
Finance
What Is A Credit Memo In Accounting
Modified: February 21, 2024
Learn about credit memos in accounting and their importance in finance. Gain a deeper understanding of how they impact financial transactions and bookkeeping practices.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
In the world of finance and accounting, there are various documents and transactions that play a crucial role in maintaining accurate records and facilitating smooth financial operations. One such document is a credit memo. Understanding what a credit memo is and how it is used in accounting is essential for businesses and individuals alike who want to effectively manage their finances.
A credit memo is a written document issued by a seller to a buyer, indicating that the seller has approved a credit or refund for a specific amount. It is essentially an acknowledgment that the buyer is entitled to a reduction in the amount owed due to various reasons, such as returns, overpayments, or allowances for damaged goods.
The purpose of a credit memo is to provide a clear record of the adjustment made to a customer’s account balance. It serves as a source document, providing evidence for the reduction in the amount receivable from the customer. The use of credit memos helps businesses maintain accurate financial records and track their sales transactions effectively.
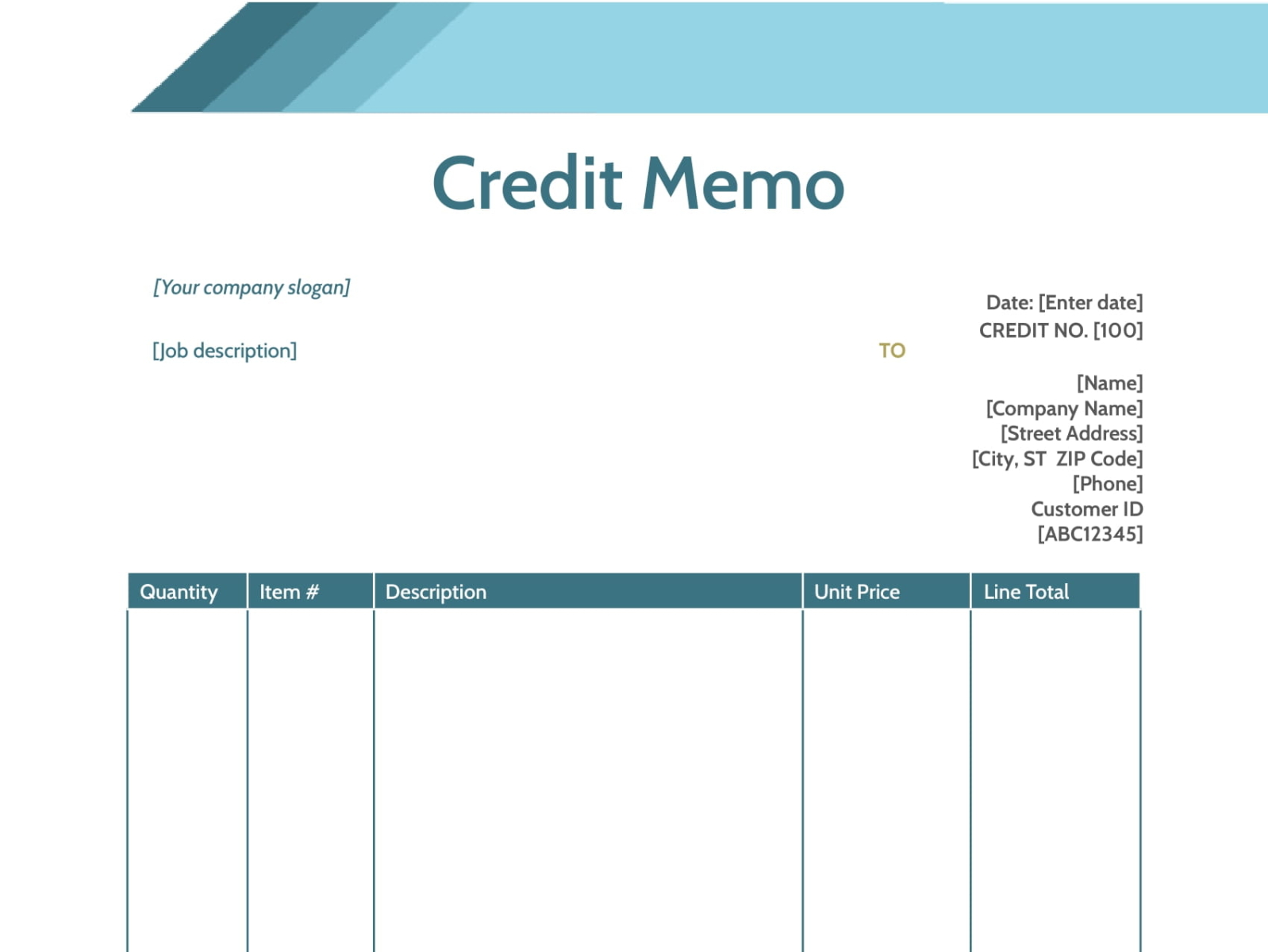
A credit memo typically includes important information such as the name and address of the buyer and seller, the date the memo is issued, a unique identification number, detailed description of the goods or services being credited, the amount being credited, and any applicable taxes or fees. This detailed information ensures transparency and clarity regarding the adjustment made to the customer’s account.
