Home>Finance>How Is Life A Insurance Policy Dividend Legally Defined?


Finance
How Is Life A Insurance Policy Dividend Legally Defined?
Modified: February 21, 2024
Discover how life insurance policy dividends are legally defined and understand the financial implications. Explore the relationship between finance and insurance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Basics of Life Insurance Policy Dividends
- Definition of Dividends in Life Insurance
- Legal Definition of Dividend in Life Insurance Policies
- Requirements for Payment of Dividends in Life Insurance
- Taxation of Dividends in Life Insurance Policies
- Common Issues and Disputes Regarding Dividends in Life Insurance
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to the world of life insurance policy dividends! If you’re new to the concept of dividends in relation to life insurance, or simply want to deepen your understanding and knowledge, you’ve come to the right place. In this article, we will explore how life insurance policy dividends are legally defined and the key aspects surrounding them.
Life insurance policies are designed to provide financial protection to policyholders and their beneficiaries. These policies offer various benefits, such as a sum assured in the event of the insured individual’s death. However, some life insurance policies also offer an additional feature – dividends.
In the context of life insurance, dividends are a unique aspect that can significantly impact the policyholder’s experience. Dividends in life insurance are not the same as dividends received from stock investments. Instead, they are a way for policyholders to potentially benefit from the favorable financial performance of the insurance company.
Understanding how life insurance policy dividends work can help policyholders make informed decisions and maximize the value of their insurance policies. So let’s dive deeper into the legal definition of dividends in the context of life insurance policies.
Basics of Life Insurance Policy Dividends
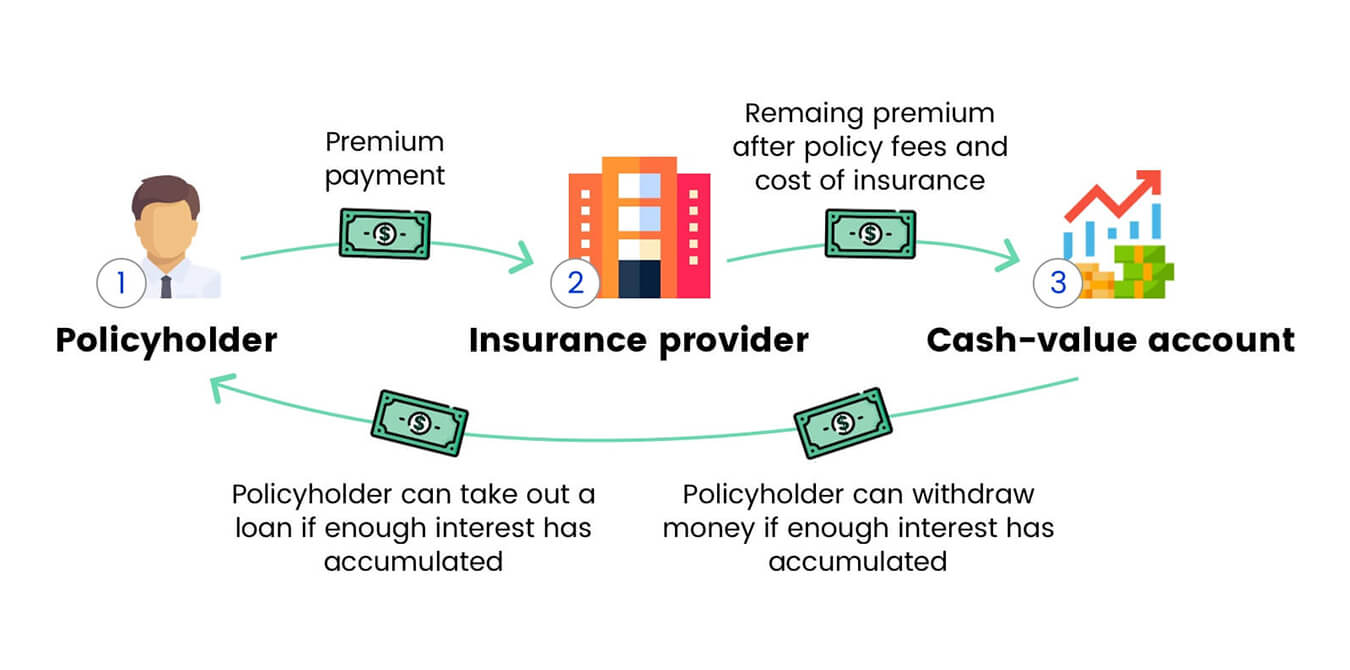
Life insurance policy dividends are a way for insurance companies to distribute a portion of their profits to policyholders. These dividends are not guaranteed and vary based on the company’s financial performance and the terms of the policy. It’s important to note that not all life insurance policies offer dividends, as it depends on the type of policy and the specific terms and conditions.
