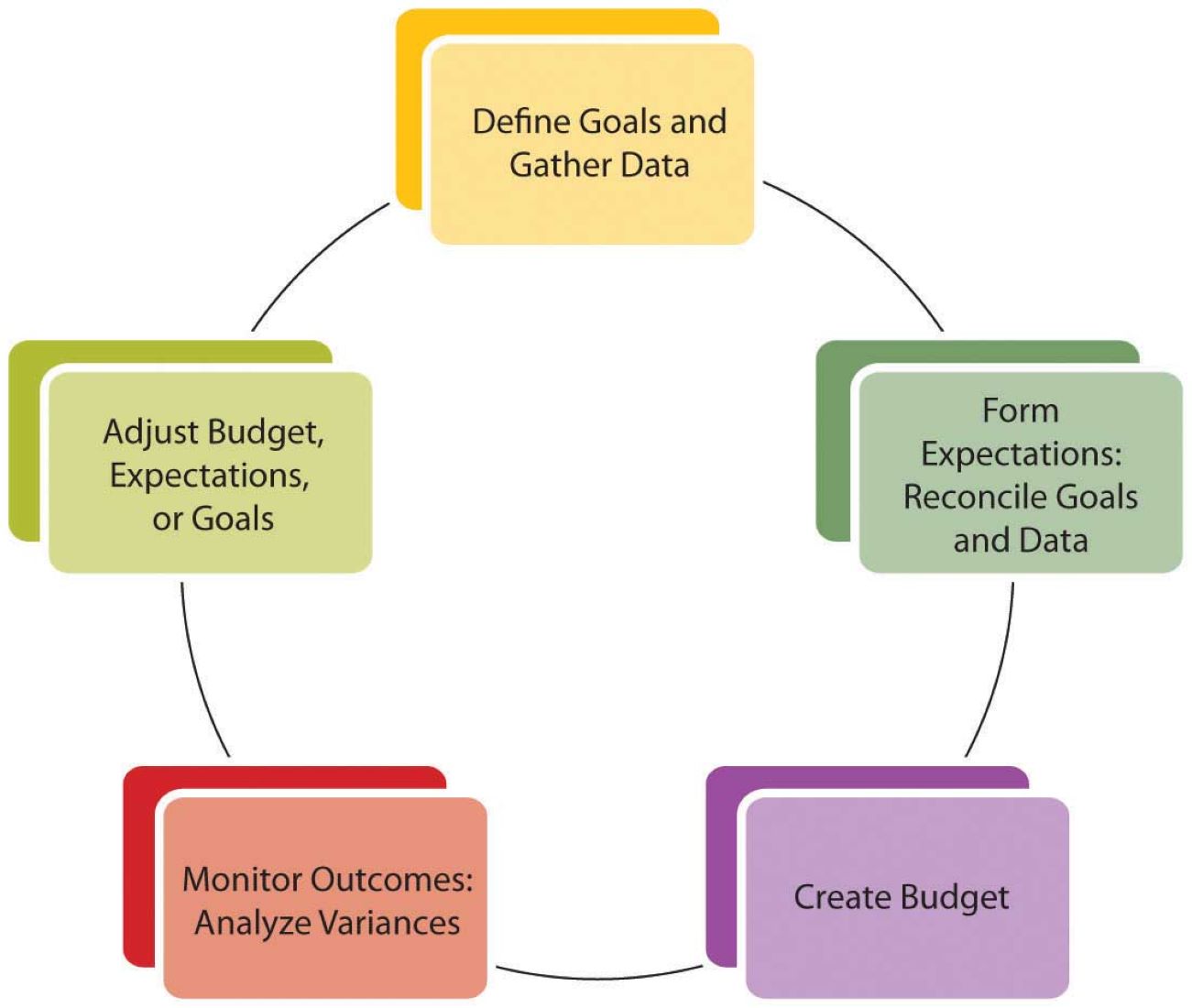
The budget cycle refers to the series of steps or phases that organizations go through to effectively plan, execute, monitor, and evaluate their financial activities. It is a continuous process that helps in managing financial resources efficiently while aligning them with the overall strategic objectives of the organization.
The budget cycle typically consists of several interconnected phases, each serving a specific purpose in the overall financial planning and control process. These phases include budget preparation, budget review and approval, budget execution, and budget monitoring and evaluation.
