Finance
How Do I Figure Out APR On A Credit Card?
Published: March 2, 2024
Learn how to calculate the APR on your credit card. Get expert advice on managing your finances and understanding credit card interest rates. Discover the best practices for financial planning.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Understanding the Importance of APR on Credit Cards
When it comes to managing your finances, understanding the concept of Annual Percentage Rate (APR) on credit cards is crucial. APR represents the annual cost of borrowing and is a key factor in determining the overall cost of using a credit card for purchases and balances. It not only impacts the amount of interest you pay but also influences your financial decisions and long-term debt management strategies.
Credit cards have become an integral part of modern-day transactions, offering convenience and flexibility in managing expenses. However, the allure of credit card perks and rewards often overshadows the significance of comprehending the financial implications associated with APR. By gaining clarity on how APR works and how it affects your financial obligations, you can make informed decisions and effectively navigate the realm of credit card usage.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of APR on credit cards, unraveling its components, exploring the methodology for calculating it, and shedding light on the factors that influence credit card APR. By the end of this journey, you will have a firm grasp of APR, empowering you to make sound financial choices and wield your credit cards responsibly. Let's embark on this enlightening exploration of APR and its implications on your financial well-being.
What is APR on a Credit Card?
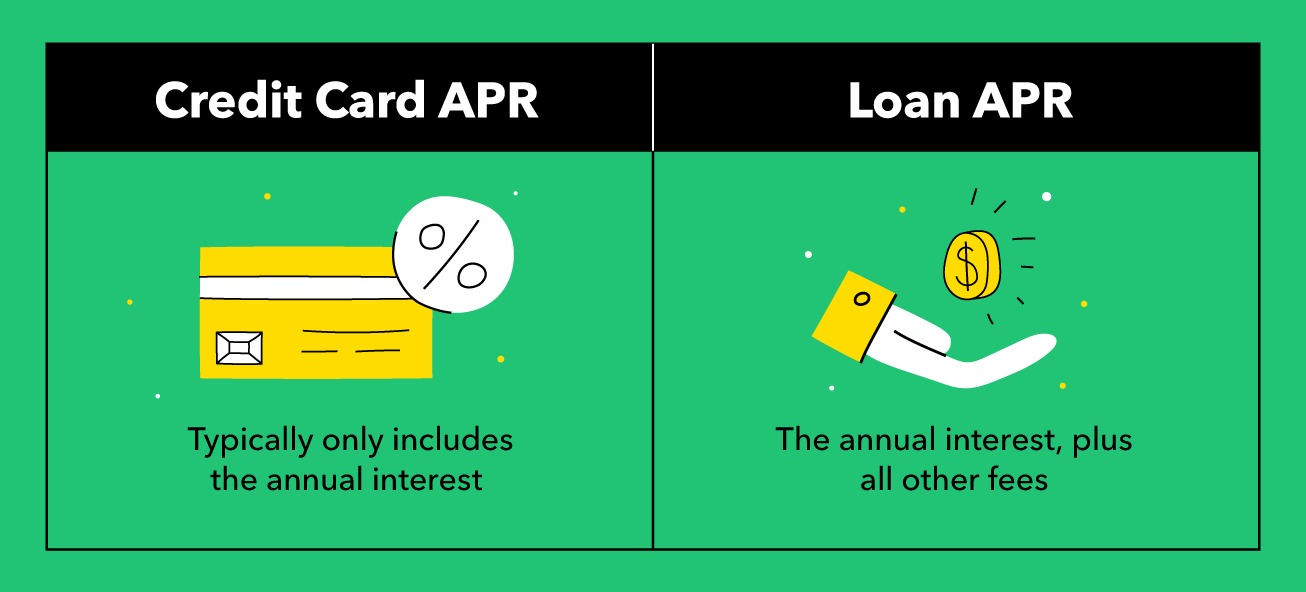
Annual Percentage Rate (APR) on a credit card is a crucial component that determines the cost of borrowing on the card. It represents the annualized interest rate applied to your outstanding balance if you carry it from month to month. Essentially, the APR reflects the cost of borrowing money through your credit card, encompassing not only the interest rate but also any additional fees or charges imposed by the card issuer.
