
Finance
What Is An API In Open Banking
Modified: December 30, 2023
Learn how APIs in open banking are revolutionizing the finance industry. Understand the role of APIs in enhancing financial services, security, and innovation.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of open banking! In this digital era, financial services are transforming rapidly, and open banking is at the forefront of this revolution. At the heart of open banking lies the concept of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). APIs play a crucial role in enabling secure and seamless data sharing between financial institutions and third-party providers.
So, what exactly is an API? In simple terms, an API is a set of rules and protocols that allow different software applications to communicate with each other. It serves as an intermediary, enabling the transfer of data and functionality between systems. APIs have become the backbone of modern computing, facilitating integration and interoperability between various platforms and services.
Open banking, on the other hand, refers to a financial ecosystem that promotes transparency, competition, and innovation by allowing customers to securely share their financial data with authorized third-party providers. This data sharing is facilitated by APIs, which enable seamless communication between banks, fintech companies, and other financial institutions.
Open banking has emerged as a game-changer in the finance industry, opening up new opportunities for customer-centric products and services. It empowers consumers to have greater control over their financial data and access a wider range of personalized solutions. At the same time, it presents a host of challenges and considerations for financial institutions and technology providers.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the world of APIs in open banking. We will explore how APIs facilitate data sharing in this context, and highlight the benefits and challenges associated with their implementation. We will also examine some real-life use cases to illustrate the practical applications of APIs in the open banking landscape.
Additionally, we will touch upon the crucial aspect of API security in open banking, emphasizing the need for robust measures to protect customer data and ensure privacy.
By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of the significance of APIs in open banking and how they have revolutionized the financial services industry. So, let us embark on this journey together to unravel the complexities and opportunities of open banking APIs.
Defining API
Before we dive deeper into the world of APIs in open banking, let’s start by understanding what an API actually is. API, which stands for Application Programming Interface, is a set of rules and protocols that defines how software applications can interact with each other. It acts as a bridge that allows different applications to communicate, exchange data, and access functionalities.
Think of an API as a messenger that facilitates communication between two parties – the sender (the application requesting data or functionality) and the receiver (the application providing the requested data or functionality). It specifies the methods, protocols, and data formats through which this communication takes place, ensuring that the interaction is seamless and standardized.
APIs come in different forms, such as web APIs, library APIs, and operating system APIs, to name a few. In the context of open banking, we mainly focus on web APIs, which enable the secure and standardized sharing of financial data between banks and external parties.
Web APIs in open banking allow third-party providers, such as fintech companies or other financial institutions, to access a bank’s customer data (with the customer’s consent) and build innovative products and services around it. These APIs define the rules and protocols for requesting specific data, such as account information, transaction history, or balance details, and allow the third-party provider to retrieve that data in a secure and efficient manner.
APIs in open banking are based on widely adopted standards and technologies, such as REST (Representational State Transfer) and JSON (JavaScript Object Notation). REST APIs use HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) as the underlying communication protocol, making them simple, scalable, and platform-independent.
Overall, APIs are the backbone of open banking, enabling the secure and standardized exchange of data and functionality between different financial institutions and third-party providers. They foster collaboration, innovation, and competition within the finance industry, ultimately benefiting the end customers by providing them with a wider range of personalized and innovative financial products and services.
Now that we have a clear understanding of what APIs are, let’s explore how they are applied in the context of open banking and why they play a crucial role in this transformative landscape.
