
Finance
How Long Do Surety Bonds Last
Published: October 12, 2023
Find out the duration of surety bonds in finance. Understand how long these bonds last and ensure you are fully protected.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Surety Bonds
- Types of Surety Bonds
- How Surety Bonds Work
- Duration of Surety Bonds
- Factors Affecting the Duration of Surety Bonds
- Differences between Short-term and Long-term Surety Bonds
- Benefits of Long-term Surety Bonds
- Common Misconceptions about Surety Bond Durations
- Conclusion
Introduction
When it comes to financial transactions, businesses and individuals often need a way to guarantee their obligations and protect their interests. This is where surety bonds come into play. Surety bonds provide financial protection and assurance to parties involved in a contract or agreement. They serve as a binding contract between the principal (the party undertaking the obligation), the obligee (the party receiving the obligation), and the surety (the party providing the bond).
Surety bonds are commonly used in various industries, such as construction, real estate, finance, and government contracts. They are designed to ensure that the principal fulfills their contractual obligations, such as completing a construction project, paying subcontractors, or adhering to regulations. If the principal fails to meet their obligations, the surety bond provides financial compensation to the obligee.
Understanding the duration of surety bonds is crucial for both principals and obligees. While some bonds are short-term and last only for the duration of a specific project or contract, others can be long-term and offer coverage for an extended period. The duration of a surety bond depends on several factors, including the type of bond, the nature of the project, and the terms agreed upon by the parties involved.
In this article, we will explore the different types of surety bonds, how they work, and the factors that affect their duration. We will also discuss the differences between short-term and long-term surety bonds, as well as the benefits and misconceptions associated with each option.
Understanding Surety Bonds
Surety bonds are a type of contract designed to protect one party in a transaction by providing financial assurance. They serve as a guarantee that the principal will fulfill their obligations according to the terms agreed upon in the contract. If the principal fails to meet their obligations, the surety bond ensures that the obligee receives compensation for any resulting losses.
Unlike insurance, which protects against unforeseen events or accidents, surety bonds are proactive in nature. They are often required by law or industry regulations to ensure the completion of specific tasks or to safeguard the interests of the obligee.
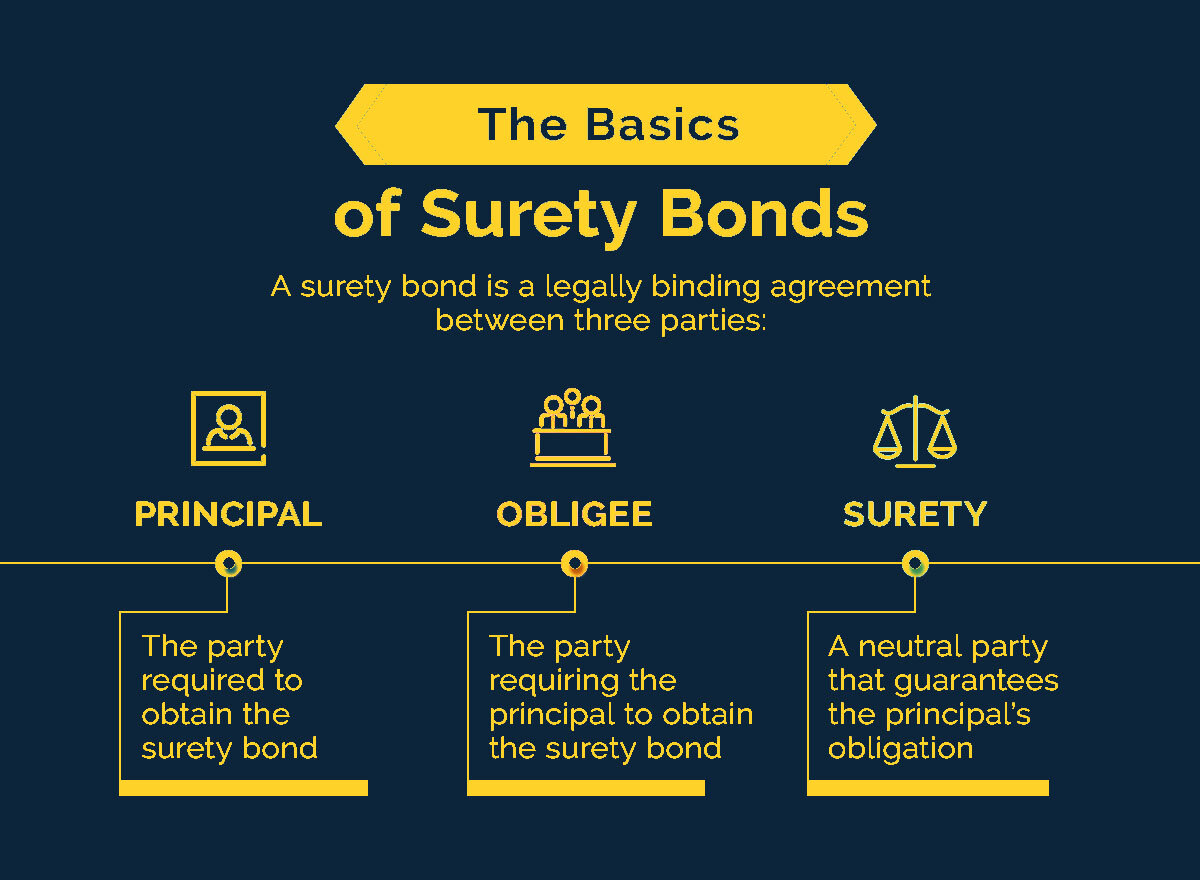
There are three main parties involved in a surety bond:
- Principal: The principal is the party that is required to fulfill the obligations outlined in the contract. It could be a contractor, developer, or any other entity undertaking a project or task.
- Obligee: The obligee is the party that is protected by the surety bond. They are typically the party receiving the work or services from the principal.
- Surety: The surety is the company or organization that provides the bond. They are responsible for ensuring that the principal meets their contractual obligations, and they provide financial compensation to the obligee if the principal fails to fulfill those obligations.