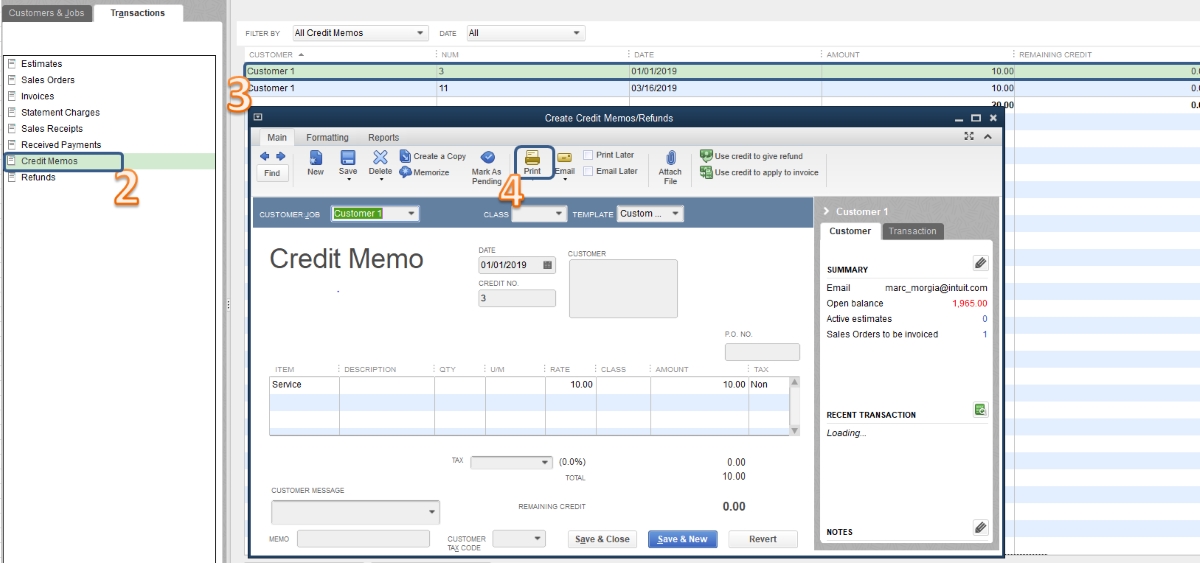
Creating a credit memo is a straightforward process. The seller or accounting department generates the credit memo and sends it to the buyer or customer. The credit memo can be produced in either paper or electronic form, depending on the company’s practices. In some cases, businesses may have specific templates or software programs designed to streamline the credit memo creation process.
When it comes to recording a credit memo in accounting, it is important to ensure accuracy and consistency. The credit memo is usually recorded as a credit entry in the seller’s books, reducing the accounts receivable or applicable revenue account. A corresponding debit entry is made to reflect the adjustment in the buyer’s account. This accounting entry helps maintain proper financial records and ensures that the transaction is accurately reflected in the company’s financial statements.
Now that we have covered the basics, let’s take a closer look at the components of a credit memo and how they are used in practice.
