Finance
What Is A Spread In Stocks
Published: January 18, 2024
Learn about the concept of spreads in stocks and how they impact your financial investments. Gain insights into different types of spreads and their significance in finance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to investing in stocks, one term that frequently comes up is “spread.” Understanding what a spread is and how it affects stock trading is essential for any investor looking to navigate the stock market successfully. In simple terms, a spread refers to the difference between the bid price (the price buyers are willing to pay) and the ask price (the price sellers are willing to accept) for a particular stock. This difference is crucial as it directly impacts the overall cost and potential profit of a trade.
The concept of a spread is not limited to the stock market alone. It is widely used in various financial markets, including forex, options, and futures. However, in this article, we will focus specifically on spreads in stocks.
Understanding spreads is not only important for individual investors but also for institutional traders and market makers. Market makers, who are responsible for maintaining liquidity in the market, often earn their profits from the spreads. Therefore, having a solid grasp of spreads can help investors make informed decisions and identify potential opportunities in the market.
Throughout this article, we will explore the definition of a spread in stocks, how spreads are determined, the different types of spreads, the benefits and risks associated with spreads, as well as some popular trading strategies to consider when dealing with spreads in stocks.
Definition of a Spread in Stocks
A spread in stocks refers to the difference between the bid price and the ask price of a particular stock. To understand this concept more clearly, let’s break it down:
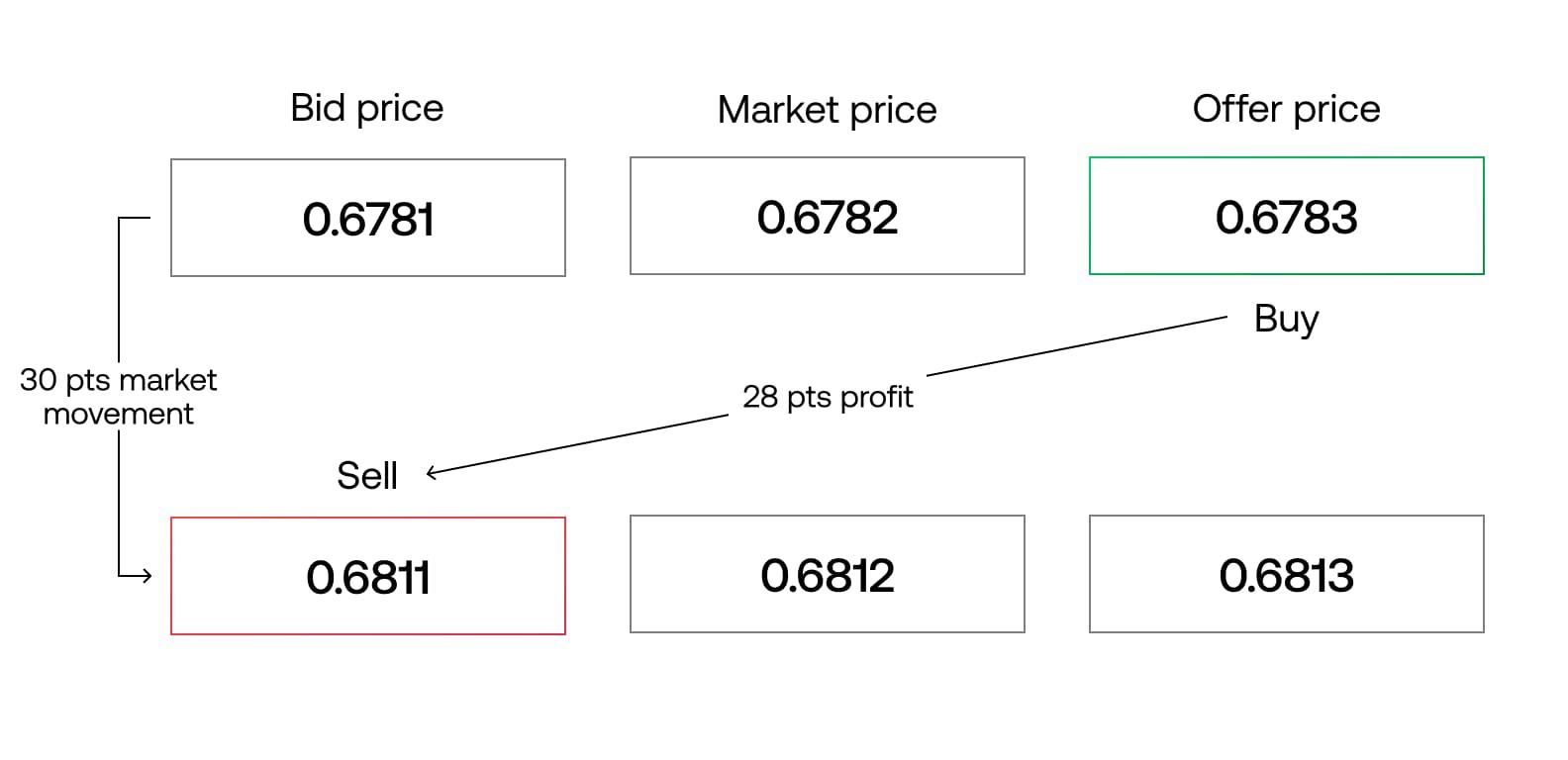
The bid price is the highest price at which buyers in the market are willing to purchase a stock. It represents the demand for the stock from buyers. On the other hand, the ask price is the lowest price at which sellers in the market are willing to sell their stock. It represents the supply of the stock from sellers.
