Finance
What Does Bid And Ask Mean In Stocks
Published: January 18, 2024
Learn the meaning of bid and ask in stocks and how they affect your financial decisions. Find out more about finance and trading at our website.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Bid and Ask Prices
- Definition of Bid Price
- Definition of Ask Price
- Spread: The Difference between Bid and Ask Prices
- Role of Bid and Ask Prices in Stock Trading
- Importance of Bid and Ask Prices for Investors
- Factors Affecting Bid and Ask Prices
- Bid-Ask Sizes: Understanding the Depth of the Market
- Bid and Ask Prices in Practice
- Conclusion
Introduction
When it comes to trading stocks, it’s important to understand the language of the market. One concept that is essential to grasp is the bid and ask prices. These two prices are fundamental to the buying and selling of stocks and play a crucial role in determining the overall market dynamics.
Imagine you’re at a flea market searching for a rare collectible item. The seller has a price in mind that they’re willing to accept for the item, while you have a price you’re willing to pay. The negotiation process begins, with offers and counteroffers being thrown back and forth until both parties agree on a price. In the stock market, this negotiation process is represented by the bid and ask prices.
Understanding bid and ask prices is essential, whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out. In this article, we’ll delve into the definition and significance of bid and ask prices, as well as explore their role in stock trading.
So, if you ever wondered about the meaning behind those numbers on the stock market ticker or wanted to gain insight into the mechanics of stock trading, read on to discover the fascinating world of bid and ask prices.
Understanding Bid and Ask Prices
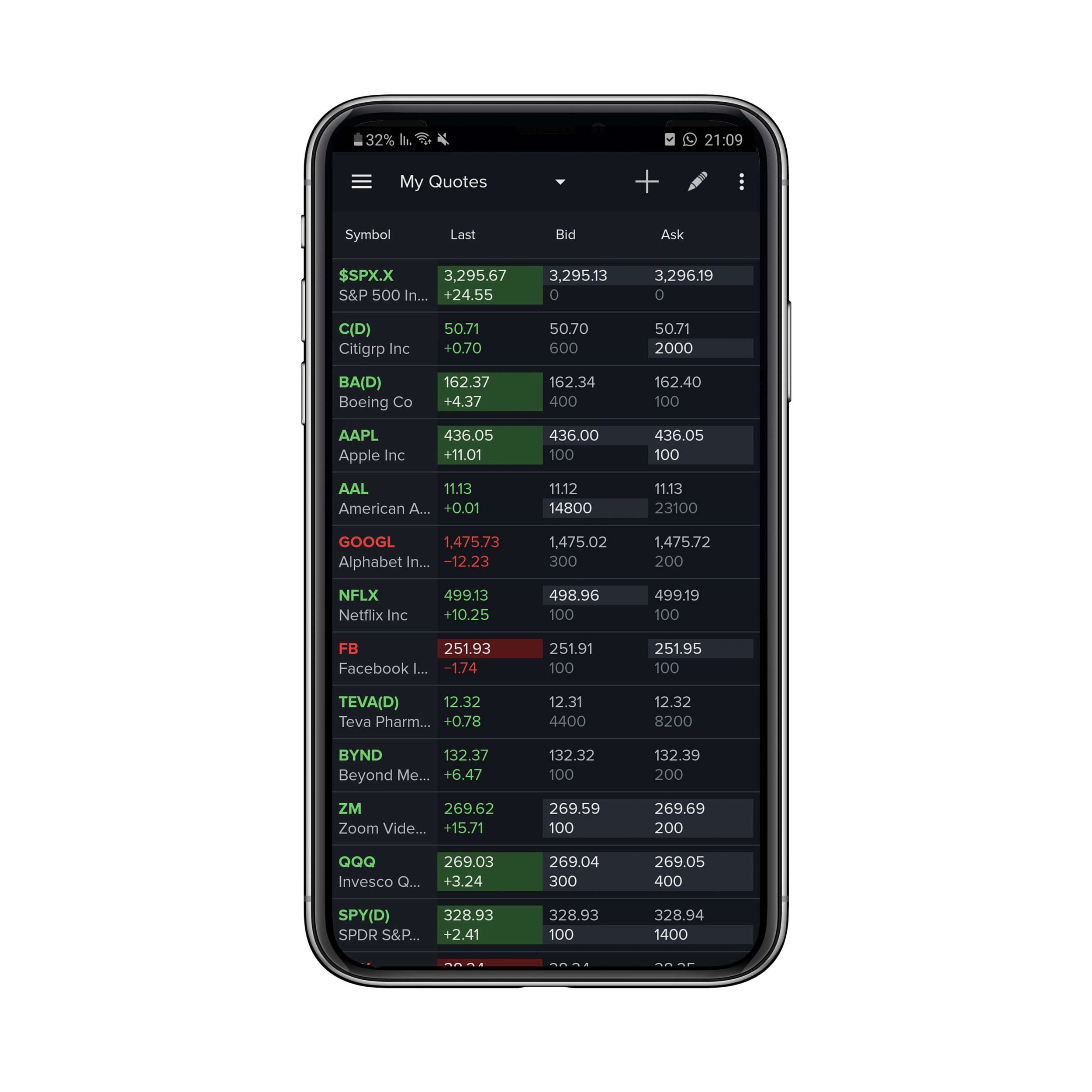
Bid and ask prices are key indicators of the supply and demand for a particular stock. They represent the maximum price a buyer is willing to pay (bid) and the minimum price a seller is willing to accept (ask) for that stock at a given point in time.