Definition of a Credit Memo
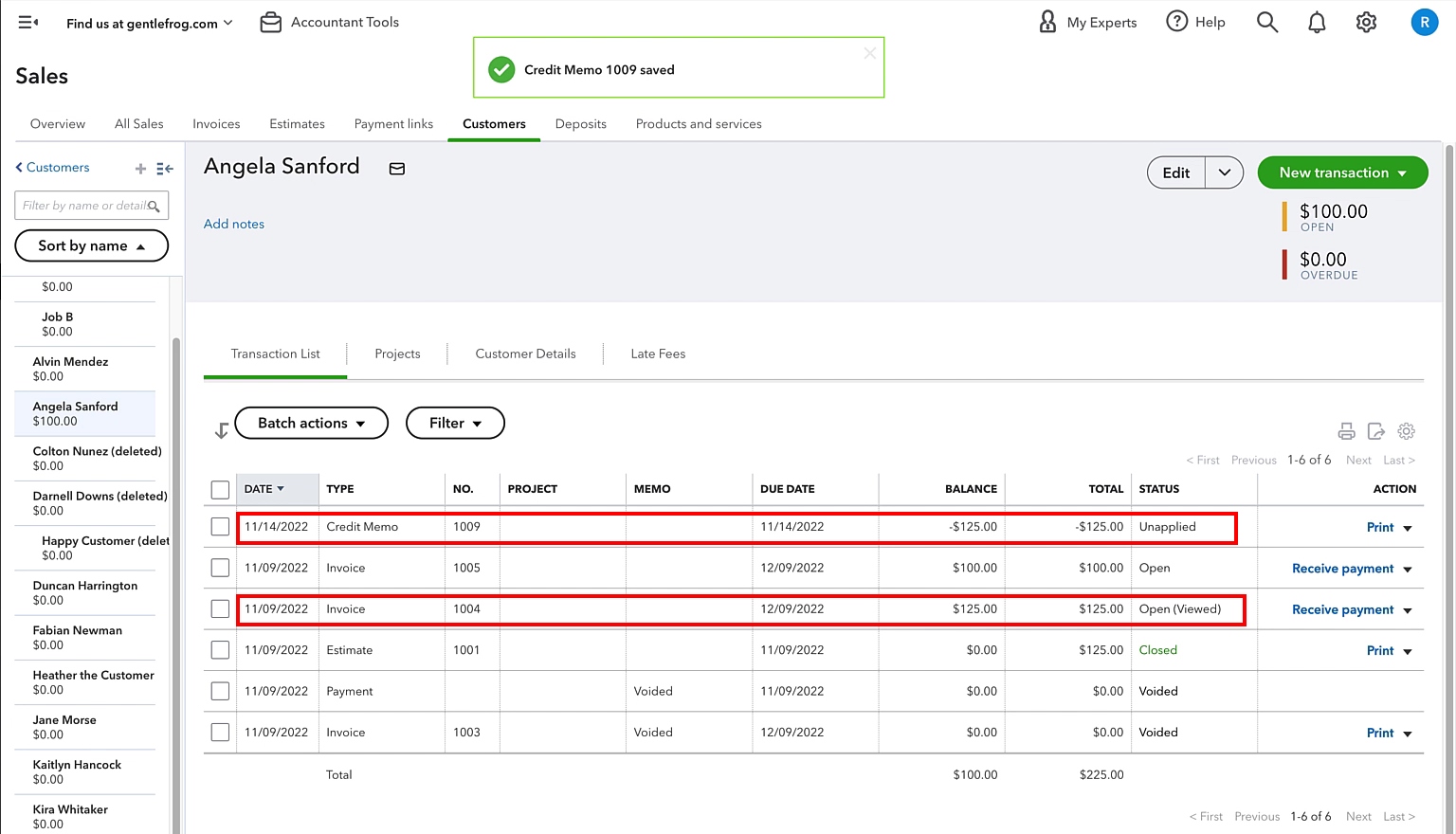
A credit memo, also known as a credit note, is a document issued by a seller to a buyer indicating that the seller has approved a credit or refund for a specific amount. It serves as evidence of the reduction in the amount receivable from the customer due to various reasons like returns, overpayments, or allowances for damaged goods.
