Finance
What Does GTC Mean In Stocks
Published: January 18, 2024
Discover the meaning of GTC in stocks and its significance in the world of finance. Gain insights into how GTC orders work and their impact on trading strategies.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
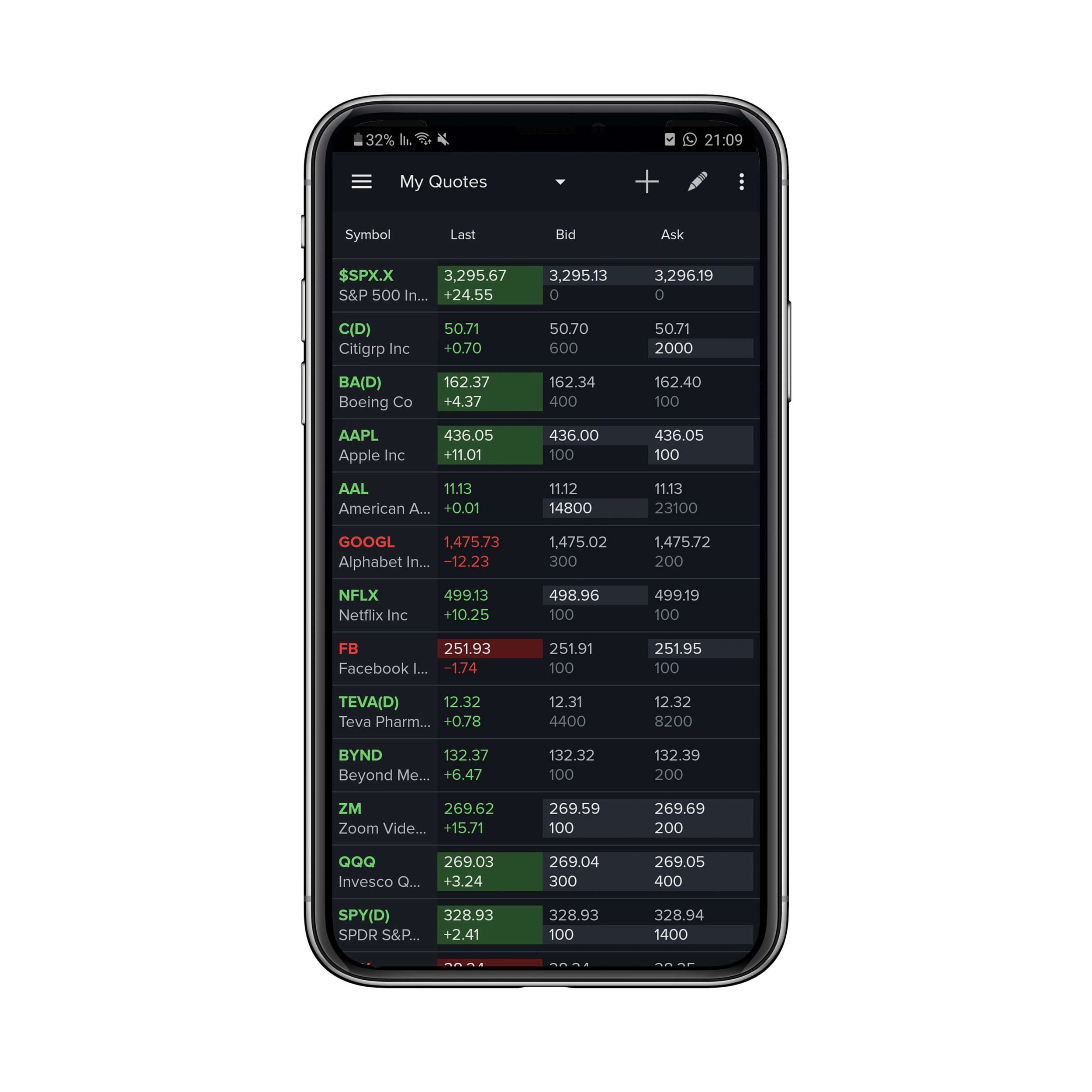
When it comes to investing in the stock market, it’s crucial to understand the different types of orders available to traders. One such order is the GTC order. For those new to the world of stocks, “GTC” stands for “Good ‘Til Cancelled.” But what does GTC really mean, and how does it affect your investment strategy?
