Home>Finance>Why Do Defined Benefit Plans Pay Out Better Than Annuities


Finance
Why Do Defined Benefit Plans Pay Out Better Than Annuities
Modified: December 29, 2023
Learn why defined benefit plans can offer better payouts than annuities and gain insights into the world of finance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Defined Benefit Plans
- Understanding Annuities
- Key Differences Between Defined Benefit Plans and Annuities
- Factors Influencing Payout Amounts in Defined Benefit Plans
- Factors Influencing Payout Amounts in Annuities
- Advantages of Defined Benefit Plans over Annuities
- Advantages of Annuities over Defined Benefit Plans
- Comparison of Longevity Risk in Defined Benefit Plans and Annuities
- Conclusion
Introduction
When planning for retirement, individuals have several options to consider when it comes to securing a reliable income stream. Two popular choices are defined benefit plans and annuities. These financial tools provide retirees with regular payments to support their lifestyle after they stop working. While both defined benefit plans and annuities offer retirement income, there are distinct differences between the two.
Defined benefit plans, also known as pension plans, are retirement plans offered by employers. These plans guarantee a specified monthly income for retired employees based on a formula that typically considers factors like years of service and salary history. On the other hand, annuities are insurance products that individuals can purchase with their own funds, either through a lump sum payment or regular contributions.
Understanding the differences between defined benefit plans and annuities is crucial when making decisions about retirement income. In this article, we will delve into the key factors that influence payout amounts in both defined benefit plans and annuities, the advantages and disadvantages of each, and the risks associated with retirement income. By gaining a deeper understanding of these financial tools, individuals can make informed choices that align with their financial goals and retirement needs.
Understanding Defined Benefit Plans
A defined benefit plan, also known as a pension plan, is a retirement plan sponsored by an employer. It provides eligible employees with a guaranteed income during retirement. The payout amount in a defined benefit plan is determined by a specific formula that takes into account factors such as the employee’s salary history and years of service with the company.
In a defined benefit plan, the responsibility for funding the plan lies with the employer. Employers contribute a certain percentage of the employee’s salary to a pension fund, which is then invested. These investments aim to generate returns that help finance the promised retirement benefits.
One of the key advantages of a defined benefit plan is the security it offers. Retirees can rely on a predictable and stable income stream throughout their retirement years. The amount received is typically based on a percentage of the employee’s final average salary or career average salary.
Defined benefit plans are subject to various regulations and guidelines established by the government. These rules ensure that employers fulfill their obligations to provide retirement benefits and protect the interests of plan participants. As a result, employees can feel confident knowing their retirement income is safeguarded.
Employees typically become eligible for a defined benefit plan after a certain number of years with the company, often referred to as a vesting period. Once vested, employees are entitled to receive a pension based on the terms of the plan. Some plans may also offer early retirement options, allowing individuals to start receiving benefits before reaching the standard retirement age.
Understanding Annuities
An annuity is a financial product that individuals can purchase either with a lump sum payment or through regular contributions. It is typically offered by insurance companies and provides a steady income stream during retirement. Annuities offer individuals the opportunity to accumulate funds over time and then receive regular payments in the form of an annuitized income.
There are different types of annuities available, including fixed annuities, variable annuities, and indexed annuities. Fixed annuities provide a guaranteed rate of return, and the payout amount is predetermined at the time of purchase. Variable annuities, on the other hand, allow individuals to invest in a range of investment options, and the payout amount fluctuates based on the performance of the underlying investments. Indexed annuities combine features of both fixed and variable annuities, with the payout amount tied to the performance of a specific index, such as the stock market.
Annuities function as a way to transfer risk from the individual to the insurance company. By purchasing an annuity, individuals can protect themselves against the risk of running out of money during retirement. Annuities also provide a level of certainty, as individuals can choose the length of the payout period and the frequency of payments, such as monthly or annual.
One of the key advantages of annuities is the tax-deferred growth they offer. This means that any earnings in the annuity are not subject to taxes until withdrawn. It allows the funds to grow faster, potentially providing a larger income stream during retirement.
It’s important to note that annuities come with fees and expenses, including administrative fees, mortality and expense charges, and investment management fees for variable annuities. These costs can vary depending on the type of annuity and the insurance company, so it’s essential to carefully review the terms and conditions before purchasing an annuity.
