Home>Finance>Option Premium: Definition, Factors Affecting Pricing, And Example


Finance
Option Premium: Definition, Factors Affecting Pricing, And Example
Published: January 4, 2024
Learn about option premiums and their definition, factors influencing pricing, and example in the world of finance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Option Premium: Definition, Factors Affecting Pricing, and Example
Welcome to our finance category! Today, we will dive into the fascinating world of option premium. If you’ve heard about options but aren’t quite sure what makes up their value, you’ve come to the right place. In this blog post, we will explore the definition of option premium, discuss the factors that affect its pricing, and provide you with a practical example to help solidify your understanding. So, let’s get started!
Key Takeaways:
- Option premium is the price an investor pays to obtain an option contract.
- Factors such as volatility, time to expiration, underlying asset price, and interest rates influence option premium.
What is Option Premium?
Before we venture into the factors that impact option premium, let’s establish a clear definition. Option premium refers to the price an investor pays for the privilege of holding an option contract. In simpler terms, it is the cost of acquiring the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price (known as the strike price) within a specific timeframe.
The value of option premium is driven by various factors that we’ll explore in a moment. But why is this important? Well, understanding these factors can help investors make informed decisions when buying or selling options, enabling them to assess the potential for profit or risk effectively.
Factors Affecting Pricing of Option Premium:
Now that we understand the basic concept of option premium, let’s delve into the key factors that influence its pricing:
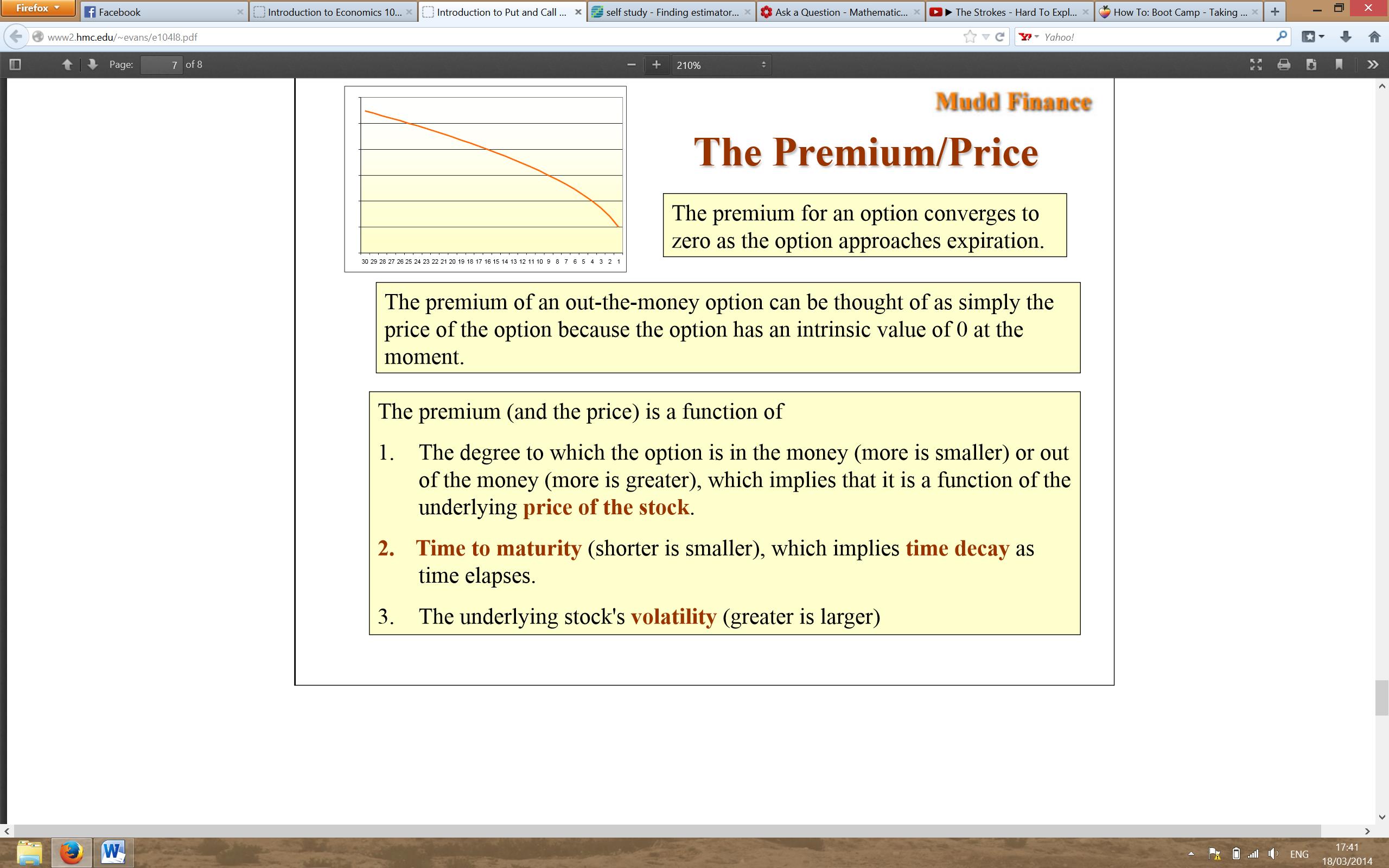
- Volatility: Option prices tend to rise with increased market volatility. Higher volatility implies greater potential price fluctuations for the underlying asset, which translates into higher risk and, consequently, higher option premium.
- Time to Expiration: The more time remaining until an option expires, the greater the potential for the underlying asset’s price to move in a favorable direction. Therefore, options with more extended durations tend to have higher premiums compared to those near expiration.
- Underlying Asset Price: The price of the underlying asset plays a crucial role in option premium. For call options (which provide the right to buy), the higher the asset’s price relative to the strike price, the higher the premium. Conversely, for put options (which provide the right to sell), the lower the asset’s price relative to the strike price, the higher the premium.
- Interest Rates: Changes in interest rates can impact option premium. Higher interest rates tend to increase the cost of carrying an investment, potentially resulting in higher put option premiums and lower call option premiums.
It’s essential to recognize that these factors do not act in isolation but rather interact and influence one another, shaping the overall pricing of option premium.
An Example of Option Premium:
Let’s bring these concepts to life with a practical example. Imagine you are considering purchasing a call option on Company XYZ, which is currently trading at $100 per share. The call option has a strike price of $110 and expires in three months. Based on the factors we discussed:
- If volatility is high: The option premium might be $5.
- If there is significant time until expiration: The option premium could be $8.
- If the stock price is well above the strike price: The option premium may reach $15.
- If interest rates are relatively low: The option premium might be $12.
These numbers are hypothetical and do not represent real-life market conditions or computations. However, they illustrate how each factor can impact the final price an investor pays for an option contract.
In Conclusion
Option premium is a fundamental concept in the world of options trading. By understanding its definition and the various factors that influence its pricing, investors can make more informed decisions when buying or selling options. Remember, volatility, time to expiration, underlying asset price, and interest rates all play a role in determining option premium. So, keep these factors in mind as you explore the exciting opportunities that options trading has to offer!
Thank you for reading our blog post on option premium. We hope you found it informative and that it helps you navigate the world of finance. Don’t forget to check out our other articles in the finance category for more valuable insights. If you have any questions or need further clarification, please feel free to reach out to our team. Happy trading!