Finance
What Is Billing In Accounting
Published: October 9, 2023
Learn about billing in accounting and how it relates to finance. Discover the importance of accurate billing processes and the impact it has on overall financial management.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Billing in Accounting
- Importance of Billing in Accounting
- Billing Process in Accounting
- Components of Billing in Accounting
- Different Types of Billing Methods
- Billing Terms and Policies
- Billing Software and Tools
- Challenges in Billing Process
- Importance of Accurate Billing
- Conclusion
Introduction
When it comes to managing finances, businesses rely on various accounting tools and processes. One essential aspect of financial management is billing, which plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth flow of revenue. In the world of accounting, billing refers to the process of generating invoices and requesting payment for goods or services provided by a company.
Billing is a fundamental part of the accounting cycle, serving as the bridge between the delivery of products or services and the collection of payment. It is a systematic approach that enables organizations to track and record financial transactions accurately. While billing may seem straightforward, it involves several components and methods that must be handled with precision to ensure financial stability.
In this article, we will delve into the world of billing in accounting, exploring its definition, importance, process, components, types, terms, and challenges. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of billing, businesses can optimize their financial operations and improve customer satisfaction.
Definition of Billing in Accounting
Billing in accounting refers to the process of creating and issuing invoices to customers for goods sold or services rendered. It involves recording and tracking financial transactions, specifically related to generating revenue. Billing is a critical part of the accounts receivable process, as it enables businesses to collect payment for the products or services they provide.
Essentially, billing serves as a formal request for payment, outlining the details of the transaction, such as the quantity, price, and total amount owed. It acts as a documented record of the sale or service, creating transparency and accountability between the business and its customers.
In accounting, billing involves various steps to ensure accuracy and efficiency. It starts with gathering all relevant transaction information, including the customer’s name, contact details, product or service details, pricing, and any applicable discounts or taxes. Once this information is compiled, an invoice is created, which outlines the specifics of the transaction and the amount owed.
Additionally, billing in accounting involves maintaining a systematic record of all invoices issued and monitoring the payment status of each invoice. This allows businesses to track outstanding payments, follow up with customers for overdue invoices, and reconcile payments received with the corresponding invoices. By efficiently managing the billing process, businesses can effectively track their revenue, identify potential cash flow issues, and ensure timely collections.
It is important to note that billing in accounting goes beyond just invoicing customers. It can also involve billing for expenses incurred, such as reimbursable costs or billable time for services provided. In these cases, businesses may generate invoices for internal purposes, tracking the expenses or services rendered for accurate record-keeping.
Overall, billing in accounting is an integral part of financial management, playing a pivotal role in revenue generation, monitoring cash flow, and maintaining financial stability. It combines accuracy, organization, and communication to facilitate smooth transactions and ensure timely payments from customers.
Importance of Billing in Accounting
Billing in accounting is of paramount importance for several reasons. It is not just a routine administrative task; it serves as a central pillar of financial management for businesses. Let’s explore the significance of billing in accounting:
1. Revenue Generation: Billing is directly tied to the generation of revenue for a business. By promptly and accurately billing customers, organizations can ensure the smooth flow of income and maintain a healthy cash flow. Timely payment collection is vital for businesses to meet their financial obligations and invest in growth opportunities.
2. Financial Tracking: Billing provides businesses with a detailed record of all transactions and financial activities. It allows for easy tracking and monitoring of sales, expenses, and outstanding payments. This information is crucial for financial analysis, budgeting, and making informed business decisions.
3. Customer Satisfaction: A well-executed billing process enhances customer satisfaction. Clear and accurate invoices help customers understand the charges and make prompt payments. Providing transparency and clarity in billing fosters trust and strengthens the relationship between the business and its customers.
4. Cash Flow Management: Effective billing practices contribute to effective cash flow management. By consistently billing customers and diligently following up on outstanding invoices, businesses can better forecast their future cash flow needs. This is essential for managing day-to-day expenses, covering operational costs, and planning for growth.
