Finance
Foreign Bond Definition, Risks, Examples
Published: November 26, 2023
Discover the definition, risks, and examples of foreign bonds in the world of finance. Explore how these bonds can diversify your portfolio and expand your investment opportunities.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Foreign Bond Definition, Risks, and Examples: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to diversifying your investment portfolio, foreign bonds can be an attractive option. But what exactly are foreign bonds, and what should you know before investing in them? In this article, we will provide you with a comprehensive guide to understanding foreign bonds, including their definition, the risks associated with them, and some examples to help you make informed investment decisions.
Key Takeaways:
- Foreign bonds are debt securities issued by foreign entities in foreign currencies.
- Investing in foreign bonds allows you to diversify your portfolio and potentially earn higher returns.
Understanding Foreign Bonds
A foreign bond is a debt security issued by a foreign entity in a currency different from that of the investor’s country. Investors purchase these bonds to diversify their portfolios and potentially earn higher returns from foreign markets. Foreign bonds are often issued by national governments, municipalities, or corporations to fund their operations or investment projects.
Risks Associated with Investing in Foreign Bonds
While foreign bonds can offer potential benefits, they also carry certain risks. It’s important to be aware of these risks before investing:
- Foreign Exchange Risk: Investing in foreign bonds exposes investors to foreign exchange rate fluctuations. Changes in currency values can affect the returns on the investment.
- Political and Economic Risks: Investments in foreign bonds can be influenced by political instability, regulatory changes, and economic conditions of the issuing country.
- Interest Rate and Inflation Risks: Interest rate movements and inflation in the issuing country can affect the bond’s yield and purchasing power.
- Default Risk: There is always a possibility that the issuer may default on interest or principal payments.
Examples of Foreign Bonds
Here are a few examples of commonly known foreign bonds:
- Japanese Government Bonds (JGBs): Issued by the government of Japan, JGBs are considered low-risk investments.
- European Union Bonds (EUROs): These bonds are issued by the European Union and are denominated in euros.
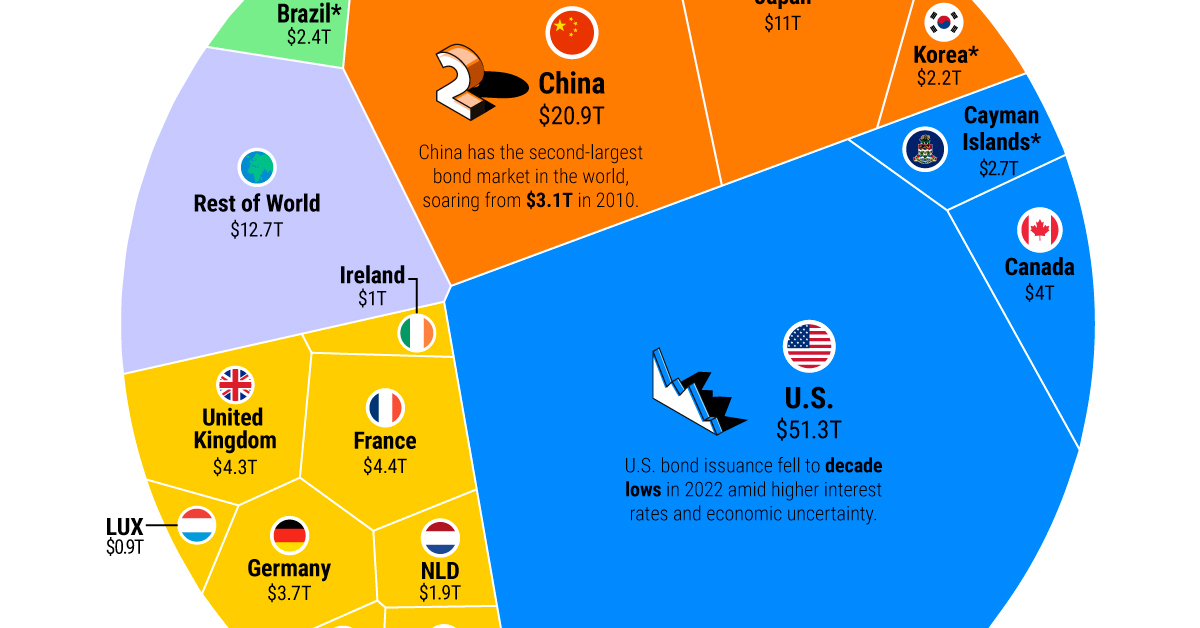
- Emerging Market Bonds: Bonds issued by developing countries, such as Brazil or China, offering potentially higher returns but also higher risk.
Investing in foreign bonds can be an effective way to diversify your portfolio globally and potentially earn higher returns. However, it’s crucial to understand the risks associated with these investments and carefully assess each issuer and its economic and political landscape.
Remember to consult with a financial advisor or conduct thorough research before making any investment decisions. By understanding the definition, risks, and examples of foreign bonds, you can make informed choices that align with your investment goals and risk tolerance.
For more finance-related topics and expert advice, explore our FINANCE category.