1. Budget Preparation: The budget preparation phase involves identifying and estimating the financial needs and resources of an organization for a specific period, usually a year. This includes gathering financial data, analyzing historical trends, and forecasting future expenses, revenues, and investments. During this phase, organizations set financial goals, establish budgetary guidelines, and allocate resources to various departments and projects.
2. Budget Review and Approval: Once the budget is prepared, it goes through a review and approval process. Stakeholders, such as senior management and the finance department, carefully examine the budget to ensure it aligns with the organizational objectives and financial constraints. Adjustments may be made at this stage to address any discrepancies or optimize resource allocation.
3. Budget Execution: After the budget is approved, the budget execution phase begins. This involves the implementation of the budget, including the allocation of funds to different activities, projects, and departments. It is crucial to closely monitor expenses and revenue inflows during this phase to ensure compliance with the budgeted figures.
4. Budget Monitoring and Evaluation: The budget monitoring and evaluation phase is an ongoing process that assesses the actual performance against the budget. It involves regular tracking of financial transactions, comparing actual results with budgeted figures, and making any necessary adjustments to ensure financial stability and meet organizational goals.
By following the budget cycle, organizations can maintain financial discipline, improve decision-making, and measure their financial performance. It provides a structured approach to budgeting and ensures that organizations have a clear understanding of their financial resources and how they are being utilized.
Importance of the Budgeting Phase
The budgeting phase is a vital component of the budget cycle, playing a crucial role in the financial planning and control process. It serves as the foundation for effective budget management and guides decision-making processes throughout the organization. Here are some key reasons why the budgeting phase is important:
- Strategic Planning: The budgeting phase allows organizations to align their financial goals with overall strategic objectives. By carefully planning and allocating resources, organizations can prioritize key initiatives and allocate funds to areas that will drive growth and success.
- Resource Allocation: Through the budgeting phase, organizations can determine how resources, including financial, human, and technological, should be allocated. It helps in optimizing the utilization of available resources by identifying priority areas and minimizing wasteful expenditures.
- Financial Discipline: The budgeting phase promotes financial discipline within organizations. By setting budgetary limits and guidelines, it helps in controlling expenses and ensures that spending remains within predefined limits. It also enables organizations to identify potential areas for cost savings and efficiency improvements.
- Performance Evaluation: The budgeting phase provides a benchmark against which actual performance can be evaluated. By comparing actual results with budgeted figures, organizations can identify variations and take corrective actions if necessary. It helps in assessing the effectiveness of financial management practices and supports continuous improvement.
- Decision Making: The budgeting phase provides valuable insights for decision-making processes within organizations. It helps in evaluating the financial implications of different options and supports informed decision-making. It also enables organizations to prioritize projects, investments, and activities based on their expected impact and alignment with strategic objectives.
Overall, the budgeting phase is crucial for effective financial management and control. It empowers organizations to plan strategically, allocate resources efficiently, maintain financial discipline, evaluate performance, and make informed decisions. By going through this phase diligently, organizations can enhance their financial stability, achieve their goals, and drive sustainable growth.
Factors Influencing the Start of the Budgeting Phase
The start of the budgeting phase can be influenced by various factors that vary from one organization to another. These factors shape the timeline and process of budgeting and help determine when the budgeting phase should begin. Here are some key factors that can influence the start of the budgeting phase:
- Organizational Goals and Strategies: The start of the budgeting phase is heavily influenced by the goals, strategies, and objectives of the organization. If the organization operates on a fiscal year basis, the budgeting phase typically begins well in advance of the upcoming fiscal year to align with strategic planning cycles.
- Economic Conditions: External economic factors can significantly impact the timing of the budgeting phase. Organizations may choose to delay or advance the start of the budgeting phase based on the prevailing economic conditions, such as changes in interest rates, inflation rates, or market downturns.
- Industry and Market Dynamics: Different industries and markets have varying levels of volatility and uncertainty. Organizations operating in highly competitive or rapidly changing industries might initiate the budgeting phase earlier to proactively respond to market fluctuations and maintain a competitive edge.
- Regulatory Requirements: Some industries are subjected to specific regulatory requirements, such as submitting annual budgets or complying with governmental fiscal regulations. These requirements can influence the start of the budgeting process, ensuring organizations meet legal obligations or regulatory deadlines.
- Internal Stakeholder Alignment: In organizations with multiple departments or divisions, it is vital to align internal stakeholders’ schedules and priorities. The budgeting phase may be delayed until stakeholders, such as department heads or key decision-makers, are available for collaborative discussions, reviews, and approvals.