Understanding Open Banking
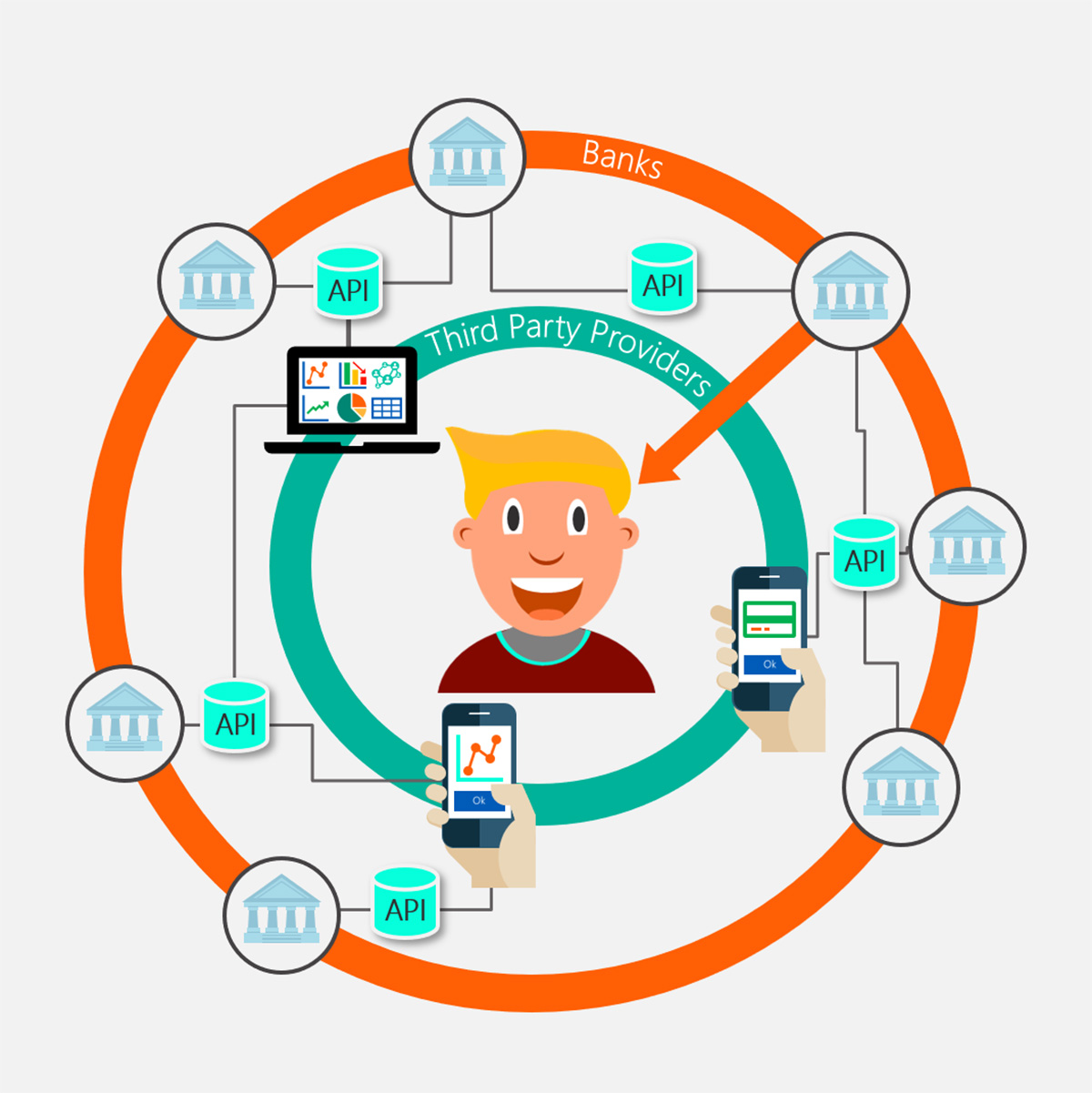
Open banking refers to a regulatory framework that allows customers to share their financial data with authorized third-party providers through the use of APIs. The objective of open banking is to promote competition, innovation, and customer-centricity within the financial services industry.
In traditional banking, customers’ financial data is typically held in silos by individual banks. This restricts customers from easily accessing and sharing their own financial information with other financial service providers. Open banking aims to break down these barriers by creating a secure and standardized way for customers to share their data with other authorized financial institutions or fintech companies.
The concept of open banking gained momentum with the implementation of various regulations, such as the European Union’s Revised Payment Services Directive (PSD2) and the United Kingdom’s Open Banking Initiative. These regulations require banks to open up their APIs to allow authorized third parties to access customer data and initiate transactions on behalf of customers, with the customers’ explicit consent.
Open banking brings numerous benefits for customers, financial institutions, and fintech companies. For customers, open banking offers greater control over their financial data and access to a broader range of personalized financial services. They can easily compare products, switch providers, and benefit from innovative solutions tailored to their specific needs.
Financial institutions also benefit from open banking as it allows them to collaborate with fintech companies and other third-party providers. By sharing customer data securely via APIs, banks can offer enhanced and personalized services, streamline their operations, and generate new revenue streams. It also fosters competition and innovation within the industry, driving better products and services for customers.
