
Finance
What Is An External Transfer In Banking
Published: October 12, 2023
Learn what an external transfer is in the world of banking and how it can impact your finances. Discover the benefits and precautions to take when making these transactions.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of finance, where money moves swiftly and seamlessly across various platforms. One such method of transferring funds is through external transfers in the banking sector. In this article, we will explore the concept of external transfers, how they work, their benefits and limitations, common uses, and how to initiate one.
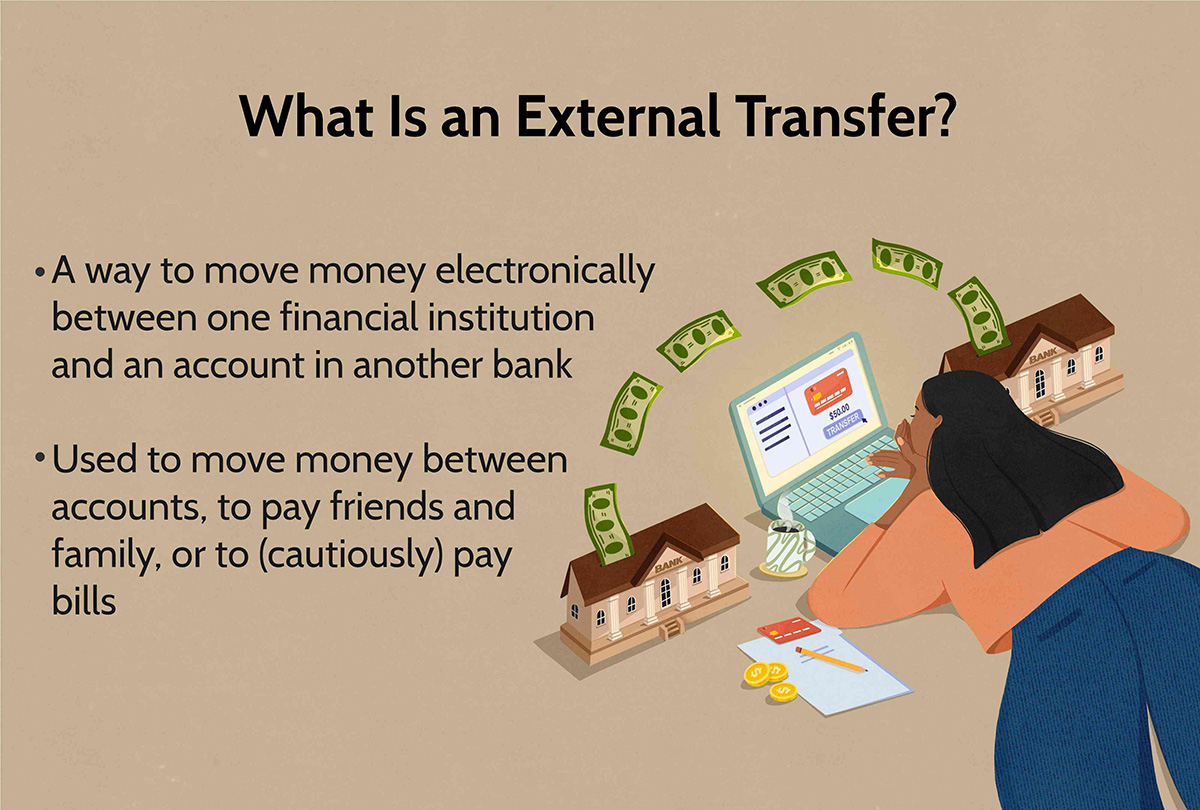
An external transfer is a process that allows individuals to move funds between two separate accounts held at different banks or financial institutions. Whether it’s transferring money from your checking account to your savings account in a different bank or sending funds to a friend’s bank account, external transfers simplify the process by eliminating the need for physical checks or cash transactions.
External transfers are typically conducted electronically, making them fast, secure, and convenient. They offer a convenient solution for individuals who have accounts at multiple banks or need to send money to someone who banks at a different financial institution.
As technology continues to advance, external transfers have become a popular choice for many individuals. These transfers are often available through online banking platforms or dedicated mobile applications, making it easy for users to initiate transactions from the comfort of their own homes or on the go.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into how external transfers work, highlight their benefits and limitations, discuss common use cases, and provide insights on how to initiate an external transfer successfully.