5. Compliance and Record-Keeping: Billing ensures compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. Accurate and well-documented invoices serve as evidence for financial transactions and can be essential during audits or tax filings. By maintaining detailed billing records, businesses can easily address any inquiries or disputes that may arise.
6. Improved Efficiency: Streamlining the billing process improves operational efficiency. By utilizing billing software or tools, businesses can automate tasks such as invoice generation, payment reminders, and reconciliation. This saves time, reduces errors, and allows employees to focus on other value-added activities.
7. Financial Planning: Monitoring billing data provides valuable insights for financial planning. By analyzing billing trends, businesses can identify seasonal fluctuations, recurring expenses, and customer preferences. This information helps in formulating strategies, setting sales targets, and forecasting future revenues.
In summary, billing in accounting is a critical function that goes beyond mere invoicing. It is instrumental in revenue generation, financial tracking, customer satisfaction, cash flow management, compliance, and operational efficiency. By prioritizing accurate and timely billing, businesses can maintain financial stability and drive growth.
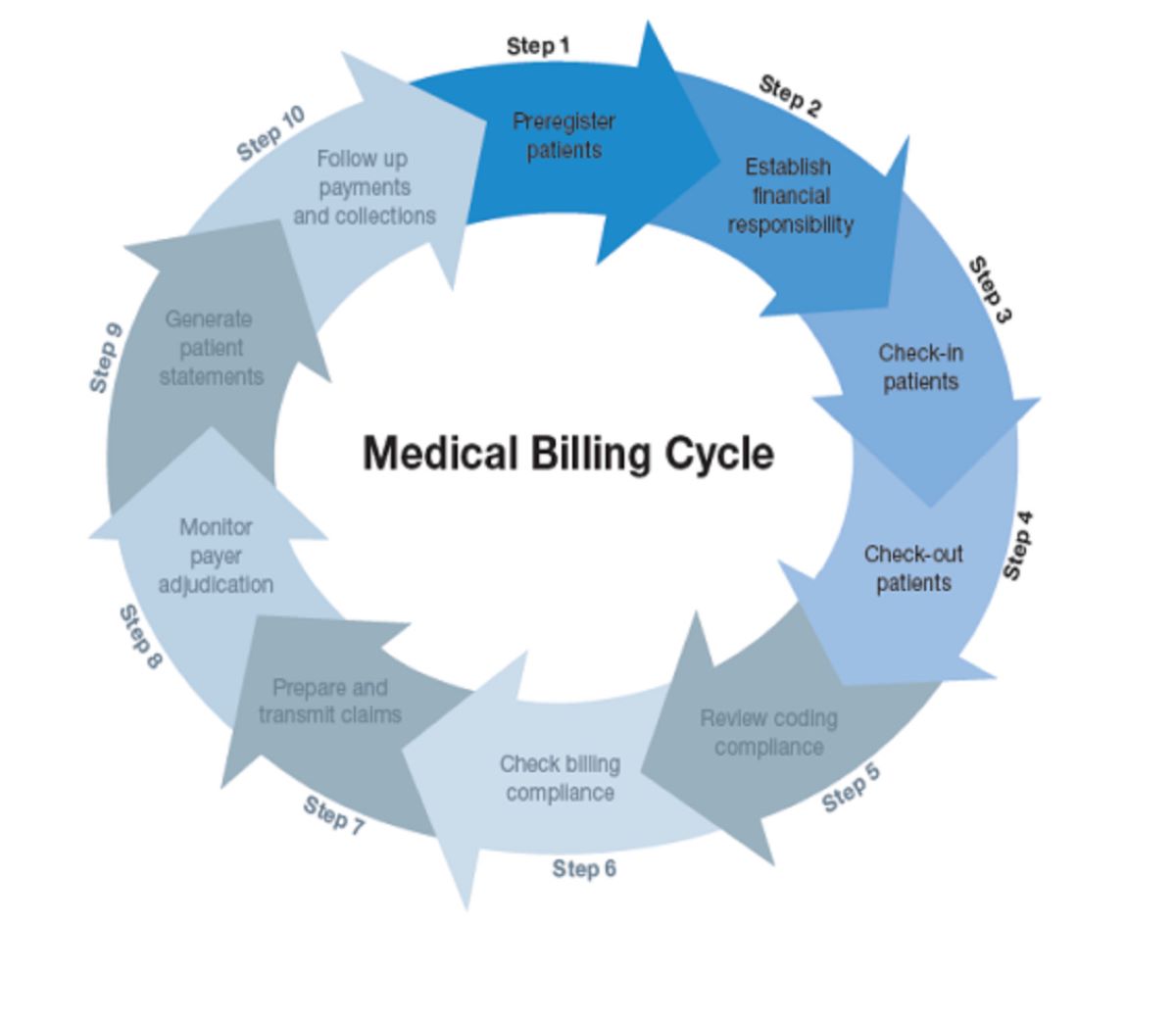
Billing Process in Accounting
The billing process in accounting involves a series of steps to ensure accurate and timely invoicing of customers. While the specific process may vary depending on the nature of the business, the following are key components typically involved in the billing process:
1. Gathering Transaction Information: The first step in the billing process is to gather all relevant transaction details. This includes customer information, such as their name, contact details, and billing address. It also involves recording the specifics of the transaction, such as the products or services sold, quantities, prices, any applicable discounts or taxes, and payment terms.
2. Generating Invoices: Once the transaction information is gathered, the next step is to create the invoice. Invoices can be generated manually using accounting software, templates, or through specialized billing software. The invoice should include the date of issuance, invoice number for tracking purposes, customer details, itemized list of goods or services provided, pricing, and any additional terms or notes.
3. Sending Invoices: After generating the invoices, they need to be sent to the customers. This can be done via email, mail, or through digital platforms such as customer portals. It is crucial to ensure that the invoices reach the customers in a timely manner and in a format that is easily understandable.
