Home>Finance>How Often Should A Risk Assessment Be Conducted?


Finance
How Often Should A Risk Assessment Be Conducted?
Published: January 15, 2024
Find out the ideal frequency for conducting risk assessments in finance to ensure proper risk management and mitigate potential threats.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
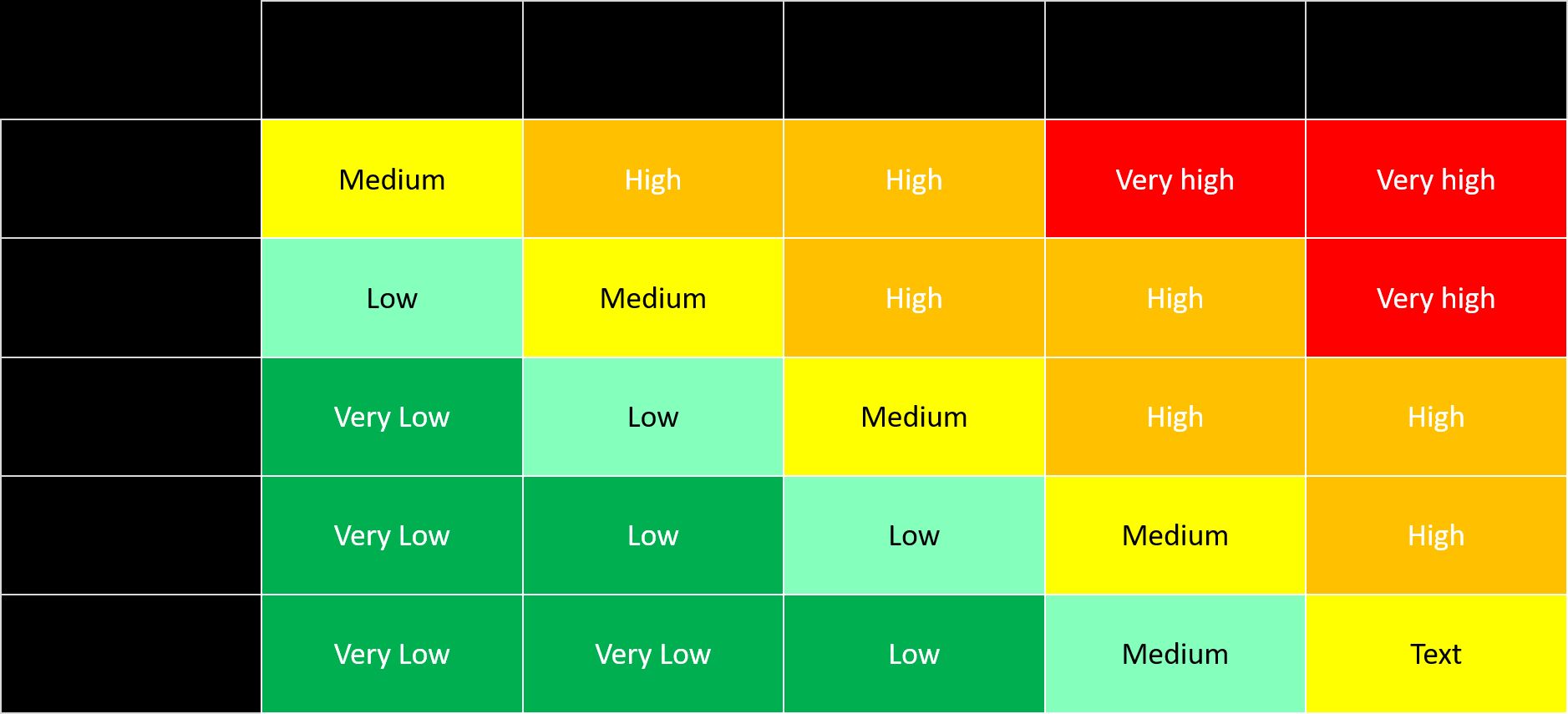
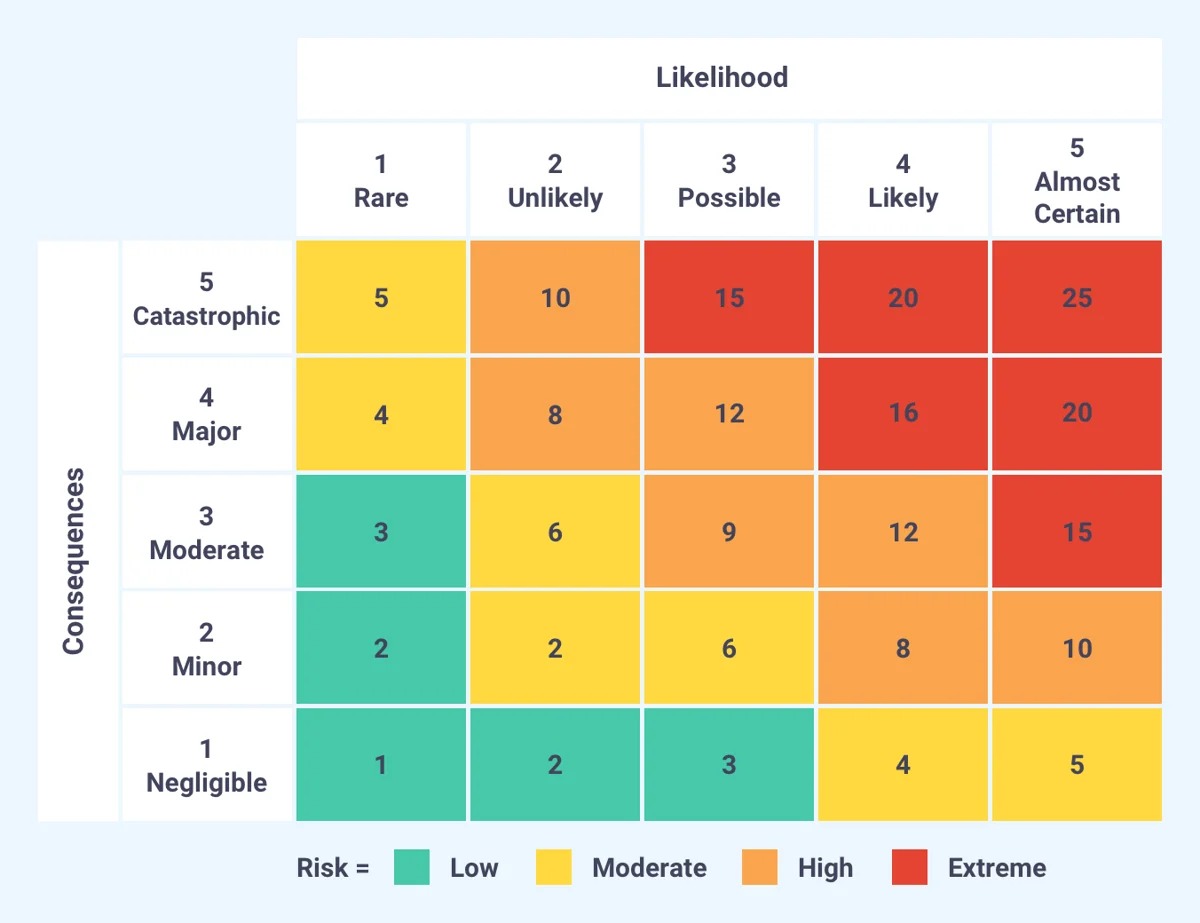
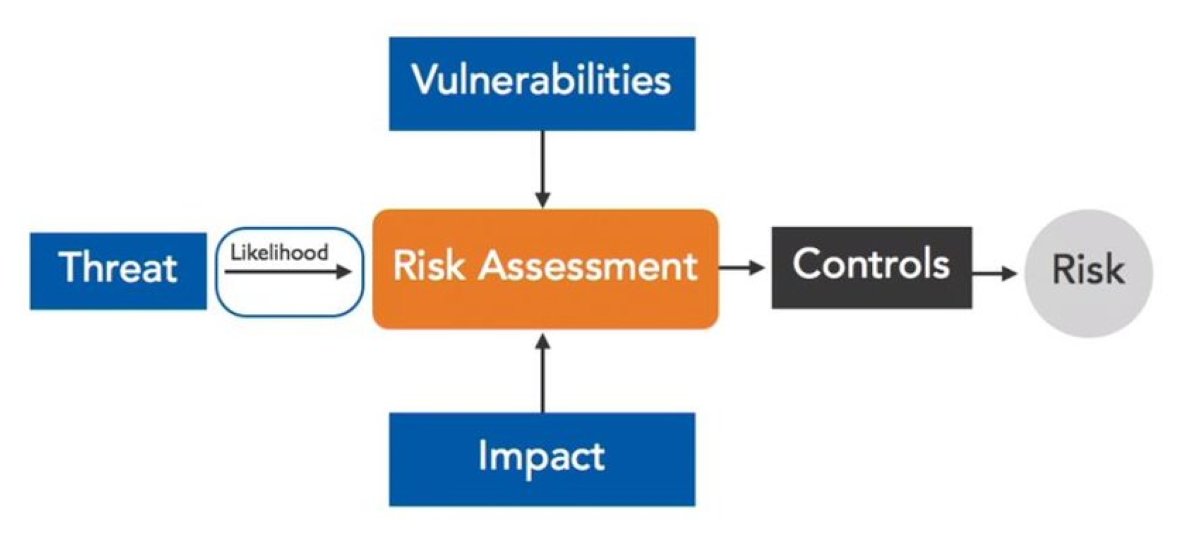
When it comes to managing risks in the finance industry, conducting regular risk assessments is vital. A risk assessment is a systematic process of identifying, analyzing, and evaluating potential risks that could impact a business or organization. By identifying these risks, financial institutions can develop effective strategies to mitigate them and protect their assets.
Risk assessments are not a one-time event; they need to be conducted regularly to stay ahead in an ever-changing financial landscape. But how often should a risk assessment be conducted? The frequency of risk assessments depends on several factors, including legal requirements, industry standards, and the nature of the business itself.
