Finance
What Is Variable APR On A Credit Card?
Published: March 3, 2024
Learn about variable APR on credit cards and how it can affect your finances. Understand the impact of fluctuating interest rates and make informed financial decisions.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Understanding the intricacies of credit card terms is crucial for responsible financial management. One such term that often perplexes credit card users is the Variable Annual Percentage Rate (APR). This article aims to demystify the concept of Variable APR on credit cards, shedding light on its significance, factors influencing it, and strategies for managing it effectively.
Credit cards have become indispensable financial tools, offering convenience and flexibility in managing expenses. However, the terminology associated with credit cards can be daunting, especially for those new to the world of personal finance. Among these terms, the Annual Percentage Rate (APR) stands out as a critical factor influencing the cost of borrowing on a credit card. While the concept of APR is relatively straightforward, the "variable" aspect introduces an element of uncertainty that can impact cardholders' financial obligations.
This article will delve into the nuances of Variable APR, providing a comprehensive understanding of its implications and offering valuable insights into managing this variable component of credit card finance. Whether you're a seasoned credit card user or a novice navigating the realm of personal finance, grasping the dynamics of Variable APR is essential for making informed decisions and optimizing your financial well-being.
Understanding Variable APR
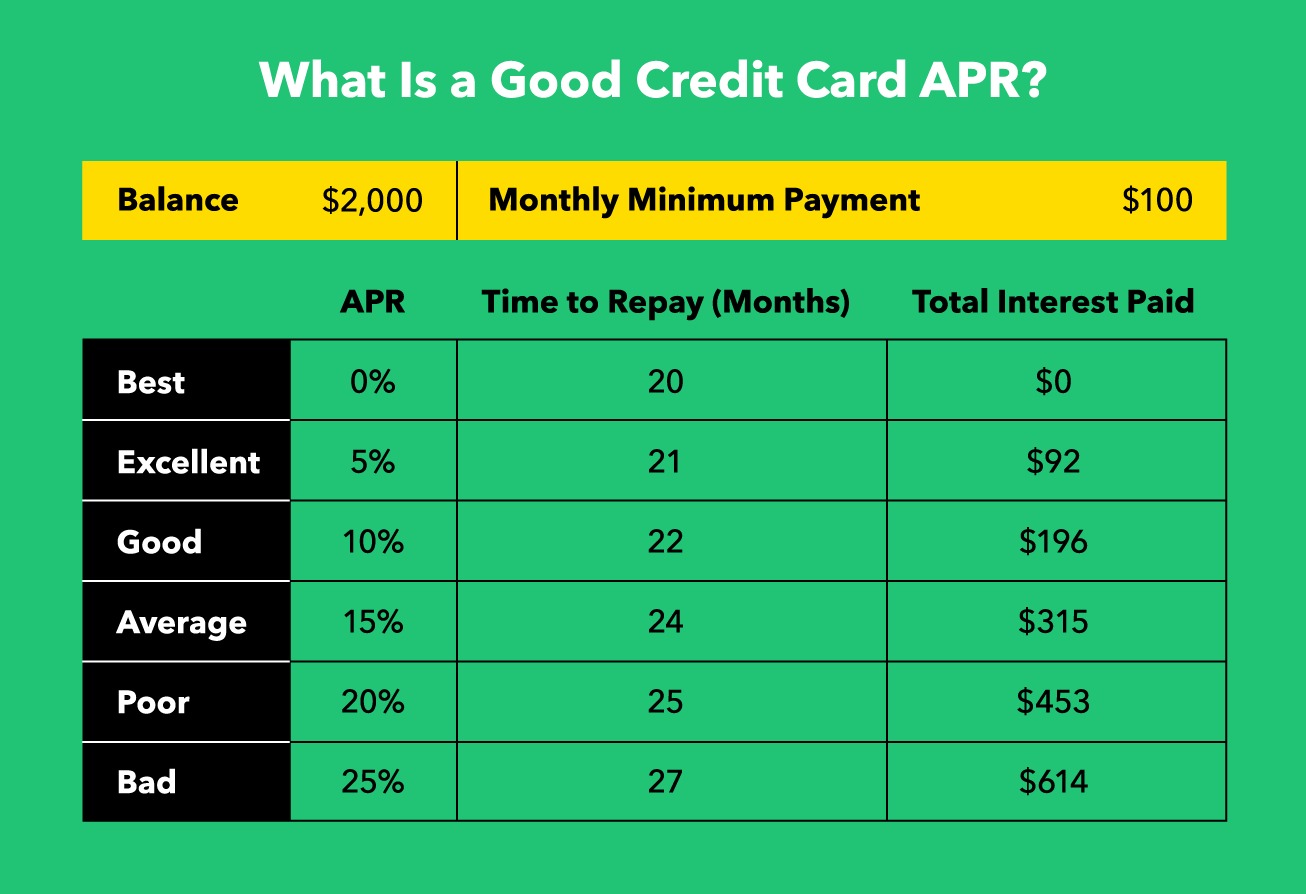
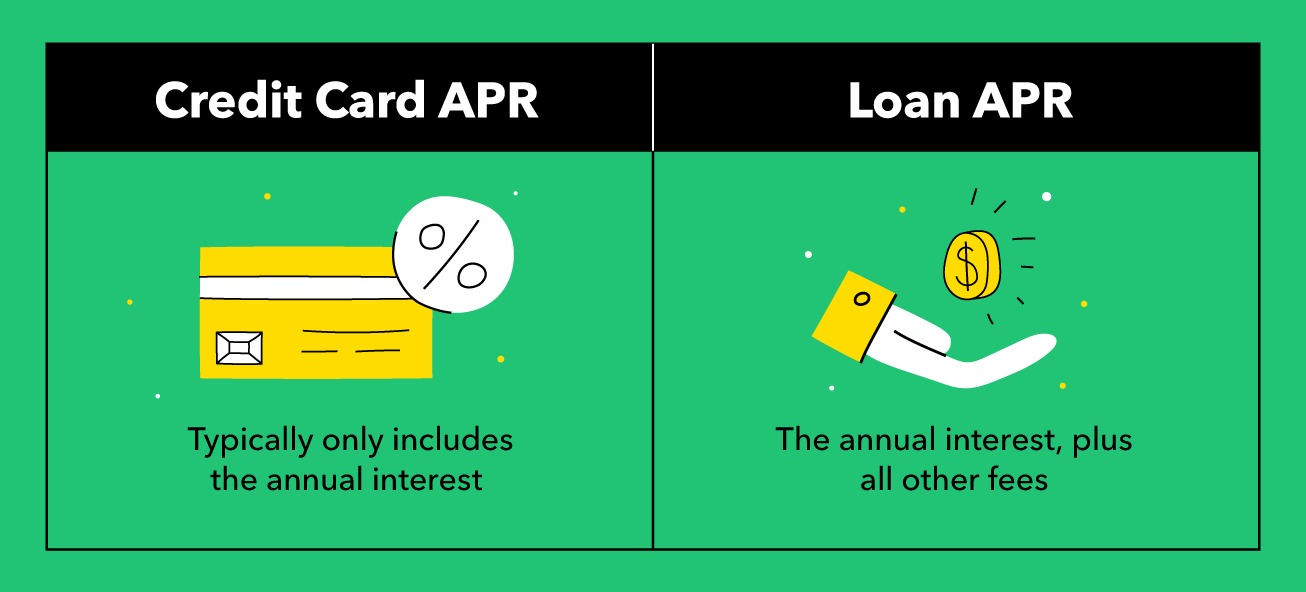
Variable APR, as the name suggests, refers to an Annual Percentage Rate on a credit card that is subject to change. Unlike a fixed APR, which remains constant, a variable APR fluctuates in tandem with an underlying index, such as the prime rate or the London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR). This means that the cost of carrying a balance on a credit card with a variable APR can vary over time, potentially impacting the cardholder’s interest expenses.
When a credit card’s APR is described as “variable,” it signifies that the issuer has the prerogative to adjust the interest rate in response to changes in the broader financial landscape. These adjustments are typically linked to movements in benchmark interest rates or other specified economic indicators. As a result, cardholders may experience fluctuations in their interest charges, making it essential to monitor and comprehend the terms governing the variable APR.
It’s important to note that the variability of the APR introduces an element of uncertainty into the cost of borrowing on a credit card. While a lower APR can translate to reduced interest expenses, a higher APR may lead to increased financial burdens for cardholders carrying balances from month to month. Consequently, understanding the dynamics of variable APR is pivotal for making informed decisions regarding credit card usage and debt management.