When a customer returns a product, encounters a billing error, or requests a refund, the seller initiates the process of issuing a credit memo. This document notifies the buyer that their account will be credited with the specified amount, providing them with a clear record of the adjustment made and ensuring transparency in the transaction.
The credit memo includes important details such as the buyer’s and seller’s information, a unique identification number, the date of issuance, a description of the original transaction, the amount being credited, and any applicable taxes or fees. It is important to include all relevant information to avoid any misunderstandings or discrepancies.
A credit memo benefits both the seller and the buyer. For the seller, it helps maintain accurate financial records by documenting the reduction in the amount owed by the buyer. It serves as a source document for internal auditing purposes and facilitates proper tracking and reconciliation of accounts receivable.
On the buyer’s side, a credit memo provides assurance that the seller has acknowledged and approved the credit or refund. It helps the buyer keep track of any adjustments made to their account balance and serves as supporting documentation for any future disputes or inquiries.
It is important to note that a credit memo is different from an invoice. While an invoice is a document sent by the seller to the buyer requesting payment for goods or services, a credit memo is issued to reflect a reduction in the amount owed. Think of it as the opposite of an invoice, where instead of requesting payment, the credit memo acknowledges a credit or refund.
In summary, a credit memo is a vital document in accounting that signifies a reduction in the amount receivable from a buyer. It provides a clear record of the adjustment made, ensures transparency in financial transactions, and serves as a supporting document for both the seller and the buyer. Now that we have a clear understanding of what a credit memo is, let’s delve into its purpose and how it is created in practice.
Purpose of a Credit Memo
A credit memo serves multiple purposes in the realm of finance and accounting. It is a crucial document that allows businesses to accurately record adjustments to customer accounts and maintain transparent and efficient financial operations. Let’s explore the key purposes of a credit memo:
- Adjustment of Account Balances: The primary purpose of a credit memo is to adjust the account balance of a customer. This adjustment can be due to various reasons such as returns, overpayments, or allowances for damaged goods. By issuing a credit memo, the seller acknowledges that the customer is entitled to a reduction in the amount owed.
- Transparency and Documentation: Credit memos provide transparency in financial transactions. They serve as supporting documents that document the adjustment made, providing a clear record of the credit or refund approved. This documentation is essential for future reference, internal auditing purposes, and potential disputes or inquiries.
- Customer Satisfaction: Issuing a credit memo demonstrates good customer service and helps maintain positive relationships with customers. It shows responsiveness to customer concerns and the willingness to rectify any errors or issues related to billing or faulty products. This can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Accurate Financial Reporting: Proper recording and documentation of credit memos ensure accuracy in financial reporting. By accurately reflecting the adjustments in customer accounts, businesses can generate reliable financial statements that accurately reflect their financial standing. This is crucial for decision-making, compliance, and building investor confidence.
- Internal Control and Audit: Credit memos play a vital role in internal control and auditing processes. They provide a clear trail of transactions, allowing businesses to track and review adjustments made to customer accounts. This helps in identifying any potential discrepancies, detecting errors or fraud, and maintaining the integrity of financial records.
Overall, the purpose of a credit memo is to facilitate accurate and transparent recording of adjustments to customer accounts. It supports proper financial reporting, fosters customer satisfaction, and promotes effective internal control and auditing practices. With a clear understanding of the purpose of credit memos, let’s move on to the next section to explore the various components of a credit memo in detail.
Components of a Credit Memo
A credit memo comprises several essential components that provide important information about the adjustment made to a customer’s account. These components ensure clarity, accuracy, and transparency in financial transactions. Let’s take a closer look at the key components of a credit memo:
- Buyer and Seller Information: A credit memo should include the names, addresses, and contact details of both the buyer and the seller. This information helps identify the parties involved in the transaction and ensures proper communication.
- Unique Identification Number: Each credit memo should have a unique identification number or reference code. This number helps in easy identification and tracking of the credit memo, especially when dealing with multiple transactions and customers.
- Date of Issuance: The credit memo should clearly state the date it is issued. This is crucial for record-keeping and helps establish the timeline of the adjustment made to the customer’s account.