- Data Availability: The budgeting phase heavily relies on accurate and up-to-date financial and operational data. Organizations may need to wait until all relevant data, such as historical financial records, market research, or sales projections, are available to ensure the budgeting process is based on reliable and comprehensive information.
- Organizational Size and Complexity: The size and complexity of an organization can impact the duration of the budgeting process. Larger organizations with more departments and complex operations may require more time for data collection, analysis, and consolidation, leading to an earlier start of the budgeting phase.
It is essential for organizations to consider these factors when determining the start of the budgeting phase. By understanding these influences and adapting the budgeting process accordingly, organizations can ensure a smooth and effective budgeting phase that aligns with their unique needs and circumstances.
Typical Timeline for the Budgeting Phase
The timeline for the budgeting phase can vary depending on the organization’s size, industry, and internal processes. However, there are certain common stages and durations that can be observed in a typical budgeting cycle. Here is a general overview of the typical timeline for the budgeting phase:
- Pre-Budgeting Preparation: This stage involves gathering and analyzing financial and operational data from various departments and stakeholders. It generally starts several months before the budgeting phase itself to ensure all necessary information is available for informed decision-making.
- Budget Kick-Off: The budgeting phase officially begins with a kick-off meeting, where key stakeholders and budget owners come together to discuss goals, objectives, and budget guidelines. This meeting sets the tone for the entire process and ensures everyone is aligned on the budgeting expectations and timelines.
- Budget Drafting: During this stage, budget owners and department heads work on developing their budget proposals based on the provided guidelines. They consider various factors, including historical data, market trends, departmental needs, and strategic objectives. This process typically takes a few weeks.
- Budget Review and Negotiation: Once the initial budgets are drafted, they go through a review and negotiation process. This involves meetings, discussions, and sometimes revisions to align the budgets with overall organizational goals and financial constraints. This stage can take several weeks, depending on the number of stakeholders involved and the complexity of the organization.
- Budget Approval: After the review and negotiation stage, the final budget proposal is presented to top management or a budget committee for approval. This stage usually takes place towards the end of the budgeting phase, as it requires thorough evaluation and consideration. The approval process may range from a few days to several weeks.
- Budget Implementation: Once the budget is approved, it is ready to be implemented. The budgeted figures are communicated to relevant departments and actions are taken to allocate resources accordingly. The implementation stage marks the transition from the budgeting phase to the budget execution phase.
The duration of each stage can vary depending on the complexity of the organization and the decision-making processes involved. Some organizations may complete the budgeting phase within a few months, while others, especially larger enterprises, may require several months or even a year to complete the process.
It is important for organizations to set realistic timelines and allow sufficient time for each stage to ensure thorough planning, accurate budgeting, and stakeholder engagement. By adhering to a typical timeline and adjusting it to suit their specific needs, organizations can effectively navigate the budgeting phase and set themselves up for financial success.
Key Initiatives during the Budgeting Phase
The budgeting phase involves several key initiatives that direct and shape the overall budget planning process. These initiatives are aimed at ensuring effective resource allocation, aligning with organizational goals, and facilitating informed decision-making. Here are some of the key initiatives that take place during the budgeting phase:
- Goal Setting: During the budgeting phase, organizations set their financial goals and objectives for the upcoming period. This includes determining revenue targets, expense reduction goals, profitability targets, and other financial metrics that align with the overall strategic plan.
- Forecasting and Projection: Accurate forecasting and projection play a crucial role in the budgeting phase. Organizations analyze historical data, market trends, and economic factors to estimate future revenues, expenses, and cash flow. This helps in setting realistic budgetary figures and identifying areas that require special attention.
- Cost and Revenue Analysis: Organizations analyze their cost structures and revenue streams to identify areas for cost reduction, revenue growth, and profitability improvement. This analysis enables them to allocate resources efficiently, prioritize initiatives, and identify potential risks and challenges.
- Departmental Budgeting: Departmental heads and managers actively participate in the budgeting phase by preparing their departmental budgets. They evaluate their needs, resources, and strategic objectives, along with considering the organization’s budgetary guidelines. This collaboration ensures that departmental budgets align with overall organizational goals and financial constraints.
- Capital Expenditure Planning: The budgeting phase includes planning for capital expenditures, such as infrastructure development, equipment purchase, or technology investments. Organizations assess the need for such investments, evaluate the financial viability, and allocate resources accordingly to ensure long-term growth and efficiency.