Fintech companies, on the other hand, gain access to valuable customer data through open banking APIs. This enables them to build innovative financial products and services, such as budgeting apps, loan comparison platforms, and investment advisory services, using real-time and accurate customer information. Open banking APIs provide the necessary infrastructure for fintech companies to develop and scale their offerings.
It is important to note that while open banking promotes data sharing and collaboration, it is built upon a foundation of strong security and privacy measures. Banks and third-party providers must comply with strict regulatory guidelines and employ robust security protocols to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of customer data.
Overall, open banking represents a significant shift in the finance industry, leveraging APIs to enable secure data sharing and collaboration between banks and third-party providers. By embracing open banking, financial institutions can unlock new opportunities for growth, innovation, and customer satisfaction.
Now that we have a clear understanding of open banking, let’s explore the crucial role that APIs play in facilitating data sharing and innovation within this framework.
Importance of APIs in Open Banking
APIs serve as the backbone of open banking and play a crucial role in enabling secure and standardized data sharing between banks and third-party providers. They have become the foundation upon which innovation, collaboration, and competition thrive within the open banking ecosystem.
One of the key reasons why APIs are vital in open banking is their ability to facilitate seamless integration and interoperability between different systems. APIs provide a common language and set of protocols that enable different applications to communicate and exchange data. This allows various financial institutions and fintech companies to connect and collaborate, creating a rich ecosystem of innovative products and services.
APIs also simplify the process of accessing and sharing customer data. In the traditional banking model, accessing customer data involved manual processes or complex integrations. With APIs, authorized third-party providers can securely request and retrieve specific customer data, such as account details or transaction history, with the customer’s consent. This speeds up the process, reduces errors, and enhances efficiency.
Furthermore, APIs in open banking ensure data standardization and consistency. By adhering to a common set of API specifications and data formats, financial institutions and third-party providers can effectively exchange and interpret data from different sources. This promotes seamless data integration and improves the accuracy and reliability of financial services.
The use of APIs in open banking also fosters competition and innovation. By opening up their APIs, banks allow third-party providers to access customer data and build value-added services. This creates a level playing field, where fintech companies, startups, and traditional banks can compete based on the quality and innovation of their products rather than the scale of their infrastructure. As a result, customers have access to a wider range of innovative and tailored financial solutions.
APIs are not only important for third-party providers but also for banks themselves. APIs allow banks to leverage external expertise, technologies, and resources through partnerships with fintech companies. This enables banks to enhance their product offerings, expand their reach, and deliver a superior customer experience. APIs also enable banks to offer personalized and contextualized services by integrating data from multiple sources, enriching the customer experience and improving customer satisfaction.
Moreover, APIs empower customers by providing them with control over their data. Through APIs, customers can securely share their financial information with authorized third-party providers, enabling them to access personalized financial products and services. This puts customers at the center of the open banking ecosystem and gives them the freedom to choose the solutions that best meet their needs.
In summary, APIs are of utmost importance in open banking as they enable seamless integration, standardized data sharing, competition, and innovation. They empower both financial institutions and customers, enabling them to benefit from the vast opportunities presented by open banking.
Now, let’s dive deeper into how APIs work in the context of open banking and explore the mechanics behind their operation.