In this article, we will explore the importance of risk assessments in the finance industry and discuss the various factors that influence the frequency of conducting risk assessments. We will also delve into different timelines for conducting risk assessments, ranging from annual assessments to continuous monitoring, to help businesses determine how often they should evaluate their risks.
Importance of Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is a crucial process that helps financial institutions identify, analyze, and evaluate potential risks to their operations, financial stability, and reputation. It plays a pivotal role in the decision-making process and helps organizations prioritize their resources and efforts towards risk mitigation.
There are several key reasons why risk assessments are important in the finance industry:
- Proactive Risk Management: By conducting regular risk assessments, financial institutions can proactively identify potential risks before they escalate into major issues. This enables them to take preventive measures and develop risk management strategies to mitigate the impact.
- Compliance with Regulations: Financial institutions operate in a heavily regulated environment. Conducting risk assessments helps organizations ensure compliance with various regulatory requirements and guidelines. It allows them to identify any gaps in their compliance procedures and take corrective actions to avoid penalties and reputational damage.
- Protecting Assets and Financial Stability: The finance industry deals with significant financial assets, sensitive data, and client information. Regular risk assessments help identify vulnerabilities and potential threats to these assets, enabling organizations to implement appropriate controls and safeguards to protect against fraud, cyberattacks, or other security breaches.
- Enhancing Business Continuity: By evaluating risks and implementing mitigation measures, financial institutions can improve their overall business continuity preparedness. Risk assessments enable organizations to identify potential disruptions and develop contingency plans to ensure the smooth operation of critical functions, even in challenging circumstances.
- Gaining Stakeholder Confidence: Conducting regular risk assessments demonstrates a commitment to risk management and sound governance practices. This instills confidence in stakeholders, including clients, investors, and regulators, as they see that the organization is proactive in identifying and managing risks.
Overall, risk assessments are essential for financial institutions to stay proactive, compliant, and resilient in a dynamic and rapidly evolving industry. By identifying risks early on and implementing appropriate controls, organizations can safeguard their assets, maintain their reputation, and instill confidence in their stakeholders.