A GTC order is a type of instruction that you can place with your broker to buy or sell a stock at a specific price, which remains in effect until it is executed or cancelled. Unlike other types of stock orders that expire at the end of the trading day, GTC orders stay active until you choose to cancel them. This allows investors to set their desired price levels and maintain flexibility in their trading approach.
Understanding how to effectively use GTC orders can significantly impact your investing success. By learning about their advantages, limitations, and how they compare to other types of stock orders, you can make more informed decisions and optimize your investment strategy.
Understanding GTC Orders
When you place a GTC order, you are essentially instructing your broker to execute the order at a specific price or better, and to keep trying until the order is fulfilled or you cancel it. This means that even if the stock price doesn’t reach your desired level immediately, the order will remain active until it does.
GTC orders are particularly useful for investors who have identified specific price targets for their trades. For example, if you want to buy shares of a company but only at a certain price point, you can place a GTC order to automatically execute the trade when the stock price reaches or falls below that level. This eliminates the need for constant monitoring and manual execution, providing convenience and peace of mind.
It’s important to note that GTC orders can stay active for an extended period of time, which could be days, weeks, or even months. While this can be advantageous for long-term investors, it’s crucial to regularly review and adjust your GTC orders as market conditions and stock prices fluctuate.
Additionally, GTC orders are not limited to buying stocks but can also be used to sell stocks at a specific price. If you own shares and want to ensure that you sell them if the price reaches a certain level, a GTC sell order can be placed to automatically execute the trade when the stock price reaches or exceeds your specified price.
It’s worth noting that GTC orders are typically executed on a first-come, first-served basis. If multiple GTC orders are placed at the same price, the oldest order will have priority. This means that it’s essential to consider the time factor when setting your GTC order.
In the next section, we will explore the advantages and benefits of using GTC orders in your stock trading strategy.
Advantages of GTC Orders
GTC orders offer several advantages that can help investors navigate the stock market with more convenience and control. Here are some key benefits of using GTC orders in your trading strategy:
- Convenience and Efficiency: Placing GTC orders saves you time and effort, as you don’t need to constantly monitor the market or manually enter trades. Once the order is set, your broker will handle the execution when the desired price is reached.
- Price Protection: By setting a specific price target with a GTC order, you can protect yourself from potential price fluctuations. For example, if you want to buy a stock at a lower price, a GTC buy order will automatically execute the trade when the stock reaches that level, even if it only occurs momentarily.
- Flexibility: GTC orders allow for greater flexibility in your investment strategy. You can set multiple orders at various price levels, enabling you to take advantage of market volatility and potentially optimize your trade execution.
- Opportunity Capture: GTC orders are particularly useful for capturing trading opportunities that arise outside of regular trading hours. Since the orders stay active until executed or cancelled, they can target price movements that occur when the market is closed.
- Emotional Discipline: Setting GTC orders can help investors avoid making impulsive decisions based on short-term market fluctuations or emotions. It allows for a more disciplined and strategic approach to investing, as trades are executed based on predetermined parameters.
By utilizing GTC orders, investors can leverage these advantages to enhance their trading efficiency, protect themselves from sudden market moves, and maintain a disciplined investment approach. However, it’s important to also consider the limitations and potential risks associated with GTC orders, as we will explore in the next section.
Limitations of GTC Orders
While GTC orders offer numerous benefits, it’s crucial to be aware of their limitations and potential risks. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions and mitigate potential drawbacks. Here are some limitations of GTC orders:
- No Guarantee of Execution: Placing a GTC order does not guarantee that your trade will be executed. The market may not reach your specified price, or there may not be enough liquidity in the stock to fulfill your order. It’s important to regularly review and adjust your GTC orders to ensure they align with current market conditions.