Think of the bid price as the highest offer on the buying side, while the ask price is the lowest offer on the selling side. The bid and ask prices are typically quoted together, with the bid price listed first, followed by the ask price.
For example, let’s say you’re looking at stock XYZ, and the bid-ask prices are displayed as $50.00 – $50.10. This means that the highest price a buyer is willing to pay for the stock, the bid price, is $50.00, while the lowest price a seller is willing to accept, the ask price, is $50.10.
It’s important to note that bid and ask prices are subject to constant changes as market conditions and investor sentiment shift. These price fluctuations reflect the ongoing negotiation between buyers and sellers in the stock market.
Market makers play a crucial role in establishing bid and ask prices. These are firms or individuals who act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers, facilitating the smooth transaction of stocks. Market makers constantly update bid and ask prices based on market conditions, ensuring the liquidity and efficiency of stock trading.
Next, let’s take a closer look at the definitions of bid and ask prices to gain a deeper understanding of their significance in stock trading.
Definition of Bid Price
The bid price, also known as the buy price or the bid-ask spread, represents the maximum price that a buyer is willing to pay for a particular stock at a given moment. It is the price at which an investor can sell their shares of stock if there is a willing buyer.
The bid price is influenced by various factors, including the overall demand for the stock, market conditions, and the number of buyers in the market. When there are more buyers than sellers, the bid price tends to be higher as investors compete to purchase the stock.
The bid price is crucial for investors looking to sell their shares. It serves as a reference point for determining the value of their investment and the potential profit or loss they may realize. In other words, if an investor wants to sell their stock, they would likely receive a price equivalent to the highest bid price.
It’s important to note that the bid price may not always match the last traded price of a stock. This is because the last traded price represents the price at which the most recent transaction occurred, while the bid price is the highest current offer.
Investors can track bid prices through various financial platforms and trading terminals. This information enables them to make informed decisions about when to buy or sell shares based on the prevailing bid prices in the market.
In summary, the bid price is the maximum price that a buyer is willing to pay for a stock at a given moment. It serves as a reference point for investors looking to sell their shares and helps determine the overall value of a stock in the market.
Definition of Ask Price
The ask price, also referred to as the sell price or the offer price, represents the minimum price that a seller is willing to accept for a particular stock at a given moment. It is the price at which an investor can buy shares of stock if there is a willing seller.
Similar to the bid price, the ask price is influenced by several factors, including market conditions, supply and demand dynamics, and the number of sellers in the market. When there are more sellers than buyers, the ask price tends to be lower as sellers compete to attract buyers.
The ask price is important for investors who wish to purchase shares of stock. It serves as a reference point for determining the cost of acquiring the shares and the potential expenses associated with the investment.
It’s worth noting that the ask price may not always match the last traded price of a stock. The last traded price represents the price at which the most recent transaction occurred, while the ask price is the lowest current offer.
Investors can track ask prices through financial platforms and trading terminals. This information helps them gauge the prevailing market conditions and make informed decisions about when to buy shares based on the ask prices being offered.
In summary, the ask price represents the minimum price that a seller is willing to accept for a stock at a given moment. It serves as a reference point for investors looking to purchase shares and helps determine the overall cost of acquiring stock in the market.
Spread: The Difference between Bid and Ask Prices
The spread refers to the difference between the bid price and the ask price in a stock market. It represents the cost of executing a trade and reflects the liquidity and efficiency of the market. The spread is a key metric that investors closely monitor when engaging in stock trading.