Definition of External Transfer
An external transfer refers to the movement of funds between two separate accounts held at different financial institutions. It allows individuals to transfer money from their own accounts to another person’s account, whether it’s a friend, family member, or business associate.
External transfers can be conducted between various types of accounts, such as checking, savings, and money market accounts, as well as between different types of financial institutions, including banks, credit unions, and online banking platforms. Regardless of the specific accounts involved, the key aspect of an external transfer is that the funds are moving across different institutions.
These transfers are generally facilitated through electronic means, using secure online banking platforms or mobile applications provided by the financial institutions. The funds are transferred digitally, eliminating the need for physical checks or cash transactions. This not only enhances efficiency but also reduces the risk of potential theft or loss during the transfer process.
External transfers can be either one-time occurrences or recurring transactions, depending on the individual’s needs. For example, you might set up a recurring external transfer to automatically move a fixed amount from your checking account to your savings account every month. Alternatively, you can initiate a one-time transfer to reimburse a friend for dinner or send funds to cover a bill.
It is important to note that external transfers are different from internal transfers. Internal transfers refer to the movement of funds between accounts held within the same financial institution. For example, transferring money from your checking account to your savings account within the same bank is considered an internal transfer.
External transfers offer individuals greater flexibility and convenience when it comes to managing their finances. Whether you need to consolidate your accounts, send money to someone, or simply manage your funds more effectively, external transfers provide a seamless and efficient way to do so.
How External Transfers Work
External transfers work by utilizing the existing infrastructure of the banking system to securely move funds between different financial institutions. Here is a step-by-step overview of how external transfers typically work:
- Initiating the Transfer: To begin the external transfer process, you need to have access to online banking or a mobile banking application provided by your financial institution. Log in to your account and look for the option to initiate an external transfer. This option may be labeled as “Transfer funds,” “Send money,” or something similar.
- Providing the Necessary Information: Once you’ve selected the external transfer option, you will be prompted to provide certain details. This includes the recipient’s name, their bank’s name, the account number, and the routing number of the receiving bank. It is crucial to double-check this information to ensure accuracy, as mistakes may result in failed or delayed transfers.
- Verification and Security Measures: To ensure the security of the transfer, most financial institutions require additional verification steps. This may involve entering a one-time password sent to your registered mobile number or email address, answering security questions, or providing other forms of authentication.
- Confirmation and Processing: After successfully verifying the transfer, you will receive confirmation of the transaction. The transfer will be processed by the financial institution and, depending on the receiving bank’s policies, the funds may be available in the recipient’s account within a few hours or up to a few business days.
- Tracking and Notifications: Throughout the transfer process, you can usually track the progress of the transfer within your online banking platform or mobile app. Additionally, many financial institutions offer notifications via email or SMS, keeping you informed about the status of your external transfer.
It is important to note that the exact process of initiating an external transfer and the time it takes for the funds to be credited to the recipient’s account may vary between financial institutions. Some institutions may charge a fee for external transfers, while others may offer them as a free service.
Furthermore, it’s worth mentioning that external transfers are subject to certain limits on the amount of money you can transfer within a specific time frame. These limits are set by the financial institution and may vary based on factors such as account type, customer relationship, and overall risk management.
Overall, external transfers provide a convenient and secure method for moving funds between different financial institutions. By leveraging the power of online banking and digital transactions, individuals can effortlessly manage their finances and send money to others with just a few clicks or taps.
Benefits of External Transfers
External transfers offer several advantages that make them an attractive option for individuals managing their finances. Here are some key benefits of using external transfers:
- Convenience: External transfers provide convenience by allowing individuals to move funds between different accounts held at separate financial institutions. This eliminates the need for physical checks or cash transactions, saving time and effort.
- Speed: With electronic transfers, funds can be moved quickly between accounts, often within a matter of hours. This ensures fast access to the transferred funds, allowing for timely transactions and payments.
- Flexibility: External transfers offer flexibility by facilitating transactions between various account types, such as checking, savings, and money market accounts. This allows individuals to manage their finances more effectively and allocate funds based on their specific needs.
- Cost Savings: External transfers can help individuals save money by avoiding fees associated with other methods of transferring funds, such as wire transfers or cashier’s checks. Many financial institutions offer external transfers as a free service, reducing the need for costly alternatives.
- Consolidation of Funds: External transfers provide the convenience of consolidating funds from multiple accounts held at different financial institutions. This simplifies the management of finances and allows individuals to have a comprehensive view of their financial situation.