Furthermore, the terms and conditions outlined in the credit card agreement provide insights into the mechanisms governing the variability of the APR. These documents detail the specific index or combination of factors used to determine the variable APR, along with any caps or limitations on the extent to which the APR can fluctuate. By familiarizing themselves with these provisions, cardholders can gain clarity on the potential adjustments to their APR and take proactive measures to mitigate the associated financial implications.
Ultimately, comprehending the nature of variable APR empowers cardholders to navigate the dynamic landscape of credit card finance with prudence and foresight. By staying informed about the factors influencing their APR and monitoring changes in the prevailing interest rate environment, individuals can adapt their financial strategies and optimize their credit card usage to align with their broader financial objectives.
Factors Affecting Variable APR
The variability of the Annual Percentage Rate (APR) on a credit card is influenced by a myriad of factors, reflecting the dynamic interplay of financial markets, economic conditions, and issuer-specific policies. Understanding these determinants is instrumental in deciphering the fluctuations in variable APR and anticipating potential changes in interest expenses. Here are the key factors that can impact the variability of a credit card’s APR:
- Index Rate: The majority of credit cards with variable APRs are linked to an index rate, such as the prime rate or LIBOR. Movements in the selected index directly influence the adjustment of the card’s APR. For instance, if the prime rate increases, the variable APR on the linked credit cards is likely to rise as well, leading to higher interest costs for cardholders carrying balances.
- Economic Conditions: Macroeconomic factors, including inflation, unemployment rates, and monetary policy decisions, can exert significant influence on interest rate movements. During periods of economic expansion or inflationary pressures, central banks may raise benchmark interest rates, triggering corresponding upticks in variable APRs on credit cards.
- Credit Card Issuer Policies: Each credit card issuer establishes its own policies governing the adjustment of variable APRs. These policies may vary in terms of frequency of rate adjustments, margin added to the index rate, and disclosure requirements. It’s essential for cardholders to review the issuer’s terms and conditions to grasp the specific parameters guiding the variability of their card’s APR.
- Consumer Credit Profiles: Individual cardholders’ creditworthiness and credit utilization can also impact the variability of their credit card APR. Those with stronger credit profiles may be better positioned to secure lower APRs, while changes in credit scores or payment behaviors can prompt adjustments in the variable APR applied to their accounts.
- Regulatory Changes: Shifts in financial regulations and industry standards can introduce alterations in the mechanisms governing variable APRs. Legislative developments, such as amendments to usury laws or modifications in disclosure requirements, can influence the flexibility and transparency of variable APR adjustments.
By recognizing these influential factors, credit card users can gain a deeper appreciation of the dynamics shaping the variability of their card’s APR. Moreover, staying attuned to market trends, economic indicators, and issuer communications enables cardholders to anticipate potential changes in their variable APR and adapt their financial strategies accordingly.
Pros and Cons of Variable APR
Variable Annual Percentage Rates (APRs) on credit cards present both advantages and drawbacks, influencing the cost of borrowing and the financial dynamics for cardholders. Understanding the pros and cons associated with variable APRs is essential for informed decision-making and prudent financial management.
Pros:
- Flexibility: Variable APRs can offer flexibility in alignment with prevailing market conditions. During periods of declining interest rates, cardholders with variable APRs may benefit from reduced interest expenses, providing potential cost savings compared to fixed APRs.
- Opportunity for Savings: In a low-interest rate environment, variable APRs can translate to lower borrowing costs, allowing cardholders to capitalize on favorable economic conditions and save on interest payments, particularly when carrying balances on their credit cards.
- Adaptability: The variability of APRs enables credit card issuers to adjust rates in response to changing economic landscapes, providing an adaptable framework that reflects market dynamics. This adaptability can benefit cardholders by aligning their interest expenses with prevailing interest rate trends.
Cons:
- Uncertainty: The variable nature of APRs introduces uncertainty, making it challenging for cardholders to anticipate future interest expenses accurately. Fluctuations in variable APRs can lead to unpredictability in monthly payments and overall borrowing costs, potentially complicating financial planning.
- Potential for Higher Costs: In rising interest rate environments, variable APRs can result in heightened borrowing expenses for cardholders carrying balances on their credit cards. This upward cost trajectory may erode potential savings and increase the financial burden on cardholders.
- Complexity: Managing variable APRs necessitates a nuanced understanding of market dynamics and interest rate movements. Cardholders must stay informed about economic indicators and issuer communications to gauge potential changes in their APR, adding a layer of complexity to credit card management.