The bid-ask spread is influenced by several factors, including market volatility, trading volume, and the size of the trade. Generally, highly liquid stocks with a large trading volume tend to have narrower spreads, meaning the difference between the bid and ask prices is relatively small. On the other hand, less liquid stocks with low trading volume may have wider spreads, indicating a larger difference between the bid and ask prices.
The spread plays a significant role in determining transaction costs. When the spread is wide, investors face higher costs when buying or selling shares. This can erode potential profits for buyers or increase losses for sellers. However, with a narrower spread, transaction costs decrease, providing more favorable conditions for trading.
Market makers, as intermediaries in stock trading, play a crucial role in determining the spread. They continually adjust the bid and ask prices based on supply and demand dynamics to attract buyers and sellers. Market makers aim to create a balance between supply and demand, ensuring smooth and efficient trading.
Investors need to consider the spread when deciding to buy or sell a stock. A narrower spread indicates a more liquid market, making it easier to execute trades at a desired price. Conversely, a wider spread suggests a less liquid market, which may result in challenges when entering or exiting a position.
It’s important to note that spreads can vary across different markets and securities. For highly liquid stocks and major exchanges, the spreads tend to be tighter. However, for less popular stocks or smaller exchanges, the spreads may be wider, requiring investors to be cautious and mindful of the associated costs.
In summary, the spread represents the difference between the bid and ask prices in the stock market. It reflects the cost of trading and indicates the liquidity and efficiency of the market. Understanding and considering the spread is vital for investors when making decisions regarding buying and selling shares.
Role of Bid and Ask Prices in Stock Trading
Bid and ask prices play a central role in stock trading, serving as important indicators of market dynamics and facilitating the buying and selling of shares. They provide crucial information to investors and traders, allowing them to make informed decisions and participate in the stock market efficiently.
Firstly, bid and ask prices help create a transparent and efficient market. By displaying the highest bid and lowest ask prices, investors have a clear understanding of the current market value of a stock and can gauge the demand and supply dynamics. This transparency ensures fair pricing and fosters a level playing field for all market participants.
In addition, these prices assist in determining the best possible execution of trades. When a buyer is looking to purchase shares, they can analyze the bid prices to identify the most favorable price at which to place their order. Similarly, sellers can utilize the ask prices to determine the most advantageous price to offer when selling their shares. This information helps investors optimize their trading strategies and potentially maximize their returns.
Bid and ask prices also serve as a basis for market analysis and decision-making. Investors and traders often analyze the movement of these prices to assess market sentiment and predict potential price changes. Changes in bid and ask prices can provide valuable insights into the demand and supply dynamics of a stock, allowing market participants to make more informed trading decisions.
Moreover, bid and ask prices contribute to the formation of market orders. A market order is an order to buy or sell a stock at the prevailing market prices. By referencing the bid and ask prices, investors can determine whether they want to buy or sell at the current market values or place limit orders to trade at a specific target price.
Lastly, bid and ask prices are crucial in determining the bid-ask spread, which represents the transaction cost of buying or selling a stock. The spread influences investors’ decision-making, as a wider spread may lead to higher transaction costs and potentially impact the overall profitability of a trade.
In summary, bid and ask prices play a significant role in stock trading, providing valuable information on market dynamics, guiding trading decisions, and influencing the execution of trades. Understanding and analyzing bid and ask prices enable investors to participate in the stock market effectively and make informed decisions based on the prevailing market conditions.
Importance of Bid and Ask Prices for Investors
Bid and ask prices hold great importance for investors, providing valuable insights and aiding in making informed decisions in the stock market. Understanding and utilizing bid and ask prices effectively can greatly benefit investors in several ways.
One of the key benefits of bid and ask prices is that they reveal the current market value of a stock. By examining the bid and ask prices, investors can assess the fair value of a stock at any given moment. This information helps investors determine if a stock is overvalued or undervalued, allowing them to make more informed investment decisions.
Furthermore, bid and ask prices offer valuable information regarding market sentiment and liquidity. When bid prices exceed ask prices, it indicates a strong demand for the stock. Conversely, when ask prices exceed bid prices, it suggests a surplus in supply. By analyzing this information, investors can gauge market sentiment and make educated guesses about future price movements.
Another critical aspect of bid and ask prices is their role in setting realistic expectations for buying and selling shares. Investors can use bid and ask prices to gauge the availability of buyers and sellers in the market. For example, if the spread between the bid and ask prices is narrow, it indicates a high level of liquidity and the presence of many active participants. This facilitates easier and faster execution of trades.