When a policyholder purchases a participating life insurance policy, they essentially become a shareholder in the insurance company. As a shareholder, the policyholder may be eligible to receive dividends if the company generates excess profits and meets certain criteria. These dividends can be paid out in various ways, including as a cash payment, a reduction in future premiums, an increase in the policy’s cash value, or as additional paid-up insurance.
The amount of dividends can fluctuate from year to year, as it is tied to the company’s financial performance. If the insurance company experiences a good financial year and generates surplus profits, the policyholders may receive higher dividends. Conversely, if the company faces financial challenges, dividends may be reduced or even eliminated.
It’s important to understand that life insurance policy dividends should not be seen as a guaranteed return on investment. While they do provide an opportunity to benefit from the financial success of the insurance company, they are subject to market conditions and the overall performance of the company.
Policyholders have the flexibility to determine how they want to utilize their dividends. They can choose to receive the dividends directly as cash, which can be used to supplement their income or meet other financial needs. Alternatively, they can reinvest the dividends back into the policy to enhance its overall value, such as increasing the death benefit or growing the policy’s cash value.
Now that we understand the basics of life insurance policy dividends, let’s take a closer look at how these dividends are legally defined within the context of life insurance policies.
Definition of Dividends in Life Insurance
In the realm of life insurance, dividends are defined as the distribution of profits made by an insurance company to its policyholders who have participating life insurance policies. These dividends represent the policyholders’ share of the company’s surplus earnings.
Unlike dividends in the context of stocks, where shareholders receive a portion of the company’s profits, life insurance policy dividends function differently. In this case, policyholders are treated as participants in the company’s financial success. When an insurance company generates excess profits, eligible policyholders may receive dividends as a form of return on their investment.
Dividends in life insurance can be seen as a reflection of two key factors – the performance of the insurance company and the experience of the policyholders. When an insurance company earns profits beyond what is necessary to cover claims, expenses, and reserves, these excess earnings are distributed as dividends. The amount of dividends policyholders receive is typically based on their policy’s participation rate, which is determined by the terms and conditions of the policy.
It’s important to note that dividends are not guaranteed. The payment of dividends is contingent upon the insurance company’s financial performance and the terms of the policy. While some policies may offer a guaranteed minimum dividend, the actual amount can vary. Policyholders should review their policy and consult with their insurance provider to understand the specifics of dividend payments.
Dividends in life insurance policies can provide policyholders with several benefits. They offer the potential for increased policy value, provide additional financial support, and can be used to reduce future premiums or purchase paid-up additions. Ultimately, dividends add an element of flexibility and potential growth to participating life insurance policies, making them an attractive choice for many individuals.
Now that we have a clearer understanding of what dividends mean in the context of life insurance, let’s delve into the legal definition of dividends in life insurance policies to gain a deeper understanding of the requirements and regulations surrounding their payment.
Legal Definition of Dividend in Life Insurance Policies
From a legal perspective, the definition of a dividend in the context of life insurance policies is outlined in the insurance laws and regulations of the governing jurisdiction. These laws establish the framework within which insurance companies operate and specify the requirements regarding the payment of dividends to policyholders.
The legal definition of a dividend in life insurance policies typically includes the following key elements:
- Participating Policies: Dividends are only applicable to participating life insurance policies. These policies are structured in a way that allows policyholders to share in the company’s profits and participate in the distribution of dividends.
