Home>Finance>How Do I Calculate The Interest Amount On Merchant Fees Paid?

Finance
How Do I Calculate The Interest Amount On Merchant Fees Paid?
Published: February 24, 2024
Learn how to calculate interest on merchant fees paid and manage your finances effectively. Explore finance tips and tools to optimize your business expenses.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Entering into the realm of finance often involves navigating through a myriad of terms, calculations, and fees. Among these, merchant fees stand as a crucial component for businesses that accept credit card payments. Understanding the intricacies of these fees and the associated interest calculations is essential for maintaining financial stability and making informed decisions.
Merchant fees, also known as credit card processing fees, are charges incurred by businesses for processing credit and debit card transactions. These fees typically encompass interchange fees, assessment fees, and payment processor charges, and they can significantly impact a company's bottom line. To comprehend the true cost of these fees, it is vital to calculate the interest amount paid on merchant fees, as this sheds light on the long-term financial implications.
In this article, we will delve into the world of merchant fees, exploring their significance and the methods for calculating the interest amount paid on these fees. By providing a comprehensive understanding of this process, we aim to equip businesses and individuals with the knowledge necessary to make informed financial decisions and optimize their financial management strategies.
Understanding Merchant Fees
Merchant fees encompass a range of charges incurred by businesses for processing credit and debit card transactions. These fees are typically composed of several components, including interchange fees, assessment fees, and payment processor charges. Understanding each of these elements is crucial for comprehending the overall cost and impact of merchant fees on a business’s finances.
Interchange Fees: These fees are paid by the merchant’s bank to the card-issuing bank for each transaction. They are set by the card networks, such as Visa and Mastercard, and are influenced by various factors, including the type of card used, the transaction method, and the merchant’s industry. Interchange fees are a significant portion of the overall merchant fees and can vary widely.
Assessment Fees: These fees are collected by the card networks and are separate from interchange fees. They are charged for the privilege of accepting a particular brand of credit card and are typically non-negotiable. Assessment fees contribute to the overall cost of processing card transactions and are an essential component of merchant fees.
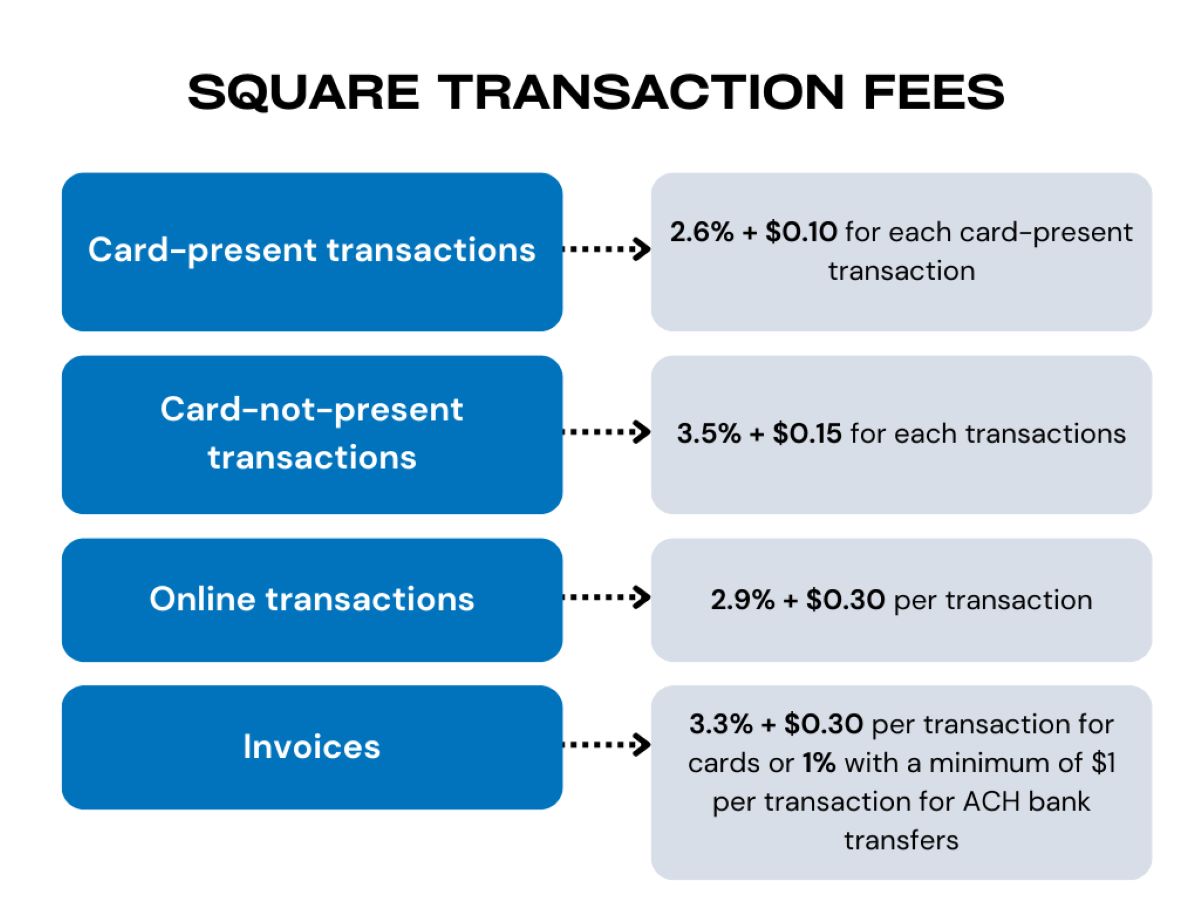
Payment Processor Charges: Payment processors, such as Square, PayPal, or traditional merchant account providers, charge fees for their services, including transaction processing, equipment rental, and additional features. These charges are often tailored to the specific needs of the business and can vary based on the provider and the services utilized.