4. Payment Collection: Once the invoices are sent, businesses must track and monitor the payment collection process. This involves recording the payment status of each invoice, such as paid, overdue, or partial payment received. Businesses may also send payment reminders or follow-up with customers who have outstanding invoices to ensure timely payment.
5. Reconciliation: Reconciliation is a critical step in the billing process. It involves matching the payments received with the corresponding invoices and recording them accurately in the accounting system. Reconciliation helps identify any discrepancies, resolve payment disputes, and maintain accurate financial records.
6. Recording and Reporting: Throughout the billing process, it is essential to maintain detailed records of all transactions. This includes keeping copies of invoices, payment receipts, and any relevant communication with customers. These records are useful for reporting purposes, financial analysis, and audit trails.
7. Follow-up and Collections: In cases where customers have overdue invoices, businesses may need to follow-up and initiate collections efforts. This can involve sending additional payment reminders, contacting customers directly, or engaging the services of a collections agency. The focus is on resolving outstanding payments and minimizing the impact on cash flow.
It is important to streamline and automate the billing process as much as possible to ensure efficiency and accuracy. Utilizing accounting software or dedicated billing tools can simplify the process, reduce manual errors, and enhance the overall effectiveness of the billing process.
By following a well-defined billing process, businesses can effectively manage their revenue generation, maintain financial stability, and foster positive relationships with their customers.
Components of Billing in Accounting
Billing in accounting involves several components that work together to ensure accurate and efficient invoicing. These components are essential for maintaining an organized and transparent billing process. Let’s explore the key components of billing in accounting:
1. Customer Information: The first component of billing is gathering and maintaining accurate customer information. This includes the customer’s name, contact details, billing address, and any other relevant information required to identify and communicate with the customer. Having up-to-date customer information is vital for accurate invoicing and effective customer communication.
2. Transaction Details: Billing requires proper documentation of transaction details. This includes recording the products or services provided, the quantity or hours worked, pricing, any applicable discounts or taxes, and any additional charges. Accurate and itemized transaction details ensure transparency and help customers understand the charges on their invoices.