Key Differences Between Defined Benefit Plans and Annuities
While both defined benefit plans and annuities provide retirement income, there are several key differences between the two. Understanding these distinctions can help individuals determine which option is most suitable for their financial needs and retirement goals.
- Source of Income: Defined benefit plans are sponsored by employers and funded by contributions made by the employer. Annuities, on the other hand, are purchased by individuals with their own funds or through regular contributions.
- Risk: In a defined benefit plan, the employer bears the investment risk. They are responsible for ensuring that the plan is adequately funded to meet the promised retirement benefits. With annuities, the risk lies with the individual, as the performance of the underlying investments can affect the payout amount.
- Payout Structure: Defined benefit plans typically provide a monthly income, often based on a percentage of the employee’s final or average salary. Annuities can offer various payout options, including a fixed payment amount, variable payments based on investment performance, or a combination of both.
- Flexibility: Defined benefit plans generally have less flexibility in terms of accessing funds. The retirement income is paid out according to the predetermined schedule. Annuities, on the other hand, may offer more flexibility, allowing individuals to access funds earlier or adjust the payment terms.
- Ownership: Defined benefit plans are owned and managed by the employer. Annuities, on the other hand, are owned by the individual. This provides individuals with more control over their retirement income and the ability to transfer or make changes to the annuity contract if needed.
It’s important to note that both defined benefit plans and annuities have their own advantages and disadvantages. Individuals should carefully consider their financial situation, risk tolerance, and retirement goals when choosing between these two options. Seeking professional advice from a financial advisor can also provide valuable insights and help individuals make informed decisions.
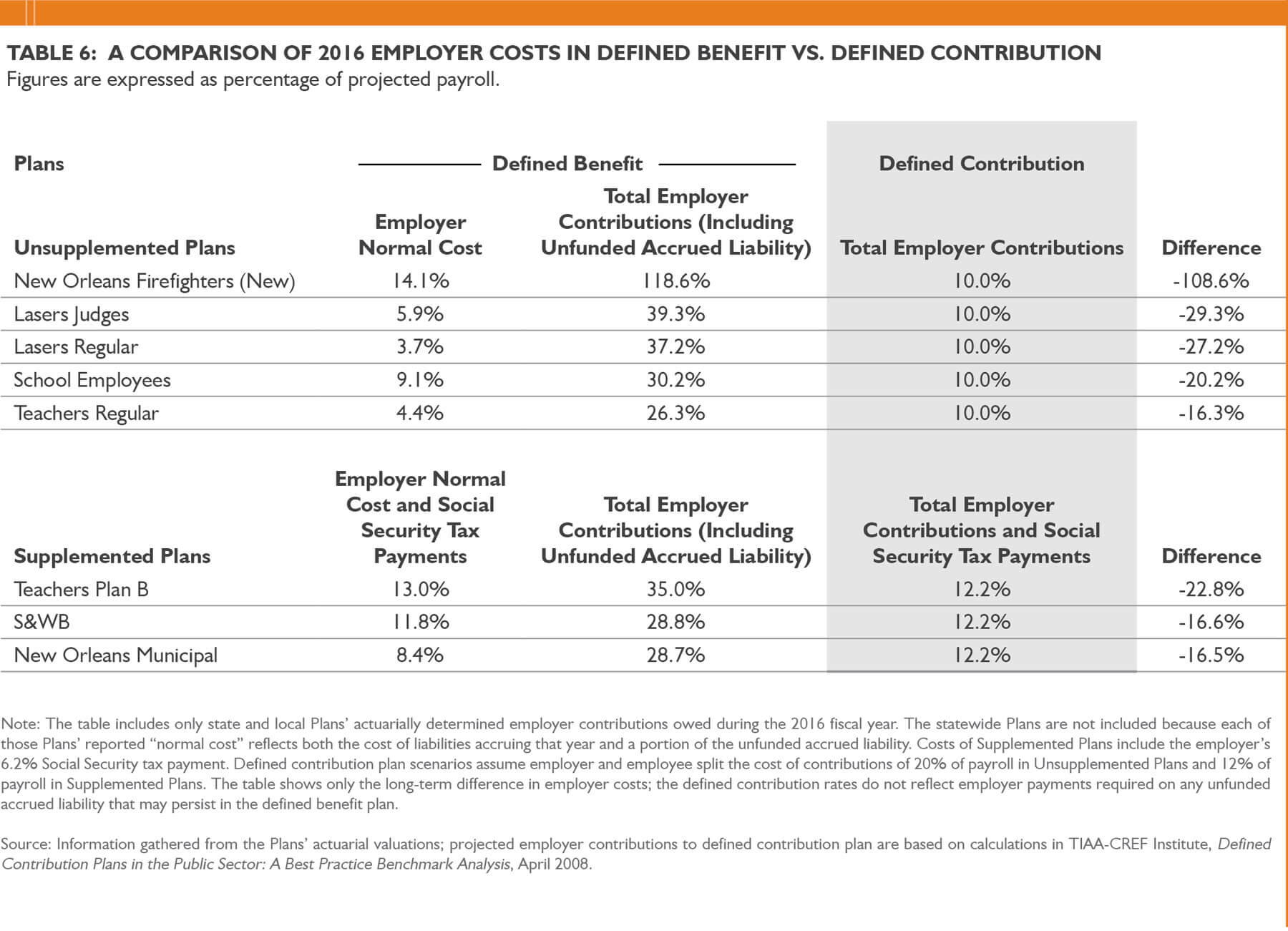
Factors Influencing Payout Amounts in Defined Benefit Plans
The payout amount in a defined benefit plan is determined by various factors, including:
- Salary: One of the primary factors that influence the payout amount in a defined benefit plan is the employee’s salary history. Typically, the higher the salary, the higher the retirement income will be.
- Years of Service: The number of years an employee has worked for the company also plays a crucial role in determining the payout amount. Defined benefit plans often use a formula that calculates the benefit based on a percentage of the employee’s average salary over the highest earning years of their career.
- Vesting Schedule: Defined benefit plans have a vesting schedule, which determines when employees become eligible to receive the full benefit. Vesting schedules vary by plan, but typically employees need to work for a certain number of years before they are fully vested and entitled to the maximum benefit.
