Home>Finance>Common Size Financial Statement: Definition And Example


Finance
Common Size Financial Statement: Definition And Example
Published: October 30, 2023
Learn about common size financial statements and gain a clear understanding of their definition and practical application. Explore finance through this detailed example.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Understanding Common Size Financial Statements for Better Financial Analysis
Finance is a critical aspect of businesses, and understanding financial statements helps in making informed decisions. One such powerful tool in financial analysis is a common size financial statement. In this article, we will dive deep into the definition and example of a common size financial statement to shed light on its importance in assessing a company’s performance.
Key Takeaways:
- Common size financial statements are an essential tool for financial analysis.
- They allow for easier comparison among companies and industries.
What is a Common Size Financial Statement?
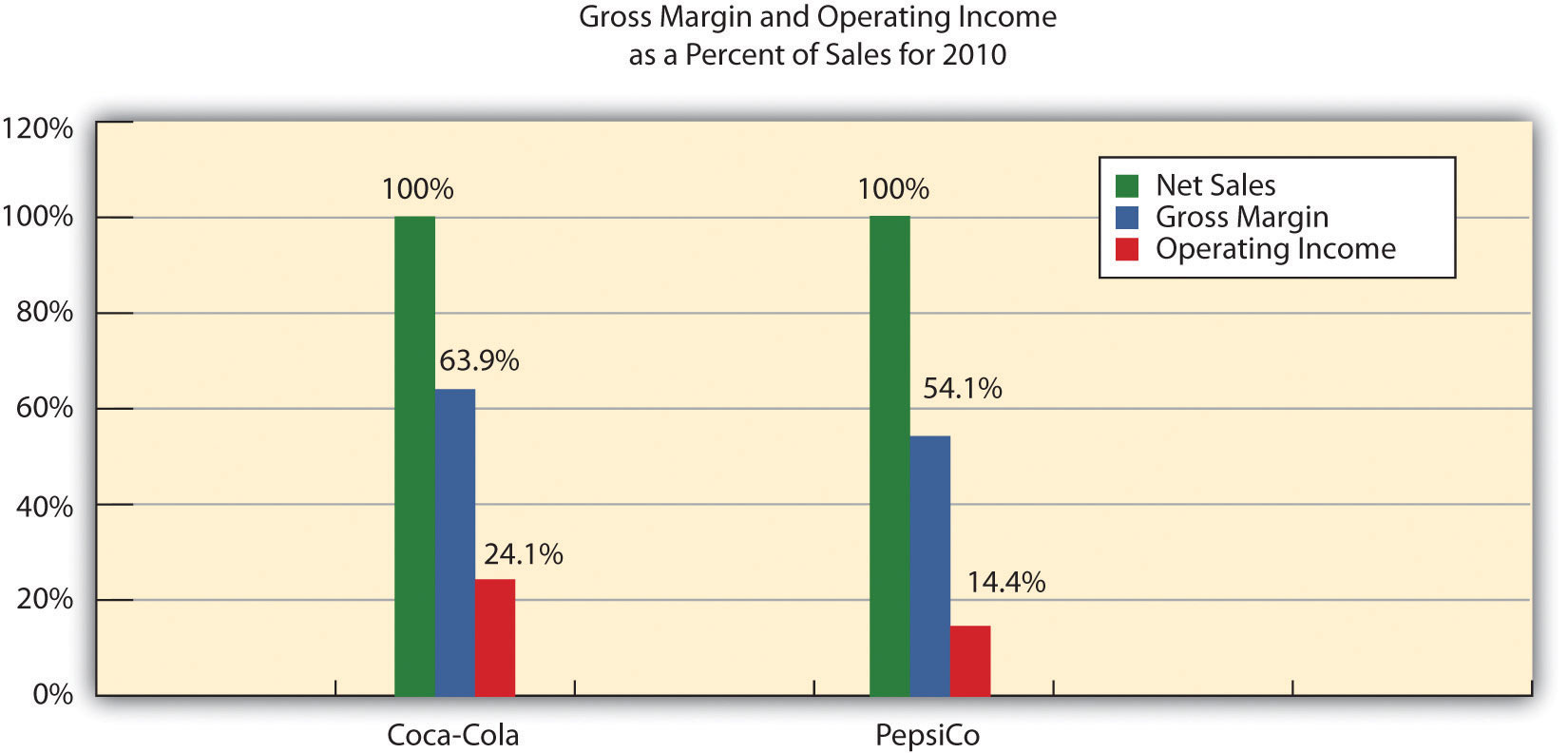
A common size financial statement is a financial report that presents all line items as a percentage of a base figure, typically sales or total assets. By expressing each item as a percentage, it becomes easier to compare and analyze financial statements of different companies or track a company’s performance over time. Common size financial statements provide a standardized framework for assessing financial data, making it an invaluable tool for investors, analysts, and business owners.
Example of a Common Size Financial Statement:
Let’s take a hypothetical example of a common size income statement for Company XYZ:
- Sales: 100%
- Cost of Goods Sold: 60%
- Gross Profit: 40%
- Operating Expenses: 25%
- Net Profit: 15%
In the example above, we can see that the cost of goods sold represents 60% of the sales, while operating expenses account for 25%. This breakdown allows us to identify the major cost components and understand the company’s profitability in a more precise manner.
Why are Common Size Financial Statements Important?
Common size financial statements are valuable for several reasons:
- Comparison: By presenting financial data in percentage form, common size financial statements enable easy comparison between different companies or industries. This comparative analysis helps identify trends, differences, and potential areas of concern or improvement.
- Trend Analysis: Common size financial statements also allow the evaluation of a company’s performance over time. By looking at the changes in the percentage breakdowns, analysts can spot trends and patterns in a company’s financial health.
- Identifying Financial Ratios: With the help of common size financial statements, analysts can calculate important financial ratios more accurately. Ratios like gross profit margin, operating profit margin, and net profit margin can provide insights into a company’s profitability, efficiency, and overall performance.
In conclusion, understanding common size financial statements is crucial for making informed financial decisions. By presenting financial data as percentages, this powerful tool simplifies comparison, trend analysis, and the calculation of important financial ratios. Whether you are an investor, analyst, or business owner, incorporating common size financial statements into your financial analysis can provide valuable insights into a company’s financial health and performance.