3. Invoice Generation: The core component of billing is the generation of invoices. Invoices serve as formal requests for payment, providing customers with a detailed breakdown of the products or services rendered, their associated costs, and any additional terms or payment instructions. The invoice should include essential information such as the invoice number, issue date, due date, and the accepted forms of payment.
4. Payment Terms: Billing involves setting clear payment terms and conditions. This includes specifying the payment due date, any early-payment discounts or late-payment penalties, and the preferred methods of payment. By establishing clear payment terms, businesses can avoid confusion and disputes regarding payment expectations.
5. Accounts Receivable Management: Managing accounts receivable is a crucial component of billing. It involves monitoring the payment status of each invoice and maintaining a record of outstanding invoices. By tracking accounts receivable, businesses can identify any overdue payments, follow up with customers, and take appropriate actions to ensure timely collection.
6. Payment Options: Offering various payment options is an important component of billing. This includes accepting different payment methods such as cash, checks, credit cards, or digital payment platforms. Providing multiple payment options enhances convenience for customers and encourages timely payments.
7. Invoicing and Billing Software: Utilizing invoicing and billing software is an efficient way to streamline the billing process. These software solutions automate invoice generation, tracking of payment status, and record-keeping. They also offer features such as recurring invoicing, customized templates, and payment reminders, making the billing process more efficient and accurate.
8. Communication and Customer Service: Effective communication and customer service play a crucial role in billing. It involves addressing customer inquiries regarding invoices, payment terms, or any billing concerns. Clear and prompt communication can help resolve any billing issues, prevent disputes, and maintain positive customer relationships.
By ensuring these components are well-integrated in the billing process, businesses can effectively manage their invoicing activities, maintain accurate financial records, and enhance overall customer satisfaction. A streamlined and transparent billing process contributes to improved cash flow, reduced payment delays, and a stronger financial foundation for the business.
Different Types of Billing Methods
When it comes to billing in accounting, businesses have several methods to choose from based on their specific needs and industry practices. Each billing method serves a particular purpose and offers distinct advantages. Let’s explore some of the commonly used billing methods:
1. Hourly Billing: This method involves charging clients based on the amount of time spent on a particular task or project. It is commonly used by professionals such as lawyers, consultants, or freelancers who bill for their time. Hourly billing allows for flexibility in pricing and is suitable when the scope of work or project duration may vary.
2. Flat-Rate Billing: With flat-rate billing, a fixed fee is charged for a specific product or service, regardless of the time or resources involved. It provides simplicity and predictability for both the business and the customer. Flat-rate billing is often used for routine services or standardized products where pricing can be easily determined.
3. Retainer Billing: This method involves charging clients a predetermined amount for ongoing services or access to specific resources over a specified period. Retainer billing is common in industries such as marketing, legal services, or IT support. It provides a consistent revenue stream for the business and assures the client of dedicated availability.
4. Progressive Billing: Progressive billing is used for long-term projects or contracts. It involves dividing the total project cost into milestones or phases, and billing the client incrementally as each milestone is achieved or time elapses. This method provides regular cash flow and aligns payments with project progression.
5. Recurring Billing: Recurring billing is commonly used for subscription-based services. It involves automatically charging customers at regular intervals, such as monthly or annually, for ongoing access to a product or service. Recurring billing offers convenience for customers, encourages customer retention, and provides businesses with consistent revenue.
6. Split Billing: Split billing is utilized when there are multiple parties responsible for payment. This often occurs in complex business transactions or joint ventures where costs are divided among different entities. Split billing ensures clear allocation of costs and helps avoid disputes regarding payment responsibility.
7. Prepaid Billing: Prepaid billing requires customers to pay in advance for goods or services before they are delivered. This method is commonly used in industries such as telecommunications, software subscriptions, or prepaid cards. Prepaid billing provides businesses with immediate cash flow and reduces the risk of non-payment.
8. Cost-Plus Billing: Cost-plus billing involves charging customers the cost of goods or services provided, along with an additional markup or percentage of profit. This method is suitable when the cost of materials or resources varies significantly. Cost-plus billing ensures that businesses cover their expenses while still generating a reasonable profit margin.