- Security: As digital transactions, external transfers incorporate robust security measures to protect personal and financial information. Encryption technologies and authentication protocols help ensure that the transfer process is safe and secure.
- Enhanced Recordkeeping: External transfers leave a digital trail, making it easier to track and reconcile transactions. This enhances recordkeeping and simplifies financial management, especially when it comes to tax reporting or auditing.
- Accessibility: External transfers can be initiated through online banking platforms or dedicated mobile applications, providing anytime, anywhere access to transfer funds. This allows individuals to manage their finances conveniently, even outside of traditional banking hours.
These benefits make external transfers a popular and preferred method for individuals looking to move funds between different accounts and financial institutions. Whether you need to send money to a friend, consolidate your accounts, or simply manage your finances more efficiently, external transfers provide a seamless and convenient solution.
Limitations of External Transfers
While external transfers offer many benefits, it is important to be aware of their limitations. Here are some key limitations to consider:
- Processing Time: Although external transfers are generally faster than traditional methods like mailing a check, they may still take some time to process. The exact processing time can vary depending on factors such as the financial institutions involved, the time of day the transfer is initiated, and the specific transfer amount.
- Transfer Limits: Financial institutions often impose limits on the amount of money that can be transferred externally within a specific time period. These limits are in place to protect against potential fraud and ensure regulatory compliance. It’s important to check with your bank or financial institution to understand the specific limits that apply to your account.
- Transaction Fees: While some financial institutions offer external transfers as a free service, others may charge a fee for each transaction. It is essential to review the fee schedule of your bank or financial institution to understand any potential charges associated with external transfers.
- Account Verification: To initiate an external transfer, you will need to provide accurate and up-to-date information about the recipient’s account, including the account number and routing number. Any errors or discrepancies in this information can result in delayed or failed transfers. It is crucial to double-check the provided details before initiating the transfer.
- Network Compatibility: Not all financial institutions may be compatible with each other’s external transfer systems. In some cases, transfers between certain banks or credit unions may not be possible due to technical limitations or the lack of a shared network. It’s important to confirm the compatibility of the two financial institutions before attempting an external transfer.
- Legal and Regulatory Restrictions: External transfers are subject to various legal and regulatory restrictions, both at the national and international levels. These restrictions are in place to prevent money laundering, fraud, and other illicit activities. It’s important to understand and comply with these restrictions to ensure smooth and lawful external transfers.
- Human Error: As with any financial transaction, there is always the potential for human error. Whether it’s inputting incorrect account details or selecting the wrong transfer amount, mistakes can happen during the transfer process. It’s essential to review all information before confirming the transfer to minimize the risk of errors.
Despite these limitations, external transfers remain a convenient and efficient method for moving money between different accounts and financial institutions. Understanding these limitations and taking necessary precautions can help you make the most of external transfers while minimizing any potential drawbacks.
Common Uses of External Transfers
External transfers serve a wide range of purposes and are utilized in various financial scenarios. Here are some common uses of external transfers:
- Transferring Funds Between Personal Accounts: One of the most common uses of external transfers is moving money between personal accounts held at different banks or financial institutions. For example, you may transfer funds from your checking account at Bank A to your savings account at Bank B to maximize your savings potential or meet specific financial goals.
- Reimbursing Family and Friends: External transfers provide a convenient way to reimburse family and friends for shared expenses or repayment of loans. Instead of relying on physical cash or checks, you can quickly and securely transfer funds directly into the recipient’s bank account.
- Settling Bills and Payments: External transfers are commonly used to settle bills and make payments. Whether it’s paying rent to a landlord, splitting utility bills with roommates, or settling outstanding invoices with vendors, external transfers simplify the payment process by allowing you to transfer funds directly from your account to the recipient’s account.
- Managing Finances Across Multiple Institutions: Many individuals have accounts at different banks or financial institutions for various reasons, such as taking advantage of different interest rates or accessing specific financial products. External transfers enable efficient management of these accounts by providing a way to move funds seamlessly between them.
- Sending Money to Family and Dependents: External transfers are commonly used to send money to family members, dependents, or students away at college. Whether it’s sending funds for living expenses, educational costs, or emergency situations, external transfers offer a secure and fast method to provide financial support.
- Consolidating Debt: External transfers can be used to consolidate debt by transferring funds from various accounts to pay off outstanding balances. This simplifies debt management and allows individuals to focus on repaying a single consolidated amount.
