Finance
Why Open Banking
Published: October 11, 2023
Discover the benefits of Open Banking in the finance industry and how it is revolutionizing the way we manage our finances.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
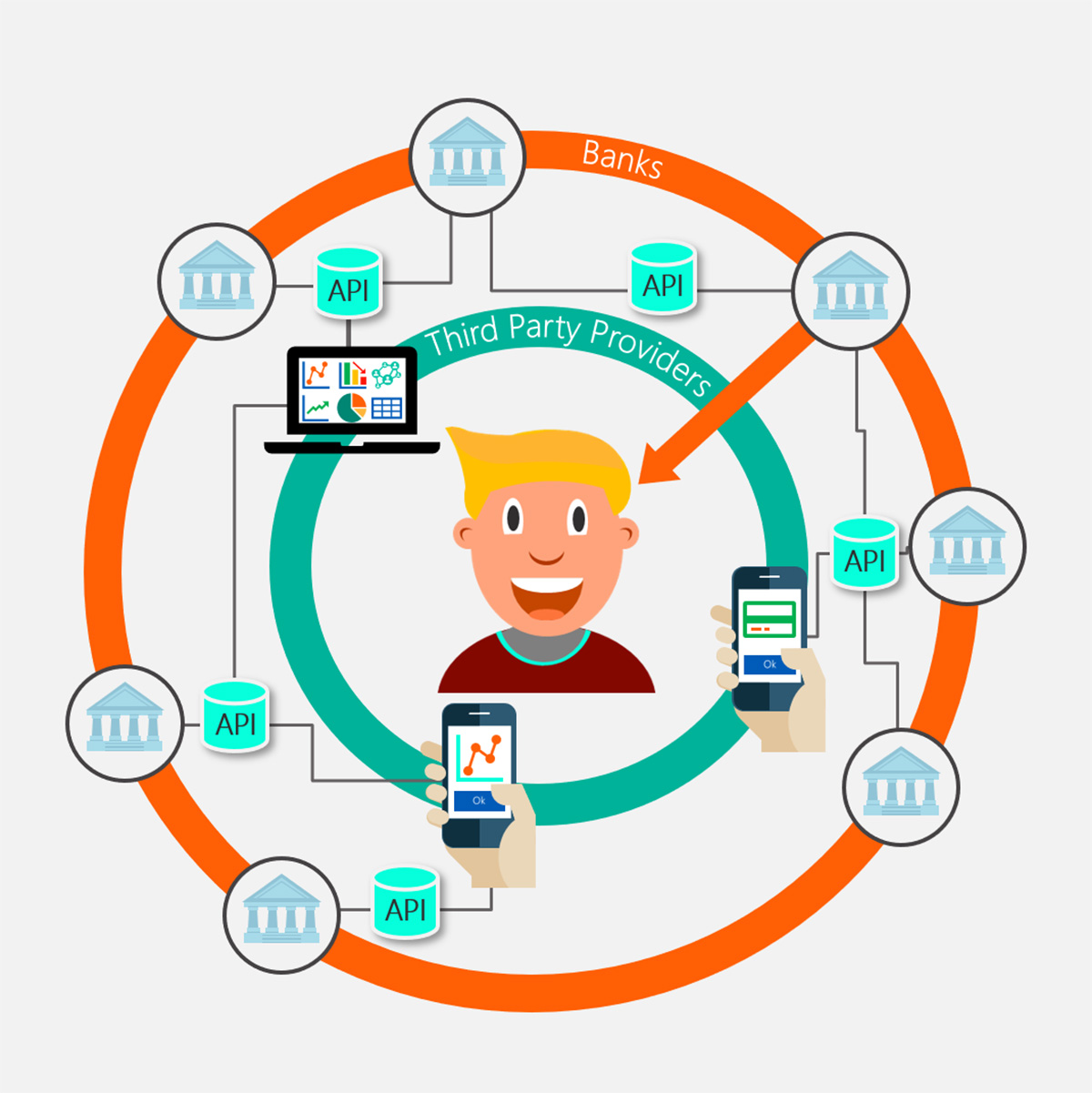
Open Banking is revolutionizing the financial industry, breaking down traditional barriers and paving the way for a more transparent and customer-centric banking experience. It is a concept that empowers consumers by granting them greater control over their financial data and enabling them to securely share it with authorized third-party providers.
