Finance
Where Is Credit Union
Published: January 6, 2024
Looking for a finance solution? Find out where you can locate a credit union near you and explore their services to meet your financial needs.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is a Credit Union?
- History of Credit Unions
- Membership and Eligibility Requirements
- Services Offered by Credit Unions
- Benefits of Joining a Credit Union
- How to Find a Credit Union
- Factors to Consider When Choosing a Credit Union
- Differences between Credit Unions and Banks
- Regulation and Oversight of Credit Unions
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to the world of credit unions, where members come first and financial services are tailored to meet their needs. In this article, we will explore what credit unions are, their history, membership requirements, services offered, how to find one, and the differences between credit unions and traditional banks.
Credit unions are not-for-profit financial institutions that are owned and operated by their members. Unlike banks, credit unions are focused on providing services to a specific community or group of individuals with common interests. This cooperative structure allows credit unions to offer competitive rates and fees, as well as personalized customer service.
Throughout history, credit unions have played a vital role in providing financial services to underserved communities. They were first introduced in the mid-19th century as a way to combat the usurious lending practices of the time. Today, credit unions continue to prioritize the financial well-being of their members, fostering a sense of community and shared responsibility.
Joining a credit union offers numerous benefits. Members have access to a wide range of financial products and services, including savings accounts, loans, credit cards, and investment opportunities. Additionally, credit unions often provide financial education and counseling to help members make informed decisions and improve their financial literacy.
So, if you’re looking for a financial institution that puts your needs first and values a sense of community, joining a credit union may be the right choice for you. In the next sections, we will delve deeper into how credit unions operate, how to find one that suits your needs, and the advantages they offer over traditional banks. Let’s explore the world of credit unions together!
What is a Credit Union?
A credit union is a type of financial institution that operates on the principle of cooperative ownership. Unlike traditional banks, credit unions are owned and controlled by their members, who are also the customers. This means that the members have a say in how the credit union is run and benefit directly from its financial products and services.
Credit unions provide a wide range of financial services, including savings accounts, loans, credit cards, and other financial products. They operate with the goal of promoting financial well-being among their member-owners, rather than maximizing profits like banks. As not-for-profit entities, credit unions typically offer competitive interest rates, lower fees, and personalized customer service.
One of the defining characteristics of credit unions is their membership requirements. Unlike banks that are open to the general public, credit unions have specific eligibility criteria. These criteria can be based on factors such as geographic location, employer, profession, or membership in a particular organization or community. By serving a specific membership base, credit unions are able to better understand the needs of their members and provide tailored financial solutions.
The democratic structure of credit unions allows members to elect a board of directors to oversee the institution and make decisions on behalf of the membership. Each member has an equal vote, regardless of the amount of money they have deposited or loaned with the credit union. This democratic governance ensures that the credit union remains focused on serving its members’ best interests.
Overall, credit unions offer a unique alternative to traditional banks, providing a member-oriented approach to banking. They operate on the cooperative principle of people helping people and strive to foster a sense of community among their members. So, if you are looking for a financial institution that prioritizes your interests and offers personalized service, a credit union may be the right choice for you.
History of Credit Unions
The concept of credit unions traces back to the mid-19th century, born out of the need to provide fair and accessible financial services to underserved communities. The pioneer of the credit union movement is often credited to Friedrich Wilhelm Raiffeisen, a German mayor who established the first cooperative lending institution in 1849.
Raiffeisen recognized the exploitative lending practices prevalent during that time and sought to create a system where individuals could pool their resources and provide affordable credit to one another. This cooperative model allowed farmers and small businesses in rural areas to access loans without having to rely on moneylenders who charged exorbitant interest rates.
The credit union movement further gained momentum in North America, with the establishment of the first credit union in Canada in 1901 and the first in the United States in 1909. These early credit unions were formed within specific communities, such as factory workers or church congregations, and aimed to meet the financial needs of their members.
The early growth of credit unions was marked by challenges and resistance from the established banking industry, which viewed them as a threat to their dominance. However, credit unions persevered and continued to expand, driven by the principles of cooperation and financial empowerment.
Over time, credit unions have played a pivotal role in facilitating economic development and social progress. They have challenged traditional notions of banking by placing people before profits. By providing accessible financial services, credit unions have helped families build assets, supported small businesses, and fostered financial inclusion.
