Finance
How Do I Report Regulated Futures Contracts
Modified: February 21, 2024
Learn how to report regulated futures contracts in the finance industry. Find out the necessary steps and regulations to ensure compliance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Regulated Futures Contracts
- Importance of Reporting Regulated Futures Contracts
- Reporting Requirements for Regulated Futures Contracts
- Steps to Report Regulated Futures Contracts
- Reporting Formats and Systems Used for Regulated Futures Contracts
- Common Challenges in Reporting Regulated Futures Contracts
- Monitoring and Compliance for Reporting Regulated Futures Contracts
- Conclusion
Introduction
Reporting regulated futures contracts is a vital aspect of financial market regulation and oversight. Regulated futures contracts are standardized derivatives contracts that are traded on regulated exchanges. These contracts allow market participants to speculate on the future price movements of various underlying assets, such as commodities, currencies, and financial instruments.
The reporting of regulated futures contracts is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it provides transparency and visibility into the trading activities and positions held by market participants. This helps regulators and policymakers monitor and assess the overall health and stability of financial markets. Secondly, it helps detect and prevent market manipulation, insider trading, and other fraudulent activities. By requiring market participants to report their positions and trades, regulators can identify any suspicious patterns or abnormal trading behaviors that may harm market integrity.
Furthermore, reporting regulated futures contracts plays a key role in risk management and systemic stability. By having a comprehensive view of market participants’ positions and exposures, regulators can better assess and address potential risks that may arise from concentrated positions or excessive leverage. This helps safeguard the financial system from systemic risks and contributes to the overall resilience of the markets.
To ensure effective reporting of regulated futures contracts, regulatory authorities have put in place specific reporting requirements and guidelines. Market participants are obligated to report their trades, positions, and other relevant information to the designated regulatory bodies within the specified timeframes. Compliance with these reporting requirements is essential to maintain regulatory compliance and avoid potential penalties or sanctions.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the reporting requirements for regulated futures contracts, the steps involved in reporting, the reporting formats and systems used, common challenges faced in reporting, as well as monitoring and compliance practices associated with reporting regulated futures contracts. Understanding these aspects is crucial for market participants to ensure they meet their reporting obligations and contribute to the overall integrity and stability of the financial markets.
Definition of Regulated Futures Contracts
Regulated futures contracts refer to standardized derivative contracts that are traded on regulated exchanges. These contracts are legally binding agreements to buy or sell a specific financial instrument or commodity at a predetermined price and future date. They are subject to strict regulatory oversight and supervision.
Regulated futures contracts are characterized by several key elements:
- Standardization: Regulated futures contracts have standardized terms and conditions, including contract size, expiration date, and delivery specifications. This standardization ensures a high level of transparency, fairness, and ease of trading.
- Exchange-Traded: These contracts are traded on regulated exchanges, such as futures exchanges and commodity exchanges. The exchanges act as intermediaries, facilitating the buying and selling of the contracts between market participants.
- Leverage: Regulated futures contracts allow market participants to trade on margin, which means they can control a larger position with a relatively smaller initial investment. This leverage amplifies potential gains or losses.
- Marked-to-Market: At the end of each trading day, the value of the positions held in regulated futures contracts is recalculated based on the prevailing market prices. This process, known as marking-to-market, ensures that any gains or losses are realized and settled on a daily basis.
- Clearinghouse: Regulated futures contracts are cleared through a central clearinghouse, which serves as a counterparty to all trades. The clearinghouse guarantees the performance of the contracts and ensures the settlement of obligations between buyers and sellers.
Regulated futures contracts are available for various underlying assets, including commodities (such as gold, crude oil, and agricultural products), financial instruments (such as stock indexes and interest rates), and currencies.
It is important to note that regulated futures contracts are distinct from over-the-counter (OTC) derivatives, which are privately negotiated contracts between two parties. Regulated futures contracts provide standardized terms, greater liquidity, and transparency compared to OTC derivatives.
Overall, regulated futures contracts are an essential tool for market participants to manage risks, speculate on price movements, and gain exposure to various asset classes. The regulatory oversight ensures fairness, transparency, and market integrity in the trading of these contracts.