When a surety bond is issued, the surety company assesses the financial stability and reputation of the principal. This evaluation helps determine the bond’s premium, which is the fee paid by the principal to secure the bond. The premium amount is typically a percentage of the total bond value.
It’s important to note that surety bonds are not the same as insurance policies. While insurance protects against potential risks and reimburses for losses, surety bonds focus on ensuring that contractual obligations are fulfilled. If a claim is made on a surety bond, the surety company may initially provide financial compensation to the obligee, but they will then seek reimbursement from the principal.
Overall, surety bonds play a vital role in various industries by providing financial security and peace of mind to parties involved in contractual agreements. They serve as a guarantee that the principal will fulfill their obligations, protecting the interests of the obligee and ensuring the successful completion of projects or tasks.
Types of Surety Bonds
There are several types of surety bonds available to cater to different industry needs and contractual requirements. Here are some of the most common types:
- Contract Bonds: Contract bonds are commonly used in the construction industry. They ensure that the principal adheres to the terms and conditions specified in a construction contract, including project completion, payment to subcontractors, and adherence to safety regulations.
- License and Permit Bonds: License and permit bonds are required by government agencies to ensure that businesses comply with regulations and licensing requirements. Examples include contractor license bonds, motor vehicle dealer bonds, and mortgage broker bonds.
- Commercial Bonds: Commercial bonds encompass a wide range of bonds used in commercial transactions. These bonds cover areas such as guaranteeing performance, protecting against fraudulent activities, and ensuring fulfillment of financial obligations.
- Judicial Bonds: Judicial bonds are often required in legal proceedings to secure a party’s financial obligations. They can be used in cases such as appeal bonds, probate bonds, or injunction bonds.
- Public Official Bonds: Public officials, such as government employees, may be required to obtain public official bonds as a guarantee of their ethical conduct and faithful performance of their duties. These bonds help protect the public against any financial losses resulting from misconduct.
Each type of surety bond serves a specific purpose and is tailored to meet the unique requirements of different industries and contractual agreements. It’s crucial for parties involved in transactions to understand the specific type of bond needed and ensure compliance with all relevant regulations and obligations.
By providing financial assurance and accountability, surety bonds contribute to a more secure and trustworthy business environment. They cultivate trust between parties, protect against potential risks, and ensure that contractual obligations are fulfilled, promoting efficiency, and enabling successful business transactions.
How Surety Bonds Work
Surety bonds work as a three-party agreement to ensure the fulfillment of contractual obligations. Let’s take a closer look at how they work:
1. The Principal: The principal is the party that purchases the surety bond to provide assurance to the obligee. The principal is the party responsible for fulfilling the obligations stated in the contract, such as completing a project or paying subcontractors.