Assessing the pros and cons of variable APRs empowers cardholders to evaluate the suitability of this pricing structure in light of their financial circumstances and risk tolerance. While variable APRs offer flexibility and the potential for cost savings in favorable interest rate environments, they also introduce uncertainty and the prospect of increased borrowing costs during periods of rising interest rates. By weighing these factors, individuals can make informed choices regarding credit card selection and debt management strategies, aligning their financial decisions with their broader objectives and risk preferences.
How to Manage Variable APR on Credit Cards
Effectively managing a credit card with a variable Annual Percentage Rate (APR) requires strategic financial acumen and proactive measures to navigate the potential fluctuations in interest expenses. By implementing prudent practices and leveraging available resources, cardholders can mitigate the impact of variable APRs and optimize their credit card usage. Here are key strategies for managing variable APR on credit cards:
- Monitor Interest Rate Trends: Stay informed about prevailing interest rate trends and economic indicators that can influence variable APRs. Regularly review financial news and updates from credit card issuers to anticipate potential changes in the cost of borrowing on your credit card.
- Opt for Fixed APR Offers: Some credit card issuers may offer promotional or long-term fixed APR options. Assess the feasibility of securing a fixed APR credit card to establish predictability in interest expenses, especially during periods of economic uncertainty or rising interest rates.
- Focus on Debt Repayment: Prioritize timely repayment of credit card balances to minimize the impact of variable APRs. By reducing outstanding balances, cardholders can mitigate the effects of interest rate fluctuations and avoid accruing substantial interest charges on their accounts.
- Explore Balance Transfer Options: Consider transferring high-interest credit card balances to cards offering introductory 0% APR on balance transfers. This can provide temporary relief from variable APRs, allowing cardholders to consolidate debts and strategize repayment without incurring additional interest costs.
- Negotiate with Credit Card Issuers: Inquire about the possibility of negotiating a lower APR with your credit card issuer, especially if you have a strong payment history and credit profile. Engaging in proactive communication with the issuer can yield opportunities to secure more favorable interest rates.
- Review Credit Card Terms: Familiarize yourself with the terms and conditions of your credit card agreement, particularly the provisions related to variable APR adjustments. Understanding the mechanisms governing the variability of your APR empowers you to make informed financial decisions and adapt to potential rate changes.
By implementing these proactive strategies, credit card users can effectively manage the variability of APRs and mitigate the potential financial implications of fluctuating interest rates. Whether through prudent debt repayment, exploring alternative credit card options, or staying attuned to market dynamics, proactive management of variable APRs can contribute to enhanced financial stability and optimized credit card usage.
Conclusion
Variable Annual Percentage Rates (APRs) on credit cards introduce a dynamic dimension to the cost of borrowing, reflecting the influence of market forces and issuer-specific policies on cardholders’ interest expenses. Grasping the intricacies of variable APRs is essential for informed financial decision-making, empowering credit card users to navigate the fluctuations in interest rates with prudence and foresight.
By understanding the factors shaping the variability of APRs and weighing the pros and cons associated with this pricing structure, individuals can make informed choices regarding their credit card selection and debt management strategies. While variable APRs offer flexibility and the potential for cost savings in favorable interest rate environments, they also present uncertainty and the prospect of increased borrowing costs during periods of rising interest rates.
Effectively managing variable APRs necessitates proactive measures, including monitoring interest rate trends, exploring fixed APR options, prioritizing debt repayment, and leveraging balance transfer opportunities. Additionally, maintaining open communication with credit card issuers and familiarizing oneself with the terms governing variable APR adjustments can contribute to a comprehensive approach to managing the variability of APRs.
Ultimately, the management of variable APRs on credit cards is a testament to the importance of financial vigilance and adaptability in the realm of personal finance. By staying attuned to market dynamics, exercising prudent debt management practices, and leveraging available resources, cardholders can navigate the nuances of variable APRs with confidence, optimizing their credit card usage to align with their broader financial objectives.
In conclusion, a nuanced understanding of variable APRs empowers individuals to make informed financial decisions, enhancing their ability to adapt to changing interest rate environments and optimize their credit card usage. By integrating proactive management strategies and leveraging available financial tools, cardholders can navigate the variability of APRs with prudence and foresight, contributing to enhanced financial stability and well-informed credit management.