- Description of the Goods or Services: It is important to provide a detailed description of the goods or services for which the credit memo is issued. This description should be clear and specific to ensure understanding by both the buyer and seller.
- Amount Being Credited: The credit memo should clearly state the specific amount that is being credited to the customer’s account. This shows the reduction in the amount owed by the customer and provides clarity regarding the financial impact of the adjustment.
- Applicable Taxes or Fees: If any taxes or fees are associated with the adjustment, they should be clearly mentioned in the credit memo. This ensures transparency in the financial transaction and helps both parties understand the total amount being credited or refunded.
- Reason for the Credit: It is crucial to include the reason or justification for the credit memo. This could include returns, overpayments, damaged goods, or any other relevant reason. Including the reason provides clarity and context for the adjustment made.
- Authorized Signatures: The credit memo should be signed by authorized individuals from the seller’s side, confirming the approval of the credit or refund. This adds validity and authenticity to the document.
By including these components, a credit memo ensures that all relevant information is documented for both the buyer and seller. It helps establish clear communication, transparency, and accuracy in financial transactions. Now that we have covered the components of a credit memo, let’s move on to understand the process of creating and recording a credit memo in accounting.
Creating a Credit Memo
The process of creating a credit memo is relatively straightforward and involves a series of steps to ensure accuracy and efficiency. Here is a breakdown of the typical process involved in creating a credit memo:
- Gather Necessary Information: Collect all the relevant information required to create the credit memo. This includes the buyer’s details, the original transaction information, the reason for the credit, and the amount being credited.
- Use a Template or Software: Many businesses utilize pre-designed templates or specialized accounting software to create credit memos. These templates often contain predefined fields for the necessary information, making the process easier and more standardized.
- Fill in the Required Fields: Enter the buyer’s information, including their name, address, and contact details, into the credit memo form. Also, provide the unique identification number and the date of issuance.
- Provide a Detailed Description: Describe the goods or services for which the credit memo is being issued. Include specific details such as product names, quantities, and any pertinent information regarding the transaction.
- Specify the Credited Amount: Clearly state the amount that is being credited to the customer’s account. This amount should be accurate and reflect the reduction in the outstanding balance resulting from the credit memo.
- Include Applicable Taxes or Fees: If there are any taxes or fees associated with the credit memo adjustment, include them in the document. This ensures transparency and provides a complete overview of the financial impact.
- Provide a Reason for the Credit: Indicate the reason for the credit memo, such as returned merchandise, overpayment, or damaged goods. Including the reason helps both parties understand the purpose behind the adjustment.
- Obtain Necessary Approvals: Ensure that the credit memo is authorized and signed by individuals with the appropriate authority within the organization. This confirms approval of the credit or refund and adds validity to the document.
- Distribute and Retain Copies: Once the credit memo is created and approved, distribute a copy to the buyer and retain a copy for internal records. This helps maintain documentation and provides a reference for future transactions or potential disputes.
By following these steps, businesses can effectively create credit memos that accurately reflect adjustments made to customer accounts. The use of templates or accounting software streamlines the process and ensures consistency in formatting. Now that we have explored the process of creating a credit memo, let’s move on to the next section to understand how a credit memo is recorded in accounting.
Recording a Credit Memo in Accounting
Recording a credit memo in accounting is vital to accurately reflect the adjustment made to a customer’s account and maintain proper financial records. Here is an overview of the process of recording a credit memo:
- Identify the Accounts: Determine the accounts to be affected by the credit memo. The primary accounts involved are the accounts receivable and revenue accounts.
- Create a Journal Entry: Prepare a journal entry to record the credit memo. The journal entry will depend on the specific accounting system and chart of accounts used by the organization.
- Debit the Accounts Receivable: Debit the accounts receivable account by the amount credited in the credit memo. This reduces the customer’s outstanding balance and reflects the reduction in the amount owed.
- Credit the Revenue Account: Credit the revenue account associated with the original transaction. This reduces the revenue recognized in the initial sale, reflecting the adjustment made with the credit memo.
- Include Other Accounts (if applicable): Depending on the transaction and company-specific circumstances, other accounts may need to be included in the journal entry. This could include inventory, sales tax payable, or any relevant contra accounts.