- Retirement Age: The age at which an individual chooses to retire can impact the payout amount in a defined benefit plan. Some plans may allow early retirement options, but the benefit may be reduced if the employee retires before reaching the standard retirement age.
- Cost-of-Living Adjustments: Some defined benefit plans offer cost-of-living adjustments (COLAs) to account for inflation. These adjustments ensure that the retirement income keeps pace with the rising cost of living.
It’s important to note that each defined benefit plan may have its own specific formula for calculating the payout amount. While the factors mentioned above are commonly used, the exact method can vary depending on the plan’s provisions.
Additionally, it’s worth mentioning that the financial health of the employer and the performance of the plan’s investment portfolio can also impact the payout amount. If the plan’s investments generate higher returns, it may result in higher benefits for the participants. Conversely, poor investment performance or financial difficulties faced by the employer may affect the sustainability of the plan and its ability to meet the promised benefits.
Before making decisions about retirement income, individuals should carefully review the provisions of their defined benefit plan and seek guidance from a financial advisor to fully understand how the payout amount is calculated and how it aligns with their retirement goals.
Factors Influencing Payout Amounts in Annuities
The payout amount in annuities is influenced by several factors, which can vary depending on the type of annuity. Here are some key factors that can affect the payout amount:
- Initial Investment: The amount of money an individual initially invests in an annuity can impact the payout amount. Generally, a larger initial investment will lead to higher income payments. However, it’s important to note that other factors such as the annuity’s terms, fees, and potential returns also play a role.
- Life Expectancy: Annuities use actuarial calculations to estimate life expectancy. The longer an individual is expected to live, the lower the payout amount per period will be to ensure that the funds last throughout their lifetime. Conversely, if an individual has a shorter life expectancy, the payout amount may be higher.
- Type of Annuity: Different types of annuities have varying payout structures. Fixed annuities provide a guaranteed payout amount, while variable annuities and indexed annuities are tied to investment performance. Variable annuities can offer higher potential returns but also carry more risk and can lead to fluctuations in the payout amount.
- Age at the Start of Annuity Payments: The age at which an individual starts receiving annuity payments can affect the payout amount. Generally, starting payments at a younger age will result in lower payout amounts because the annuity is expected to be paid out over a longer period of time.