The concept of Open Banking emerged as a response to growing demands for more personalized and efficient financial services. It leverages Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) to facilitate the secure exchange of financial data between banks and authorized third-party providers such as fintech startups, mobile apps, and other financial service providers.
With Open Banking, customers can access their financial information from multiple providers in a single platform, compare products and services, and make more informed decisions. It eliminates the need for customers to switch between various banking apps or websites and streamlines the overall banking experience.
In addition to improving convenience for customers, Open Banking also fosters increased competition and innovation within the financial industry. It encourages financial institutions to enhance their services, develop new products, and leverage data-driven insights to better meet the needs of their customers. This increased competition ultimately benefits customers, as it leads to more affordable and tailored financial solutions.
While Open Banking presents significant opportunities, it also introduces various challenges and concerns. The primary concerns revolve around privacy and data security, as the sharing of financial information between different parties raises questions about the protection of sensitive data. Additionally, compliance with regulatory requirements is essential to ensure that Open Banking operates in a safe and regulated manner.
In this article, we will delve into the concept of Open Banking, examine its benefits, and explore the challenges it faces. We will also discuss the importance of privacy and data security, as well as the need for regulatory compliance. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of Open Banking and its impact on the financial industry.
What is Open Banking?
Open Banking is a system that allows customers to grant permission to banks and other financial service providers to securely access their financial data. It is built on the principle of data sharing, empowering consumers to control and share their financial information with authorized third-party providers.
To enable this data sharing, banks and other financial institutions create Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) that allow secure and standardized access to customer data. APIs act as bridges, facilitating the exchange of information between different systems. They ensure that data is accessed and shared in a secure and regulated manner.
Open Banking provides customers with the ability to manage their financial accounts more efficiently. It allows them to view all their accounts, including current accounts, savings accounts, loans, and investments, in a single platform. This centralized view of financial information simplifies financial management, making it easier for customers to track their spending, analyze their financial health, and make informed decisions.
Additionally, Open Banking promotes competition by leveling the playing field for financial service providers. It breaks down the monopoly previously held by traditional banks and allows smaller fintech startups and innovative financial companies to enter the market. With access to customer data and the ability to provide tailored financial solutions, these new players can offer more competitive products and services, improving customer choice and driving innovation within the industry.
Open Banking is not just limited to consumer banking. It also has implications for various sectors within the financial industry, such as lending, insurance, and investment management. By sharing financial data across different sectors, Open Banking fosters collaboration and enables the development of more comprehensive and personalized financial solutions.
It is important to note that Open Banking operates on a consent-based approach. Customers have full control over their data and can decide which providers they want to share their information with. They can revoke consent at any time, and their data remains protected under strict data protection regulations.
Open Banking has gained significant traction in recent years, with various countries around the world implementing regulations to promote its adoption. These regulations aim to ensure the security and privacy of customer data and to define the rights and obligations of both financial institutions and third-party providers.
Overall, Open Banking represents a significant shift in the financial industry, empowering customers with greater control over their financial data and driving competition and innovation. It has the potential to transform how financial services are delivered, making the banking experience more personalized, efficient, and customer-centric.
Benefits of Open Banking
Open Banking brings forth numerous advantages for both customers and the financial industry as a whole. Let’s explore some of the key benefits of Open Banking:
1. Enhanced Customer Control and Convenience
One of the primary benefits of Open Banking is the ability for customers to have greater control over their financial data. They can securely grant access to their information to authorized third-party providers, enabling personalized and tailored financial services. Open Banking platforms allow customers to aggregate their accounts from multiple providers, providing a holistic view of their financial situation. This centralized access simplifies financial management, making it easier to track expenses, budget effectively, and set financial goals.
2. Increased Competition and Innovation
Open Banking fosters greater competition within the financial industry by leveling the playing field. It enables new entrants, such as fintech startups, to access customer data and develop innovative financial products and services. This increased competition leads to better offerings, improved customer experience, and more affordable financial solutions. By promoting innovation and encouraging collaboration between financial institutions, Open Banking drives the development of technology-driven solutions that address customer needs more effectively.
3. Improved Financial Decision Making
With access to real-time financial data, customers can make more informed decisions. Open Banking platforms provide tools and insights that help customers analyze their spending patterns, identify areas for potential savings, and gain a deeper understanding of their financial health. By having a comprehensive view of their finances, customers can make better choices when it comes to budgeting, investments, and loan applications.