Importance of Reporting Regulated Futures Contracts
Reporting regulated futures contracts is of paramount importance for ensuring the transparency, integrity, and stability of financial markets. The reporting process provides regulatory authorities with crucial insights into the trading activities, positions, and risks associated with these contracts. Here are some key reasons highlighting the importance of reporting regulated futures contracts:
Transparency and Market Oversight: Reporting regulated futures contracts provides regulatory authorities with a comprehensive view of the trading activities and positions held by market participants. This transparency allows regulators to monitor and assess the overall health and stability of financial markets. By analyzing the reported data, regulators can identify potential risks, detect market anomalies, and take necessary actions to maintain market integrity.
Market Surveillance and Detection of Manipulation: Reporting regulated futures contracts plays a crucial role in detecting and preventing market manipulation, insider trading, and other fraudulent activities. By analyzing the reported data, regulators can identify any suspicious patterns or abnormal trading behaviors that may harm market fairness. This helps maintain a level playing field for all market participants and protects investors’ interests.
Risk Management and Systemic Stability: Comprehensive reporting of regulated futures contracts enables regulators to monitor and assess the risks associated with these contracts. By having detailed information on market participants’ positions and exposures, regulators can better understand and address potential risks that may arise from concentrated positions or excessive leverage. This contributes to the overall stability and resilience of the financial system.
Pricing and Valuation: Reporting regulated futures contracts helps in ensuring accurate pricing and valuation of these contracts. By having access to timely and accurate trade and position data, regulators can monitor the fair value of these contracts, enabling market participants to make informed investment decisions. This promotes efficiency and trust in the pricing mechanisms of regulated futures contracts.
Regulatory Compliance: Reporting regulated futures contracts is a legal obligation for market participants. Complying with reporting requirements demonstrates the commitment to regulatory compliance and helps maintain the trust and confidence of regulators and other market participants. Failure to report or providing inaccurate information can result in penalties, fines, and reputational damage.
Overall, reporting regulated futures contracts is essential for maintaining transparency, investor protection, market surveillance, risk management, and regulatory compliance. It facilitates the smooth functioning of financial markets and fosters trust among market participants.
Reporting Requirements for Regulated Futures Contracts
Regulatory authorities impose specific reporting requirements for regulated futures contracts to ensure transparency, market oversight, and compliance. Market participants, including traders, clearing members, and exchanges, are obligated to report key information related to their positions, transactions, and other relevant data. The reporting requirements may vary across jurisdictions and regulatory bodies, but generally include the following:
- Trade Reporting: Market participants are required to report details of their trades in regulated futures contracts, including the contract identifier, trade date, time, price, and quantity. This information helps regulators monitor trading activities, analyze market trends, and detect any potential suspicious activities.
- Position Reporting: Reporting the positions held in regulated futures contracts is an important requirement as it provides insights into market participants’ exposure and risk profiles. Market participants are typically required to report their open positions, including long and short positions, on a regular basis.
- Clearing Member Reporting: Clearing members, who act as intermediaries between market participants and the clearinghouse, have additional reporting obligations. They are typically required to report aggregated position data of their clients to the regulatory authorities for risk management and monitoring purposes.