The spread is calculated by subtracting the ask price from the bid price. For example, if a stock has a bid price of $50 and an ask price of $51, the spread would be $1. This means that buyers would have to pay $51 to purchase the stock, while sellers would receive $50 if they decide to sell it.
The spread is typically expressed in terms of “pips” or “points” in the stock market. A pip represents the minimum increment by which a stock price can change. It varies depending on the stock and its trading volume. Understanding the spread is crucial for investors as it directly affects the cost of buying or selling a stock.
It’s important to note that spreads can vary across different stocks and market conditions. Highly liquid stocks with high trading volumes usually have narrower spreads since there are many buyers and sellers actively trading the stock. On the other hand, less liquid stocks with lower trading volumes tend to have wider spreads due to the limited number of buyers and sellers.
Spreads are essential for market makers as well. Market makers are entities that facilitate trading by providing liquidity in the market. They earn their profits from the difference between the bid and ask prices, known as the spread. Market makers quote both the bid and ask prices simultaneously, allowing investors to buy or sell stocks instantly at these prices.
Now that we understand the definition of a spread in stocks let’s dive deeper into how spreads are determined.
How Spreads Are Determined
The determination of spreads in the stock market is influenced by various factors, including market conditions, trading volume, liquidity, and volatility. Let’s explore these factors in more detail:
- Market Conditions: Spreads can widen or narrow depending on the overall market conditions. During periods of high market activity and increased trading volume, spreads tend to narrow as there are more buyers and sellers competing in the market. Conversely, in times of low market activity or during after-hours trading, spreads may widen as there are fewer participants in the market.
- Trading Volume and Liquidity: Stocks with high trading volumes and liquidity usually have narrower spreads. This is because there are more buyers and sellers actively trading these stocks, which leads to tighter bid-ask spreads. On the other hand, low-volume stocks tend to have wider spreads since there are fewer participants in the market, resulting in a less competitive environment.
- Volatility: The volatility of a stock can also impact its spread. Volatility refers to the degree of price fluctuations and market uncertainty. Stocks that exhibit high volatility often have wider spreads to account for the potential price swings and increased risk. Conversely, stable stocks with low volatility tend to have narrower spreads.
- Market Maker Activity: Market makers play a significant role in determining spreads. They quote both the bid and ask prices for stocks, and the difference between these two prices constitutes the spread. Market makers adjust their quotes based on market conditions, trading volume, and their own inventory. If a market maker senses increased buying interest, they may tighten the spread to encourage more trading activity.
It is important to keep in mind that spreads can vary between different brokers and trading platforms. Each broker may apply their own pricing models and fee structures, which can affect the spreads offered to investors. Therefore, it is wise for investors to compare and consider multiple brokers to ensure they are getting the most favorable spreads for their stock trading activities.
Understanding how spreads are determined is crucial for investors as it allows them to assess the cost-effectiveness of their trades and make informed decisions. Now that we have covered the determination of spreads, let’s explore the different types of spreads in stocks.
Types of Spreads
In the stock market, there are several types of spreads that investors can encounter. These spreads can help investors assess the market sentiment, identify potential profit opportunities, and implement various trading strategies. Let’s explore some of the common types of spreads:
- Fixed Spread: A fixed spread is a constant difference between the bid and ask prices of a stock. This type of spread remains the same regardless of changing market conditions. It is commonly used by brokers as a way to generate revenue by charging a fixed fee for each trade.