It is important to note that the structure of merchant fees can vary widely based on the payment processing methods employed by a business. Whether using a traditional merchant account, a third-party payment processor, or a mobile payment solution, the fee structure and associated costs will differ, impacting the overall financial implications for the business.
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the components that constitute merchant fees, businesses can effectively assess the true cost of processing card transactions and make informed decisions regarding their payment processing strategies and financial management.
Calculating Interest on Merchant Fees
Calculating the interest amount on merchant fees is a fundamental aspect of understanding the financial impact of these fees over time. This process involves assessing the total amount of merchant fees paid and utilizing the applicable interest rate to determine the additional cost incurred over a specific period. By gaining insights into the interest amount on merchant fees, businesses can make informed decisions regarding their payment processing strategies and mitigate potential financial burdens.
To begin the calculation, businesses should gather comprehensive data on the total merchant fees paid over a specific timeframe, typically monthly or annually. This encompasses all components of the merchant fees, including interchange fees, assessment fees, and payment processor charges, providing a holistic view of the financial outlay attributed to processing card transactions.
Once the total merchant fees are determined, the next step involves applying the relevant interest rate to ascertain the additional cost incurred. The interest rate can vary based on the financial agreements in place, such as the terms of the merchant account or the agreements with payment processors. By multiplying the total merchant fees by the interest rate and the time period, businesses can calculate the interest amount paid on these fees, gaining clarity on the long-term financial implications.
It is essential to consider the compounding effect of interest, especially for businesses with prolonged payment terms or outstanding balances. By factoring in the compounding nature of interest, businesses can gain a comprehensive understanding of the cumulative impact of merchant fees on their financial position, enabling them to proactively manage their financial resources and optimize their payment processing strategies.
Furthermore, businesses can leverage this insight to assess the feasibility of alternative payment processing methods, negotiate favorable terms with payment processors, or explore cost-saving measures to mitigate the impact of merchant fees and associated interest costs. By integrating the calculation of interest on merchant fees into their financial management practices, businesses can enhance their financial resilience and make informed decisions to support their long-term growth and stability.
Example of Interest Calculation
Consider a retail business that processes credit card transactions and incurs monthly merchant fees totaling $1,500. To calculate the interest amount on these merchant fees, the business must first determine the applicable interest rate, which, for this example, is set at 12% annually.
Using the formula for simple interest, the business can calculate the additional cost incurred over a specific period. In this instance, the interest amount on the monthly merchant fees can be determined as follows:
Interest Amount = Principal Amount x Interest Rate x Time
Substituting the values, the calculation would be:
Interest Amount = $1,500 x 12% x (1/12) = $150
Therefore, the business would incur an additional $150 in interest on the monthly merchant fees, contributing to the overall cost of processing credit card transactions. This example illustrates the tangible impact of interest on merchant fees and emphasizes the financial significance of understanding and managing these costs effectively.
Furthermore, by considering the compounding nature of interest, the business can gain insights into the cumulative impact of these fees over time. For instance, if the merchant fees remain consistent over the course of a year, the compounded interest would result in a higher overall cost, underscoring the long-term financial implications of these fees.
By leveraging this example as a reference point, businesses can gain a practical understanding of interest calculations on merchant fees and utilize this knowledge to inform their financial management strategies. This empowers businesses to make informed decisions regarding their payment processing methods, negotiate favorable terms with payment processors, and explore avenues to mitigate the financial impact of merchant fees and associated interest costs.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of merchant fees and the associated interest calculations is paramount for businesses seeking to optimize their financial management strategies and mitigate potential financial burdens. By delving into the components that constitute merchant fees, including interchange fees, assessment fees, and payment processor charges, businesses can gain a comprehensive understanding of the true cost of processing credit card transactions. This knowledge empowers them to make informed decisions regarding their payment processing strategies and financial management.
Calculating the interest amount on merchant fees provides businesses with valuable insights into the additional costs incurred over time. By assessing the total merchant fees paid and applying the relevant interest rate, businesses can gain clarity on the long-term financial implications of these fees. Factoring in the compounding nature of interest further enhances this understanding, enabling businesses to proactively manage their financial resources and optimize their payment processing strategies.
Through a practical example of interest calculation on monthly merchant fees, businesses can visualize the tangible impact of interest and comprehend the cumulative effect of these fees over time. Armed with this knowledge, businesses can make informed decisions to support their long-term growth and stability, such as exploring cost-saving measures, negotiating favorable terms with payment processors, or assessing the feasibility of alternative payment processing methods.
Ultimately, the ability to calculate and comprehend the interest amount on merchant fees empowers businesses to navigate the complex landscape of payment processing, mitigate financial risks, and optimize their financial resilience. By integrating this understanding into their financial management practices, businesses can proactively steer their financial trajectory and make informed decisions that align with their long-term objectives.