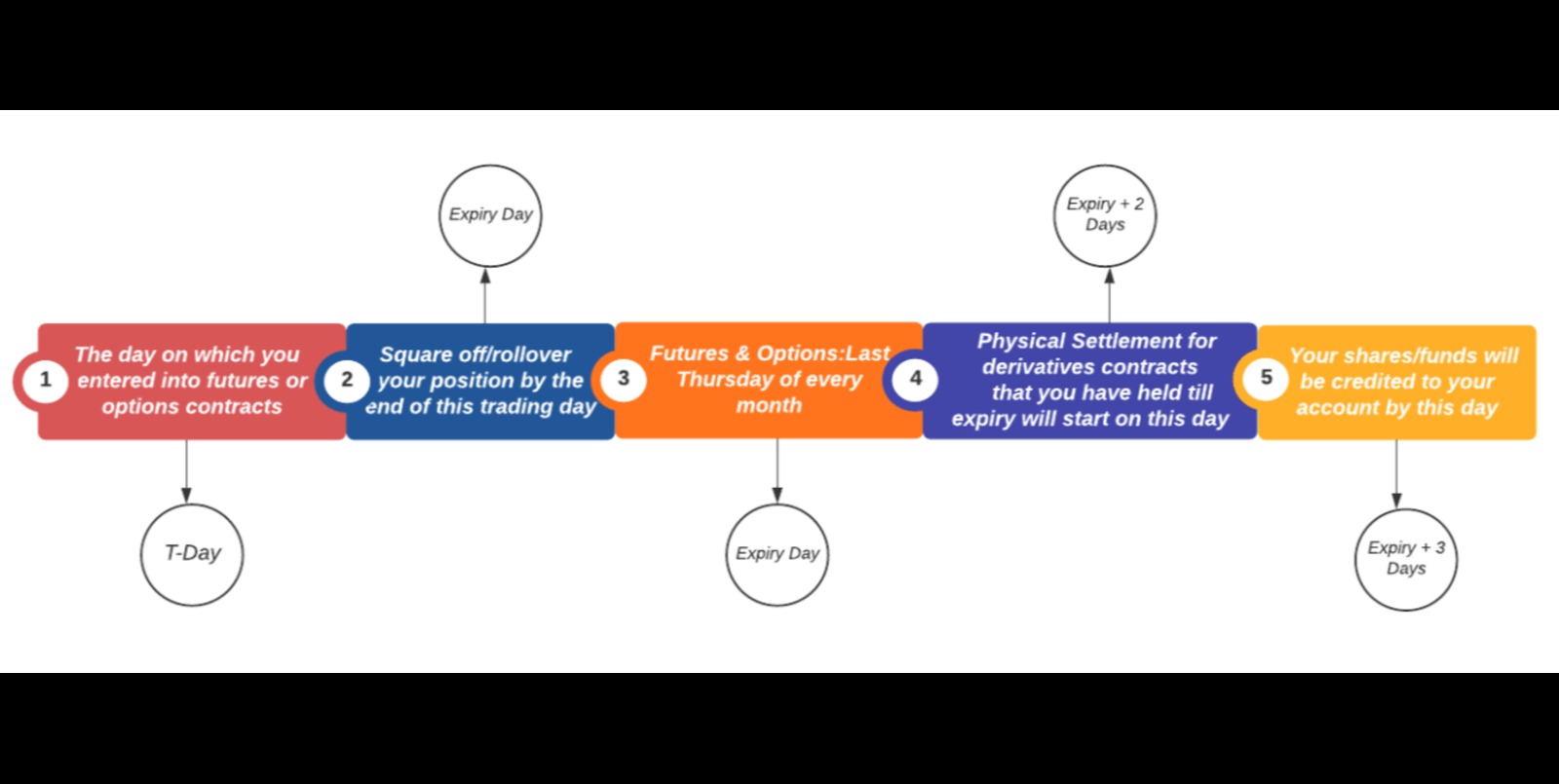
- Delivery and Expiration Reporting: For physically settled regulated futures contracts, reporting the delivery and expiration details is necessary. This includes information on the delivery locations, delivery dates, and any actions or adjustments related to the contract expiration process.
- Reporting of Additional Information: Apart from trade and position data, regulatory authorities may require market participants to provide additional information, such as the underlying asset, contract specifications, and any other relevant details related to the regulated futures contracts being reported.
Reporting requirements are typically accompanied by specific formats, timelines, and reporting systems designated by the regulatory authorities. Market participants must ensure compliance with these requirements to avoid penalties or regulatory actions.
It is worth noting that reporting requirements may also extend to other related activities, such as reporting of large positions, reporting of certain types of transactions (e.g., block trades), and reporting of any changes or updates to previously reported data. The specific requirements will depend on the regulations and guidelines set by the relevant regulatory agencies.
Market participants should stay updated on the reporting requirements prescribed by the regulatory authorities governing the jurisdiction in which they operate. This can be done by regularly reviewing regulatory publications, participating in industry forums, and seeking guidance from regulatory and compliance experts.