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Organizations identify and assess potential risks and uncertainties that could impact the budget. This includes factors such as market fluctuations, regulatory changes, or operational risks. Risk mitigation strategies are developed to minimize the impact of these risks on the budget and overall financial stability.
- Communication and Collaboration: Effective communication and collaboration are crucial during the budgeting phase. Stakeholders, including top management, department heads, and finance teams, work together to exchange information, ensure transparency, and gain consensus on budgetary decisions. This collaborative approach fosters alignment, engagement, and commitment throughout the organization.
These key initiatives contribute to the development of a comprehensive and well-rounded budget. By focusing on these initiatives during the budgeting phase, organizations can enhance financial performance, optimize resource allocation, and achieve their strategic objectives.
Challenges and Considerations in the Budgeting Phase
The budgeting phase, like any complex process, presents its fair share of challenges and considerations. These challenges can impact the accuracy of the budget, the effectiveness of resource allocation, and the overall success of the budgeting process. Here are some common challenges and considerations in the budgeting phase:
- Data Accuracy and Availability: Obtaining accurate and reliable financial and operational data is crucial for effective budgeting. Organizations may face challenges in accessing accurate data or ensuring the timeliness of data collection. Data integrity issues can lead to budgeting inaccuracies and decision-making based on faulty information.
- Uncertain Economic Environment: A volatile or uncertain economic environment can pose challenges in the budgeting phase. Factors such as fluctuating exchange rates, interest rates, or market conditions can make forecasting and revenue estimation difficult, affecting the accuracy of budget projections.
- Cross-Functional Coordination: Budgeting requires collaboration and coordination among multiple departments and stakeholders. Ensuring effective communication, agreement on priorities, and consensus on resource allocation can be challenging, especially in large organizations with decentralized decision-making processes.
- Changing Business Conditions: Businesses operate in a dynamic environment, and conditions can change rapidly. Mid-budget cycle changes in market conditions, industry dynamics, or technological advancements can disrupt the budget. Flexibility and the ability to adapt to changing circumstances are key considerations in the budgeting phase.
- Minimal Margin for Error: Budgets are critical financial plans, and accuracy is paramount. Setting unrealistic goals, underestimating expenses, or overestimating revenues can lead to budget shortfalls or inadequate resource allocation. Careful consideration and analysis are necessary to minimize margin for error in the budgeting phase.
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating risks is a key consideration during budgeting. Uncertainties in the global economy, regulatory changes, or competitive pressures can impact budget assumptions. Organizations need to evaluate potential risks and develop contingency plans to ensure budgetary stability and resilience.
- Long-Term Perspective: Balancing short-term goals with long-term objectives is a challenge in the budgeting phase. Organizations need to consider investments and strategic initiatives that may have long-term payoffs but require upfront costs. Striking the right balance between short-term profitability and long-term growth is a key consideration.
Despite these challenges, organizations can overcome them by carefully considering these factors during the budgeting phase. Ensuring data accuracy, incorporating flexibility, fostering collaboration, and monitoring external market conditions can help organizations navigate these challenges and achieve successful budget outcomes.
Conclusion
The budgeting phase is a critical part of the budget cycle, playing a pivotal role in effective financial planning and control. It sets the stage for resource allocation, decision-making, and goal achievement within organizations. By understanding the importance of the budgeting phase, organizations can optimize their financial resources and drive sustainable growth.
Throughout the budgeting phase, various factors influence its start, including organizational goals, economic conditions, and industry dynamics. Aligning the budgeting process with these factors ensures relevance and effectiveness in financial planning.
The typical timeline for the budgeting phase consists of various stages, including pre-budgeting preparation, budget drafting, review and approval, and budget implementation. Organizations should allow ample time at each stage to ensure comprehensive planning, accurate budgeting, and stakeholder collaboration.
During the budgeting phase, key initiatives such as goal setting, forecasting, cost analysis, and communication drive the budgeting process. These initiatives enable organizations to allocate resources efficiently, mitigate risks, and make informed decisions.
However, challenges such as data accuracy, uncertain economic environments, and cross-functional coordination must be considered and overcome to ensure successful budget outcomes. Organizations need to be agile and adaptable, taking into account changing business conditions and prioritizing long-term objectives alongside short-term goals.
In conclusion, the budgeting phase is a critical component of effective financial management. By incorporating the key initiatives, considering the challenges, and aligning the budgeting process with organizational goals, organizations can navigate the budgeting phase with confidence, achieve financial stability, and drive sustainable growth.