In the 1930s, credit unions faced a significant turning point with the passage of the Federal Credit Union Act in the United States. This legislation provided a regulatory framework and federal support for credit unions, ensuring their stability and growth. Similarly, countries around the world have implemented legal frameworks to govern credit unions and promote their contributions to the economy.
Today, credit unions continue to thrive and evolve to meet the changing needs of their members. They have embraced technological advancements to offer digital banking services while still maintaining their cooperative structure and commitment to community development. The credit union movement has grown globally, with millions of individuals benefiting from their unique approach to finance.
The history of credit unions reflects a legacy of empowerment, social responsibility, and economic resilience. As these institutions continue to adapt and innovate, they remain true to their cooperative principles while providing financial services that prioritize the well-being of their members and communities.
Membership and Eligibility Requirements
Joining a credit union offers numerous benefits, but it’s important to note that membership is typically restricted to individuals who meet specific eligibility requirements. These requirements vary from one credit union to another, depending on the institution’s field of membership. Here are some common factors that determine eligibility:
1. Geographic Location: Many credit unions serve a particular geographical area, such as a specific city, county, or state. This allows them to focus on meeting the financial needs of the local community.
2. Employer or Profession: Some credit unions are formed to serve employees of a specific company or organization. These employer-based credit unions provide financial services exclusively to the employees and their immediate family members.
3. Affiliation with a Specific Group: Certain credit unions are established to serve members of a particular organization, association, or community. This could include labor unions, religious groups, alumni associations, or cultural organizations.
4. Family Relationship: Many credit unions allow immediate family members, such as spouses, children, parents, and siblings, to join based on their existing membership. This allows for a broader membership base while maintaining the sense of community.
5. Membership in an Affiliated Organization: Some credit unions extend eligibility to individuals who are members of an affiliated organization. For example, being a member of a nonprofit organization or participating in a community program may grant eligibility.
It’s important to review the membership and eligibility requirements specific to each credit union you are interested in joining. These requirements can typically be found on the credit union’s website or by contacting them directly. If you meet the eligibility criteria, becoming a member requires completing an application and opening an account with the credit union.
One notable aspect of credit unions is their commitment to inclusivity and providing access to financial services. They strive to serve individuals who may have been underserved by traditional banks, including those with lower incomes or limited credit history.
Overall, credit unions offer a unique opportunity to become part of a cooperative financial institution that prioritizes its member-owners. By meeting the eligibility requirements, you can gain access to a range of valuable financial services and contribute to a community-focused financial institution.
Services Offered by Credit Unions
Credit unions offer a wide range of financial services designed to meet the needs of their members. Through their cooperative structure, credit unions strive to provide affordable and personalized services that promote financial well-being. Here are some of the key services typically offered by credit unions:
1. Savings Accounts: Credit unions offer various types of savings accounts, including regular savings accounts, youth accounts, and certificates of deposit (CDs). These accounts often offer competitive interest rates and low minimum balance requirements, allowing members to save money and earn returns on their deposits.
2. Checking Accounts: Just like traditional banks, credit unions provide checking accounts that offer convenient access to funds for everyday transactions. Credit union checking accounts often come with features such as no monthly fees, free debit cards, online banking, and mobile banking options.
3. Loans: Credit unions offer a range of loan products, including personal loans, auto loans, home loans, and credit cards. They typically provide competitive interest rates and flexible terms. Credit unions are known for their willingness to work with members to find the best loan solutions based on their individual needs and financial situations.
4. Credit Cards: Many credit unions issue their own branded credit cards with competitive interest rates and rewards programs. Credit union credit cards often have lower fees and interest rates compared to those offered by traditional banks, providing members with a cost-effective way to manage their spending and build credit.
5. Online and Mobile Banking: Credit unions have adapted to technological advancements and offer online banking services and mobile banking apps. Members can access their accounts, view transaction history, transfer funds, pay bills, and manage their finances conveniently from any device with internet access.
6. Financial Counseling and Education: As member-focused institutions, credit unions often provide financial counseling and education programs to help members make informed decisions about their money. They may offer workshops, seminars, and online resources to improve financial literacy, budgeting skills, and debt management.
7. Investment Services: Some credit unions offer investment services to help members plan for the future. These services may include retirement accounts (such as IRAs and 401(k) rollovers), mutual funds, and access to financial advisors who can provide guidance on investment strategies.
8. Other Financial Products and Services: Credit unions may also offer additional services, such as insurance products (auto, home, life), wire transfers, notary services, safe deposit boxes, and more. The exact range of services varies by credit union, so it’s important to explore the specific offerings of each institution.