2. The Obligee: The obligee is the party that receives the benefit of the surety bond. They are typically the party who initiated the contract with the principal and seeks protection in case the principal fails to fulfill their obligations.
3. The Surety: The surety is the company or organization that underwrites the bond and guarantees the principal’s performance. The surety assesses the financial stability and reputation of the principal before issuing the bond. If the principal fails to fulfill their obligations, the surety steps in to provide financial compensation to the obligee.
When a surety bond is in place, the principal and the obligee enter into a contract that outlines the specific obligations, terms, and conditions. If the principal fails to meet the agreed-upon obligations, the obligee can file a claim against the surety bond to seek compensation for any resulting losses.
Once a claim is made, the surety investigates the claim to determine its validity. If the claim is found to be valid and the principal is indeed in breach of their obligations, the surety will provide financial compensation to the obligee, up to the amount specified in the bond. The surety then seeks reimbursement from the principal for the amount paid out.
It’s essential to note that surety bonds are not insurance policies. The surety’s role is to provide a guarantee or financial backing for the principal, ensuring the obligee’s protection. However, the principal remains ultimately responsible for fulfilling their contractual obligations.
By providing a layer of financial security, surety bonds foster trust between parties and contribute to the successful completion of projects or transactions. They provide peace of mind to obligees, assuring them that the principal will meet their commitments, and offer a recourse for compensation in case of non-compliance.
Duration of Surety Bonds
The duration of a surety bond refers to the period for which the bond remains in effect. It varies depending on the specific terms and requirements of the bond. While some bonds have a fixed duration and expire once the obligations are fulfilled, others may be renewable or have a longer-term duration.
In the case of short-term surety bonds, they are typically tied to specific projects or contracts that have a defined timeline. Once the project is completed, or the contractual obligations are fulfilled, the bond’s duration comes to an end. These bonds provide coverage for the duration of the project or until the completion of the agreed-upon obligations.
On the other hand, long-term surety bonds are designed for ongoing or continuous obligations. These bonds have a longer duration and may be renewable on an annual or multi-year basis. They are commonly used for licenses, permits, or regulations that require continuous coverage to ensure compliance over an extended period.
It’s important for parties involved to carefully review the terms and conditions of the surety bond to understand the specific duration and coverage provided. The duration can vary depending on factors such as the type of bond, industry requirements, and the nature of the obligations involved.
Additionally, the duration of a surety bond may also be influenced by external factors. For example, changes in the principal’s financial status, reputation, or business operations can impact the surety’s decision to continue providing coverage. In such cases, the surety may request additional information, reassess the risk, or make adjustments to the bond’s duration or terms.
Understanding the duration of a surety bond is crucial for effective planning and risk management. It allows parties to ensure continuous coverage, assess the need for renewals, and comply with any contractual or regulatory requirements. By having a clear understanding of the bond’s duration, parties can confidently proceed with their projects or transactions, knowing that they are protected by the surety bond for the specified period.
Factors Affecting the Duration of Surety Bonds
Several factors influence the duration of surety bonds. Understanding these factors is essential for both the principal and the obligee to effectively manage their contractual obligations and ensure that they have the necessary coverage in place. Here are some key factors that affect the duration of surety bonds:
- Project Length: The duration of a surety bond is often tied to the timeline of the project or contractual obligations. Short-term bonds are typically associated with specific projects that have a defined start and end date. Once the project is completed, the bond expires. Long-term bonds, on the other hand, are designed to provide coverage over an extended period, such as ongoing operational requirements or regulatory compliance.
- Industry Requirements: Certain industries, such as construction or government contracts, have specific regulations and requirements regarding the duration of surety bonds. These regulations aim to provide adequate protection for all parties involved in the transaction. It is crucial to be aware of any industry-specific regulations that may dictate the duration of the bond.
- Obligation Type: The type of obligation being secured by the surety bond can also impact its duration. Some obligations may require short-term coverage, while others may necessitate long-term or renewable bonds. For example, a license or permit bond may need to be in effect for the duration of the business’s operations, which could be long-term.
- Principal’s Financial Stability: The financial stability and reputation of the principal can affect the duration of the surety bond. The surety company assesses the principal’s financial strength when underwriting the bond. If the principal’s financial standing significantly changes during the bond’s duration, the surety may reassess the risk and potentially adjust the bond’s terms or duration accordingly.