4. Streamlined Processes and Efficiency
Open Banking facilitates seamless integration of different financial services and systems. Through APIs, banks and third-party providers can securely and efficiently exchange data, eliminating the need for manual processes and reducing administrative burdens. This streamlining of processes leads to increased efficiency, reduced operational costs, and quicker access to financial services for customers.
5. Personalized Products and Services
Open Banking allows for the creation of personalized financial products and services tailored to individual customer needs. With customers’ consent, third-party providers can access their financial data and develop customized offerings, such as personalized investment portfolios, personalized lending options, and targeted insurance plans. This level of personalization ensures that customers receive financial products and services that align with their goals and preferences.
Overall, Open Banking revolutionizes the financial landscape by empowering customers, promoting competition, and driving innovation. It enhances customer control, streamlines processes, and enables the creation of personalized and efficient financial solutions. As Open Banking continues to evolve, it will pave the way for a more customer-centric and technologically advanced financial industry.
Enhanced Customer Control and Convenience
Open Banking offers customers unprecedented control over their financial data, enabling them to have a more personalized and convenient banking experience. Here are some of the key ways in which Open Banking enhances customer control and convenience:
1. Single Platform Access
With Open Banking, customers can access all their financial accounts and data from various providers in a single platform. This eliminates the need for customers to switch between different banking apps or websites, streamlining the management of their finances. They can view their transaction history, balances, and other account details in one place, making it easier to track their spending and stay on top of their financial situation.
2. Aggregated Financial Information
Open Banking allows for the aggregation of financial information from multiple accounts, such as current accounts, savings accounts, loans, and credit cards. Customers can see a comprehensive view of their financial landscape, providing a clearer picture of their financial health. This holistic view enables customers to make better-informed decisions about their money and identify areas where they can improve their financial well-being.
3. Real-time Updates
Through Open Banking, customers can receive real-time updates on their accounts and transactions. They no longer have to wait for monthly statements or log into multiple banking systems to check their balances. Instead, they can receive instant notifications and updates on their financial activities, ensuring they are always aware of their financial status.
4. Secure Data Sharing
Open Banking adheres to strict data security and privacy standards, ensuring that customers’ financial information is kept secure. When customers grant consent, their data is securely shared with authorized third-party providers through encrypted channels. This level of security gives customers peace of mind, knowing that their personal and financial information is protected.
5. Customized Financial Services
Open Banking enables personalized and tailored financial services by allowing third-party providers to access customer data. With the customer’s consent, these providers can leverage the data to offer customized products and services that suit the customer’s needs and preferences. For example, customers can receive personalized investment recommendations based on their financial goals and risk tolerance or receive loan offers that align with their creditworthiness.
6. Open Innovation and Collaboration
Open Banking promotes collaboration between traditional banks and fintech startups, encouraging the development of innovative financial solutions. By sharing access to data, banks can partner with fintech companies to offer innovative products and services that combine the stability of traditional banking with the agility and innovation of the fintech ecosystem. This collaboration creates a win-win situation for both customers and financial institutions by enhancing product offerings and providing customers with a wider range of choices.
In summary, Open Banking puts customers in the driver’s seat, granting them greater control over their financial information and providing the convenience of a consolidated view of their finances. With enhanced control and convenience, customers can make better financial decisions, improve their financial well-being, and ultimately have a more satisfying banking experience.
Increased Competition and Innovation
Open Banking has had a transformative impact on the financial industry by fostering increased competition and driving innovation. Here are the key ways in which Open Banking has led to stronger competition and accelerated innovation:
1. Leveling the Playing Field
Open Banking has broken down the barriers to entry for new players in the financial industry. Traditional banks historically had a monopoly on customer data and services, making it difficult for smaller fintech startups and innovative financial companies to compete. However, with Open Banking, these new entrants can access customer data, develop innovative solutions, and provide competitive products and services. This has leveled the playing field, encouraging healthy competition and placing more options in the hands of customers.
2. New Business Models and Service Offerings
Open Banking has paved the way for the emergence of new business models and service offerings within the financial industry. Fintech startups and other third-party providers are leveraging customer data to create innovative solutions that address specific customer needs. For example, budgeting apps that analyze spending patterns and offer personalized financial advice, or lending platforms that use open data to provide faster and more accessible loan options. These new business models and service offerings enhance customer choice and provide tailored solutions that traditional banks may not be able to offer.
