
Finance
What Is An API In Banking
Published: October 11, 2023
Learn what an API is in banking and how it impacts the world of finance. Discover the role of APIs in enabling seamless financial transactions and innovation.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
The banking industry has always been at the forefront of adopting new technologies to improve efficiency, convenience, and customer experience. One such technology that has revolutionized the way banking services are delivered is the Application Programming Interface, or API. APIs have become an integral part of digital banking, allowing different software applications and systems to communicate with each other seamlessly.
But what exactly is an API? An API is a set of rules and protocols that enables different software applications to interact and share data with each other. It acts as a bridge, allowing developers to access certain functionalities or data from a platform or service without having to understand the underlying infrastructure. In the context of banking, APIs have opened up a world of possibilities by enabling the integration of banking services with a wide range of applications, from personal financial management apps to e-commerce platforms.
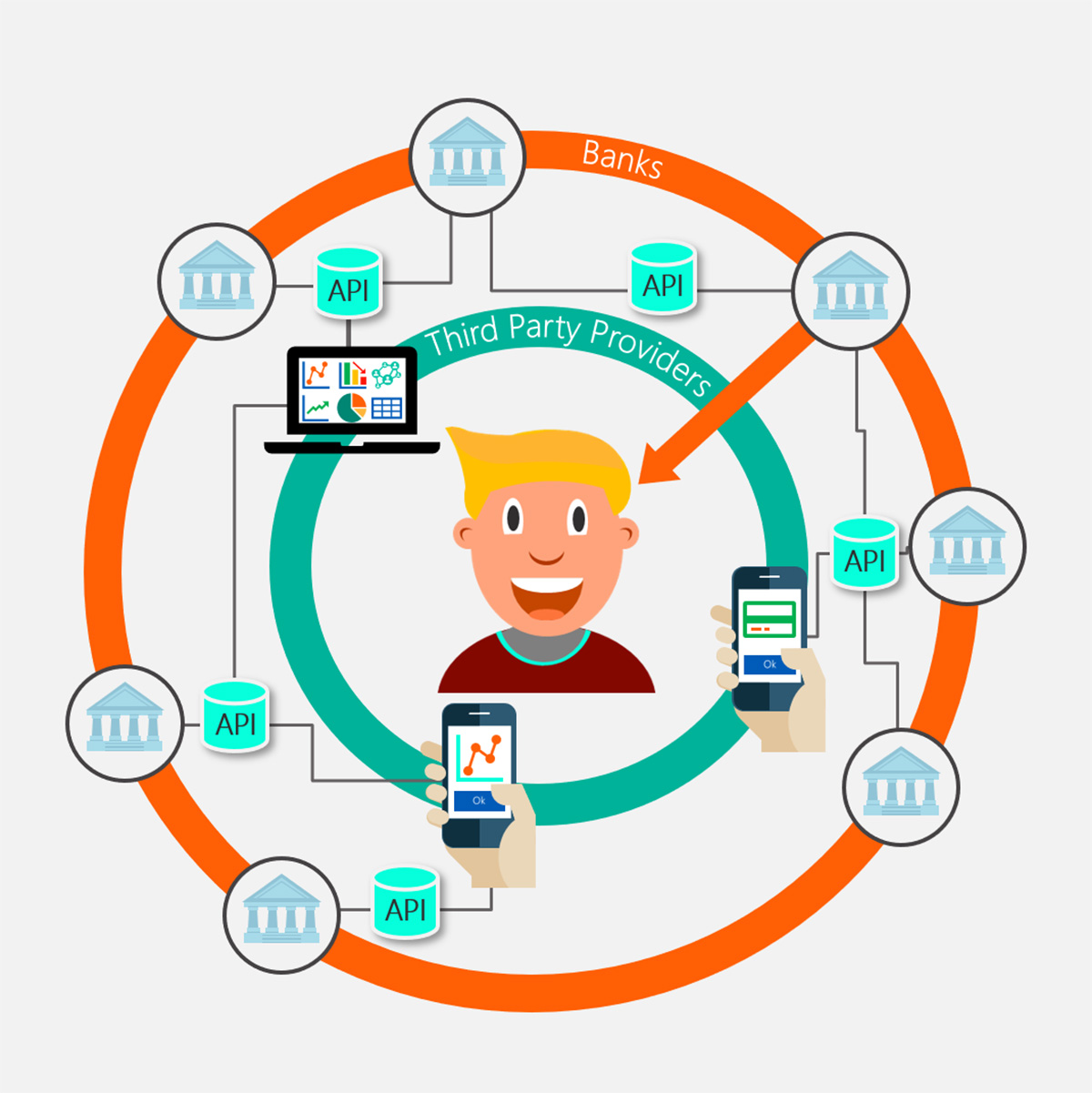
The advent of APIs in the banking industry has brought about a paradigm shift in how financial services are delivered. Traditionally, banks operated in a closed ecosystem, where all products and services were offered through their own platforms. However, with the rise of APIs, banks are now able to collaborate with third-party developers and leverage their expertise to offer a more comprehensive and personalized banking experience to their customers.