- Eligibility Criteria: Insurance laws usually set forth specific eligibility criteria for policyholders to receive dividends. This criteria may include factors such as the policy type, premium payment history, duration of the policy, and adherence to certain policy conditions.
- Profit Distribution Formula: Insurance laws may specify the formula or method by which insurance companies calculate and distribute dividends. This formula takes into account factors such as the company’s profitability, expenses, reserves, and the amount available for distribution among eligible policyholders.
- Disclosure Requirements: Insurance companies are typically required by law to provide clear and transparent information to policyholders about the potential for dividends, including how they are calculated, the frequency of distribution, and any conditions or limitations that apply.
- Governing Authority Approval: In some jurisdictions, insurance companies may need approval from the governing authority to distribute dividends to policyholders. This requirement ensures compliance with regulations and safeguards the interests of policyholders.
It’s important for policyholders to review their policy documentation and consult with their insurance provider to understand the specific legal definition of dividends in their jurisdiction. This will enable them to have a clear understanding of their rights and entitlement to receive dividends as part of their life insurance policy.
In the next section, we will explore the requirements for the payment of dividends in life insurance, shedding light on the conditions that must be met for policyholders to receive these financial benefits.
Requirements for Payment of Dividends in Life Insurance
In order to be eligible for the payment of dividends in a life insurance policy, policyholders must meet certain requirements outlined in the terms and conditions of their policy. These requirements may vary depending on the insurance company and the specific policy being held. Here are some common requirements for the payment of dividends in life insurance:
- Policy Type: Dividends are typically available only for participating life insurance policies. These policies are designed to allow policyholders to participate in the financial success of the insurance company by sharing in the company’s profits.
- Premium Payments: Policyholders must have a history of consistent premium payments. Payment of premiums is a fundamental requirement for the maintenance of the policy and eligibility for dividends. Late or missed premium payments may affect the policyholder’s ability to receive dividends.
- Policy Duration: Some policies require a minimum policy duration before policyholders become eligible for dividends. This ensures that policyholders have maintained their policies for a certain period of time and have demonstrated commitment to the policy.
- Policy Conditions: Certain policy conditions may need to be met for dividends to be paid. These conditions could include keeping the policy in force, abiding by specific policy provisions, and fulfilling any additional requirements stated in the policy contract.
- Participation Rate: The participation rate is a factor that determines the portion of the insurance company’s profits that policyholders are entitled to receive as dividends. This rate is set at the time of policy purchase and may vary based on the policy terms and conditions.
It’s important for policyholders to carefully review their policy documents and consult with their insurance provider to understand the specific requirements for dividend payment. Compliance with these requirements can ensure that policyholders receive their entitled dividends and maximize the benefits of their life insurance policies. Failure to meet these requirements may result in the forfeiture of potential dividend payments.
Now, let’s explore the taxation aspect of dividends in life insurance policies and understand how they are treated in terms of taxes.
Taxation of Dividends in Life Insurance Policies
The taxation of dividends in life insurance policies can vary depending on the jurisdiction and the specific tax laws in place. Generally, dividends received from life insurance policies are subject to specific tax treatment that distinguishes them from other types of income.
In many jurisdictions, life insurance policy dividends are considered to be a return of premium rather than ordinary income. This means that they are not typically subject to income tax. Since policyholders have already paid taxes on the premiums they have contributed, dividends are seen as a refund of a portion of those premiums rather than new income.
However, there are certain conditions that must be met for dividends to maintain their tax-exempt status. For example, the dividends may need to remain within the policy, either as additional insurance coverage or as a means to increase the policy’s cash value. If the dividends are withdrawn or taken as cash by the policyholder, they may be subject to taxation.
It’s important for policyholders to consult with a tax professional or financial advisor to understand the specific tax regulations that apply to dividends in their jurisdiction. This will ensure compliance with the tax laws and help policyholders make informed decisions regarding the use and withdrawal of dividends.
Furthermore, it’s important to note that if policyholders surrender or cancel their life insurance policy, any accumulated dividends may be subject to tax. This can occur if the policyholder receives more in dividends than they originally paid in premiums. In such cases, the excess amount may be deemed taxable as ordinary income.