When considering joining a credit union, it’s essential to evaluate the services they offer and determine whether they align with your financial needs and goals. Credit unions excel at providing personalized and member-focused services that can help you achieve your financial objectives while maintaining a sense of community and shared responsibility.
Benefits of Joining a Credit Union
Joining a credit union can offer numerous advantages compared to traditional banks. These member-focused financial institutions prioritize the needs of their members and strive to provide personalized services. Here are some of the key benefits of joining a credit union:
1. Competitive Rates and Fees: Credit unions often offer favorable interest rates on savings accounts and loans. Since credit unions are not-for-profit organizations, they can pass on their earnings to members in the form of lower fees and better rates compared to traditional banks.
2. Personalized Customer Service: Credit unions pride themselves on providing exceptional customer service. As member-owned institutions, credit unions prioritize building relationships with their members and meeting their individual needs. Members can expect personalized attention and tailored financial solutions.
3. Community-Oriented Approach: Credit unions operate on the principle of people helping people. By joining a credit union, you become part of a cooperative financial institution that is deeply connected to the local community. Credit unions often support community development initiatives and foster a sense of shared responsibility among their members.
4. Financial Education and Counseling: Many credit unions offer financial education programs and counseling services to help their members improve their financial literacy and make informed financial decisions. These resources can include workshops, seminars, online resources, and one-on-one counseling sessions.
5. Access to Diverse Financial Products: Credit unions provide a range of financial products and services, including savings accounts, checking accounts, loans, credit cards, investment options, and more. Members can access comprehensive financial solutions under one roof, simplifying their financial management.
6. Enhanced Member Control: As a member of a credit union, you have a voice in the decision-making process. Credit unions operate democratically, allowing members to elect a board of directors who make decisions on behalf of the institution. This level of member control ensures that the credit union remains focused on meeting the needs of its members.
7. Financial Inclusion: Credit unions embrace inclusivity and strive to serve individuals who may have been overlooked by traditional banks. They often provide services to those with lower incomes, limited credit history, or unique financial circumstances. Credit unions offer opportunities for financial inclusion and provide support to members in achieving their financial goals.
8. Stronger Sense of Community: Joining a credit union means becoming part of a close-knit community of members who share similar interests or affiliations. Credit unions often organize social events, workshops, and community initiatives that foster a sense of belonging and encourage interaction among members.
9. Support for Local Economy: Credit unions reinvest their earnings back into the local community, supporting economic growth and development. By choosing a credit union, you contribute to the local economy and help create a positive impact in your community.
Overall, joining a credit union provides numerous benefits, including competitive rates, personalized service, community engagement, and access to a wide range of financial products. As member-owned institutions, credit unions prioritize the well-being of their members, creating a unique and member-centric banking experience.
How to Find a Credit Union
If you’re interested in joining a credit union, there are several steps you can take to find the right one for your financial needs. Here are some methods to help you locate a credit union:
1. Research Online: The internet is a valuable resource for finding credit unions in your area. Use search engines and online directories to search for credit unions based on your location or specific criteria. Websites such as the National Credit Union Administration (NCUA) and local credit union league websites can provide a list of credit unions in your region.
2. Ask for Recommendations: Reach out to friends, family, colleagues, or associates who are members of credit unions. They can provide valuable insights into their experiences and recommend credit unions that may be suitable for you. Personal recommendations often carry more weight and can help you find credit unions with a strong reputation.
3. Check with Your Employer or Organization: Many employers partner with specific credit unions to provide financial services to their employees. Inquire with your workplace’s human resources department or employee benefits coordinator to find out if there is a credit union affiliated with your company. Similarly, certain organizations or unions may have established credit unions for their members.
4. Explore Community-Based Credit Unions: Credit unions often serve specific communities or geographic areas. Research credit unions in your local community or neighborhoods to find those that cater to your area. These community-based credit unions may have a deep understanding of the needs and challenges of the communities they serve.
5. Use Mobile Apps or Online Platforms: Many financial technology (fintech) platforms and mobile apps offer tools to help users find credit unions or compare different options. These resources often provide information on eligibility requirements, services offered, and member reviews to assist you in making an informed decision.
6. Check with Local Financial Institutions: Contact nearby banks or traditional financial institutions and inquire if they offer credit union services or have partnerships with credit unions. Some larger financial institutions either own credit unions or have collaboration agreements, which may provide access to credit union services.