3. Enhanced Customer Experience
Open Banking has incentivized financial institutions to improve the customer experience. To stay competitive, banks have had to invest in user-friendly interfaces, seamless integrations with third-party providers, and enhanced digital services. This has resulted in a more personalized and convenient banking experience for customers. They can now easily access and manage their accounts, make transactions, and access tailored financial products and services, all from a single platform. The focus on customer-centricity has become a priority, leading to improved overall satisfaction.
4. Collaboration between Banks and Fintech Startups
Open Banking has created opportunities for collaboration between traditional banks and fintech startups. Banks can partner with fintech companies to leverage their expertise and innovative solutions. This collaboration allows for the creation of hybrid products and services that combine the stability and trust of traditional banks with the agility and innovation of fintech startups. For example, banks might incorporate fintech solutions for mobile payments, investment management, or robo-advisory services, providing customers with a wider range of options and an improved user experience.
5. Data-Driven Insights
Open Banking provides financial institutions with access to a wealth of customer data. This data can be analyzed and used to gain valuable insights into customer behavior, preferences, and needs. Financial institutions can use these insights to develop targeted marketing strategies, create personalized product recommendations, and identify new market opportunities. Data-driven decision-making allows for more effective resource allocation, product development, and overall business strategy, bolstering innovation and enabling financial institutions to better serve their customers.
Open Banking is a catalyst for increased competition and innovation within the financial industry. It fosters collaboration between traditional banks and fintech startups, encourages the development of new business models and service offerings, enhances the customer experience, and drives data-driven insights. As Open Banking continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly lead to even greater competition and innovation, benefitting customers with improved financial products, services, and overall customer experience.
Improved Financial Decision Making
Open Banking empowers customers to make better-informed financial decisions by providing access to real-time data, personalized insights, and comprehensive financial management tools. Here are the key ways in which Open Banking improves financial decision-making:
1. Holistic View of Finances
Open Banking allows customers to aggregate data from various financial accounts, giving them a comprehensive view of their finances. They can easily see all their accounts, including checking accounts, savings accounts, credit cards, loans, and investments, in one place. This holistic view enables customers to understand their financial position and make more informed decisions about their money.
2. Real-time Updates and Notifications
With Open Banking, customers receive real-time updates and notifications about their financial activities. They can receive alerts for transactions, balance updates, bill payments, and other important information. This real-time visibility ensures that customers stay on top of their finances and can take immediate action if necessary.
3. Budgeting and Spending Insights
Open Banking platforms often offer robust budgeting tools that analyze spending patterns and categorize expenses. This empowers customers to understand their spending habits and make informed decisions about budgeting. Customers can set budget goals, track their progress, and receive personalized recommendations to help them save money and make smarter financial choices.
4. Personalized Investment Recommendations
Open Banking enables customers to receive personalized investment recommendations based on their financial goals, risk tolerance, and available investment options. By accessing data from multiple financial institutions, investment platforms can provide customized portfolios that align with the customer’s investment objectives. This personalization helps customers make more informed investment decisions and optimize their investment strategies.
5. Access to Competitive Loan and Mortgage Rates
Through Open Banking, customers can access a wider range of loan and mortgage options from different financial institutions. By sharing their financial data, customers can receive personalized loan offers that consider their financial health and creditworthiness. This allows customers to compare rates and terms and choose the most competitive option, saving them money in the long run.
6. Improved Financial Planning
Open Banking provides customers with advanced financial planning tools and calculators that help them set and achieve their financial goals. Customers can simulate different scenarios, such as retirement planning, college savings, or major purchases, to understand the impact of their financial decisions. This enables customers to make more informed choices and create robust financial plans for their future.
Open Banking equips customers with the tools and information they need to make better financial decisions. By offering a holistic view of finances, real-time updates, personalized insights, and budgeting tools, customers can gain a deeper understanding of their financial situation. They can make informed decisions about budgeting, investment, borrowing, and financial planning, ultimately leading to improved financial well-being and long-term financial success.
Challenges and Concerns
While Open Banking brings about numerous benefits, it also presents challenges and concerns that need to be addressed. Here are some of the key challenges and concerns associated with Open Banking:
1. Privacy and Data Security
One of the primary concerns surrounding Open Banking is the security and privacy of customer data. The sharing of financial information between different parties raises questions about data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information. It is crucial for financial institutions and third-party providers to implement robust security measures, encryption protocols, and data protection policies to safeguard customer data and maintain customer trust.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Open Banking operates under specific regulatory frameworks to ensure that data sharing is conducted in a safe and regulated manner. Financial institutions and third-party providers must adhere to these regulations, which include obtaining proper consent from customers, securely sharing data through authorized channels, and protecting customer rights. Compliance with these regulations can be complex and requires ongoing monitoring and adherence to evolving regulatory standards.