It is important for businesses to carefully consider their industry, customer preferences, and the nature of their products or services when choosing the most appropriate billing method. By selecting the right billing method, businesses can optimize revenue generation, manage cash flow effectively, and meet customer expectations.
Billing Terms and Policies
Billing terms and policies are an essential component of the billing process in accounting. They provide clarity and set expectations for both businesses and their customers. Let’s explore some key aspects of billing terms and policies:
1. Payment Terms: Payment terms outline the agreed-upon timeframe for customers to remit payment after receiving an invoice. Common payment terms include “net 30,” which means payment is due within 30 days, or “due on receipt,” requiring immediate payment. Defining clear payment terms helps businesses manage cash flow and ensures timely payment collection.
2. Late Payment Charges: Late payment charges are fees imposed on customers for delayed payments. These charges serve as an incentive for customers to pay on time and compensate businesses for the additional administrative and financial burden caused by late payments. Late payment charges should be clearly communicated to customers to avoid disputes or misunderstandings.
3. Invoice Disputes: Billing terms should address how invoice disputes are handled. In the event of discrepancies or disagreements regarding the charges on an invoice, businesses and customers should have a clear process for resolving issues. This may involve providing evidence, initiating discussions, or involving a third party, such as a mediator or arbitrator, to reach a resolution.
4. Refund and Returns Policy: If applicable, billing terms should outline the policies and procedures for handling refunds or returns. This includes specifying the conditions under which refunds are granted, the process for requesting a refund, and any associated fees or restocking charges. A well-defined refund and returns policy helps manage customer expectations and fosters trust.
5. Cancellation Policy: In some cases, services or subscriptions may have a cancellation policy. This policy outlines the terms and conditions for terminating the contract or subscription and any associated fees or penalties. A clear cancellation policy ensures that both the business and the customer understand the obligations and consequences of cancelling a service or subscription.
6. Privacy and Data Security: Billing terms should address how customer data is handled and protected. This includes complying with applicable data protection and privacy regulations, ensuring secure payment processing, and maintaining the confidentiality of customer information. Clearly communicating data security measures helps build trust and confidence in the billing process.
7. Audit Trail and Record-Keeping: Billing terms should emphasize the importance of maintaining accurate records and an audit trail. Businesses should specify the retention period for invoices and supporting documents, ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. Proper record-keeping not only facilitates financial reporting and analysis but also assists in resolving disputes and audits.
8. Notification of Changes: If billing terms or policies are revised, businesses should establish a process for notifying customers of these changes. This may include sending updated terms and policies with invoices or communicating changes through email or a customer portal. Proactively notifying customers of any changes in billing terms ensures transparency and mitigates any potential confusion or dissatisfaction.
It is crucial for businesses to communicate their billing terms and policies clearly to customers. This helps establish a fair and transparent relationship, reduces disputes, and facilitates timely payment collection. By defining these terms and policies, businesses can streamline their billing process and foster positive customer experiences.
Billing Software and Tools
In today’s digital age, businesses have access to a wide range of billing software and tools that can streamline and automate the billing process. These tools offer various features designed to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction. Let’s explore some popular billing software and tools:
1. Accounting Software: Many accounting software solutions include built-in billing modules or dedicated billing features. These software programs allow businesses to create and send invoices, track payment status, and generate financial reports. They often integrate with other accounting functions, such as expense tracking and financial reconciliation, providing a comprehensive financial management solution.
2. Online Invoicing Platforms: Online invoicing platforms offer a user-friendly interface for businesses to create and send professional-looking invoices. These platforms typically allow customization of invoice templates, automated invoice generation, and the option to attach supporting documents. They also often provide features such as payment reminders, recurring invoicing, and online payment options for customer convenience.
3. Payment Gateways: Payment gateways enable businesses to accept online payments securely. These tools allow integration with websites or online stores, enabling seamless transactions and real-time payment processing. Payment gateways often offer a range of payment methods, including credit cards, digital wallets, and bank transfers, increasing convenience for customers.
4. Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) Systems: EFT systems facilitate electronic transfer of funds between businesses and customers. They enable businesses to set up recurring payments, authorize direct debit from customer accounts, and automate payment collection. EFT systems reduce administrative tasks and provide a reliable method of tracking and managing payment transactions.
5. Customer Portals: Customer portals allow businesses to offer self-service options for customers to view and manage their invoices and payments. These portals provide customers with access to their billing history, payment status, and the ability to update their payment information. Customer portals empower customers to take control of their billing experience and reduce the need for manual intervention.
6. Mobile Apps: Mobile apps are becoming increasingly popular for invoicing and billing purposes. They allow businesses to create, send, and track invoices directly from a mobile device. Mobile apps often offer features such as invoice customization, instant notifications, and mobile payment options, allowing businesses to manage billing on the go.
7. Financial Reporting and Analytics: Billing software and tools often provide robust reporting and analytics capabilities. These features enable businesses to gain insights into billing trends, payment patterns, and revenue analysis. By leveraging these tools, businesses can make data-driven decisions, identify opportunities for improvement, and optimize their billing processes.
When selecting billing software and tools, businesses should consider their specific needs, budget, scalability, and integration capabilities. It is crucial to choose solutions that align with the business’s industry and growth goals. Implementing the right billing software and tools can significantly improve efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction, ultimately contributing to the overall success of the business.
Challenges in Billing Process
While billing is a critical aspect of financial management, businesses often face various challenges in the billing process. These challenges can impact cash flow, customer relationships, and overall business operations. Let’s explore some common challenges faced in the billing process:
1. Inaccurate Data: One of the major challenges in billing is dealing with inaccurate or incomplete data. This can include errors in customer information, product or service details, pricing, or discounts. Inaccurate data can lead to incorrect invoices, delayed payments, and disputes with customers.
2. Invoice Discrepancies: Discrepancies in invoices can arise due to various reasons, such as incorrect calculations, missing items, or incorrect billing terms. These discrepancies can cause confusion for customers, resulting in delayed payment or disputes. Resolving invoice discrepancies can be time-consuming and may require additional communication with customers.
3. Late or Non-Payment: Late or non-payment is a significant challenge faced in the billing process, impacting cash flow and financial stability. It may occur due to various reasons, including customer disputes, financial difficulties, or internal issues at the customer’s end. Businesses must have policies and processes in place to address late or non-payment and initiate appropriate actions.
4. Billing Errors: Billing errors can occur in various forms, such as duplicate invoices, incorrect pricing, or incorrect application of discounts or taxes. These errors can lead to customer dissatisfaction, strained relationships, and potential loss of revenue. Regular reviewing and auditing of bills can help mitigate billing errors.
5. Complex Billing Requirements: Some businesses have complex billing requirements, such as handling multiple currencies, managing international tax regulations, or billing for services with varying pricing structures. Dealing with complex billing requirements can be time-consuming and require specialized knowledge or software tools to ensure accuracy.
6. Changing Regulatory Requirements: Billing processes need to comply with changing regulatory and legal requirements, such as tax laws, data privacy regulations, or invoicing standards. Staying updated with these regulations and adapting the billing process accordingly can be a challenge, requiring continuous monitoring and training.
7. Customer Communication and Disputes: Effective communication with customers is crucial for successful billing. However, challenges can arise when dealing with billing-related inquiries, disputes, or late payments. Businesses must have strong customer service processes in place to promptly and efficiently address customer concerns and resolve disputes.
8. System Integration and Software Compatibility: Integrating billing software with other systems in the organization, such as accounting or CRM systems, can be a challenge. Software compatibility issues may arise, leading to data discrepancies, delayed invoicing, or difficulties in generating accurate financial reports.
To overcome these challenges, businesses can implement strategies such as investing in robust billing software, conducting regular audits, training staff on accurate data entry, establishing clear billing policies, and maintaining open and transparent communication with customers. By addressing these challenges proactively, businesses can streamline their billing processes, enhance customer satisfaction, and improve financial performance.