Factors to Consider
When determining the frequency of conducting risk assessments in the finance industry, several factors need to be taken into account. These factors will help organizations assess the level of risk they face and determine the appropriate timeline for conducting assessments. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Regulatory Requirements: Financial institutions must comply with various regulatory guidelines and requirements set by governing bodies. These regulations often specify the frequency of risk assessments. Organizations need to ensure they meet these obligations to maintain regulatory compliance.
- Industry Standards and Best Practices: Different sectors within the finance industry may have specific standards and best practices regarding risk assessments. Organizations should align with these industry-specific guidelines and consider the recommendations when determining the frequency of risk assessments.
- Business Complexity and Nature: The complexity and nature of the business can influence the level of risk it faces. Organizations dealing with intricate financial products or operating in volatile markets may need more frequent risk assessments to stay ahead of potential risks and market fluctuations.
- Internal Controls and Risk Management Framework: Organizations with robust internal controls and a well-established risk management framework may require less frequent risk assessments. Conversely, organizations with weaker controls or a history of risk incidents may need more regular assessments to strengthen their risk management practices.
- External Factors: External factors, such as changes in regulations, economic conditions, or technological advancements, can significantly impact the risk landscape. Organizations need to consider these external factors when determining the frequency of risk assessments to ensure they remain proactive in identifying and managing emerging risks.
- Historical Risk Incidents: Organizations should assess their past risk incidents and the frequency with which they have occurred. If there have been frequent incidents or near misses, it may indicate the need for more frequent risk assessments to address the underlying vulnerabilities.
It is essential for organizations to take a comprehensive approach and consider these factors collectively. By assessing these key factors, financial institutions can develop a risk assessment frequency that is tailored to their specific needs, enabling them to maintain a proactive and effective risk management strategy.
Legal and Industry Requirements
In the finance industry, risk assessments are not only best practice but also often mandated by legal and industry-specific requirements. These requirements outline the minimum standards that organizations must meet to ensure the soundness and stability of their operations. Here are some key legal and industry requirements to consider:
- Regulatory Compliance: Financial institutions are subject to various regulatory bodies, such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA), or the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC). These regulatory bodies often mandate specific risk assessment requirements that organizations must follow to ensure compliance.
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX): Publicly traded companies in the United States are required to comply with the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, which includes provisions for internal controls and risk assessments. Section 404 of SOX specifically requires organizations to assess and evaluate their internal control over financial reporting.
- Industry-Specific Standards: Different sectors within the finance industry may have industry-specific standards that organizations must adhere to. For example, banks may need to follow the Basel III framework, which includes risk assessment requirements to ensure the stability of the banking system.
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS): Organizations that handle credit card transactions are required to comply with the PCI DSS. This standard includes requirements for conducting regular risk assessments to identify and address potential vulnerabilities in payment card processing systems.
- International Standards: Depending on the global reach of the organization, international standards such as ISO 31000 (Risk Management) or ISO 27001 (Information Security Management) may need to be considered when determining risk assessment frequency.
Organizations must familiarize themselves with the applicable legal and industry requirements and ensure they meet the mandated risk assessment standards. Failure to comply with these requirements can result in penalties, reputational damage, and potentially legal implications.
It is important for financial institutions to stay up to date with any changes in regulations and industry standards that may impact their risk assessment practices. Regularly monitoring legal and industry requirements will help organizations maintain compliance and uphold the highest standards of risk management.
Frequency of Risk Assessment
The frequency of conducting risk assessments in the finance industry can vary based on several factors, including legal requirements, industry standards, and the specific needs of the organization. Different timelines for risk assessment allow financial institutions to adapt their risk management strategies based on changing circumstances. Here are some common timelines for conducting risk assessments:
Annual Risk Assessment
An annual risk assessment is a common practice for many financial institutions. Conducting a comprehensive assessment once a year allows organizations to evaluate the overall risk landscape, identify emerging risks, and update their risk management strategies accordingly. This timeframe provides sufficient time to gather and analyze data, involve key stakeholders, and implement risk mitigation measures.
Quarterly Risk Assessment
For organizations operating in dynamic and rapidly changing environments, conducting quarterly risk assessments may be more appropriate. This frequency enables financial institutions to assess risks on a more regular basis, identify any shifts in the risk landscape, and make timely adjustments to their risk mitigation strategies. Quarterly assessments allow for proactive risk management and help organizations stay agile in response to new challenges.