3. Customer Consent and Control
Open Banking relies on customer consent for the sharing of financial data. It is essential for customers to have a clear understanding of what data is being shared, with whom it is being shared, and how it will be used. Providing customers with transparent consent mechanisms, clear privacy policies, and easy-to-use data management tools is crucial to ensuring that customers maintain control over their data and feel empowered to make informed decisions about data sharing.
4. Interoperability and Standardization
For Open Banking to be effective, there needs to be interoperability and standardization across different financial institutions and third-party providers. Uniform standards and protocols for data exchange need to be implemented to enable seamless integration and compatibility between various systems. Promoting collaboration and establishing industry-wide standards are essential for the success and widespread adoption of Open Banking.
5. Consumer Awareness and Education
Open Banking is still a relatively new concept, and many customers may not fully understand its implications and benefits. There is a need for increased awareness and education about Open Banking to ensure that customers can make informed decisions about data sharing and fully leverage the advantages it offers. Financial institutions and regulators play a crucial role in educating customers about Open Banking, its benefits, and the steps taken to ensure the security and privacy of customer data.
6. Tech-Infrastructure and Scalability
Implementing Open Banking requires robust and scalable technological infrastructure. Financial institutions and third-party providers need to invest in advanced API systems, data analytics capabilities, and secure cloud-based platforms to handle the volume of data and requests effectively. Ensuring the reliability and scalability of these systems is essential for a seamless and efficient Open Banking ecosystem.
Addressing these challenges and concerns is crucial for the successful implementation and adoption of Open Banking. By prioritizing privacy and data security, maintaining regulatory compliance, empowering customers with control over their data, establishing interoperability and standardization, promoting customer awareness and education, and investing in robust technological infrastructure, Open Banking can truly unlock its potential and drive positive transformation in the financial industry.
Privacy and Data Security
One of the primary concerns surrounding Open Banking is privacy and data security. As financial information is shared between multiple parties, it is crucial to ensure the protection and safeguarding of customer data. Here are the key aspects related to privacy and data security in Open Banking:
1. Robust Encryption and Security Measures
Financial institutions and third-party providers must implement robust encryption and security measures to protect customer data during transit and storage. This includes industry-standard encryption protocols, secure socket layers (SSL), and multi-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized access.
2. Secure Data Sharing Protocols
Open Banking operates under strict protocols for sharing financial data. Financial institutions and third-party providers must comply with these protocols and use authorized interfaces to securely share the data. Implementing secure APIs and adhering to defined standards ensures the integrity and privacy of customer information.
3. Consent-Based Data Sharing
Customer consent is a fundamental aspect of Open Banking. Institutions must obtain explicit consent from customers before sharing their financial data. This consent should be clear, transparent, and specific, allowing customers to understand what data is being shared, with whom, and for what purposes. Customers should have the ability to revoke or modify their consent at any time.
4. Data Minimization and Purpose Limitation
Financial institutions and third-party providers should practice data minimization by only collecting and sharing necessary information for specific purposes. They should adhere to the principle of purpose limitation, where data is utilized strictly for the purpose for which it was consented. Unnecessary or excessive data collection should be avoided to reduce the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
5. Regular Data Audits and Risk Assessments
Financial institutions should conduct regular data audits and risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with relevant privacy and security standards. This includes reviewing access controls, monitoring data flows, and promptly addressing any identified risks or vulnerabilities. Ongoing assessments help mitigate potential threats and maintain the security of customer data.
6. Compliance with Data Protection Regulations
Open Banking operates within a regulatory framework to protect customer data. Financial institutions and third-party providers must comply with data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, to ensure transparency, accountability, and customer rights with regards to data processing. Compliance with these regulations helps maintain customer trust and confidence in Open Banking.
7. Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response
Financial institutions and third-party providers should establish robust monitoring systems to detect and respond to security incidents promptly. This includes logging and monitoring data access, conducting regular vulnerability assessments, and implementing incident response plans. Swift response to incidents helps mitigate potential data breaches and minimize the impact on customer data.
