Finance
How Do I Calculate Merchant Fees Paid?
Published: February 24, 2024
Learn how to calculate merchant fees paid and manage your finances effectively. Understand the impact of transaction costs on your business.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of merchant fees, where the intricate dance of financial transactions meets the digital realm. As a business owner or financial enthusiast, understanding the ins and outs of merchant fees is crucial for navigating the landscape of payment processing. In this article, we will delve into the realm of merchant fees, exploring their significance, the factors influencing them, and the methods for calculating these fees. By the end of this journey, you will be equipped with the knowledge to make informed decisions and optimize your financial strategies.
Merchant fees play a pivotal role in the realm of commerce, affecting businesses of all sizes and industries. Whether you operate a brick-and-mortar store, an e-commerce platform, or a service-based business, the impact of merchant fees reverberates through every transaction. Understanding how these fees are determined and calculated empowers you to manage your finances effectively and maximize your profitability.
Join us as we unravel the complexities of merchant fees, shedding light on the factors that influence them and providing practical insights into the calculation process. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of merchant fees, you can harness this knowledge to optimize your financial operations and drive the success of your business.
Understanding Merchant Fees
Merchant fees, also known as credit card processing fees, are the costs associated with accepting electronic payments from customers. When a customer makes a purchase using a credit or debit card, the merchant (business owner) incurs fees for processing that transaction. These fees are typically expressed as a percentage of the transaction amount, along with a flat fee for each transaction.
It’s essential to recognize that merchant fees are not uniform and can vary based on a multitude of factors, including the type of card used (credit, debit, rewards card, etc.), the processing method (in-person, online, mobile), and the overall sales volume of the business. Additionally, the payment processing industry is dynamic, with fees subject to change due to market conditions and regulatory factors.
Merchant fees are a fundamental component of the payment ecosystem, enabling businesses to offer convenient payment options to their customers. However, it’s crucial for merchants to grasp the nuances of these fees to effectively manage their cost structures and optimize their profitability. By comprehending the intricacies of merchant fees, businesses can make informed decisions regarding their payment processing strategies and pricing models.
As we delve deeper into the realm of merchant fees, we will explore the various factors that influence the determination of these fees, shedding light on the dynamic nature of payment processing and the strategies for mitigating the impact of merchant fees on businesses.
Factors Affecting Merchant Fees
Merchant fees are influenced by a myriad of factors that collectively determine the cost of processing electronic payments. Understanding these factors is essential for merchants seeking to optimize their payment processing strategies and manage their expenses effectively.
- Card Type: The type of card used in a transaction significantly impacts the merchant fees. Credit cards, especially those offering rewards or cashback, often incur higher processing fees compared to debit cards. Premium cards with enhanced benefits may also result in elevated fees for merchants.
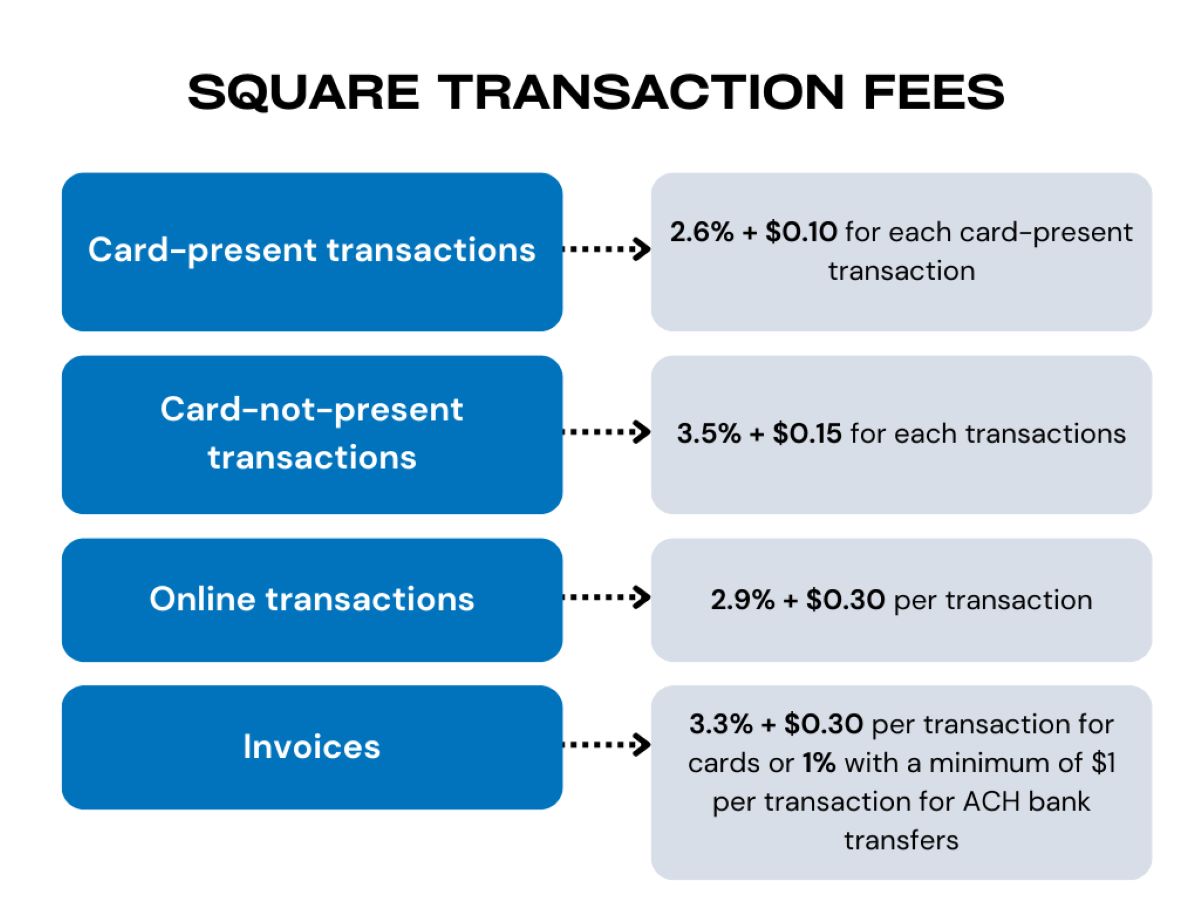
- Transaction Method: The method through which a transaction is processed, whether it’s in-person, online, or via mobile devices, can influence the associated fees. Card-present transactions, where the physical card is swiped or inserted, typically carry lower fees compared to card-not-present transactions, which are prevalent in e-commerce and remote sales.