The importance of APIs in the banking industry cannot be overstated. APIs enable banks to securely share customer data with authorized third-party providers, allowing for the development of innovative financial products and services. Furthermore, APIs facilitate the integration of banking services with other digital platforms, making it easier for customers to access and manage their financial information and transactions.
In this article, we will explore the benefits of APIs in banking, the different types of APIs used, and the challenges and considerations in implementing APIs in the banking sector. We will also discuss real-world examples of APIs in banking applications and examine the future trends and possibilities of APIs in the financial industry. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of the significance of APIs in transforming the banking landscape and empowering both banks and their customers with enhanced financial capabilities.
Definition of an API
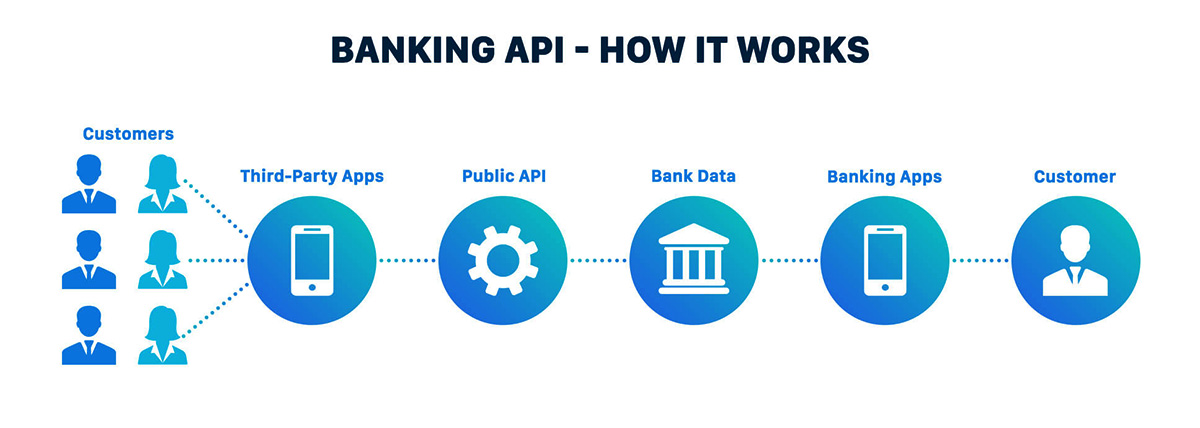
An Application Programming Interface (API) is a set of rules, protocols, and tools that allows different software applications to communicate and interact with each other. In simpler terms, an API acts as a bridge or intermediary that enables the sharing of data and functionalities between different systems. It defines how software components should interact and the methods of accessing and manipulating data.
In the context of the banking industry, an API serves as a gateway that allows banks to expose their data and services to authorized external developers and third-party applications. Banks can define and publish APIs that specify the available functionalities and the format in which data should be accessed. These APIs can be accessed by developers who want to integrate banking services into their own applications.
APIs are typically made up of a collection of functions, classes, protocols, and data structures. They define the operations that can be performed, the input parameters required, and the expected output format. Developers can use these APIs to access and interact with the underlying systems and services without needing to understand the complex inner workings.