- Variable Spread: A variable spread refers to a spread that can change based on market conditions. Unlike a fixed spread, which remains constant, a variable spread fluctuates in response to factors such as volatility, liquidity, and trading volume. Variable spreads are often seen in highly liquid markets where prices can change rapidly.
- Bid-Ask Spread: The bid-ask spread is the most common type of spread in the stock market. It represents the difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay (bid price) and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept (ask price). This spread is essential for investors as it determines the cost of buying or selling a stock.
- Vertical Spread: A vertical spread is a strategy that involves simultaneously buying and selling options of the same stock but with different strike prices and expiration dates. This strategy allows investors to profit from the price difference between the two options. Vertical spreads can be either bullish (used when the investor expects the stock price to rise) or bearish (used when the investor expects the stock price to fall).
- Horizontal Spread: A horizontal spread, also known as a calendar spread, is a strategy that involves simultaneously buying and selling options of the same stock with the same strike price but different expiration dates. This strategy aims to benefit from the difference in time decay between the options. Horizontal spreads can be used when investors anticipate a period of low volatility in the stock’s price.
- Butterfly Spread: A butterfly spread is a strategy that involves buying and selling options of the same stock with three different strike prices and the same expiration date. This spread aims to profit from a limited price movement in the underlying stock. It is called a butterfly spread because the shape of the options’ payoff diagram resembles a butterfly.
These are just a few examples of the types of spreads that investors may encounter in the stock market. Each type of spread has its own unique characteristics and can be utilized in different market scenarios. It is important for investors to understand the various types of spreads and their implications in order to make informed trading decisions.
Now that we have covered the different types of spreads, let’s explore the benefits and risks associated with spreads in stocks.
Benefits of Spreads in Stocks
Spreads in stocks offer several benefits to investors, making them a valuable tool in the stock market. Let’s explore some of the key advantages:
- Liquidity: Spreads play a crucial role in maintaining market liquidity. Market makers, who provide liquidity, earn profits from the spread. Their presence ensures that there are always buyers and sellers in the market, making it easier for investors to buy or sell stocks at fair prices.
- Tight Bid-Ask Spread: A narrow bid-ask spread is beneficial for investors as it reduces the overall cost of buying or selling a stock. It allows investors to enter and exit positions at better prices, maximizing their potential profits.
- Price Transparency: Spreads provide investors with important price information. The bid and ask prices quoted by market makers reveal the current supply and demand levels for a particular stock. This transparency helps investors assess the market sentiment and make informed trading decisions.
- Opportunity for Profit: Spreads can create profit opportunities for investors, particularly those who engage in advanced trading strategies such as arbitrage and options trading. By taking advantage of price discrepancies between bid and ask prices or utilizing complex option spreads, investors can aim to generate consistent profits.
- Risk Mitigation: Spreads can help reduce the impact of volatility and market uncertainties. By widening the spread, market makers and brokers account for potential price fluctuations, which can protect investors from sudden and extreme price movements.
- Efficient Market Operations: Spreads contribute to the overall efficiency of the stock market. They incentivize market makers to provide continuous liquidity, enabling smooth trading operations. This leads to faster execution of trades and reduces the likelihood of order delays or slippage.
It is important to note that while spreads offer these benefits, they also come with associated risks. Understanding and managing these risks is crucial for investors. Let’s explore the risks of spreads in stocks in the next section.
Risks of Spreads in Stocks
While spreads in stocks offer various benefits, it is essential for investors to be aware of the associated risks. Understanding and managing these risks is crucial for successful trading in the stock market. Let’s explore some of the key risks:
- Market Volatility: Spreads can widen significantly during periods of high market volatility. This can result in higher trading costs and potential slippage, where the executed trade price differs from the expected price. Investors should be prepared for increased risks and potential losses during volatile market conditions.
- Market Manipulation: In certain cases, spreads can be manipulated by unscrupulous market participants. This can involve artificially widening spreads to take advantage of unsuspecting traders. Investors should be cautious and choose reputable brokers to mitigate the risk of falling victim to such manipulations.
- Liquidity Risk: Spreads can widen for stocks with low trading volumes or during after-hours trading. This can lead to difficulties in executing trades at desired prices, as there are fewer buyers and sellers in the market. Investors should consider the liquidity of a stock before entering into a trade to avoid potential liquidity risks.
- Execution Risk: During fast-moving market conditions, spreads can change rapidly, leading to potential execution risks. It is important for investors to have reliable and efficient trading systems to quickly adapt to changing spreads and execute trades in a timely manner.