Importance of Accurate Billing
Accurate billing is crucial for businesses in maintaining financial stability, fostering positive customer relationships, and ensuring smooth operations. Here are key reasons why accurate billing is of utmost importance:
1. Financial Integrity: Accurate billing ensures the financial integrity of a business. It guarantees that sales and revenue figures are recorded correctly, aiding in financial analysis, forecasting, and decision-making. Accurate billing provides confidence in the accuracy of financial statements and strengthens the overall financial health of the business.
2. Cash Flow Management: Accurate billing is essential for effective cash flow management. By invoicing promptly, including all applicable charges, and ensuring invoice accuracy, businesses can improve their cash flow. Timely and accurate billing allows for timely payment collection, reducing the risk of late or non-payment and ensuring a healthy cash flow position.
3. Customer Satisfaction: Accurate billing is directly linked to customer satisfaction. When businesses provide accurate invoices that clearly outline the products or services provided, pricing details, and payment terms, customers feel more confident in the transaction. Accurate billing builds trust, fosters positive customer relationships, and enhances customer satisfaction levels.
4. Dispute Resolution: Accurate billing helps in resolving disputes efficiently. In cases where billing disputes arise, having accurate records and documentation plays a significant role in finding resolutions. Detailed and accurate billing information can be used as evidence to address customer concerns and resolve disputes swiftly, minimizing any negative impact on the business-customer relationship.
5. Compliance and Legal Requirements: Accurate billing ensures compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. It helps businesses adhere to tax laws, accounting standards, and data privacy regulations. Accurate billing records serve as valuable documentation during audits, ensuring transparency and integrity in financial transactions.
6. Operational Efficiency: Accurate billing enables operational efficiency by minimizing errors, reducing the need for rework or adjustments, and streamlining administrative tasks. It saves time and resources that would otherwise be spent on rectifying billing inaccuracies. Additionally, accurate billing contributes to efficient reporting, financial reconciliation, and improved overall business processes.
7. Revenue Maximization: Accurate billing leads to optimized revenue generation. It ensures that all billable products or services are correctly invoiced, maximizing revenue potential. By capturing all billable items accurately, businesses can avoid revenue leakage and drive profitability.
8. Professional Reputation: Accurate billing enhances the professional reputation of a business. Organizations that consistently provide accurate and reliable billing are seen as trustworthy and dependable partners. This reputation strengthens the business’s standing in the industry, attracts new customers, and encourages repeat business.
To achieve accurate billing, businesses should invest in robust billing systems, provide proper training to staff, conduct regular audits, and establish clear billing policies and procedures. By prioritizing accuracy in billing, businesses can foster financial stability, build customer loyalty, and position themselves for long-term success.
Conclusion
Billing in accounting is a vital process that enables businesses to generate revenue, track financial transactions, and maintain financial stability. It involves creating and issuing invoices, collecting payments, and ensuring accurate record-keeping. Throughout this article, we have explored the definition, importance, process, components, types, terms, and challenges of billing in accounting.
Accurate billing is of utmost importance as it directly impacts financial integrity, cash flow management, customer satisfaction, and overall business operations. Businesses rely on accurate billing to maintain financial stability, make informed financial decisions, and comply with legal and regulatory requirements. Accurate billing enhances customer satisfaction, fosters trust, and strengthens customer relationships.
However, the billing process is not without challenges. Inaccurate data, invoice discrepancies, late payments, billing errors, and complex billing requirements can pose obstacles to businesses. To overcome these challenges, businesses should invest in robust billing software and tools, train staff, establish clear billing policies, and prioritize open communication with customers.
In conclusion, accurate billing is fundamental in accounting, benefiting both businesses and customers. By embracing accurate billing practices, businesses can optimize their financial performance, improve cash flow management, and bolster their professional reputation. Moreover, accurate billing facilitates seamless transactions, fosters customer satisfaction, and supports long-term growth and success. Through attention to detail, efficient processes, and a customer-centric approach, businesses can harness the power of accurate billing and elevate their financial management practices.