- Contractual Agreement: The terms and conditions agreed upon in the contractual agreement between the principal and the obligee play a significant role in determining the duration of the surety bond. The agreement may specify the project or operational timeline, renewal options, and any other relevant provisions that impact the bond’s duration.
It is important for all parties involved to communicate and consider these factors when obtaining a surety bond. The principal should ensure that the bond’s duration aligns with the project’s timeline or ongoing obligations. The obligee should verify that the bond’s duration provides adequate coverage for the desired period.
By understanding the factors that affect the duration of surety bonds, both parties can make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and ensure that they have the appropriate coverage in place throughout the duration of their contractual obligations.
Differences between Short-term and Long-term Surety Bonds
Short-term and long-term surety bonds differ in their duration and purpose. Understanding the distinctions between these two types of bonds is crucial for businesses and individuals seeking to secure adequate financial protection for their contractual obligations. Here are key differences between short-term and long-term surety bonds:
- Duration: The primary difference between short-term and long-term surety bonds is the duration of coverage. Short-term surety bonds are designed to provide coverage for a specific project or contract with a defined timeline. Once the project or contract is completed, the bond expires. Long-term surety bonds, on the other hand, offer coverage for an extended period, often renewable on an annual or multi-year basis. They are better suited for ongoing obligations, such as licenses, permits, or regulatory compliance.
- Project Scope: Short-term surety bonds are typically associated with a specific project or task. They provide protection during the project’s duration and ensure that the principal fulfills their contractual obligations. In contrast, long-term surety bonds often cover broader obligations, such as ongoing business operations or compliance with industry regulations.
- Premium Costs: Short-term surety bonds generally have lower premiums compared to long-term bonds. Since short-term bonds provide coverage for a shorter duration, the risk exposure for the surety is typically lower. Long-term bonds, on the other hand, require higher premiums due to their extended coverage and potential risks over a more extended period.
- Renewal Options: Short-term surety bonds do not usually offer renewal options as they are tied to specific projects or contracts. Once the project is completed, the bond expires, and additional coverage is required for subsequent projects. In contrast, long-term surety bonds often have renewal options, allowing the parties to extend the coverage for another period, subject to underwriting review and approval.
- Flexibility: Short-term surety bonds offer flexibility by providing coverage for specific project needs. Once the project is finished, the bond no longer imposes any obligations on the principal or the obligee. Long-term bonds provide stability and continuity, ensuring coverage for ongoing obligations and reducing the need for repeated bond applications with each new project.
Choosing between short-term and long-term surety bonds depends on the nature of the project or contractual obligations. Short-term bonds are ideal for discrete projects with defined timelines, while long-term bonds suit ongoing obligations, compliance requirements, or licenses that extend beyond a single project.
It is essential to assess the specific needs and risks involved in order to determine which type of surety bond is more suitable. Consulting with a surety bond professional can help provide guidance and ensure that the chosen bond aligns with the duration and scope of the intended project or obligations.
Benefits of Long-term Surety Bonds
Long-term surety bonds offer several benefits for businesses and individuals who require continuous coverage for ongoing obligations. These bonds provide stability, reassurance, and convenience over an extended period. Here are some of the key benefits of long-term surety bonds:
- Continuous Coverage: One of the primary advantages of long-term surety bonds is the ability to maintain coverage without the need for frequent renewals. Instead of obtaining a new bond for each project or obligation, a long-term bond ensures that the principal has continuous protection throughout a specified time period, often renewable on an annual or multi-year basis.
- Streamlined Process: Long-term surety bonds eliminate the need for repetitive paperwork and application processes for each project. Once the initial bond is in place, subsequent renewals involve a more straightforward and streamlined process, easing the administrative burden for both the principal and the surety.
- Cost Savings: Long-term surety bonds often offer cost savings compared to obtaining multiple short-term bonds. The premiums for long-term bonds generally take into account the extended duration of coverage, resulting in potential cost benefits for the principal. Additionally, long-term bonds may lock in favorable rates, protecting against potential premium increases in the future.
- Built-in Flexibility: Long-term surety bonds can often be tailored to accommodate changes or modifications during the bond’s duration. This flexibility allows for adjustments to the covered obligations, project scope, or other terms as necessary, providing both the principal and the obligee with more adaptability and assurance for evolving circumstances.