Project-based Risk Assessment
In addition to regular assessments, organizations may conduct risk assessments on a project-by-project basis. This is particularly relevant for financial institutions involved in large-scale projects, such as mergers and acquisitions, new product launches, or expansions into new markets. Project-based risk assessments help identify and manage risks specific to the project and ensure that risk mitigation measures are in place throughout its lifecycle.
Continuous Risk Assessment
Some financial institutions opt for continuous risk assessment, where risk identification and evaluation occur on an ongoing basis. This approach involves real-time monitoring of risks, leveraging technology and data analytics to detect emerging threats promptly. Continuous risk assessment allows organizations to respond swiftly and proactively to changes in the risk landscape, ensuring that risk management strategies are always up to date.
It is important for organizations to carefully evaluate their risk profiles, business environment, and regulatory requirements when determining the frequency of risk assessments. By aligning the assessment frequency with their specific needs, financial institutions can effectively identify and manage risks and maintain a robust risk management framework.
Annual Risk Assessment
An annual risk assessment is a widely adopted practice in the finance industry. Conducting a comprehensive assessment once a year allows financial institutions to evaluate the overall risk landscape, identify potential risks, and develop effective risk mitigation strategies. Here are some key considerations for an annual risk assessment:
- Data Collection and Analysis: Conducting an annual risk assessment involves collecting and analyzing a vast amount of data from various sources. This includes reviewing internal policies and procedures, conducting interviews with key stakeholders, analyzing historical risk incidents, external market trends, and regulatory changes. The goal is to obtain a comprehensive understanding of the organization’s risk exposure.
- Risk Identification and Evaluation: Once the data is collected, financial institutions can identify and evaluate risks across different business areas and functions. This includes assessing risks in areas such as credit, market, operational, legal, and compliance. The evaluation process involves quantifying the potential impact and likelihood of risks occurring, prioritizing them based on their significance.
- Risk Mitigation Strategies: After the risk assessment, financial institutions develop risk mitigation strategies to manage identified risks effectively. This may involve implementing controls, enhancing technology infrastructure, improving policies and procedures, or revising risk transfer mechanisms such as insurance coverage. The strategies aim to reduce the likelihood and impact of risks.
- Stakeholder Engagement: An annual risk assessment involves engaging with key stakeholders within the organization. This may include executives, risk management teams, compliance officers, and internal auditors. By involving stakeholders, financial institutions can utilize their expertise and perspectives, ensuring that all relevant risks are considered, and mitigation strategies are well-informed.
- Documentation and Reporting: It is essential to document the findings, analysis, and mitigation strategies resulting from the annual risk assessment. This documentation serves as a reference for future assessments and provides evidence of the organization’s risk management efforts. Additionally, reporting the outcomes to management, the board of directors, and regulators demonstrates transparency and compliance with regulatory requirements.
An annual risk assessment provides financial institutions with a holistic view of their risk landscape and enables them to adapt their risk management strategies accordingly. While an annual assessment offers a comprehensive approach, it is important for organizations to remain vigilant throughout the year and address emerging risks promptly, even in between assessments.
Financial institutions should review their risk assessment methodology regularly to ensure it remains relevant and effective. By consistently improving their risk assessment processes, organizations can enhance their ability to identify, evaluate, and mitigate risks, thereby strengthening their overall risk management framework.
Quarterly Risk Assessment
For financial institutions operating in dynamic and rapidly changing environments, conducting quarterly risk assessments is an effective risk management approach. Quarterly assessments allow organizations to monitor risks on a more frequent basis, identify shifts in the risk landscape, and make timely adjustments to their risk mitigation strategies. Here are the key aspects of conducting a quarterly risk assessment:
- Data Gathering: Quarterly risk assessments involve collecting relevant data from multiple sources, including internal systems, market trends, regulatory updates, and emerging risks. It is important to ensure that the data being collected is accurate, up-to-date, and comprehensive.
