Home>Finance>Delivery Month Definition In Futures Contracts Plus Codes


Finance
Delivery Month Definition In Futures Contracts Plus Codes
Published: November 10, 2023
Learn the meaning of delivery month in futures contracts and how it is defined in the world of finance. Understand the importance of delivery codes and their role in trading.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Understanding Delivery Month Definition in Futures Contracts Plus Codes
When it comes to the world of finance, understanding the intricacies of various investment instruments is crucial. One such instrument is futures contracts, which provide investors with the opportunity to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a future date. However, to fully comprehend futures contracts, it is essential to grasp the concept of delivery month definition and the role of plus codes. In this article, we will delve into these topics, shedding light on their importance and how they function in the world of finance.
Key Takeaways:
- Delivery month definition refers to the specific month during which a futures contract expires. It determines when the physical delivery of the underlying asset will take place if the contract is not closed before the delivery period.
- Plus codes are symbols used to represent specific months within the delivery month definition. These codes are helpful for traders and investors to identify the expiration and delivery dates for different futures contracts.
Understanding Delivery Month Definition
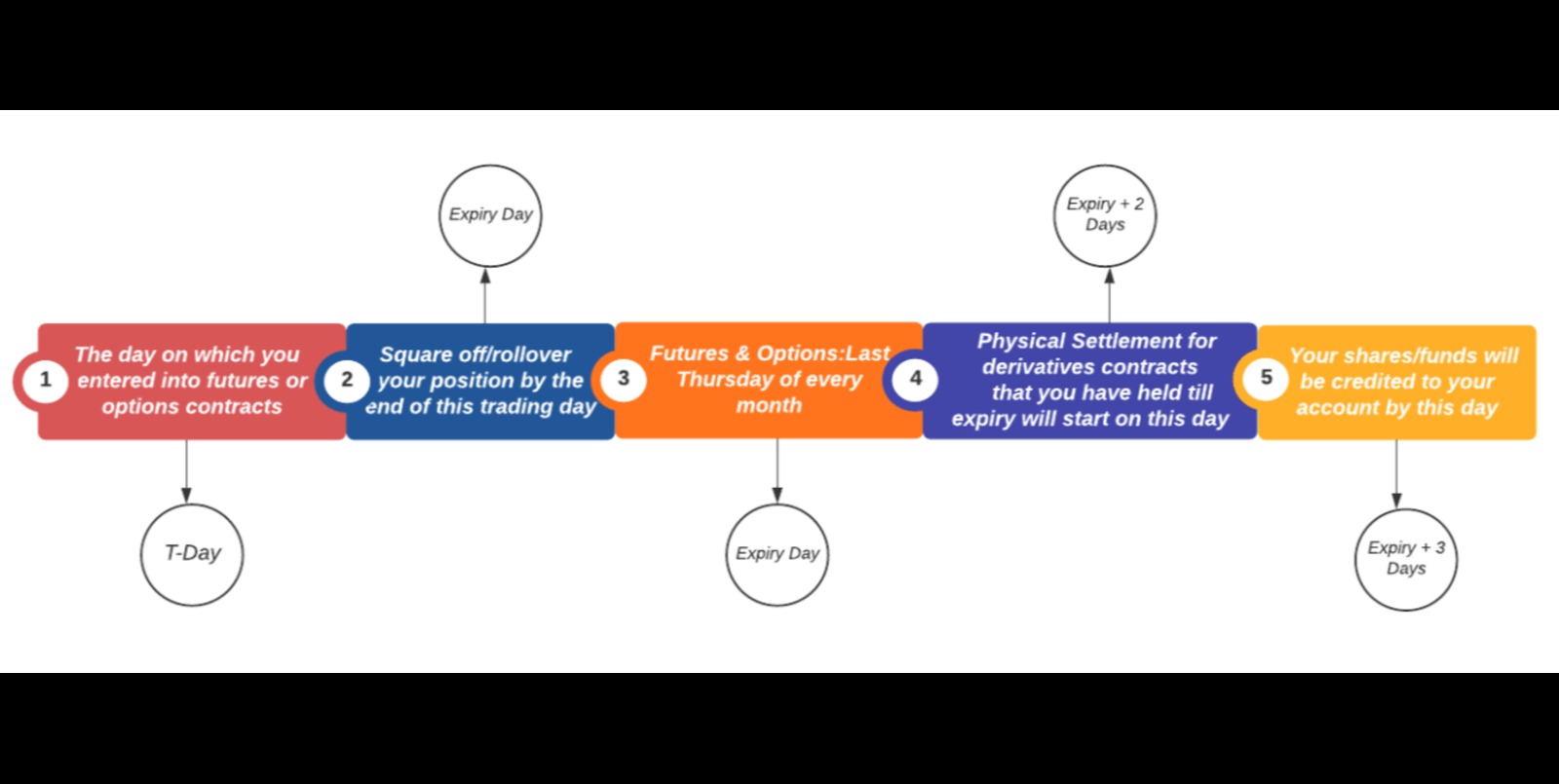
In futures trading, each contract has a designated delivery month. This delivery month refers to the specific month during which the contract expires. It is important to distinguish between different delivery months as it defines when the physical delivery of the underlying commodity or financial instrument will occur if the contract is not closed out beforehand.
For example, let’s say you are trading futures contracts for crude oil. You hold a contract with a delivery month of December. This means that the contract will expire in December, and if you hold the position until expiration, you will be obligated to take or make delivery of the specified amount of crude oil in that month.
The delivery month is typically denoted by a plus code, which is a unique symbol assigned to each month. Understanding these plus codes is essential for traders and investors to identify the expiration and delivery dates for different futures contracts.
The Role of Plus Codes
Plus codes are a shorthand method used to represent specific months within the delivery month definition. These codes are usually made up of either one or two letters, and they vary across different markets and exchanges. Some of the commonly used plus codes include:
- F – January
- G – February
- H – March
- J – April
- K – May
- M – June
- N – July
- Q – August
- U – September
- V – October
- X – November
- Z – December
For instance, if you come across a futures contract with the plus code “Z,” you would know that the delivery month is December.
By using plus codes, traders can easily identify and track the expiration and delivery months of various futures contracts. These codes allow for effective communication and ensure clarity within the futures market.
Conclusion
Understanding the delivery month definition and plus codes in futures contracts is crucial for anyone involved in futures trading. By knowing when contracts expire and when delivery is expected, traders can make informed decisions and manage their positions effectively. The use of plus codes simplifies the identification of different delivery months, making it easier to navigate the futures market. So, whether you are a seasoned trader or a novice investor, it is important to grasp these concepts to maximize your success in futures trading.