Complying with reporting requirements is essential for maintaining regulatory compliance, contributing to market transparency, and ensuring the overall integrity and stability of regulated futures contract markets.
Steps to Report Regulated Futures Contracts
Reporting regulated futures contracts involves a series of steps that market participants need to follow to fulfill their reporting obligations. While the specific steps may vary depending on the jurisdiction and the regulatory requirements, the following are common steps involved in reporting regulated futures contracts:
- Understand Reporting Obligations: Market participants should have a clear understanding of the reporting requirements imposed by the regulatory authorities. This includes knowledge of the specific instruments, transactions, and positions that need to be reported, as well as the reporting formats and timelines.
- Collect Relevant Data: Market participants need to gather the necessary data for reporting regulated futures contracts. This includes trade details such as contract identifier, trade date, time, price, and quantity, as well as position information such as open positions and delivery-related data if applicable.
- Choose Reporting System: Select the appropriate reporting system or platform as mandated by the regulatory authorities. Depending on the jurisdiction, market participants may need to report through a designated trade repository or reporting platform that complies with the required reporting standards.
- Format and Validate Data: Ensure that the collected data is formatted according to the specified reporting standards and the requirements of the reporting system. Validate the data to ensure accuracy, completeness, and compliance with the regulatory guidelines.
- Submit Reports: Submit the reports electronically through the designated reporting system within the prescribed timeframe. This may involve uploading the data files, manually entering the information, or utilizing electronic messaging protocols, depending on the reporting system in place.
- Monitor Confirmation and Acknowledgment: After submitting the reports, monitor for confirmation or acknowledgment from the reporting system or regulatory authorities. This helps ensure that the reports have been successfully received and processed.
- Review and Rectify Errors: Regularly review the reported data for any errors or discrepancies. If any inaccuracies are identified, promptly rectify them and resubmit the corrected reports, if necessary, to maintain data integrity and compliance.
- Maintain Documentation: Keep a record of the submitted reports, including any supporting documentation or audit trails, as required by the regulatory authorities. This helps demonstrate compliance with reporting requirements and facilitates any future inquiries or audits.
- Stay Updated and Compliant: Stay informed about any regulatory updates or changes in reporting requirements. Regularly review regulatory communications, participate in relevant industry forums, and seek guidance from compliance professionals to ensure ongoing compliance with reporting obligations.
Market participants should consider implementing robust reporting processes and systems to streamline their reporting efforts. This may involve leveraging automated reporting solutions or engaging third-party service providers specializing in regulatory reporting.
By following these steps and staying diligent in reporting regulated futures contracts, market participants can fulfill their obligations, contribute to market transparency, and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements.
Reporting Formats and Systems Used for Regulated Futures Contracts
Reporting regulated futures contracts requires the use of specific formats and reporting systems that comply with the regulatory standards set forth by the governing authorities. The choice of reporting formats and systems can vary depending on the jurisdiction, regulatory requirements, and the type of market participants involved. Here are some common reporting formats and systems used for reporting regulated futures contracts:
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI): EDI is a commonly used format for reporting regulated futures contracts. It allows for the structured and standardized exchange of data between different systems and entities. EDI formats often follow specific industry standards, such as FIX (Financial Information eXchange) protocol, which enables seamless communication between market participants, exchanges, and regulators.
XML (eXtensible Markup Language): XML is a flexible format that allows for the representation and exchange of structured data. It is widely used in financial reporting, including the reporting of regulated futures contracts. XML formats can be customized to meet specific reporting requirements and enable interoperability between different reporting systems.
CSV (Comma-Separated Values): CSV is a simple, text-based format that uses commas to separate data values. It is often used for reporting regulated futures contracts, particularly for bulk data uploads and manual data entry. CSV files can be easily generated and manipulated using spreadsheet software, making it a popular choice for market participants with lower reporting volumes.
Reporting Platforms and Trade Repositories: Many regulatory jurisdictions require market participants to report regulated futures contracts through dedicated reporting platforms or trade repositories. These platforms serve as centralized repositories for receiving, storing, and validating reported data. They often offer web-based interfaces, APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), or standardized file formats for data submission.