APIs can be categorized into different types based on their purpose. Some common types of APIs in the banking industry include:
- Public APIs: These are APIs made available to external developers and third-party applications to access specified banking functionalities or data. Public APIs provide a standardized way for developers to integrate banking services into their applications.
- Private APIs: These APIs are meant for internal use within the bank. They are used to enable communication between different systems and departments within the bank and are not accessible to external developers.
- Partner APIs: These APIs are provided to trusted partners of the bank, such as fintech companies or other financial institutions. Partner APIs enable collaboration and integration between the bank and its partners.
It is important to note that APIs in the banking industry are subject to strict security measures and compliance regulations. Banks must ensure the proper authentication, authorization, and encryption mechanisms are in place to safeguard customer data and protect against unauthorized access.
Importance of APIs in the banking industry
APIs have become increasingly important in the banking industry, playing a pivotal role in transforming how financial services are delivered. Here are some key reasons why APIs are crucial in the banking sector:
- Enhanced customer experience: APIs enable banks to collaborate with third-party developers and integrate their services with other digital platforms. This opens up a world of possibilities for customers, allowing them to access banking services within apps they already use, such as personal financial management apps or e-commerce platforms. Through the use of APIs, banks can provide a seamless and consistent experience, making it easier for customers to manage their finances and access a wide range of financial products and services. This enhanced customer experience is key in attracting and retaining customers in today’s competitive banking landscape.
- Increased innovation and agility: APIs enable banks to tap into the innovative capabilities of external developers and fintech companies. By exposing their core functionalities and data through APIs, banks can leverage the expertise of these developers to create new and innovative financial products and services. This collaborative approach also allows for quicker development and deployment of new features, giving banks a competitive advantage in the fast-paced digital era.
- Expanded reach and customer base: APIs enable banks to easily connect with third-party platforms and reach new customer segments. By integrating their services with popular digital platforms, banks can expand their customer base and attract tech-savvy customers who prefer managing their finances through mobile apps and online platforms. APIs also enable banks to tap into the customer bases of their partners, creating a win-win situation for both parties.
- Streamlined processes and cost savings: APIs allow banks to automate and streamline processes by integrating different systems and applications. This reduces manual intervention, improves efficiency, and saves costs by eliminating the need for redundant data entry or manual reconciliation. For example, by integrating with third-party payment platforms, banks can facilitate fast and secure payment transfers, reducing the dependency on traditional payment methods and manual processes.
- Compliance and security: APIs play a crucial role in ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and maintaining data security. Banks can implement security measures such as authentication and encryption within their APIs to protect customer data and prevent unauthorized access. APIs also provide better control over data sharing, as access to sensitive customer information can be restricted to authorized and trusted third-party providers.
In summary, APIs have become an essential component in the banking industry, driving innovation, enhancing customer experience, and enabling seamless integration with third-party digital platforms. Banks that embrace APIs will have a competitive edge, offering their customers more convenience, access to a wider range of services, and a superior banking experience overall.
Benefits of APIs in banking
The use of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) in the banking industry offers a multitude of benefits for both financial institutions and their customers. These benefits are driving the widespread adoption of APIs in the banking sector. Here are some key advantages of using APIs in banking:
- Enhanced customer experience: APIs enable banks to provide a seamless and personalized banking experience to their customers. By integrating banking services with third-party applications, customers can perform financial transactions, access account information, and manage their finances within the platforms they are already familiar with. This convenience and accessibility lead to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Improved product offerings: APIs allow banks to leverage the expertise of external developers and fintech companies to create innovative financial products and services. By exposing their core functionalities and data through APIs, banks can collaborate with these partners to develop new solutions that meet the evolving needs of customers. This leads to a more diverse and competitive range of products in the market.
- Streamlined operations: APIs enable banks to automate processes and improve operational efficiency. By integrating various systems and applications through APIs, banks can reduce manual data entry, eliminate data duplication, and minimize errors. This streamlines processes such as customer onboarding, payment transfers, and account management, resulting in cost savings and faster turnaround times.