- Payout Options: Annuities offer various payout options, such as a fixed period or for the duration of the individual’s lifetime. Choosing a shorter payout period or a joint and survivor option (which continues to provide income to a spouse or beneficiary after the individual’s death) can result in higher payout amounts, but it may reduce the overall duration of income payments.
- Interest Rates: Interest rates at the time of annuity purchase can impact the payout amount. Higher interest rates generally result in higher annuity payments, while lower interest rates may lead to lower payouts.
It’s important for individuals to consider these factors when selecting an annuity. The specific terms and conditions of the annuity contract, including fees and expenses, should also be carefully reviewed in order to make an informed decision.
Seeking advice from a financial professional can be valuable when navigating the annuity market and understanding how different factors can influence the payout amount. They can help individuals determine the most suitable annuity type and payout options based on their financial goals and retirement needs.
Advantages of Defined Benefit Plans over Annuities
Defined benefit plans offer several advantages over annuities. These advantages can make them an attractive option for individuals planning for retirement. Here are some key advantages of defined benefit plans:
- Guaranteed Income: One of the significant advantages of defined benefit plans is the guaranteed income they provide. Retirees can rely on a predictable and stable income stream throughout their retirement years. Unlike annuities, which are subject to investment performance and market fluctuations, defined benefit plans offer a fixed monthly payment amount, providing financial security and peace of mind.
- Employer Contributions: Defined benefit plans are funded by employer contributions. This means that individuals do not have to worry about making their own contributions or managing investment decisions. Employers are responsible for ensuring that the plan is adequately funded to cover the promised retirement benefits.
- Professional Management: Defined benefit plans are typically managed by professional investment managers appointed by the employer. These experts have the knowledge and expertise to make investment decisions on behalf of the plan participants. This can relieve individuals of the burden of managing their own investments and potentially lead to better returns and a higher retirement income.
- Potential for Higher Payout: In some cases, defined benefit plans may offer higher payout amounts compared to annuities. The payout in a defined benefit plan is based on factors such as salary history and years of service, which can result in a higher income during retirement. However, it’s important to note that this may vary depending on the specific plan and individual circumstances.
- Protection Against Longevity Risk: Defined benefit plans offer protection against longevity risk, which is the risk of outliving one’s retirement savings. Since the plan provides a guaranteed income for life, individuals do not have to worry about running out of money in their later years. Annuities also address longevity risk, but defined benefit plans may provide additional peace of mind due to their strong guarantees.
It’s worth noting that the advantages of defined benefit plans may vary depending on individual circumstances and the specific terms of the plan. Individuals should carefully review the plan’s provisions and seek professional advice to determine if a defined benefit plan aligns with their retirement goals and financial needs.
Advantages of Annuities over Defined Benefit Plans
Annuities offer several advantages over defined benefit plans, making them a viable option for individuals planning for retirement. Here are some key advantages of annuities:
- Flexibility: Annuities provide individuals with greater flexibility when it comes to accessing their funds and determining the payout terms. They can choose between different types of annuities, such as fixed, variable, or indexed, based on their risk tolerance and financial goals. Annuities also offer options for lump sum withdrawals, periodic payments, or even a combination of both.
- Ownership and Portability: Annuities are individually owned, allowing individuals to have more control over their retirement savings. Unlike defined benefit plans, which are tied to an employer, annuities can generally be carried from one job to another or transferred if an individual changes employers. This flexibility enables individuals to maintain and build upon their retirement funds, regardless of their employment status.
- Tax Advantages: Annuities offer tax-deferred growth, meaning that any earnings within the annuity are not taxed until withdrawn. This allows the funds to potentially grow faster over time. Additionally, annuities can provide tax-free transfers between different investment options within the annuity contract, allowing for greater control and potential tax efficiency.
- Inheritance Planning: Annuities can be advantageous in terms of inheritance planning. Depending on the annuity contract, individuals may have the ability to name beneficiaries who can receive the remaining value of the annuity upon their death. This feature ensures that any remaining funds can be passed on to loved ones, providing a potential financial legacy.