By implementing comprehensive privacy and data security measures, Open Banking can minimize the risks associated with data sharing and foster trust among customers. Prioritizing robust encryption, secure data sharing protocols, consent-based data practices, data audits and risk assessments, compliance with regulations, continuous monitoring, and incident response ensures that customer data remains protected in the Open Banking ecosystem.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is a critical aspect of Open Banking to ensure the protection of customer data, maintain transparency, and establish trust among all stakeholders. Here are the key considerations for regulatory compliance in Open Banking:
1. Data Protection Regulations
Open Banking must adhere to data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States. These regulations aim to protect the privacy and rights of individuals by articulating the legal requirements for the collection, processing, and transfer of personal data. Financial institutions and third-party providers operating under Open Banking need to adhere to these regulations to ensure transparency, accountability, and customer control over their data.
2. Consent Requirements
Regulatory compliance in Open Banking involves obtaining customer consent for the sharing of financial data. Consent should be explicit, informed, and freely given by customers, and it should be provided in a manner that is clear, concise, and easily understandable. Institutions must ensure that customers understand what data is being shared, with whom, and for what purposes. Consent should be obtained prior to any data sharing activities and customers should have the option to revoke or modify their consent at any time.
3. Standards and Interoperability
Regulatory bodies often define standards and protocols to establish a secure and interoperable Open Banking ecosystem. Compliance with these standards ensures that financial institutions and third-party providers can securely exchange data and provide services in a consistent and standardized manner. This promotes transparency, reliability, and seamless integration across various platforms and providers.
4. Security and Data Breach Notifications
Regulatory compliance in Open Banking entails maintaining the security of customer data and promptly notifying customers and relevant authorities in case of a data breach or security incident. Financial institutions and third-party providers must have robust security measures in place to protect customer data and establish protocols for timely incident response. Notification procedures should be defined and communicated to customers, ensuring transparency and appropriate follow-up actions in the event of a security breach.
5. Regulatory Reporting and Audits
Regulatory compliance requires financial institutions and third-party providers to provide regular reports and undergo audits to demonstrate adherence to regulatory requirements. This involves documenting and reporting data protection practices, consent management processes, and security protocols. Compliance audits conducted by regulatory bodies verify that the necessary safeguards are in place to protect customer data and ensure regulatory compliance.
6. Strong Governance and Compliance Programs
Organizations operating in the Open Banking landscape should establish strong governance frameworks and compliance programs to monitor and enforce adherence to regulatory requirements. This includes implementing policies and procedures, conducting regular risk assessments, providing training and awareness programs for employees, and designating compliance officers responsible for overseeing regulatory compliance.
Compliance with regulatory requirements is essential for maintaining trust, protecting customer data, and ensuring the successful implementation of Open Banking. Financial institutions and third-party providers must stay up-to-date with relevant regulations, establish robust compliance programs, and prioritize data protection to build a secure and compliant Open Banking ecosystem.
Conclusion
Open Banking has emerged as a transformative force in the financial industry, revolutionizing the way customers interact with their finances. By granting customers greater control over their financial data and enabling secure data sharing with authorized third-party providers, Open Banking has the potential to improve customer experiences, foster competition, and drive innovation.
The benefits of Open Banking are clear. Customers have access to a consolidated view of their finances, enhanced convenience, and personalized financial solutions. They can make better-informed financial decisions, track their spending, and receive tailored recommendations. Open Banking also encourages competition, as new players enter the market, offering innovative products and services. This competition results in increased efficiency, better customer experience, and more affordable financial solutions.
However, Open Banking is not without its challenges. Privacy and data security concerns require robust encryption, secure data sharing protocols, and strict compliance with data protection regulations. Customer consent and control over their data are critical to maintaining trust and ensuring transparency. Interoperability and standardization are necessary to enable seamless integration and collaboration between different financial institutions and third-party providers. Ongoing regulatory compliance and strong governance are vital to address privacy and security risks and to foster a secure and trustworthy Open Banking ecosystem.
As Open Banking continues to evolve, it is crucial for financial institutions, third-party providers, regulators, and customers to work together to address these challenges and maximize the benefits. Collaboration between traditional banks and fintech startups can lead to the development of innovative solutions that better serve customer needs. Increased awareness and education about Open Banking will empower customers to make informed decisions about data sharing and take advantage of the opportunities it offers.
In conclusion, Open Banking has the potential to transform the financial industry by placing customers at the center, driving competition, and fostering innovation. By prioritizing privacy, data security, customer control, regulatory compliance, and collaboration, Open Banking can deliver a more seamless, personalized, and customer-centric banking experience, benefiting customers and the financial industry as a whole.