- Increased security: APIs play a crucial role in ensuring the security and privacy of customer data. Banks can implement robust security measures within their APIs, such as encryption, authentication, and access controls, to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. APIs also provide better control over data sharing, allowing banks to securely share customer data with authorized third-party providers, while maintaining compliance with data protection regulations.
- Expanded business opportunities: APIs create new avenues for banks to expand their business and reach new customer segments. By exposing their services through APIs, banks can collaborate with partners in different industries, such as e-commerce, travel, or insurance, to offer integrated solutions. This collaboration opens up cross-selling opportunities and allows banks to tap into the customer base of their partners, resulting in increased revenue streams.
- Agility and adaptability: APIs enable banks to quickly adapt to changing market dynamics and customer expectations. By decoupling the front-end applications from the underlying systems through APIs, banks can easily upgrade or replace individual components without disrupting the entire ecosystem. This agility allows banks to stay competitive and deliver new features and functionalities to customers in a timely manner.
As the banking industry continues to evolve, the benefits of APIs in enabling innovation, improving customer experience, and optimizing operational efficiency are becoming increasingly evident. Banks that embrace APIs as a strategic tool will be well-positioned to thrive in the digital era and meet the expectations of tech-savvy customers.
Types of APIs used in banking
When it comes to the banking industry, there are several types of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) that are utilized to facilitate various functionalities and services. These different types of APIs enable seamless integration between different systems and applications, allowing banks to offer innovative solutions to their customers. Here are some common types of APIs used in banking:
- Payment APIs: Payment APIs enable banks to offer secure and convenient payment processing services to their customers. These APIs facilitate the seamless transfer of funds between bank accounts or between a bank account and a merchant. Payment APIs are crucial for enabling online transactions, mobile payments, and person-to-person payment transfers.
- Account APIs: Account APIs give authorized third-party applications access to a customer’s account information, including transaction history, balance, and account details. These APIs enable customers to view their account information and perform various actions, such as making transfers or initiating payments, directly from external platforms or applications without the need to log into their bank’s web or mobile app.
- Identity APIs: Identity APIs are used to authenticate and verify the identity of customers during account creation, login, or transaction authorization. These APIs integrate with identity verification services to ensure the security and integrity of customer data, helping to prevent fraud and unauthorized access.
- Risk assessment APIs: Risk assessment APIs provide banks with tools to assess and manage risk associated with lending and financial decision-making. These APIs leverage data analytics and machine learning algorithms to analyze creditworthiness, detect fraud, and provide real-time risk assessment for loan approvals or investment decisions.
- Product APIs: Product APIs expose the details and functionalities of specific financial products offered by banks. These APIs allow third-party applications to showcase and sell banking products and services, such as mortgages, loans, or insurance policies. Product APIs enable banks to reach new customers through partner platforms, expanding their product distribution channels.
- Market data APIs: Market data APIs provide real-time access to financial market information, such as stock prices, exchange rates, or commodity prices. These APIs enable developers to build applications that incorporate up-to-date market data for investment analysis, trading, or financial planning.
- Compliance APIs: Compliance APIs help banks automate compliance processes and stay on top of regulatory requirements. These APIs integrate with anti-money laundering (AML) systems, know your customer (KYC) processes, and other compliance tools to verify customer identities, monitor transactions, and ensure adherence to regulatory standards.
By leveraging these different types of APIs, banks can offer a wide range of services, foster collaboration with external partners, and provide customized experiences for their customers. The utilization of APIs in banking has opened up new avenues for innovation, improved customer experience, and streamlined operations throughout the industry.
Examples of APIs in banking applications
The use of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) in the banking industry has led to the development of numerous innovative applications and services. These APIs enable seamless integration with third-party platforms and applications, enhancing the banking experience for customers and opening up new opportunities for collaboration. Here are some examples of APIs in banking applications:
- Payment gateway APIs: Payment gateway APIs are widely used in e-commerce platforms to facilitate secure and efficient online payments. These APIs integrate with banking systems to process payments using various methods, including credit/debit cards, digital wallets, and online banking. Payment gateway APIs enable customers to make purchases and complete transactions seamlessly within the e-commerce platform.