Once you have identified potential credit unions, take the time to research and compare them. Consider factors such as membership requirements, services offered, fees, interest rates, online and mobile banking capabilities, and customer reviews. It’s also important to review the credit union’s financial stability and membership satisfaction ratings.
Before finalizing your decision, visit the websites of the credit unions you are interested in and explore their offerings in detail. If possible, reach out to their customer service departments to inquire about any additional information or clarifications you need.
Finding the right credit union may take some time and effort, but the benefits of joining a credit union that aligns with your financial goals and values can be significant. By conducting thorough research and considering your specific needs, you can find a credit union that offers the services you require while providing a member-focused and community-oriented banking experience.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Credit Union
When selecting a credit union to join, it’s important to consider various factors to ensure it aligns with your financial needs and preferences. Here are some key factors to consider when choosing a credit union:
1. Membership Eligibility: Review the membership requirements of the credit union to ensure that you meet the criteria. Consider whether the eligibility criteria are based on your geographic location, employer, profession, or affiliation with a specific organization. Additionally, check if the credit union allows family members to join based on your membership.
2. Range of Services: Evaluate the range of financial products and services offered by the credit union. Consider whether they provide the services you require, such as savings accounts, checking accounts, loans, credit cards, investment options, and online banking capabilities. The more comprehensive the services offered, the more convenient it will be for managing your finances.
3. Fees and Interest Rates: Compare the fees and interest rates charged by different credit unions. Look for credit unions that offer competitive rates on savings accounts and loans and have reasonable fees for services such as overdrafts, ATM usage, and account maintenance. Consider how these rates and fees will impact your overall banking experience and financial goals.
4. Customer Service: Investigate the quality of customer service offered by the credit union. Read reviews, check their social media channels, and reach out to their customer service department to gauge their responsiveness and willingness to address your concerns. Look for a credit union that values member satisfaction and provides personalized support.
5. Financial Stability: Assess the financial stability and reputation of the credit union. Research their financial statements, credit ratings, and longevity in the industry. A financially stable credit union will be better equipped to handle your financial transactions and provide consistent and reliable services.
6. Access to ATMs and Branches: Consider the convenience of accessing ATMs and branches of the credit union. Determine the availability of ATMs within your area and whether the credit union is part of a network that allows you to use other ATMs with minimal or no fees. Also, assess the proximity of branches if you prefer in-person assistance.
7. Online and Mobile Banking: Evaluate the online and mobile banking capabilities of the credit union. Check if they have a user-friendly website, mobile app, and other digital tools that allow you to conveniently manage your accounts, make transactions, and access financial information. Robust online and mobile banking services can enhance your banking experience.
8. Commitment to Community: Consider the credit union’s commitment to community development and social responsibility. Explore their involvement in community initiatives, financial education programs, and support for local causes. A credit union that actively contributes to the community aligns well with the cooperative principles and can make you feel more connected to the institution.
9. Member Reviews and Recommendations: Seek out member reviews and recommendations of the credit unions you are considering. Look for feedback on their experiences with customer service, account management, loan processes, and overall satisfaction. Member reviews can provide valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of the credit union.
By carefully considering these factors, you can find a credit union that best meets your financial needs and preferences. Take the time to research your options, compare their offerings, and make an informed decision. Joining a credit union that aligns with your values and provides exceptional service can enhance your banking experience and contribute to your long-term financial goals.
Differences between Credit Unions and Banks
Credit unions and banks are both financial institutions that offer a range of financial services, but there are key differences between them. Understanding these differences can help you decide which type of institution is best suited to meet your financial needs. Here are some of the main distinctions:
1. Ownership and Structure: One of the fundamental differences between credit unions and banks is their ownership and structure. Credit unions are member-owned and operated, meaning the members are also the owners of the institution. Banks, on the other hand, are typically owned by shareholders and operate for-profit.
2. Purpose and Focus: Credit unions have a primary focus on providing financial services to their members and fostering a sense of community. Their purpose is to promote the financial well-being of their members. Banks, in contrast, aim to generate profits for their shareholders and often have a broader customer base that may not necessarily be members.
3. Membership Eligibility: Credit unions have membership requirements that individuals must meet to become members. These requirements can be based on factors such as geographic location, employer, profession, or membership in a specific organization or community. Banks, on the other hand, are open to the general public and do not have specific eligibility criteria for customers.