APR serves as a fundamental metric for evaluating the financial implications of using a credit card for various transactions. It directly influences the amount of interest accrued on unpaid balances, impacting the overall cost of maintaining a revolving balance on the card. Understanding the APR on your credit card is essential for making informed decisions about carrying balances, comparing different credit card offers, and devising effective debt repayment strategies.
It’s important to note that credit card APRs can vary based on several factors, including the type of transaction (purchases, balance transfers, cash advances), the cardholder’s creditworthiness, and prevailing market conditions. Additionally, credit card issuers may offer different types of APRs, such as introductory or promotional rates, standard rates, and penalty rates, each with distinct implications for cardholders.
By grasping the concept of APR and its significance in the realm of credit cards, individuals can gain valuable insights into the true cost of utilizing credit and make informed choices aligned with their financial goals and circumstances. The next section will delve deeper into the components that constitute the APR on a credit card, providing a comprehensive understanding of its composition and implications.
Understanding the Components of APR
Annual Percentage Rate (APR) on a credit card comprises various components that collectively determine the cost of borrowing and the financial obligations associated with the card. By dissecting these elements, cardholders can gain a comprehensive understanding of how APR is structured and how it influences their financial decisions.
1. Interest Rate: The core component of APR is the interest rate, which represents the cost of borrowing expressed as a percentage of the outstanding balance. This rate may be fixed or variable, depending on the terms of the credit card agreement. Understanding the interest rate is crucial, as it directly impacts the amount of interest accrued on unpaid balances over time.
2. Additional Fees: In addition to the interest rate, credit card APR may encompass various fees, such as annual fees, balance transfer fees, cash advance fees, and late payment fees. These fees contribute to the overall cost of maintaining a balance on the card and should be considered when evaluating the true cost of borrowing.
3. Grace Period: The presence or absence of a grace period, during which no interest is charged on new purchases if the previous month’s balance is paid in full, can significantly impact the effective APR. Understanding the terms of the grace period is essential for optimizing the use of the credit card and minimizing interest expenses.
4. Promotional Rates: Some credit card offers feature promotional or introductory APRs, which are temporary, lower-than-normal rates applicable for a specified period. These rates may apply to purchases, balance transfers, or both, providing cardholders with an opportunity to save on interest costs during the promotional period.
By comprehending the components that constitute the APR on a credit card, individuals can make informed decisions regarding their credit card usage, debt management strategies, and financial planning. In the following section, we will explore the methodology for calculating the APR on a credit card, empowering readers to demystify this crucial aspect of credit card finance.
Calculating APR on a Credit Card
Understanding how the Annual Percentage Rate (APR) on a credit card is calculated is essential for gaining clarity on the true cost of borrowing and making informed financial decisions. The methodology for determining the APR involves considering various factors, including the interest rate, compounding frequency, and additional fees, to arrive at the effective annualized cost of using the credit card for borrowing.
The following steps outline the general approach to calculating the APR on a credit card:
- Identify the Periodic Interest Rate: The first step involves determining the periodic interest rate, which is the interest rate applied to the outstanding balance within a specific time frame, typically a month. This rate may be expressed as a monthly or daily rate, depending on the credit card terms.
- Consider the Compounding Frequency: Understanding how often the interest is compounded is crucial for accurate APR calculation. Compounding refers to the frequency at which the accrued interest is added to the principal balance, leading to interest on interest. The more frequent the compounding, the higher the effective APR.
- Incorporate Additional Fees: If the credit card entails additional fees, such as annual fees or transaction fees, these should be factored into the APR calculation. Including these fees provides a more comprehensive view of the total cost of borrowing on the card.
- Compute the Effective APR: By considering the periodic interest rate, compounding frequency, and any applicable fees, individuals can calculate the effective APR using mathematical formulas or online APR calculators. The resulting figure represents the annualized cost of borrowing on the credit card, encompassing both the interest rate and any associated fees.
By familiarizing themselves with the methodology for calculating APR, credit card users can gain insights into the cost implications of maintaining a balance on their cards and optimize their financial strategies accordingly. It’s important to note that while the APR provides a standardized metric for comparing credit card offers, individual financial circumstances and usage patterns also play a significant role in determining the actual cost of using a credit card.