- Cost of Trading: Depending on the brokerage firm and the type of account, investors may incur additional costs such as commissions, fees, and wider spreads. These costs can impact the overall profitability of trades, especially for active traders. It is important for investors to consider these costs when formulating trading strategies.
- Overdependence on Spreads: Relying solely on spreads as a trading strategy may limit profitability and fail to capture other market indicators. It is important for investors to consider additional factors such as technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and market trends to make well-informed trading decisions.
By being aware of these risks and implementing proper risk management strategies, investors can navigate the stock market more effectively and minimize potential losses. Spreads should be considered as one aspect of a comprehensive trading plan rather than the sole determinant of investment decisions.
Now that we have explored the risks associated with spreads in stocks, let’s move on to discussing some popular trading strategies for utilizing spreads.
Trading Strategies for Spreads in Stocks
Spreads in stocks present investors with various trading opportunities. By utilizing different strategies, investors can potentially profit from the price difference between the bid and ask prices. Let’s explore some popular trading strategies for utilizing spreads:
- Directional Spread: This strategy involves taking a position based on the anticipated direction of the stock’s price movement. For bullish outlooks, investors can use a call spread, where they buy a call option with a lower strike price and simultaneously sell a call option with a higher strike price. Conversely, for bearish outlooks, investors can utilize a put spread, where they buy a put option with a higher strike price and simultaneously sell a put option with a lower strike price.
- Calendar Spread: Also known as a horizontal spread, this strategy involves simultaneously buying and selling options with different expiration dates but the same strike price. Investors use this strategy when they anticipate minimal price movement in the stock’s price but expect volatility over a longer period. The goal is to take advantage of time decay while reducing the cost of the options position.
- Vertical Spread: A vertical spread involves buying and selling options with different strike prices but the same expiration date. This strategy allows investors to profit from the price difference between the two options. Bullish vertical spreads, known as bull call spreads, involve buying a call option with a lower strike price and simultaneously selling a call option with a higher strike price. Bearish vertical spreads, known as bear put spreads, involve buying a put option with a higher strike price and simultaneously selling a put option with a lower strike price.
- Butterfly Spread: A butterfly spread involves buying and selling options with three different strike prices but the same expiration date. This strategy is used when investors anticipate minimal price movement in the stock. The goal is to profit from both the upside and downside potential within a specific range of prices. Butterfly spreads can be constructed using either calls or puts.
- Ratio Spread: This strategy involves buying and selling options with a different number of contracts. The goal is to create a spread that benefits from volatility or slight price changes in the underlying asset. Ratio spreads can be constructed using either calls or puts.
It’s important for investors to carefully consider their risk tolerance, market conditions, and their outlook on the stock before implementing any trading strategy. Additionally, conducting thorough research, utilizing technical and fundamental analysis, and staying updated with market news can greatly increase the chances of success when using spread trading strategies.
Remember that trading strategies involving spreads can be complex and may carry their own risks. Investors should consider consulting with a financial advisor or a qualified professional before implementing any spread trading strategies.
Now that we have explored various trading strategies for utilizing spreads, let’s conclude our discussion.
Conclusion
Understanding spreads in stocks is crucial for any investor looking to navigate the stock market effectively. A spread represents the difference between the bid and ask prices of a stock and directly impacts the cost and potential profit of a trade. Throughout this article, we have covered the definition of a spread, how spreads are determined, the different types of spreads, the benefits and risks associated with spreads, and popular trading strategies for utilizing spreads.
Spreads in stocks offer several benefits, including liquidity, tight bid-ask spreads, price transparency, profit opportunities, risk mitigation, and efficient market operations. However, they also come with risks, such as market volatility, liquidity risk, execution risk, and the cost of trading. It is important for investors to be aware of these risks and to implement proper risk management strategies.
When it comes to trading strategies, investors can consider directional spreads, calendar spreads, vertical spreads, butterfly spreads, and ratio spreads, depending on their market outlook and risk appetite. It is crucial to conduct thorough research and analysis, stay updated with market news, and seek professional advice to increase the chances of success when utilizing these strategies.
In conclusion, understanding spreads and incorporating them into your investment approach can provide valuable insights and opportunities in the stock market. By mastering the concept of spreads and implementing appropriate trading strategies, investors can navigate the market with confidence and potentially enhance their investment returns. Remember to stay informed, adapt to market conditions, and manage risks effectively to achieve long-term success in the dynamic world of stock trading.