4. Profit Distribution: Since credit unions are not-for-profit institutions, any profits they generate are typically reinvested back into the credit union or returned to members in the form of lower fees, better rates on loans and savings accounts, or additional services. In contrast, banks aim to maximize profits for their shareholders and may distribute them as dividends.
5. Rates and Fees: Credit unions often offer favorable rates on loans, savings accounts, and credit cards compared to banks. Additionally, credit unions typically have lower fees for services such as overdrafts, ATM usage, and account maintenance. Banks may have higher fees and may offer varying interest rates based on market conditions and their profit goals.
6. Customer Service: Credit unions are known for their personalized and member-focused customer service. Members often have direct access to decision-makers and benefit from individualized attention. Banks, being larger institutions, may offer a wider range of services but may not provide the same level of personalized service.
7. Loan Approval Process: The loan approval process can differ between credit unions and banks. Credit unions often consider personal relationships and the context of the loan application when evaluating loan requests. They may be more flexible in lending decisions and take into account factors beyond credit scores. Banks typically have stricter lending criteria and rely heavily on credit scores and financial history when making loan decisions.
8. Social Responsibility: Credit unions often prioritize community development initiatives and support local causes. They work closely with their members to address financial needs and promote financial literacy. Banks may also engage in corporate social responsibility, but their primary focus is usually on generating profits for shareholders.
It’s important to note that both credit unions and banks are regulated and insured by government entities. Credit unions are typically insured by the National Credit Union Administration (NCUA), while banks are insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC).
When considering whether to choose a credit union or a bank, it’s essential to assess your own financial needs, preferences, and values. Credit unions excel in providing personalized service, competitive rates, and a sense of community, while banks may offer a broader range of services and convenience. Carefully evaluating your options will help you make an informed decision that aligns with your financial goals.
Regulation and Oversight of Credit Unions
Credit unions, like banks, are subject to regulation and oversight to ensure their safety and soundness and to protect the interests of their members. Understanding the regulatory framework surrounding credit unions can provide confidence and peace of mind for those considering joining or already members of these financial institutions. Here’s an overview of the regulation and oversight of credit unions:
1. National Credit Union Administration (NCUA): In the United States, credit unions are regulated by the National Credit Union Administration (NCUA), an independent federal agency. The NCUA supervises and insures federal credit unions and works to maintain the safety and soundness of the credit union system. They conduct examinations, enforce regulations, and provide oversight to ensure compliance with federal laws.
2. State Regulatory Agencies: State-chartered credit unions are regulated by the appropriate state regulatory agency. These agencies have similar responsibilities as the NCUA but focus specifically on credit unions operating within their respective states. State regulatory agencies work in collaboration with the NCUA to ensure consistent regulation and oversight across the credit union industry.
3. Safety and Soundness Regulations: Credit unions are subject to safety and soundness regulations to ensure they have the proper financial controls, risk management practices, and capital requirements in place to protect the interests of their members. These regulations help to maintain the stability and financial strength of credit unions and protect against fraud and other risks.