Regulatory Reporting Systems: Some regulatory authorities provide their own reporting systems for market participants to fulfill their reporting obligations. These systems may be web-based portals or specialized software tools designed to capture and validate the required data. Market participants may need to register and obtain access to these systems to ensure compliance with reporting requirements.
API Integrations: For larger market participants or technology-savvy firms, API integrations can be used to directly connect their internal systems with regulatory reporting systems. This enables automated data transmission and real-time reporting, minimizing manual efforts and improving efficiency in meeting reporting obligations.
The choice of reporting format and system depends on various factors, including the regulatory requirements, the volume of trades and positions, the technological capabilities of market participants, and the level of integration with reporting systems.
Market participants should ensure that they adhere to the prescribed reporting formats and utilize the designated systems or platforms as required by the regulatory authorities. It is important to stay updated on any changes or updates in reporting formats or systems and promptly align reporting practices to ensure compliance.
Engaging with technology providers and consulting regulatory experts can help market participants navigate the complexities of reporting formats and systems, ensuring accurate and timely reporting of regulated futures contracts.
Common Challenges in Reporting Regulated Futures Contracts
Reporting regulated futures contracts can be a complex and demanding task for market participants. Various challenges can arise during the reporting process, which may hinder accurate and timely compliance with regulatory requirements. Here are some common challenges that market participants face when reporting regulated futures contracts:
Data Accuracy and Completeness: Ensuring the accuracy and completeness of the reported data is crucial for regulatory compliance. Market participants may encounter challenges in obtaining accurate data from different systems or sources within their organization. Data inconsistencies, missing information, or discrepancies in trade and position data can lead to reporting errors and non-compliance.
Data Integration and System Compatibility: Integrating data from different internal systems and ensuring compatibility with the reporting format and systems can be a significant challenge. Market participants often have multiple internal systems, such as trading platforms, risk management systems, and back-office systems, which may store data in different formats. Integrating these systems to extract and consolidate the required data for reporting can be a complex and time-consuming process.
Lack of Standardization: The lack of standardized reporting formats across jurisdictions or exchanges can pose challenges for market participants. Each regulatory authority may have its own set of reporting requirements, which may differ in terms of data fields, formats, and reporting frequencies. Market participants need to adapt to these variations and ensure compliance with the specific requirements of each jurisdiction.
Timeliness of Reporting: Meeting the prescribed reporting timelines can be challenging, especially for market participants with high trading volumes or complex reporting processes. Ensuring that reports are submitted within the required timeframe may require efficient data aggregation, processing, and validation mechanisms. Delays in reporting can result in regulatory penalties or sanctions.
Regulatory Changes and Updates: Regulatory requirements for reporting regulated futures contracts are subject to frequent changes and updates. Keeping up with these changes, including new reporting fields, additional data requirements, or modifications in reporting formats, can be a challenge. Market participants need to closely monitor regulatory announcements and engage with industry groups or technology providers to stay informed and adapt their reporting processes accordingly.
Compliance with Cross-Border Reporting: Market participants operating in multiple jurisdictions face the challenge of complying with cross-border reporting requirements. Each jurisdiction may have its own regulatory framework and reporting obligations, requiring market participants to navigate through varying rules and protocols. Ensuring consistent and accurate reporting across different jurisdictions can be complex and resource-intensive.
Data Security and Privacy: Reporting regulated futures contracts involves handling sensitive and confidential data. Market participants need to implement robust data security measures to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the reported data. Compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), adds an additional layer of complexity to reporting requirements.
Overcoming these challenges requires market participants to invest in robust reporting infrastructures, data governance frameworks, and compliance processes. This may involve leveraging technology solutions, engaging regulatory experts or consultants, and fostering strong partnerships with reporting platforms or service providers.
By addressing these challenges proactively, market participants can enhance their reporting capabilities, ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, and contribute to the overall integrity and transparency of regulated futures contract markets.