- Personal financial management (PFM) apps: PFM apps use APIs to connect with customers’ bank accounts and aggregate their financial data in one place. These apps offer budgeting tools, transaction categorization, and financial insights to help users manage their finances effectively. APIs allow PFM apps to access transaction history, account balances, and other data securely, providing users with a holistic view of their finances.
- Open banking platforms: Open banking platforms leverage APIs to create ecosystems where banks, fintech companies, and other service providers can collaborate and offer a range of financial products and services. These platforms use APIs to facilitate secure access to customer data, enabling third-party developers to build innovative solutions such as loan comparison tools, investment apps, or personalized financial advice services.
- Mobile banking apps: Mobile banking apps use various APIs to enable customers to perform banking transactions, such as account transfers, bill payments, or balance inquiries, directly from their smartphones. APIs provide the necessary connectivity with banking systems, ensuring that transactions are secure and real-time. Mobile banking apps also incorporate biometric APIs for fingerprint or facial recognition authentication, enhancing security and user experience.
- Integrated accounting platforms: APIs are used in accounting software to enable seamless integration with business bank accounts. These APIs pull transaction data from bank accounts and automatically reconcile it with the corresponding entries in the accounting software. This integration streamlines financial record-keeping, minimizes manual data entry, and ensures accurate and up-to-date financial statements.
- Loan origination systems: Loan origination systems use APIs to streamline the loan application and approval process. APIs integrate with credit bureaus, income verification services, and other third-party data providers to gather relevant financial information and assess creditworthiness. This enables banks to make quick and informed lending decisions, improving the efficiency of loan origination processes.
- Investment platforms: Investment platforms utilize APIs to provide seamless access to financial markets and investment products. APIs allow investors to view real-time market data, place trades, and manage their investment portfolios within a single platform. By integrating with banking systems and brokerage services, these platforms offer a comprehensive and user-friendly investment experience.
These examples demonstrate how APIs are revolutionizing the banking industry and enabling the development of innovative applications and services. By leveraging APIs, banks can enhance customer experiences, offer a broader range of products and services, and foster collaboration with external partners, ultimately transforming the way financial services are delivered.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing APIs in Banking
While the adoption of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) in the banking industry offers numerous benefits, there are also challenges and considerations that financial institutions need to address when implementing APIs. This section explores some of the key challenges and considerations in implementing APIs in banking:
- Data Security and Privacy: Banks handle sensitive customer data, making data security and privacy a top priority. Implementing APIs requires robust security measures to protect customer information from unauthorized access or data breaches. Encryption, authentication, and access control mechanisms should be in place to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of data shared through APIs.
- Regulatory Compliance: The banking industry is heavily regulated, and APIs are no exception. Banks must comply with data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS), when implementing APIs. Compliance with these regulations requires careful monitoring of data access, consent management, and auditing capabilities.
- Integration Complexity: Banks often have complex legacy systems that may pose challenges when integrating with APIs. Ensuring seamless integration between existing systems and APIs requires careful planning, system updates, and sometimes even the development of middleware to bridge the gap between different technologies. Legacy system constraints should be considered during the API implementation process.
- API Documentation and Developer Support: Clear and comprehensive documentation is essential for developers who will be integrating with the bank’s APIs. The documentation should include details of API endpoints, request/response formats, required authentication methods, and any limitations or rate limits. Additionally, providing developer support and forums for troubleshooting can help ensure smooth integration and foster collaboration within the developer community.
- API Versioning and Stability: As banking systems and requirements evolve, APIs may need to be updated or deprecated. Managing API versions and ensuring backward compatibility is critical to avoid disrupting existing integrations. Banks should establish a versioning strategy and communicate changes to developers to minimize the impact on external applications reliant on their APIs.
- Monitoring and Performance: Banks must monitor API performance to ensure that they meet service level agreements and provide customers with a seamless experience. This includes monitoring response times, error rates, and capacity planning to handle fluctuations in API usage. Proactive monitoring can help identify issues and bottlenecks, allowing for timely adjustments and optimizations.
- Partnership and Collaboration: Banks need to establish strong partnerships and collaborations with third-party developers and fintech companies to leverage the full potential of APIs. It is essential to establish clear contractual agreements, define responsibilities, and ensure alignment in terms of security protocols, data sharing, and business objectives. Collaboration frameworks should be in place to foster effective communication and collaboration with external partners.