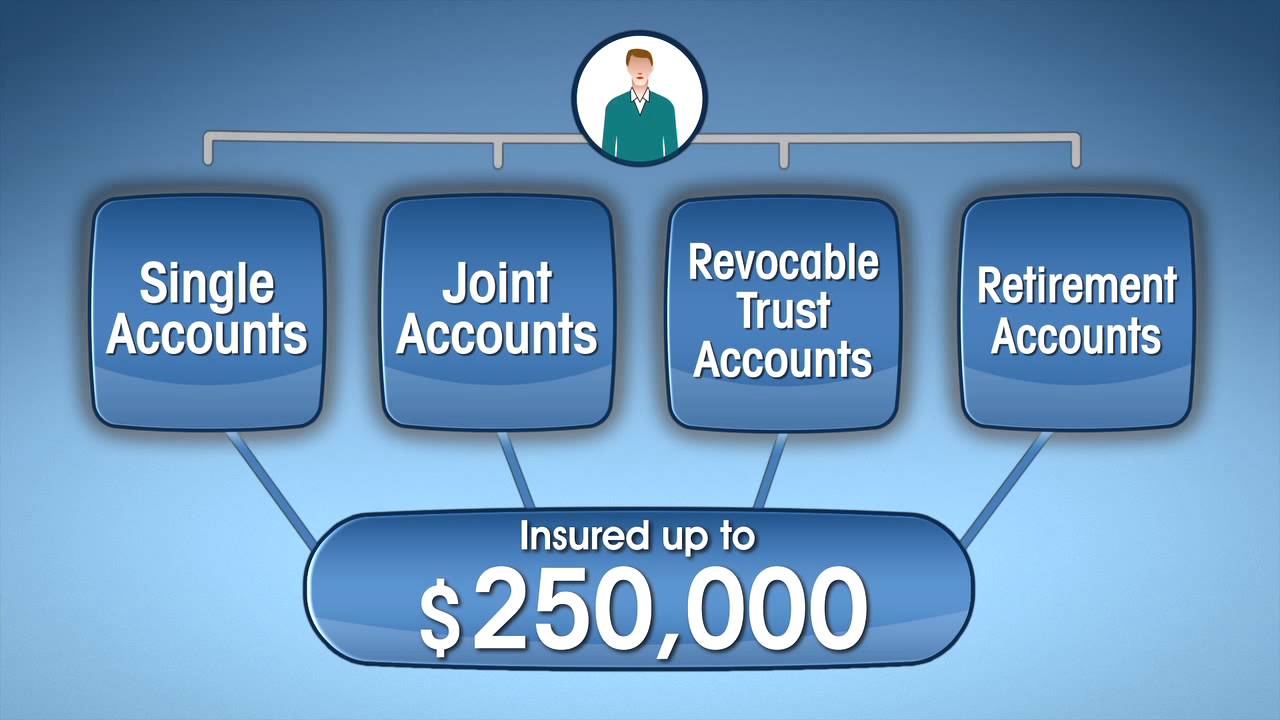
4. Deposit Insurance: Just like banks, credit unions provide deposit insurance to protect their members’ funds. In the United States, credit unions are insured by the National Credit Union Share Insurance Fund (NCUSIF), which is administered by the NCUA. The NCUSIF provides coverage of up to $250,000 per depositor, similar to the coverage provided by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) for bank deposits.
5. Consumer Protection: Credit unions are also subject to consumer protection laws at both the federal and state levels. These laws govern various aspects of credit union operations, including fair lending practices, disclosure requirements, privacy protection, and dispute resolution. These regulations ensure that credit unions treat their members fairly and transparently and provide avenues for recourse in case of any issues.
6. Industry Association Guidance: Credit unions can also rely on guidance and best practices provided by industry associations such as the Credit Union National Association (CUNA) or state-level credit union leagues. These associations offer resources, training, and support to credit unions in areas such as compliance, governance, operations, and member service excellence.
It’s important to note that credit unions and their regulatory environment may vary across different countries. The regulatory bodies and specific regulations governing credit unions will depend on the legal and regulatory framework of each jurisdiction.
By adhering to regulatory requirements and undergoing regular examinations, credit unions demonstrate their commitment to financial soundness and member protection. This oversight and regulation provide reassurance to members about the safety and stability of their deposits and investments, instilling confidence in the credit union system.
Conclusion
Credit unions offer a unique alternative to traditional banks, providing member-focused and community-oriented financial services. As member-owned and operated institutions, credit unions prioritize the needs and well-being of their members, offering personalized service, competitive rates, and a sense of community.
By joining a credit union, you become part of a cooperative financial institution that values inclusivity, financial education, and social responsibility. Credit unions provide a wide range of financial products and services, including savings accounts, loans, credit cards, and investment options. They often offer competitive rates and lower fees compared to traditional banks.
Membership in a credit union is usually based on specific eligibility requirements, such as geographic location, employer, profession, or affiliation with an organization or community. These requirements ensure that credit unions can better understand and meet the unique financial needs of their members.
When choosing a credit union, it’s important to consider factors such as the range of services offered, customer service quality, fees and interest rates, online and mobile banking capabilities, and the credit union’s commitment to the community. Conducting thorough research and comparing different credit unions will help you find an institution that aligns with your financial goals and values.
Credit unions are regulated and overseen by entities such as the National Credit Union Administration (NCUA) in the United States. This regulatory oversight ensures the safety and soundness of credit unions and protects the interests of their members.
In conclusion, joining a credit union provides numerous benefits, including personalized service, competitive rates, community engagement, and access to a range of financial products. Credit unions offer an attractive alternative to traditional banks and can contribute to the financial well-being of their members. Consider your financial needs and aspirations, and explore the available credit unions in your area to make an informed decision about joining a credit union that will best serve your interests.