How APIs Work in Open Banking
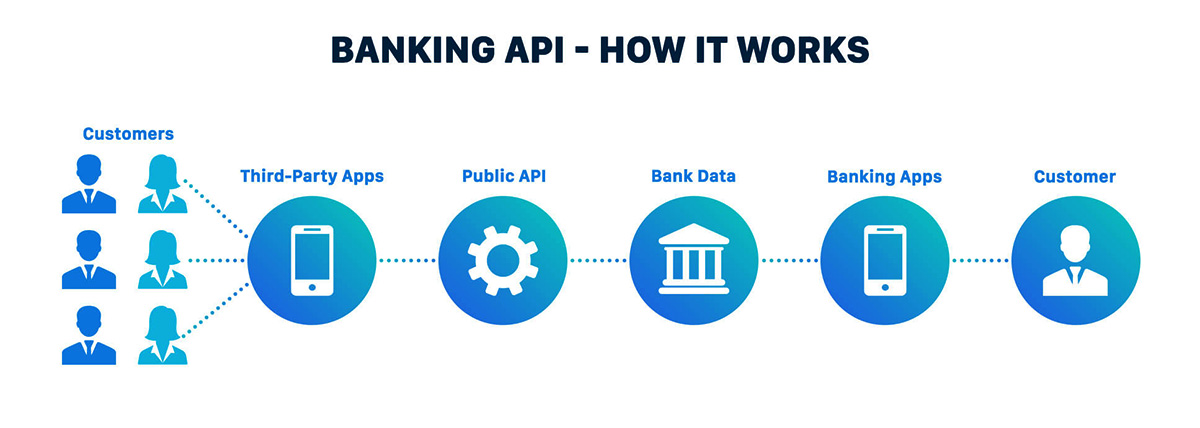
APIs play a vital role in facilitating data sharing and communication between banks and third-party providers in the open banking ecosystem. They provide a standardized and secure way for financial institutions to expose their data and services to authorized external parties. Let’s explore how APIs work in the context of open banking.
1. Authorization and Consent: Before accessing customer data, third-party providers need to obtain explicit authorization and consent from the customer. This is typically done through a secure authentication process, where the customer grants permission for the provider to access their financial data. The authorization and consent process ensures that customer data is protected and accessed only by authorized parties.
2. API Registration: Banks and financial institutions offer APIs that allow authorized third-party providers to interact with their systems and access customer data. To use these APIs, third-party providers must register with the bank and obtain the necessary credentials, such as an API key or access token. This registration process helps maintain control and security over API access.
3. API Documentation and Specifications: Banks provide API documentation and specifications to assist third-party developers in integrating and utilizing their APIs effectively. This documentation outlines the available endpoints, data formats, authentication methods, and any usage limitations or technical requirements. It serves as a guide for developers, ensuring that they have the necessary information to interact with the API correctly.
4. Data Retrieval and Exchange: Once authorized and registered, third-party providers can make API calls to request specific customer data from the bank’s systems. These API calls are made using standardized protocols, such as REST or SOAP, and include parameters specifying the requested data. The bank’s API processes the request, retrieves the relevant data, and returns it to the third-party provider in a structured format, such as JSON or XML. This data exchange happens securely over encrypted connections.
5. Real-Time Updates: APIs in open banking support real-time updates, ensuring that third-party providers have access to the most up-to-date customer data. Banks may notify third-party providers of any changes or updates to customer information, such as new transactions or balance updates, through webhook notifications or periodic API calls. This real-time data availability enables the development of dynamic and responsive financial services.
6. Security and Compliance: Security is a paramount concern in open banking. Banks implement robust security measures, such as strong authentication, encryption, and access controls, to protect customer data and prevent unauthorized access. Compliance with regulatory requirements, such as data privacy and protection regulations, is also crucial. Banks must ensure that API operations adhere to strict security and compliance standards to maintain customer trust and meet legal obligations.
Through these mechanisms, APIs enable seamless and secure data sharing between banks and third-party providers in open banking. They facilitate the exchange of information in a standardized manner, ensuring interoperability and fostering innovation within the financial services industry.
Next, let’s explore some of the benefits and challenges associated with the use of APIs in open banking.
Benefits and Challenges of APIs in Open Banking
APIs play a pivotal role in open banking, bringing a host of benefits to both financial institutions and consumers. However, they also present certain challenges that need to be addressed. Let’s explore the benefits and challenges of APIs in the context of open banking.
Benefits of APIs in Open Banking:
1. Enhanced Customer Experience: APIs enable the development of innovative and personalized financial products and services. Customers can access a wide range of offerings tailored to their specific needs, resulting in an improved overall user experience.
2. Increased Competition and Innovation: By opening up their APIs, banks foster competition and encourage the development of innovative solutions by third-party providers. This leads to a more vibrant and dynamic financial ecosystem.
3. Speed and Efficiency: APIs enable seamless integration and data exchange, reducing manual processes and streamlining operations. This results in faster and more efficient financial transactions and services.
4. Access to New Revenue Streams: By leveraging APIs, financial institutions can collaborate with third-party providers and tap into new revenue streams. They can offer value-added services and benefit from revenue-sharing models.