Bid and ask prices also provide a basis for determining the potential profitability of a trade. Investors can evaluate the spread between the bid and ask prices to assess the transaction costs associated with buying or selling a stock. A narrower spread reduces the transaction costs, increasing the potential profitability of a trade. This information helps investors optimize their portfolio management and trading strategies.
Moreover, bid and ask prices help investors place limit orders effectively. By setting a target price within the bid-ask spread, investors can place a buy or sell order at a specific price, ensuring that the transaction occurs when the market reaches the desired level. This method allows investors to exercise greater control over their trading activities.
Overall, bid and ask prices are essential tools for investors in the stock market. They provide valuable insights into market dynamics, aid in assessing the fair value of stocks, guide trading strategies, and facilitate more informed decision-making. By understanding and utilizing bid and ask prices effectively, investors can enhance their trading outcomes and navigate the complexities of the stock market successfully.
Factors Affecting Bid and Ask Prices
Bid and ask prices in the stock market are influenced by various factors that shape the supply and demand dynamics for a particular stock. Understanding these factors can help investors make more informed decisions and navigate the ever-changing landscape of the market.
1. Market Conditions: The overall market conditions have a significant impact on bid and ask prices. Factors such as economic indicators, geopolitical events, and market sentiment can drive the buying or selling pressure for stocks, leading to fluctuations in bid and ask prices.
2. Supply and Demand: The basic principle of supply and demand plays a crucial role in determining bid and ask prices. When there is high demand for a stock and limited supply, the bid price tends to increase. Conversely, if there is an oversupply of shares and less demand, the ask price may decrease.
3. Company Performance: The financial performance and outlook of a company can influence bid and ask prices. Positive earnings reports, new product launches, or favorable news about a company can attract more buyers, driving up the bid price. Conversely, disappointing earnings or negative news can lead to a decrease in the bid price.
4. Industry Trends: Trends within a specific industry or sector can affect bid and ask prices for stocks within that sector. Positive industry developments, such as new technological advancements or increased consumer demand, may lead to higher bid prices. Conversely, unfavorable industry news or economic downturns can result in lower bid prices.
5. Market Maker Activities: Market makers, who facilitate the buying and selling of stocks, play a significant role in bid and ask price determination. Their actions, such as adjusting bid and ask prices based on market conditions, supply, and demand, can directly impact the bid-ask spread and overall pricing in the market.
6. Trading Volume: The volume of trading activity in a stock can influence bid and ask prices. Higher trading volume typically indicates greater market interest and liquidity, resulting in narrower bid-ask spreads. On the other hand, lower trading volumes may contribute to wider spreads and potentially less liquidity.
7. Investor Sentiment: The overall sentiment of investors can affect bid and ask prices as well. Positive investor sentiment can lead to increased demand, driving up the bid price. Conversely, negative sentiment can decrease demand and push the ask price lower.
8. Market Order Flow: The influx of market orders can impact bid and ask prices. Market orders to buy increase the bid price, while market orders to sell decrease the bid price. Conversely, market orders to sell increase the ask price, while market orders to buy decrease the ask price.
It’s important to note that these factors are interconnected and can influence bid and ask prices simultaneously. Additionally, the impact of these factors may vary depending on the specific stock and market conditions at any given time.
By staying informed about these factors and monitoring their influence on bid and ask prices, investors can make more informed trading decisions and adapt to changing market dynamics.
Bid-Ask Sizes: Understanding the Depth of the Market
Bid-ask sizes provide valuable insights into the depth of the market and refer to the number of shares available at the bid and ask prices. Understanding bid-ask sizes is essential for investors, as it helps gauge the liquidity and trading activity surrounding a stock.
The bid size represents the number of shares that potential buyers are willing to purchase at the current bid price. It indicates the demand for the stock at that specific price level. A larger bid size suggests a higher level of interest from buyers and can be an indication of market strength or potential price support.
On the other hand, the ask size represents the number of shares that sellers are offering to sell at the current ask price. It reflects the supply of the stock at that particular price level. A larger ask size indicates a higher level of supply of the stock, potentially signaling market weakness or resistance to price increases.
By examining the bid-ask sizes, investors can gain insights into the depth of the market and the strength of the buying and selling pressure. For example, a stock with a large bid size and a small ask size may indicate a strong buying interest compared to its selling pressure, potentially leading to upward price movement.
Conversely, when the ask size is significantly larger than the bid size, it may suggest an abundance of supply and weaker demand, leading to potential downward pressure on the stock price.