Overall, the taxation of dividends in life insurance policies is designed to provide policyholders with favorable treatment. By understanding the tax implications, policyholders can make informed choices regarding the management and potential utilization of their dividends.
Now, let’s explore some common issues and disputes that may arise in relation to dividends in life insurance policies.
Common Issues and Disputes Regarding Dividends in Life Insurance
While dividends in life insurance policies are intended to provide additional value and benefits to policyholders, there can be situations where issues and disputes arise. Here are some common issues and disputes that policyholders may encounter in relation to dividends:
- Non-Payment: One of the most common issues is when an insurance company fails to pay dividends that policyholders believe they are entitled to. This can occur due to errors, misinterpretation of policy terms, or disputes over the calculation or availability of dividends. In such cases, policyholders should communicate with their insurance provider to address the issue and seek resolution.
- Reduction in Dividends: Insurance companies have the right to reduce or even eliminate dividend payments if they face financial difficulties or poor investment performance. While reductions are typically rare, they can occur. Policyholders should review their policy terms to understand the company’s rights in relation to dividend payments and be aware of any potential changes in dividend amounts.
- Dividend Crediting Methods: Insurance companies may use various methods to credit dividends to policyholders. These methods can include using a percentage of the policy’s face value, the policy’s cash value, or a combination of both. Some policyholders may have disputes over the chosen crediting method and its impact on the overall value of the policy.
- Policy Adjustments: Dividends can impact the policy’s overall performance and value. Some policyholders may have concerns or disputes regarding how dividends affect premium amounts, cash value accumulation, or death benefit adjustments. It is important for policyholders to understand how dividends interact with their specific policy type and features.
- Transparency and Communication: Clear communication and transparency from the insurance company regarding dividend calculations, distribution, and changes in dividend policies are essential. Policyholders may have disputes or concerns if they feel that the insurance company is not providing adequate information or explanations regarding dividend-related matters.
In the event of any issues or disputes related to dividends in a life insurance policy, it is recommended that policyholders communicate with their insurance provider directly. Discussing the concerns, seeking clarification, and reviewing the policy contract can help in resolving disputes and finding a mutually agreeable solution.
It’s important for policyholders to regularly review their life insurance policy and stay informed about dividend-related matters. By staying vigilant and proactive, policyholders can ensure that they fully understand their entitlements, rights, and any potential issues that may arise regarding dividends in their life insurance policies.
Now, let’s wrap up our exploration of life insurance policy dividends.
Conclusion
Life insurance policy dividends provide an additional layer of benefits and potential value to policyholders. While not all life insurance policies offer dividends, participating policies allow policyholders to share in the financial success of the insurance company through the distribution of dividends.
Dividends in life insurance are not guaranteed and vary based on the insurance company’s financial performance and the terms of the policy. Policyholders must meet specific requirements, such as consistent premium payments and adherence to policy conditions, to be eligible to receive dividends.
From a legal perspective, dividends in life insurance policies are defined by insurance laws and regulations. These laws outline the eligibility criteria, profit distribution formula, and disclosure requirements that insurance companies must adhere to when paying dividends to policyholders.
Taxation of dividends in life insurance policies varies depending on the jurisdiction. Generally, dividends are considered a return of premium and are not subject to income tax. However, specific conditions must be met for dividends to maintain their tax-exempt status.
Common issues and disputes regarding dividends in life insurance policies can arise, such as non-payment, reduction in dividends, concerns over dividend crediting methods, policy adjustments, and lack of transparency or communication. It is important for policyholders to address these issues directly with their insurance provider and seek resolution.
Understanding the basics, legal definitions, requirements, taxation, and potential issues involved in life insurance policy dividends empowers policyholders to make informed decisions about their life insurance coverage. By staying informed and proactive, policyholders can fully utilize the benefits of dividends and maximize the value of their life insurance policies.
Remember, if you have specific questions or concerns about dividends in your life insurance policy, it is advisable to consult with a qualified insurance professional or financial advisor who can provide personalized guidance based on your unique circumstances.