- Investing and Trading: Some investors and traders use external transfers to move funds between their brokerage accounts and bank accounts. This allows for seamless transfer of funds for investment purposes, such as buying or selling securities or accessing investment opportunities.
- Emergency Fund Management: External transfers play a crucial role in managing emergency funds. By quickly transferring funds from a savings account held at a different financial institution, individuals can access the funds they need to address unexpected expenses or financial emergencies.
These are just a few examples of how external transfers are commonly used. The flexibility and convenience of external transfers make them a versatile tool in managing personal finances, supporting others, settling financial obligations, and optimizing overall financial well-being.
How to Initiate an External Transfer
Initiating an external transfer is a straightforward process when you have access to online banking or a mobile banking application provided by your financial institution. Here are the general steps to follow:
- Log in to your Online Banking Account: Visit the official website of your financial institution or open the mobile banking application on your smartphone. Enter your login credentials, such as your username and password, to access your account.
- Navigate to the Transfer Section: Once logged in, locate the section or tab for initiating transfers. This may be labeled as “Transfer Funds,” “Send Money,” or something similar, depending on your financial institution’s online banking platform.
- Select the External Transfer Option: Within the transfer section, choose the option for an external transfer. Be sure to read any information or instructions provided by your financial institution regarding external transfers.
- Provide the Recipient’s Information: To initiate the transfer, you will need to enter the recipient’s information accurately. This typically includes the recipient’s full name, their bank’s name, the recipient’s account number, and the routing number of the receiving bank. Double-check this information for accuracy to avoid any delays or errors.
- Verify the Transfer: Depending on your financial institution’s security measures, you may be required to authenticate the transfer using additional verification steps. This may involve entering a one-time password sent to your registered mobile number or email address or answering security questions.
- Confirm the Transfer Details: Review the transfer details, including the amount to be transferred and the selected accounts for debiting and crediting. Ensure that all the information is correct before confirming the transfer.
- Submit the Transfer: After confirming the transfer details, submit the transaction. You will likely receive a confirmation message or notification indicating that the transfer has been initiated successfully.
- Monitor and Track the Transfer: Keep an eye on the progress of the transfer through your online banking platform or mobile app. Some financial institutions provide real-time tracking or send notifications when the transfer has been completed.
It is essential to note that the specific steps may vary slightly depending on your financial institution and their online banking platform. Some institutions may require additional information or have specific procedures in place for initiating external transfers.
If you encounter any difficulties or have questions about initiating an external transfer, it is advisable to reach out to your financial institution’s customer support for assistance. They can provide guidance and ensure a smooth transfer process.
Security Measures for External Transfers
Ensuring the security of external transfers is of paramount importance to financial institutions and their customers. Here are some common security measures implemented to safeguard the transfer process:
- Encryption: Financial institutions use encryption technologies to protect the sensitive information involved in external transfers. This includes encrypting data transmission between your device and the financial institution’s servers, ensuring that unauthorized individuals cannot intercept or access the information.
- Secure Login: Online banking platforms require users to authenticate themselves using multiple layers of security, such as usernames, passwords, and personal identification numbers (PINs). Some institutions also offer two-factor authentication methods, adding an extra layer of security by requiring a verification code sent to a registered mobile phone number or email address.
- Authentication Protocols: When initiating an external transfer, financial institutions may employ additional authentication protocols. This may involve answering security questions, providing specific account details, or validating your identity through biometric measures such as fingerprints or facial recognition, depending on the capabilities of the online banking platform or mobile app.
- Fraud Monitoring: Financial institutions employ sophisticated fraud monitoring systems to detect and prevent potential fraudulent activities related to external transfers. These systems use pattern recognition, anomaly detection, and transaction monitoring to identify suspicious behavior and trigger alerts or additional verification procedures if necessary.
- Transaction Limits and Authorization: To mitigate the risk of unauthorized transfers, financial institutions set transaction limits for external transfers. These limits restrict the maximum amount of money that can be transferred within a specific time period. Additionally, some institutions require additional authorization for large transfers or transfers to unfamiliar accounts.
- Secure Communication: Financial institutions ensure secure communication channels for transmitting sensitive information related to external transfers. This involves using secure protocols such as HTTPS, SSL, or TLS to encrypt and protect data during transmission, minimizing the risk of interception or data breaches.