Monitoring and Compliance for Reporting Regulated Futures Contracts
Monitoring and compliance play a crucial role in ensuring the accuracy, timeliness, and integrity of reporting regulated futures contracts. Market participants must establish robust monitoring and compliance practices to fulfill their reporting obligations and adhere to regulatory requirements. Here are some key aspects of monitoring and compliance for reporting regulated futures contracts:
Internal Controls and Processes: Market participants should implement effective internal controls and processes to ensure accurate and timely reporting. This includes establishing clear lines of responsibility, segregating duties, and implementing regular data reconciliation and validation procedures. Internal controls should address data collection, aggregation, formatting, and submission to minimize reporting errors.
Automated Reporting Systems: Leveraging automated reporting systems can enhance monitoring and compliance efforts. Automated systems can help streamline data collection, formatting, and submission processes, reducing the potential for human error and ensuring adherence to reporting requirements. These systems can also provide real-time data validation checks to enhance accuracy and compliance.
Data Analytics and Reconciliation: Regular data analytics and reconciliation processes should be in place to identify any inconsistencies or discrepancies in reported data. By performing regular checks, market participants can detect potential errors or outliers, rectify them promptly, and maintain data integrity. Data reconciliation helps ensure that reported positions, transactions, and other relevant information match with the records held by the market participants.
Regulatory Oversight and Audits: Regulatory authorities may conduct periodic audits or examinations to evaluate market participants’ compliance with reporting requirements. Market participants should be prepared to provide documentation and evidence to demonstrate compliance. Maintaining accurate records of submitted reports, supporting documentation, and any changes made to previously reported data is essential. Engaging with regulatory experts or consultants can help market participants navigate regulatory examinations and mitigate compliance risks.
Ongoing Education and Training: To ensure compliance, market participants should invest in ongoing education and training for their staff. This includes keeping employees updated on regulatory changes, reporting requirements, and best practices. Training programs should cover data collection, formatting, reconciliation, internal control procedures, and the proper use of reporting systems to minimize errors and promote compliance awareness.
Engagement with Regulatory Bodies: Market participants should maintain open lines of communication with regulatory bodies and stay informed about any updates or clarifications related to reporting requirements. Participating in industry forums, attending regulatory meetings, and seeking guidance from regulatory authorities can help ensure ongoing compliance and foster a collaborative relationship with regulators.
Compliance Monitoring Tools and Technologies: Implementing compliance monitoring tools and technologies can enhance the effectiveness of monitoring and compliance efforts. These tools can provide real-time visibility into reporting activities, generate compliance reports, and flag any potential reporting issues or anomalies. Compliance monitoring technologies can also alert market participants to regulatory changes and automate compliance checks.
By actively monitoring reporting processes, implementing robust compliance practices, and staying proactive in addressing any reporting issues, market participants can ensure regulatory compliance, reduce reporting errors, and contribute to the integrity and transparency of regulated futures contract markets.
Conclusion
Reporting regulated futures contracts is a critical component of financial market regulation. It provides transparency, oversight, and trust in the trading activities and positions held by market participants. By adhering to reporting requirements, market participants contribute to market integrity, investor protection, and systemic stability.
In this article, we explored the definition of regulated futures contracts and examined their importance in the financial ecosystem. We discussed the reporting requirements and the steps involved in reporting regulated futures contracts. Additionally, we highlighted the various reporting formats and systems that market participants use, along with the common challenges they face in the reporting process.
Monitoring and compliance for reporting regulated futures contracts are essential to ensure accurate and timely reporting. Market participants must establish robust internal controls, leverage automated reporting systems, perform regular data analytics and reconciliation, and engage in ongoing education and training. Additionally, maintaining open communication with regulatory bodies and utilizing compliance monitoring tools and technologies can support effective monitoring and compliance practices.
It is vital for market participants to stay informed about regulatory changes and updates, maintain high data accuracy and completeness, and submit reports within the prescribed timelines. By doing so, market participants can fulfill their reporting obligations, mitigate compliance risks, and contribute to the transparent and efficient functioning of regulated futures contract markets.
In conclusion, reporting regulated futures contracts is not only a regulatory requirement but also an essential practice to uphold market integrity, investor confidence, and systemic stability. Market participants play a crucial role in ensuring accurate and timely reporting, which ultimately benefits the entire financial ecosystem.