In addition, monitoring bid-ask sizes can assist in determining the ease of executing trades. If the bid and ask sizes are relatively balanced, it indicates a liquid market with a sufficient amount of shares available for buying and selling. This can result in smoother transactions and potentially narrower bid-ask spreads.
However, if the bid-ask sizes appear imbalanced, with a significant difference between the two, it may imply a less liquid market. This can result in challenges when attempting to execute trades at desired prices or larger bid-ask spreads, potentially increasing transaction costs.
It’s important to note that bid-ask sizes can change rapidly as market conditions and investor sentiment shift. Therefore, it’s crucial for investors to continuously monitor bid-ask sizes and stay aware of any fluctuations that could impact their trading decisions.
In summary, bid-ask sizes provide insights into the depth of the market, indicating the level of demand and supply for a stock at specific price levels. By understanding bid-ask sizes, investors can assess market strength, determine potential price support or resistance levels, and evaluate the ease of executing trades.
Bid and Ask Prices in Practice
Bid and ask prices are integral components of the stock market ecosystem and have practical implications for investors and traders. Understanding how bid and ask prices work in practice can help individuals navigate the intricacies of buying and selling stocks effectively.
When placing a market order to buy a stock, an investor will typically pay the ask price. This is the minimum price at which a seller is willing to sell their shares. On the other hand, when placing a market order to sell, an investor will receive the bid price, which is the maximum price a buyer is willing to pay.
For example, suppose an investor wants to purchase shares of stock XYZ. If the current quoted bid and ask prices are $50.00 – $50.10, the investor will likely pay a price closer to the ask price of $50.10 when buying the shares.
In contrast, if an investor is selling shares of stock XYZ, they will receive a price closer to the bid price of $50.00. The difference between the bid and ask prices is called the bid-ask spread, which represents the transaction cost associated with buying or selling the stock.
Market orders to buy or sell stocks are more likely to be executed quickly, as they match with the available bid or ask prices in the market. However, investors also have the option to place limit orders, which allow them to specify a desired buying or selling price.
For example, if an investor wants to purchase shares of stock XYZ at a price lower than the current ask price, they can place a limit order specifying their desired price. The order will be executed only if the market reaches or falls below their desired price. Similarly, if an investor wants to sell shares of stock XYZ at a price higher than the current bid price, they can place a limit order, and the order will be executed when the market reaches or exceeds their desired price.
It’s important to note that the availability of shares at the bid and ask prices, as well as the bid-ask spread, can change rapidly in response to market activity. Therefore, it’s crucial for investors to keep a close eye on real-time market data or utilize advanced trading platforms to make informed decisions.
Moreover, bid and ask prices can also vary across different exchanges and trading platforms. Therefore, investors should consider factors such as transaction costs, liquidity, and order execution speed when choosing where to place their trades.
In summary, bid and ask prices are crucial components of the stock market that impact buying and selling decisions. They determine the price at which transactions occur, influence the bid-ask spread, and provide investors with options to place market or limit orders. Constant monitoring of bid and ask prices, along with the proper use of trading strategies, can help investors optimize their trading activities and navigate the complexities of the stock market.
Conclusion
Understanding bid and ask prices is essential for anyone involved in stock trading or investing. These prices represent the maximum price that a buyer is willing to pay (bid) and the minimum price that a seller is willing to accept (ask) for a stock at a given point in time.
The bid and ask prices play a critical role in determining the dynamics of the stock market. They provide valuable insights into market sentiment, liquidity, and the balance between supply and demand. By analyzing bid and ask prices, investors can make informed decisions, gauge market conditions, and optimize their trading strategies.
Additionally, bid and ask prices are indicators of the fair value of a stock, helping investors evaluate the potential profitability of their trades. They also guide the execution of market orders and provide the foundation for placing limit orders to buy or sell shares at specific target prices.
Monitoring bid and ask sizes further enhances investors’ understanding of the depth of the market. The sizes represent the number of shares available at the bid and ask prices, allowing investors to assess the strength of buying and selling pressure and potential price support or resistance levels.
Factors such as market conditions, supply and demand, company performance, industry trends, market maker activities, trading volume, investor sentiment, and market order flow all influence bid and ask prices. Being aware of these factors and their impacts enables investors to adapt to changing market dynamics and make more informed trading decisions.
In conclusion, bid and ask prices are fundamental concepts in stock trading. They provide crucial information about market dynamics, liquidity, and the balance between buying and selling pressure. By understanding bid and ask prices and their implications, investors can enhance their trading strategies, optimize their decision-making, and navigate the complexities of the stock market more effectively.