- Enhanced Reputation: Having a long-term surety bond can enhance the reputation of the principal in the eyes of clients, stakeholders, or regulatory authorities. It showcases a commitment to stability, reliability, and compliance, giving confidence to potential partners or customers when entering into business relationships or transactions.
Long-term surety bonds are particularly advantageous for industries or businesses with ongoing or continuous obligations. They offer peace of mind, ensuring that the principal remains compliant with regulations, contract terms, or licensing requirements over an extended period. Additionally, the convenience and cost savings associated with long-term bonds can contribute to a more efficient workflow and improved financial planning for businesses.
It is essential for potential bondholders to assess their specific needs and consult with a surety bond professional to determine whether a long-term bond is the most suitable option for their situation. The professional can provide guidance based on industry knowledge and expertise, ensuring that the chosen bond aligns with the desired coverage duration and meets the necessary contractual requirements.
Common Misconceptions about Surety Bond Durations
There are several misconceptions surrounding surety bond durations that can lead to misunderstandings and confusion among those seeking to secure these bonds. It is crucial to dispel these misconceptions to ensure a clear understanding of how surety bond durations work. Here are some common misconceptions:
- All Surety Bonds Have the Same Duration: This is a common misconception. The duration of a surety bond varies depending on factors such as the type of bond, industry requirements, contractual obligations, and project length. Some bonds may have a short-term duration tied to a specific project, while others may be long-term with coverage lasting for an extended period.
- Surety Bonds Cannot Be Renewed: Another misconception is that surety bonds cannot be renewed. In reality, many bonds, especially long-term ones, offer renewal options. Once the bond term is completed, the parties can typically renew the bond for an additional period subject to the surety’s review and approval.
- Short-term Bonds Provide Inadequate Coverage: Some may assume that short-term bonds do not provide sufficient coverage due to their limited duration. However, short-term bonds are specifically designed to provide coverage for the duration of a specific project or contract, ensuring that the obligee is protected until the obligations are fulfilled.
- Long-term Bonds Are Always More Expensive: While long-term bonds may have higher upfront costs, they can actually result in cost savings in the long run. Long-term bonds eliminate the need for frequent renewals, which can reduce administrative costs and potentially lock in favorable premium rates.
- The Duration of a Bond Cannot Be Adjusted: This is not true. In certain cases, the duration of a surety bond can be adjusted or modified to accommodate changes in project timelines or contractual obligations. This flexibility allows the parties involved to make necessary adjustments to ensure adequate coverage throughout the bond’s duration.
It is important for businesses and individuals to have a clear understanding of surety bond durations to make informed decisions and avoid misunderstandings. Working with a reputable surety bond professional can help dispel these misconceptions and provide guidance on choosing the most appropriate bond duration for specific needs and obligations.
By debunking these misconceptions, parties involved can approach surety bonds with a more accurate understanding of how the duration of the bond aligns with their unique requirements, leading to smoother transactions and enhanced confidence in the surety bond process.
Conclusion
Surety bonds play a crucial role in ensuring the fulfillment of contractual obligations and providing financial protection for businesses and individuals. Understanding the duration of surety bonds is essential for effectively managing projects, complying with regulations, and safeguarding the interests of all parties involved.
Short-term surety bonds are designed for specific projects or contracts with a defined timeline, providing coverage until the obligations are fulfilled. On the other hand, long-term surety bonds offer continuous coverage for ongoing obligations, such as licenses, permits, or regulatory compliance, often renewable on an annual or multi-year basis.
Factors such as the project length, industry requirements, the nature of obligations, the principal’s financial stability, and the contractual agreement can all impact the duration of a surety bond. It is crucial to consider these factors to ensure the appropriate type and duration of bond is obtained.
Long-term surety bonds offer several benefits, including continuous coverage, streamlined processes, potential cost savings, flexibility, and enhanced reputation. They provide stability and convenience for businesses with ongoing obligations, reduce administrative burdens, and offer peace of mind to both principals and obligees.
Despite common misconceptions surrounding surety bond durations, it is important to understand that not all bonds have the same duration, renewals are possible, short-term bonds can provide adequate coverage, and adjustments to bond durations are sometimes feasible.
In conclusion, surety bond durations should be carefully considered to align with the specific needs, requirements, and timelines of projects or ongoing obligations. By understanding the different types of surety bonds available, the factors influencing their duration, and the benefits they offer, businesses and individuals can navigate the world of surety bonds with confidence and ensure successful and protected transactions.