- Verify Accuracy: Double-check the journal entry for accuracy before finalizing it. Make sure that the debits and credits are equal and that the accounting records are updated correctly.
- Post the Journal Entry: Post the journal entry to the appropriate general ledger accounts. This ensures that the adjustment made with the credit memo is properly reflected in the financial records.
- Update Customer’s Account: Update the customer’s account within the accounting system to reflect the reduced balance resulting from the credit memo. This helps maintain accurate customer records and facilitates future transactions.
- Retain Documentation: Retain a copy of the credit memo, the journal entry, and any supporting documentation for future reference and audit purposes. This ensures that there is a clear audit trail and evidence of the adjustment made.
By following the proper accounting procedures and recording the credit memo accurately, businesses can maintain accurate financial records and ensure transparency in their accounting practices. This information is crucial for generating reliable financial statements and reports, facilitating decision-making, and complying with regulatory requirements.
Now that we have explored the process of recording a credit memo in accounting, let’s move on to an example to illustrate how a credit memo is used in a practical scenario.
Example of a Credit Memo
To better understand how a credit memo works in practice, let’s consider an example:
Company XYZ sells electronic devices and recently received a customer complaint regarding a defective laptop. After investigating the issue, the company determined that the laptop indeed had a manufacturing defect and decided to issue a credit memo to the customer.
The credit memo for Company XYZ might look like this:
- Buyer Information: John Smith
- Seller Information: Company XYZ
- Credit Memo Number: CM-2021-00123
- Date: June 15, 2021
- Description: Credit for defective laptop purchase
- Amount Being Credited: $1,000
- Reason for the Credit: Manufacturing defect in laptop
In this example, Company XYZ acknowledges the issue with the laptop and approves a credit memo of $1,000 to compensate John Smith for the defective product. The credit memo clearly states the reason for the credit, the amount being credited, and the date of issuance.
Once the credit memo is created, Company XYZ records the transaction in their accounting system. They debit John Smith’s accounts receivable by $1,000, reducing his outstanding balance. They also credit the revenue account associated with the original sale by $1,000, reflecting the adjustment made.
The credit memo, along with the journal entry and any supporting documentation, is retained for record-keeping and auditing purposes. This ensures that the adjustment is properly documented and provides evidence of the credit given to John Smith.
This example illustrates how a credit memo is used to address a specific issue with a transaction and provide a credit or refund to the customer. It showcases the importance of accurately documenting the adjustment made and maintaining proper accounting records.
Now that we have seen an example of a credit memo, let’s explore the importance of credit memos in accounting and the key differences between credit memos and invoices.
Importance of Credit Memos in Accounting
Credit memos play a vital role in accounting, providing several important benefits for businesses. Let’s delve into the importance of credit memos in maintaining accurate financial records and facilitating smooth financial operations.
- Accurate Tracking of Adjustments: Credit memos help businesses accurately track and document adjustments made to customer accounts. Whether it’s for returns, overpayments, or allowances for damaged goods, credit memos provide a clear record of the adjustment, ensuring transparency and accuracy in financial transactions.
- Compliance with Accounting Principles: By issuing credit memos, businesses can adhere to accounting principles such as revenue recognition and proper recording of adjustments. This helps ensure compliance with financial reporting standards and promotes transparency and consistency in financial records.
- Transparent Financial Reporting: Credit memos contribute to transparent financial reporting by reflecting accurate adjustments made to customer accounts. This ensures that financial statements, such as the balance sheet and income statement, reflect the true financial position and performance of the business.
- Evidence for Auditing and Disputes: By maintaining well-documented credit memos, businesses have reliable evidence to support auditing procedures. Credit memos serve as supporting documents for internal and external audits, providing a clear audit trail. They also serve as documentation to resolve any potential disputes with customers regarding the adjustment made.
- Customer Satisfaction and Relationship Management: Issuing credit memos demonstrates good customer service and fosters positive customer relationships. By promptly addressing issues, such as returns or billing errors, businesses can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. Clear communication through credit memos ensures transparency and fairness in resolving customer concerns.