- Investment Options: Variable annuities offer individuals the opportunity to invest their annuity funds in a range of investment options, such as stocks, bonds, or mutual funds. This can allow for potential growth and higher returns depending on market performance. While investment options involve risk, individuals have the potential to generate greater wealth with a well-diversified portfolio.
It’s important to note that the advantages of annuities over defined benefit plans may vary depending on individual circumstances and financial goals. It is crucial for individuals to carefully review the terms and conditions of the annuity, including fees, surrender charges, and payout options, to ensure they align with their retirement needs.
Seeking guidance from a financial advisor can help individuals navigate the annuity market, understand the advantages they offer, and make informed decisions based on their unique financial situation and retirement objectives.
Comparison of Longevity Risk in Defined Benefit Plans and Annuities
Longevity risk refers to the risk of outliving one’s retirement savings. Both defined benefit plans and annuities address this risk, but in different ways.
In defined benefit plans, the employer assumes the longevity risk. Retirees are guaranteed a specific monthly income for life, regardless of how long they live. This provides a level of security, as individuals do not have to worry about their savings running out. The responsibility for managing the investment risk and ensuring the sustainability of the plan falls on the employer. This means that retirees can receive regular income payments until their passing, without the concern of exhausting their retirement savings.
Annuities, on the other hand, transfer the longevity risk from the individual to the insurance company. The insurance company is responsible for providing a lifetime income stream to the annuitant, even if they live longer than expected. This allows individuals to ensure that they will receive a steady income throughout their life, regardless of market conditions or their longevity. Annuities offer protection against the risk of running out of money in old age, as the payments are guaranteed as long as the annuitant is alive.
While both defined benefit plans and annuities address longevity risk, there are some differences to consider:
- Source of Risk: In defined benefit plans, the employer assumes the risk and is responsible for funding the plan to meet retirees’ ongoing payments. In annuities, the insurance company assumes the risk and manages investments to sustain the payments over the annuitant’s lifetime.
- Potential Adjustments: Some defined benefit plans offer cost-of-living adjustments (COLAs) to protect against inflation and maintain the purchasing power of the retirees. Annuities may offer inflation-protected options as well, but they generally involve additional costs.
- Flexibility: Annuities may offer more flexibility in terms of tailoring the payout options to accommodate individual needs and preferences. This can include options like joint and survivor annuities, which provide income for a spouse or beneficiary after the annuitant’s death. Defined benefit plans often provide less flexibility in terms of structuring income payments.
- Investment Performance: The performance of the investments underlying an annuity can impact the insurance company’s ability to meet its payment obligations. Defined benefit plans are typically managed by professional investment managers, aiming to ensure the plan’s sustainability and protect against investment risks.
It’s important to carefully evaluate the terms and conditions of both defined benefit plans and annuities, considering factors like inflation, payout options, and investment performance, to make an informed decision regarding the best approach to address longevity risk based on individual financial circumstances and retirement goals.
Conclusion
When planning for retirement, individuals have various options to consider for securing a reliable income stream. Defined benefit plans and annuities are two popular choices, each offering their own advantages and considerations.
Defined benefit plans, also known as pension plans, provide retirees with a guaranteed income for life. They offer financial security and stability, as the responsibility for managing investments and ensuring sustainable payouts lies with the employer. Defined benefit plans are a suitable choice for individuals looking for a predictable income and who prefer to delegate investment decisions to professionals.
Annuities, on the other hand, offer individuals more flexibility and control over their retirement savings. They provide options for tailoring payout terms and offer tax advantages, allowing for potentially higher returns. Annuities transfer the longevity risk from the individual to the insurance company, ensuring a steady income stream throughout retirement.
When comparing the two, it’s important to consider key factors such as guaranteed income, employer contributions, investment options, tax advantages, and flexibility. The choice between defined benefit plans and annuities depends on individual preferences, risk tolerance, and financial circumstances.
Seeking guidance from a financial advisor can provide valuable insights and help individuals make informed decisions based on their unique needs and goals. They can assess individual financial situations, evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of each option, and recommend the most suitable approach for securing a comfortable retirement.
Ultimately, the decision between defined benefit plans and annuities should be based on careful consideration of one’s financial situation, risk tolerance, and retirement objectives. By understanding the differences and weighing the advantages and disadvantages of each option, individuals can choose the path that aligns with their long-term financial needs and provides them with peace of mind in retirement.