Addressing these challenges and considerations is crucial for the successful implementation of APIs in banking. By ensuring data security, regulatory compliance, seamless integration, developer support, and effective monitoring, banks can leverage APIs to deliver innovative services, enhance customer experiences, and drive industry-wide transformation while maintaining strong security and privacy standards.
Future Trends and Possibilities of APIs in Banking
The use of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) in the banking industry is continuously evolving, presenting exciting future trends and possibilities. As technology advances and customer expectations evolve, APIs will play a crucial role in shaping the future of banking. Here are some key trends and possibilities for APIs in the banking sector:
- Open Banking: Open banking initiatives are driving the adoption of APIs, enabling customers to share their financial data securely and transparently with trusted third-party providers. This empowers customers with greater control over their data and expands the range of personalized financial services available to them.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration: APIs will increasingly integrate with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies. This integration will enable banks to gain valuable insights from customer data, automate processes, and deliver personalized services such as chatbots for customer support or AI-powered investment recommendations.
- Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology: APIs will play a significant role in integrating banking systems with blockchain and distributed ledger technology. This integration will enable faster and more secure transactions, simplified remittances, and efficient know-your-customer (KYC) and anti-money laundering (AML) processes.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: APIs will enable banks to connect with IoT devices and leverage real-time data from interconnected devices for enhanced risk assessment, payment processing, and fraud prevention. For example, APIs can facilitate secure payment transactions through connected devices such as smartwatches or voice-activated assistants.
- Collaboration with Fintech Startups and Third-Party Developers: APIs will foster deeper collaborations between banks and fintech startups or external developers. This collaboration will drive innovation, result in the development of new financial products and services, and bring diverse perspectives to the banking industry.
- API Marketplaces: Banks may create API marketplaces, similar to app stores, where developers can discover, access, and integrate with their APIs. These marketplaces will provide a centralized platform for developers to explore and leverage banking APIs, promoting collaboration and increasing the availability of innovative financial solutions.
- Expanded Role in Financial Ecosystems: APIs will enable banks to become key players in broader financial ecosystems. By providing access to their core banking functionalities through APIs, banks can partner with other industries, such as retail, travel, or healthcare, to offer integrated financial services as part of the customer experience in those sectors.
These future trends and possibilities highlight the transformative potential of APIs in banking. As APIs continue to evolve and integrate with emerging technologies, banks will be able to deliver more personalized and innovative services, enhance operational efficiency, and keep pace with changing customer expectations. Embracing these trends and leveraging APIs strategically will be crucial for banks to stay competitive and relevant in the evolving digital landscape of banking.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the adoption of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) has brought about a significant transformation in the banking industry. APIs have enabled banks to enhance customer experiences, streamline operations, and drive innovation. By connecting various systems and applications, APIs facilitate seamless data sharing, collaboration with external developers, and integration with third-party platforms.
The importance of APIs in banking cannot be overstated. APIs offer a range of benefits, including improved customer experience, increased innovation and agility, expanded reach and customer base, streamlined processes, and enhanced security. APIs have paved the way for open banking initiatives, enabling customers to access a wider range of financial products and services and giving them more control over their financial data.
The future of APIs in banking holds great promise. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see further integration of APIs with AI, ML, blockchain, and IoT technologies. This integration will enable banks to leverage real-time data, automate processes, and deliver personalized services. Collaboration with fintech startups and third-party developers will drive continuous innovation and lead to the development of new financial solutions.
It is important for banks to strategically implement APIs while addressing challenges such as data security, regulatory compliance, integration complexity, and developer support. By doing so, they can leverage the full potential of APIs and stay at the forefront of the rapidly evolving digital banking landscape.
In summary, APIs have revolutionized the banking industry, empowering both banks and their customers with enhanced financial capabilities. As APIs continue to evolve and integrate with emerging technologies, banks have the opportunity to provide personalized, secure, and innovative financial services to meet the evolving needs of their customers. Embracing APIs and staying abreast of future trends will be crucial for banks to thrive in the digital era and deliver exceptional value to their customers.