5. Data Sharing and Collaboration: APIs enable secure and standardized data sharing between financial institutions and third-party providers, fostering collaboration and enabling the development of comprehensive financial solutions.
Challenges of APIs in Open Banking:
1. Security and Privacy Concerns: APIs introduce potential security and privacy risks, as they involve the exchange of sensitive customer data. Strong security measures and compliance with data protection regulations are crucial to mitigate these risks.
2. Technical Complexity: Implementing and integrating APIs can be technically complex, requiring expertise in API management and development. Ensuring compatibility and smooth integration across different systems can pose technical challenges.
3. API Standardization: Interoperability and standardization across different APIs can be a challenge. Harmonizing specifications, data formats, and authentication methods is essential to achieve seamless integration and data exchange.
4. Customer Trust and Consent: Building customer trust and obtaining their consent for data sharing is critical. Ensuring that customers understand the implications of sharing their financial data and providing transparent consent mechanisms are key challenges.
5. Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with regulatory requirements, such as data protection and privacy regulations like GDPR, is a significant challenge. Financial institutions need to ensure that their API operations adhere to strict compliance standards.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of APIs in open banking outweigh the challenges, as they enable collaboration, innovation, and customer-centric financial services. Overcoming these challenges requires a collective effort from regulators, financial institutions, and technology providers to ensure secure and standardized API implementation.
Now, let’s explore some real-life use cases that demonstrate the practical applications of APIs in open banking.
Use Cases of APIs in Open Banking
APIs in open banking have paved the way for a multitude of use cases, enabling financial institutions and third-party providers to offer innovative and personalized financial products and services. Let’s explore some real-life examples of how APIs are being used in the context of open banking.
1. Account Aggregation and Personal Financial Management:
APIs allow customers to consolidate and view their financial information from multiple accounts in one place. Personal financial management apps and platforms use APIs to aggregate data from various banks and provide users with a comprehensive overview of their financial health, transaction history, and spending patterns. These apps offer valuable insights, budgeting tools, and personalized recommendations to help users manage their finances effectively.
2. Payment Initiation and Account Verification:
APIs enable secure initiation of payments directly from a customer’s bank account through authorized third-party providers. This eliminates the need for customers to provide their banking details to merchants, enhancing security and convenience. APIs also facilitate real-time account verification, enabling businesses to verify the authenticity and funds availability of a customer’s bank account during online transactions.
3. Loan Origination and Underwriting:
Financial institutions can leverage APIs to streamline the loan origination and underwriting processes. APIs allow lenders to access a customer’s financial data, such as income, credit history, and banking transactions, to assess their creditworthiness. This accelerates the loan approval process, improves accuracy, and enables the provision of personalized loan options tailored to the customer’s financial profile.
4. Investment Advisory and Wealth Management:
APIs enable the integration of investment and wealth management platforms with banks, allowing customers to access personalized investment advice and portfolio management services. APIs provide real-time access to customer account balances, investment performance, and market data, enabling investment platforms to offer tailored recommendations and automated portfolio rebalancing based on the customer’s financial goals and risk tolerance.
5. Fraud Detection and Prevention:
APIs assist in fraud detection and prevention by enabling real-time data exchange between banks and third-party fraud detection providers. APIs allow banks to share transaction data and patterns with advanced analytics systems, which analyze the data for suspicious activities and identify potential fraud attempts. This proactive approach helps detect and prevent fraudulent transactions, safeguarding customer accounts and enhancing the security of open banking.
6. Credit Scoring and Alternative Lending:
APIs enable lenders to access a customer’s financial data, including credit history and transaction information, to assess their creditworthiness. This opens up opportunities for alternative lending platforms to provide loans to individuals or small businesses that may not have sufficient credit history or collateral. APIs facilitate secure and seamless data sharing, allowing these platforms to make faster lending decisions and extend credit to underserved populations.
These are just a few examples of the wide range of use cases made possible by the use of APIs in open banking. APIs drive innovation, competition, and customer-centricity within the financial services industry, empowering individuals and businesses with a plethora of tailored and convenient financial solutions.
Now, let’s explore the vital aspect of API security in open banking.