Having explored the calculation of APR, the next section will delve into the factors that can influence the APR on a credit card, shedding light on the dynamic nature of credit card finance and the variables that impact borrowing costs.
Factors Affecting Credit Card APR
The Annual Percentage Rate (APR) on a credit card is influenced by a myriad of factors, each contributing to the variability and dynamics of borrowing costs for cardholders. Understanding these factors is essential for comprehending the nuances of credit card finance and making informed decisions regarding credit card usage and debt management strategies.
1. Creditworthiness: A primary determinant of the APR on a credit card is the cardholder’s creditworthiness, as assessed by their credit score, credit history, and overall credit profile. Individuals with higher credit scores and robust credit histories are often eligible for lower APRs, reflecting a lower perceived risk by the card issuer.
2. Market Conditions: The prevailing economic environment and market conditions can influence credit card APRs. Fluctuations in benchmark interest rates, such as the prime rate, can impact the cost of borrowing for credit card issuers, potentially leading to adjustments in APRs for cardholders.
3. Type of Transaction: Different types of credit card transactions, such as purchases, balance transfers, and cash advances, may carry varying APRs. For example, balance transfer APRs may differ from purchase APRs, offering cardholders distinct rates for specific transaction categories.
4. Introductory Offers: Many credit card issuers provide promotional or introductory APR offers to attract new cardholders. These temporary rates, often lower than standard APRs, may apply for a specified period, after which the APR reverts to the standard rate.
5. Penalty APR: In cases of delinquency or default, credit card issuers may impose penalty APRs, significantly increasing the cost of borrowing for the cardholder. Penalty APRs are triggered by late payments or other violations of the card agreement terms.
6. Regulatory Changes: Shifts in financial regulations and legislative measures can impact credit card APRs, as card issuers adapt to compliance requirements and market dynamics. Regulatory changes may lead to adjustments in APR structures and terms for cardholders.
By recognizing the multifaceted nature of factors influencing credit card APRs, individuals can navigate the landscape of credit card finance with greater insight and awareness. The interplay of these variables underscores the importance of actively managing one’s credit profile, staying informed about market conditions, and leveraging promotional offers to optimize the cost of borrowing on credit cards.
As we conclude this exploration of credit card APR, it becomes evident that a holistic understanding of APR and its determinants empowers individuals to wield their credit cards responsibly and strategically, aligning their financial decisions with their long-term goals and well-being.
Conclusion
As we conclude this comprehensive guide to understanding Annual Percentage Rate (APR) on credit cards, it becomes evident that APR is a pivotal metric that shapes the cost of borrowing and the financial implications of utilizing credit cards. By unraveling the intricacies of APR and its components, individuals can equip themselves with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions, optimize their credit card usage, and navigate the realm of debt management with confidence.
Throughout this journey, we have delved into the essence of APR, elucidating its role as a barometer of borrowing costs and a key consideration for evaluating credit card offers. From dissecting the components of APR to exploring the methodology for calculating it, we have demystified this critical aspect of credit card finance, empowering readers to comprehend the true cost of maintaining balances on their cards.
Furthermore, our exploration of the factors influencing credit card APR has shed light on the dynamic interplay of creditworthiness, market conditions, transaction types, and regulatory influences, emphasizing the multifaceted nature of APR determination. By recognizing these factors, individuals can proactively manage their credit profiles, seize promotional opportunities, and stay attuned to market dynamics to optimize their borrowing costs.
Ultimately, the knowledge gained from this guide serves as a compass for making prudent financial choices, aligning credit card usage with personal financial goals, and cultivating responsible debt management practices. By leveraging this understanding, individuals can harness the potential of credit cards as financial tools while mitigating the risks associated with high borrowing costs and interest expenses.
As you embark on your financial journey, may the insights gleaned from this exploration of APR on credit cards empower you to wield your credit cards judiciously, navigate the nuances of borrowing costs with acumen, and embark on a path of financial empowerment and well-being.
Remember, behind every credit card transaction lies the opportunity to make informed choices that resonate with your financial aspirations and pave the way for a secure and prosperous future.