- Potential Price Changes: The stock market is subject to constant fluctuations, and price levels may change significantly between the time you place a GTC order and its execution. This means that the actual executed price may differ from your desired price, which can impact your overall trading strategy and potential returns.
- Market Volatility: In highly volatile market conditions, GTC orders can be exposed to increased risk. Fast-moving markets can cause prices to gap or move rapidly, leading to execution at prices significantly different from the desired target.
- Tied-up Capital: When you place a GTC order, the corresponding funds or shares are typically held in reserve until the trade is executed or cancelled. This means that your capital or shares may be tied up and unavailable for other trading opportunities for the duration of the GTC order.
- Expiration Date: While GTC orders don’t have a specific expiration time, some brokers may impose certain limitations on the duration of GTC orders. It’s important to be aware of your broker’s policies and review and renew your GTC orders periodically to avoid unintended cancellations.
Understanding these limitations can help you navigate the potential risks associated with GTC orders. By regularly reviewing and adjusting your orders, staying informed about market conditions, and diversifying your investment approach, you can mitigate some of these limitations.
In the next section, we will look at other types of stock orders that you can consider incorporating into your trading strategy.
Other Types of Stock Orders
While GTC orders are a useful tool in stock trading, it’s important to be aware of other types of stock orders that can complement your investment strategy. Here are some commonly used stock orders:
- Market Orders: Market orders are executed at the current market price. With this type of order, you prioritize speed of execution over the specific price. Market orders are typically executed immediately.
- Limit Orders: Limit orders allow you to set a specific price at which you want to buy or sell a stock. These orders are only executed if the stock reaches the specified price or better. Limit orders offer greater control over the price at which you enter or exit a position.
- Stop Orders: Stop orders, also known as stop-loss orders, are designed to limit losses or protect profits. With a stop order, you set a specific trigger price at which the order becomes a market order and is executed. This helps you limit potential downside or lock in gains.
- Trailing Stop Orders: Trailing stop orders are similar to stop orders but with a dynamic twist. With a trailing stop order, you set a trailing value or percentage that adjusts with the stock price. As the stock price moves in your favor, the trailing stop order adjusts and provides a predefined level of protection.
- Immediate-or-Cancel Orders: Immediate-or-cancel orders are intended to be executed immediately. If the entire order cannot be filled immediately, the unfilled portion of the order is cancelled. These orders are often used for large volume trades or in fast-moving markets.
- Fill-Or-Kill Orders: Fill-or-kill orders are similar to immediate-or-cancel orders, but with a slight difference. With fill-or-kill orders, the entire order must be executed immediately, or it is cancelled. These orders are commonly used for trades that require complete execution.
Each type of stock order serves a specific purpose and offers distinct advantages depending on your trading goals and preferences. By understanding the different order types, you can choose the most appropriate one for each trade and maximize your trading strategy’s effectiveness.
Now that we have explored various stock order types, let’s conclude our discussion on GTC orders and their role in stock trading.
Conclusion
GTC (Good ‘Til Cancelled) orders are a valuable tool for investors in the stock market. By understanding their benefits and limitations, investors can effectively incorporate GTC orders into their trading strategies.
GTC orders offer convenience, as they allow investors to set specific price targets and free themselves from constantly monitoring the market. Moreover, these orders provide price protection, flexibility, and the ability to capture trading opportunities that arise outside of regular trading hours.
However, it’s important to acknowledge the limitations of GTC orders. There is no guarantee of execution, potential price changes can affect trading outcomes, and market volatility can introduce increased risk. Capital may also be tied up, and some brokers may impose expiration dates on GTC orders.
Additionally, it’s crucial to be aware of other types of stock orders, such as market orders, limit orders, stop orders, trailing stop orders, immediate-or-cancel orders, and fill-or-kill orders. Understanding these order types can help investors diversify their trading approach and optimize their strategies.
In conclusion, GTC orders offer convenience and flexibility in stock trading, enabling investors to set specific price targets and automate trades. By balancing the advantages and limitations of GTC orders and incorporating other types of stock orders, investors can make informed decisions in pursuit of their investment goals.