- Risk Identification and Evaluation: Once the data is gathered, financial institutions can identify and evaluate risks specific to the quarter. This involves categorizing risks into various areas such as credit, market, operational, regulatory, and reputational risks. Each risk is then assessed based on its potential impact and likelihood of occurrence in the short term.
- Updating Risk Profiles: Quarterly risk assessments provide an opportunity to update the organization’s risk profiles. By considering the identified risks, financial institutions can revise and refine their risk profiles to reflect the current risk landscape accurately.
- Risk Mitigation Strategies: Following the evaluation of risks, financial institutions develop and adjust risk mitigation strategies for the upcoming quarter. This may involve implementing additional controls, enhancing monitoring systems, training employees on new risk protocols, or updating policies and procedures.
- Internal Reporting: It is crucial to communicate the findings and recommendations resulting from the quarterly risk assessment within the organization. This ensures that stakeholders are aware of emerging risks and the action plans in place to mitigate them. Internal reporting facilitates better collaboration and alignment between business functions.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Review: Quarterly risk assessments are part of an ongoing monitoring process. It is essential to continuously review and assess the effectiveness of risk mitigation strategies, respond to new risks, and make necessary adjustments as the business environment evolves throughout the quarter.
The frequency of quarterly risk assessments allows financial institutions to stay agile in responding to emerging risks and market fluctuations. By conducting assessments more frequently, organizations can identify risks in a timely manner, take proactive measures to address them, and adapt their risk management strategies according to changing circumstances. However, it is important to note that even with quarterly risk assessments, organizations should maintain a continuous awareness of risks and adjust controls when necessary.
Financial institutions should document the findings and actions resulting from quarterly risk assessments to maintain a comprehensive record of their risk management efforts. Regularly reviewing and analyzing these records can help organizations identify patterns, trends, and areas for improvement, ultimately enhancing their overall risk management effectiveness.
Project-based Risk Assessment
Project-based risk assessments are essential for financial institutions involved in specific initiatives or projects that carry inherent risks. Whether it’s a merger and acquisition, new product launch, or expansion into a new market, conducting a project-based risk assessment helps organizations identify and manage risks that are unique to the project. Here are the key aspects of conducting a project-based risk assessment:
- Project Risk Identification: The first step in a project-based risk assessment is to identify the risks associated with the specific project. This involves analyzing the project’s objectives, scope, stakeholders, timelines, and potential impacts on the organization.
- Risk Analysis and Evaluation: After identifying the project risks, financial institutions analyze and evaluate their potential impact and likelihood of occurrence. This process helps prioritize risks and allocate resources effectively to mitigate them.
- Risk Mitigation Strategies: Once the risks are evaluated, organizations develop tailored risk mitigation strategies for the project. This may involve implementing additional controls, conducting training programs, establishing contingency plans, or allocating sufficient budget and resources.
- Monitoring and Control: Throughout the project lifecycle, financial institutions monitor the identified risks and assess their effectiveness in managing them. Regular monitoring allows for the timely identification of emerging risks and the implementation of necessary adjustments to mitigate them.
- Continuous Communication: Communication among project stakeholders is critical during a project-based risk assessment. Clear and consistent communication ensures that all stakeholders are aware of the identified risks, the mitigation strategies in place, and any changes or updates to the risk profile.
- Periodic Review: It is essential to periodically review the project-based risk assessment to track the progress of risk mitigation efforts and identify any changes in the risk landscape. This enables organizations to adapt their strategies as the project evolves.
Project-based risk assessments provide financial institutions with a focused approach to manage risks that are specific to a particular project. By conducting these assessments, organizations can anticipate potential pitfalls, minimize project delays or failures, and enhance the likelihood of project success. It is crucial to integrate project-based risk assessments into the overall risk management framework of the organization.
Applying project-based risk assessments reinforces the importance of risk management in all aspects of the organization’s operations. It promotes a proactive approach to identifying, evaluating, and mitigating risks, ensuring that risks are adequately managed throughout the project’s lifecycle. Effective project risk management ultimately contributes to the successful accomplishment of organizational objectives and boosts overall business performance.