- Sales Volume: The volume of transactions processed by a business can impact the merchant fees. Higher sales volumes may provide leverage for negotiating lower fees with payment processors, while lower volumes could result in comparatively higher per-transaction costs.
- Industry Risk: Certain industries, such as travel and subscription services, are deemed higher risk due to factors like chargeback potential and delayed fulfillment. As a result, merchants operating in these sectors may face elevated processing fees to mitigate the associated risks.
- Payment Processor: The choice of payment processor or merchant service provider can significantly influence the fees incurred by a business. Different providers offer varying fee structures, pricing models, and additional services, impacting the overall cost of payment processing.
- Regulatory Environment: Regulatory changes and compliance requirements within the payment industry can impact merchant fees. Shifts in regulations, such as interchange fee adjustments, can directly influence the cost of processing transactions for merchants.
By comprehending the multifaceted nature of these influencing factors, merchants can strategically navigate the landscape of payment processing, optimize their fee structures, and enhance their financial performance.
Calculating Merchant Fees
Calculating merchant fees involves a nuanced process that encompasses various components, including the percentage-based fee, flat transaction fees, and potential additional charges. By understanding the calculation methodology, merchants can gain clarity on the costs associated with processing electronic payments and make informed decisions regarding their pricing strategies and operational expenses.
The primary elements involved in calculating merchant fees are:
- Percentage-Based Fee: Payment processors typically charge a percentage of the transaction amount as a processing fee. This percentage, often referred to as the discount rate, varies based on the factors discussed earlier, such as card type and transaction method. For instance, a processor may charge 2.5% of the transaction amount for credit card sales.
- Flat Transaction Fee: In addition to the percentage-based fee, merchants may incur a flat fee for each transaction processed. This fee, often denoted as a per-transaction or authorization fee, is a fixed amount charged for facilitating the payment, regardless of the transaction size.
- Additional Charges: Payment processors may levy additional charges for specific services or circumstances, such as chargeback fees, statement fees, and non-compliance penalties. These supplementary charges contribute to the overall cost of payment processing for merchants.
To calculate the total merchant fee for a specific transaction, one can employ the following formula:
Total Merchant Fee = (Transaction Amount x Percentage-Based Fee) + Flat Transaction Fee + Additional Charges
By applying this formula, merchants can ascertain the comprehensive cost of processing a transaction, enabling them to evaluate the impact of merchant fees on their revenue and make informed decisions regarding pricing, profitability, and the selection of payment processing partners.
Furthermore, leveraging technology and payment management solutions can facilitate the streamlined calculation and management of merchant fees, empowering businesses to optimize their financial operations and enhance their competitiveness in the market.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the realm of merchant fees encompasses a dynamic landscape of costs and considerations that significantly impact businesses engaged in electronic payment processing. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of merchant fees, merchants can navigate this terrain with clarity and strategic acumen, optimizing their financial operations and bolstering their profitability.
Understanding the multifaceted factors that influence merchant fees empowers businesses to make informed decisions regarding their payment processing strategies, pricing models, and choice of payment partners. From the type of card used in transactions to the regulatory environment and the intricacies of payment processor fee structures, each element plays a pivotal role in shaping the cost of processing electronic payments.
Furthermore, the calculation of merchant fees involves a nuanced process, encompassing percentage-based fees, flat transaction fees, and additional charges. By leveraging a comprehensive understanding of the calculation methodology, merchants can gain clarity on the costs associated with payment processing, enabling them to optimize their fee structures and enhance their financial performance.
As businesses continue to embrace digital payments and e-commerce, the significance of comprehending and effectively managing merchant fees becomes increasingly pronounced. By proactively engaging with the intricacies of merchant fees, businesses can position themselves for financial resilience and competitive advantage in the evolving landscape of commerce.
In essence, the journey of understanding and calculating merchant fees is a strategic imperative for businesses seeking to thrive in the digital economy. By harnessing this knowledge, businesses can unlock opportunities for operational efficiency, cost optimization, and sustainable growth, ultimately shaping a future where financial acumen and strategic foresight converge to drive success.