API Security in Open Banking
API security is of paramount importance in open banking, as it involves the exchange of sensitive financial data between banks and third-party providers. Strong security measures are crucial to protect customer information, maintain trust, and comply with regulatory requirements. Let’s explore the key aspects of API security in the context of open banking.
1. Authentication and Access Control:
APIs in open banking require robust authentication mechanisms to ensure that only authorized parties can access and exchange data. Strong authentication methods, such as two-factor authentication or OAuth, are implemented to verify the identity of the users and securely manage access to the APIs. Access control measures are also employed to limit the data that can be accessed by different users based on their roles and permissions.
2. Encryption and Data Privacy:
Encryption is essential to protect data transmitted over APIs in open banking. Secure Socket Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols are leveraged to encrypt the data during transmission, ensuring that it cannot be intercepted or tampered with by unauthorized individuals. Encryption at rest is also implemented to protect stored data, preventing unauthorized access in case of a security breach. Compliance with data privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), is a vital consideration to protect customer data and ensure privacy.
3. Threat Detection and Prevention:
APIs are vulnerable to various security threats, including unauthorized access, injection attacks, and data breaches. To mitigate these risks, advanced threat detection and prevention systems are deployed. These systems monitor API traffic, analyze patterns, and detect suspicious activities or anomalies. Intrusion detection and prevention mechanisms, along with regular security assessments and vulnerability management, are incorporated to prevent and respond to potential threats.
4. Audit Trails and Logging:
Comprehensive audit trails and logging mechanisms are vital to track API activity and maintain an audit history. Logging API requests, responses, and other relevant information allows for forensic analysis in case of security incidents or compliance audits. Audit trails help identify potential security breaches, unauthorized activities, or suspicious behavior, ensuring accountability and facilitating effective incident response.
5. Security Standards and Compliance:
Banks and third-party providers must adhere to security standards and regulations to ensure API security in open banking. Industry standards, such as the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) guidelines, provide best practices for secure API development. Compliance with regulatory frameworks, such as PSD2 or Open Banking standards, ensures that security requirements specific to open banking are met.
6. Secure Communication Channels:
APIs in open banking rely on secure communication channels to transmit data securely. Implementing secure protocols, such as HTTPS, ensures encrypted communication between the parties involved. Regular assessments and monitoring of the security of communication channels are essential to maintain the integrity and confidentiality of data transmitted through APIs.
Effective API security measures require a multi-layered approach, encompassing technical controls, user awareness, and ongoing monitoring. Collaboration between financial institutions, third-party providers, and regulators is crucial to establish and enforce robust API security practices to protect customer data and maintain trust in the open banking ecosystem.
Finally, let’s summarize the key points discussed in this article on APIs in open banking.
Conclusion
In conclusion, APIs have revolutionized the financial services industry and are a fundamental component of open banking. APIs enable secure and standardized data sharing between banks and third-party providers, fostering innovation, competition, and collaboration within the financial ecosystem.
Through APIs, customers can access personalized financial products and services, gaining control over their financial data and expanding their options. APIs facilitate the development of innovative solutions such as account aggregation, payment initiation, investment advisory, and more, enhancing the overall customer experience.
Financial institutions also benefit from APIs in open banking. APIs enable banks to collaborate with fintech companies, leverage external expertise, and tap into new revenue streams. They offer opportunities for enhanced efficiency, streamlined processes, and improved product offerings, allowing banks to stay competitive in an evolving landscape.
However, implementing APIs in open banking comes with its challenges. Security and privacy concerns, technical complexities, and compliance with regulations are key areas that need to be addressed. Robust security measures, including authentication, encryption, and threat detection, are crucial to protect customer data and maintain trust.
APIs in open banking have transformed the way financial services are delivered, benefiting both consumers and financial institutions alike. They have opened up opportunities for collaboration, innovation, and customer-centricity, giving rise to a more dynamic and inclusive financial ecosystem.
As open banking continues to evolve and expand, it is essential for financial institutions, third-party providers, and regulators to work together to establish and enforce best practices in API security, data privacy, and compliance. By doing so, we can ensure the continued growth and success of open banking while safeguarding the interests and trust of customers.
In conclusion, APIs are the driving force behind the transformation of traditional banking into a more open, connected, and customer-centric landscape. It is an exciting time for the financial services industry as APIs enable innovation, foster collaboration, and empower individuals and businesses with personalized financial solutions.