Continuous Risk Assessment
Continuous risk assessment is a proactive approach to risk management that involves monitoring risks in real-time rather than relying on periodic assessments. In today’s rapidly changing financial landscape, where new risks can emerge at any time, conducting continuous risk assessments can provide financial institutions with a competitive advantage. Here are the key aspects of continuous risk assessment:
- Real-time Risk Monitoring: Continuous risk assessment involves monitoring risks on an ongoing basis. This can be accomplished through the use of advanced technologies, data analytics tools, and automated risk monitoring systems. By continuously monitoring risks, financial institutions can detect emerging threats and take immediate action to mitigate them.
- Data-driven Risk Analysis: Continuous risk assessment relies on analyzing real-time data to identify and evaluate risks. Financial institutions collect, analyze, and interpret data from various sources, including internal systems, external market data, news feeds, and social media. This data-driven approach enables organizations to make informed decisions to mitigate risks and respond to changing risk profiles.
- Alerts and Early Warning Systems: Continuous risk assessment involves setting up alerts and early warning systems that notify stakeholders about potential risks. These systems automatically trigger alerts when a risk threshold is breached or when certain risk indicators show unusual patterns. Early warnings allow organizations to react promptly and implement mitigation strategies before risks escalate.
- Collaboration and Communication: Continuous risk assessment requires regular collaboration and communication among stakeholders. This includes risk management teams, business units, compliance officers, and senior executives. Effective communication ensures that all relevant parties are aware of the identified risks, their potential impact, and the actions taken to address them.
- Adaptive Risk Mitigation Strategies: With continuous risk assessment, financial institutions can adapt and update their risk mitigation strategies in real-time. As new risks are identified or existing risks evolve, organizations can adjust their controls, policies, and procedures to ensure the effectiveness of risk mitigation measures. This agility allows them to stay ahead of potential risks and respond swiftly to changes in the risk landscape.
Continuous risk assessment complements the traditional periodic assessments by providing a more dynamic and up-to-date view of risks. It allows financial institutions to proactively manage risks, detect early warning signs, and respond in a timely manner. By continuously assessing risks, organizations can demonstrate a commitment to effective risk management and maintain a robust risk culture.
Implementing continuous risk assessment requires a strong foundation in data analysis, risk analytics expertise, and technological capabilities. Financial institutions should invest in the necessary tools and systems to enable real-time risk monitoring and analysis. By embracing continuous risk assessment, organizations can anticipate and mitigate risks more effectively, protect their assets, and enhance their overall risk culture and resilience.
Conclusion
Risk assessment is a critical component of effective risk management in the finance industry. The frequency of conducting risk assessments depends on various factors, including legal requirements, industry standards, and the specific needs of the organization. By evaluating risks, financial institutions can implement effective strategies to mitigate them and safeguard their operations, financial stability, and reputation.
Annual risk assessments provide a comprehensive overview of the risk landscape and allow organizations to update their risk management strategies accordingly. Quarterly risk assessments offer a more frequent evaluation of risks, ensuring that financial institutions can proactively identify and address emerging risks in a rapidly changing environment. Project-based risk assessments focus on risks specific to a particular project, enabling organizations to manage project-related risks effectively.
For organizations seeking a more proactive approach, continuous risk assessment allows for real-time monitoring and analysis of risks. This approach enables financial institutions to detect emerging threats promptly and adapt their risk mitigation strategies accordingly.
It is important for financial institutions to remember that risk assessment is not a one-time event but an ongoing process. Regular evaluation and adjustment of risk management strategies are essential to proactively manage risks and maintain a robust risk culture. Additionally, compliance with legal and industry requirements is crucial to ensure sound risk management practices and regulatory adherence.
By conducting risk assessments at the appropriate frequency and aligning them with the specific needs of the organization, financial institutions can effectively identify, evaluate, and mitigate risks. This proactive approach to risk management enhances business resilience, protects assets, and instills confidence in stakeholders.
In conclusion, conducting risk assessments at the right frequency is a vital aspect of risk management in the finance industry. Organizations must carefully consider legal requirements, industry standards, and their unique risk profiles to determine the most suitable timeline for risk assessments. By doing so, financial institutions can proactively manage risks, adapt to changes in the risk landscape, and ensure long-term success and sustainability.