- User Education: Financial institutions play an active role in educating their customers about online security practices. They provide guidelines on creating strong passwords, avoiding phishing scams, and exercising caution when sharing personal and financial information. User awareness is crucial in maintaining the security of external transfers.
- Transaction Verification: Before submitting an external transfer, it is essential to review all the details carefully. Confirm that the recipient’s information, including the account number and bank routing number, is accurate. Taking the time to verify the transfer details helps prevent errors and minimize the risk of transferring funds to incorrect accounts.
By implementing these security measures, financial institutions strive to ensure the integrity and safety of external transfers. However, it is equally important for individuals to follow best practices, such as keeping login credentials confidential, using secure networks, and promptly reporting any suspicious activities to their financial institution.
Remember, maintaining good cyber hygiene and staying vigilant are crucial in protecting your financial information and ensuring secure external transfers.
Fees Associated with External Transfers
While many financial institutions offer external transfers as a convenient service, it’s important to be aware that there may be fees associated with these transactions. Here are some key points to consider regarding fees for external transfers:
- Varying Fee Structures: The fee structure for external transfers can differ from one financial institution to another. Some banks may offer external transfers as a free service to their customers, while others may charge a flat fee per transfer or a fee based on the transfer amount.
- Individual Bank Policies: Each financial institution sets its own policies and fee structures for external transfers. It’s crucial to review your bank’s fee schedule or contact a customer service representative to understand the specific fees that may apply to your external transfers.
- Transfer Types: Some banks may differentiate fees based on the type of transfer being conducted. For instance, while transfers between your own accounts may be free, transfers to external accounts held by individuals or businesses at different banks may incur a fee.
- Timeframe of Transfer: In certain situations, banks may offer expedited or same-day external transfers for an additional fee. This option is particularly useful when time sensitivity is a factor, such as for urgent bill payments or time-sensitive transactions.
- Third-Party Charges: In some cases, banks may pass along any charges incurred from interbank networks or other financial institutions involved in processing the external transfer. These charges are typically transparently communicated to the customer.
- Package or Account Fees: Some banks offer packages or accounts that include a certain number of free external transfers per month or year. If you frequently make external transfers, it may be worth exploring these options to potentially minimize fees.
- Fee Waivers: Certain banks may offer fee waivers for external transfers for specific account types or customer relationships. It’s worth inquiring with your bank if you qualify for any such waivers or if they have promotional offers that temporarily waive fees for new customers.
- Other Cost-Effective Alternatives: Depending on the specific nature of your transaction, there may be more cost-effective alternatives to external transfers. For instance, if you need to send a large sum of money, a wire transfer may be a more suitable option despite its higher fees.
Remember, banks regularly update their fee schedules, so it’s important to stay informed about any changes that may affect your external transfer fees. Regularly reviewing your bank’s fee schedule, exploring fee waiver opportunities, and considering the overall cost-effectiveness of different transfer methods can help you make informed decisions when initiating external transfers.
Conclusion
External transfers play a vital role in today’s increasingly digital financial landscape. They offer a convenient and secure means of transferring funds between different accounts held at separate financial institutions. With the click of a button or a few taps on a mobile app, individuals can move money quickly and easily, eliminating the need for physical checks or cash transactions.
Throughout this article, we have explored the definition of external transfers, how they work, their benefits, limitations, common uses, and security measures. External transfers provide convenience, speed, and flexibility, allowing individuals to manage their finances with ease. They enable transferring funds between personal accounts, reimbursing family and friends, settling bills, and consolidating debt, among other common uses.
While there are limitations to consider, such as processing time and potential fees, financial institutions have implemented robust security measures to protect the integrity of external transfers. Encryption, secure login procedures, authentication protocols, and fraud monitoring systems all contribute to enhancing the security of these transactions.
It’s important to remain aware of the fees associated with external transfers, as they can vary depending on the financial institution and the specific transfer type. Understanding your bank’s fee structure, exploring fee waiver options, and considering the cost-effectiveness of different transfer methods can help you make informed decisions.
Overall, external transfers have revolutionized the way we move funds between different accounts and financial institutions. Embracing the convenience, speed, and security they offer allows individuals to effectively manage their finances, support others, settle obligations, and make the most of their financial resources.
Remember to always double-check the accuracy of transfer details, adhere to best security practices, and stay informed about any changes or updates to external transfer processes in order to have a smooth and secure experience.