- Effective Internal Control: Credit memos are an integral part of internal control procedures. They assist in maintaining accurate financial records, preventing errors, and deterring fraudulent activities. By following proper processes and documentation with credit memos, businesses can strengthen their internal control environment.
Overall, credit memos are essential in accounting for maintaining accurate financial records, complying with accounting principles, and fostering transparency in financial reporting. They provide valuable evidence for audits and dispute resolution and contribute to customer satisfaction and effective internal control. By recognizing the importance of credit memos, businesses can effectively manage their finances and build trust with customers and stakeholders.
Now that we understand the importance of credit memos, let’s explore the key differences between credit memos and invoices.
Differences between Credit Memo and Invoice
While credit memos and invoices are both important documents in financial transactions, they serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics. Let’s examine the key differences between credit memos and invoices:
- Purpose: The primary purpose of an invoice is to request payment from a buyer for goods or services provided. On the other hand, a credit memo is issued to acknowledge a credit or refund owed to the buyer due to various reasons such as returns, overpayments, or allowances for damaged goods.
- Direction of Flow: Invoices are sent from the seller to the buyer, requesting payment. Credit memos, on the other hand, are sent from the seller to the buyer, acknowledging a reduction in the amount owed.
- Financial Impact: Invoices have a positive financial impact on the seller as they lead to an increase in accounts receivable and revenue. Credit memos, on the contrary, result in a reduction in accounts receivable and revenue for the seller as they acknowledge a credit or refund to the buyer.
- Timing: Invoices are typically issued prior to or upon the delivery of goods or completion of services. They indicate the amount owed by the buyer and set the terms for payment. Credit memos, on the other hand, are issued after the initial transaction has taken place, acknowledging an adjustment or credit to the buyer’s account.
- Content: Invoices contain detailed information about the goods or services being provided, including a description, quantity, unit price, and total amount due. They often include payment terms and any applicable taxes or fees. Credit memos, on the other hand, provide information about the adjustment made, including the reason for the credit, the amount being credited, and any applicable taxes or fees.
- Accounting Treatment: In accounting, invoices are recorded as sales revenue and increase the accounts receivable. Credit memos, on the other hand, are recorded as a reduction in accounts receivable or applicable revenue accounts, reflecting the adjustment made to the buyer’s account.
Understanding the differences between credit memos and invoices is essential for accurate financial record-keeping and effective communication between buyers and sellers. While invoices request payment for goods or services, credit memos acknowledge a credit or refund owed to the buyer due to an adjustment. Both documents play important roles in maintaining transparent financial operations.
Now that we have explored the differences between credit memos and invoices, let’s conclude our discussion.
Conclusion
Credit memos are essential documents in finance and accounting, playing a crucial role in accurately recording adjustments made to customer accounts and facilitating transparent financial transactions. By understanding what a credit memo is and how it is used in accounting, businesses can effectively manage their finances and maintain proper financial records.
A credit memo serves as evidence of a reduction in the amount receivable from a customer and provides transparency and documentation for the adjustment made. It includes important components such as buyer and seller information, a unique identification number, the date of issuance, a description of the goods or services, the amount being credited, and any applicable taxes or fees.
To create a credit memo, businesses gather the necessary information, utilize templates or accounting software, and fill in the required fields. The credit memo is then distributed to the buyer and retained for internal records. The recording of a credit memo in accounting involves identifying the accounts, creating a journal entry, debiting the accounts receivable, and crediting the relevant revenue account.
Credit memos are important in accounting as they contribute to accurate financial reporting, compliance with accounting principles, and effective internal control. They provide evidence for auditing purposes, contribute to customer satisfaction, and foster transparency in financial operations.
It is crucial to differentiate credit memos from invoices. While invoices request payment for goods or services, credit memos acknowledge a credit or refund owed to the buyer due to an adjustment. Invoices lead to an increase in accounts receivable and revenue, while credit memos result in a reduction in accounts receivable and revenue.
In conclusion, credit memos are valuable tools in finance and accounting that facilitate accurate record-keeping, transparency, and customer satisfaction. By understanding their purpose, components, creation process, accounting treatment, and differences from invoices, businesses can effectively manage their financial transactions and maintain reliable financial records.