
Finance
How To Bill Insurance
Published: November 18, 2023
Learn how to bill insurance for your finance needs and maximize your reimbursement. Master the process of filing claims and navigating through insurance policies.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
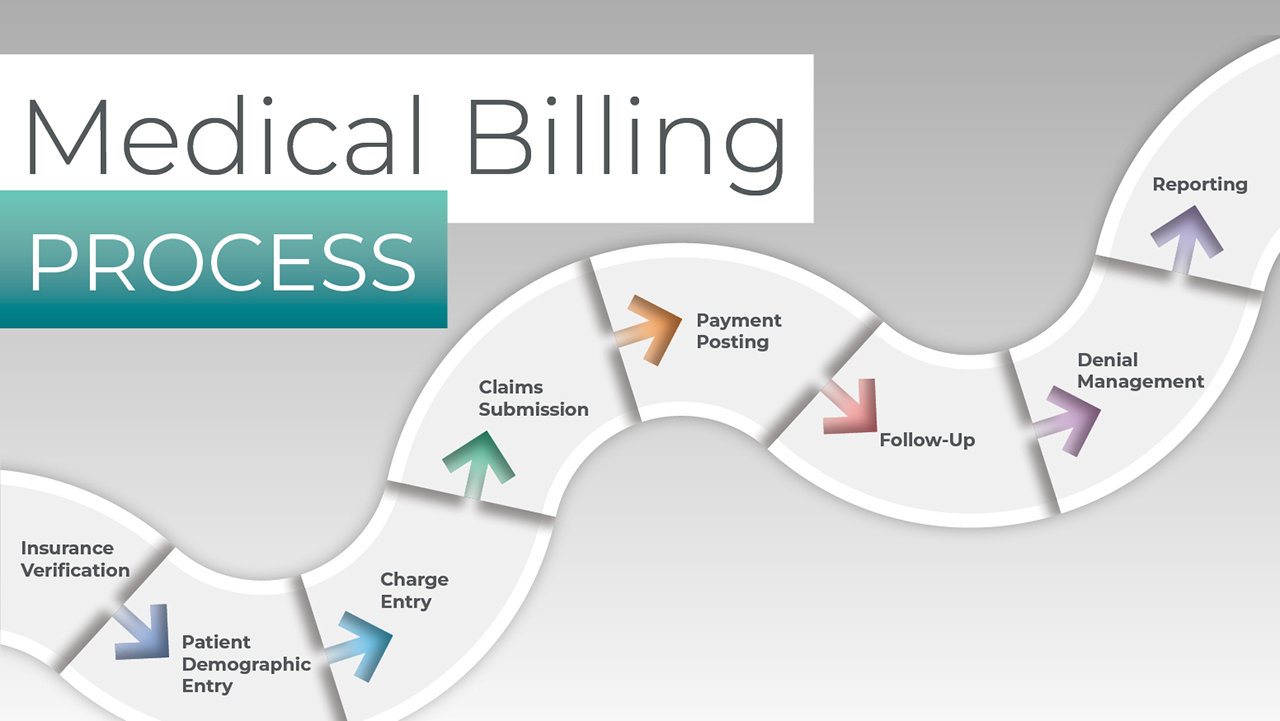
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Insurance Billing
- Gathering Patient Information
- Verifying Insurance Coverage
- Coding Properly
- Submitting Claims
- Following Up on Claims
- Handling Insurance Denials
- Appealing Denied Claims
- Resubmitting Claims
- Understanding Reimbursement
- Tracking Payments
- Dealing with Insurance Audits
- Maintaining Compliance
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to the world of insurance billing! Whether you are a healthcare provider or a medical billing specialist, understanding how to effectively bill insurance is crucial for ensuring timely reimbursement and maintaining a smooth financial workflow. Insurance billing involves the process of submitting claims to insurance companies on behalf of patients to receive payment for medical services rendered. It is a complex yet essential aspect of healthcare administration that requires a deep understanding of insurance policies, coding guidelines, and proper documentation.
In this article, we will guide you through the fundamental steps involved in insurance billing. From gathering patient information to submitting claims and dealing with denials, we will provide you with the knowledge and strategies to navigate this intricate landscape successfully. We will also cover the importance of proper coding, tracking payments, handling insurance audits, maintaining compliance, and much more.
It is essential to note that insurance billing practices can vary depending on the type of insurance plan, whether it is private insurance, Medicare, Medicaid, or a managed care organization. Different insurance companies may also have specific requirements and guidelines. Therefore, it is crucial to stay up-to-date with the latest industry changes and adapt your billing processes accordingly.
So, whether you are new to insurance billing or looking to refine your skills, let’s embark on this informative journey together and learn how to navigate the ins and outs of billing insurance effectively.
Understanding Insurance Billing
Before diving into the intricacies of insurance billing, it is crucial to have a solid understanding of the basics. Insurance billing refers to the process of submitting claims to insurance companies for reimbursement of medical services provided to patients. The goal is to receive timely and accurate payment for the services rendered.
Insurance billing involves various stakeholders, including healthcare providers, patients, and insurance companies. As a healthcare provider, you need to have detailed knowledge of the insurance plans you accept, as well as the specific requirements and guidelines of each insurance company.
When a patient receives medical services, the provider generates a claim that includes relevant details such as the patient’s demographics, diagnosis codes, procedure codes, and the provider’s information. This information is submitted to the insurance company, either electronically or through paper claims.
The insurance company then reviews the claim, processes it, and determines the amount to be reimbursed based on the patient’s insurance coverage and the provider’s contract with the insurance company. The reimbursement may vary depending on factors such as deductibles, co-pays, and coverage limitations.
It is important to note that insurance billing follows specific coding guidelines to ensure accurate and consistent documentation. The two main coding systems used are the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) and the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code sets. These codes classify medical diagnoses and procedures and help facilitate proper reimbursement.
Understanding insurance billing also requires familiarity with common terminology such as Explanation of Benefits (EOB), which is a document sent by the insurance company to the patient and provider explaining how the claim was processed and indicating the amount of reimbursement.
Furthermore, it is essential to keep abreast of changes in insurance regulations and policies, as they can impact the billing and reimbursement process. Staying informed about code updates, documentation requirements, and industry changes is vital to ensure compliance and maximize reimbursement.
In the next sections, we will delve into the step-by-step process of insurance billing, from gathering patient information to submitting claims, and effectively handling denials and audits. Let’s explore each stage in detail and equip ourselves with the knowledge and tools needed for successful insurance billing.
Gathering Patient Information
One of the essential steps in the insurance billing process is gathering accurate and complete patient information. Properly documenting patient demographics and insurance details is crucial for a successful claim submission and reimbursement.
When a patient arrives at your healthcare facility, it is vital to collect their personal information, including their full name, date of birth, address, and contact information. This information serves as the foundation for creating a patient record and initiating the billing process.
In addition to personal details, it is imperative to acquire the patient’s insurance information. This includes their insurance carrier, policy number, group number (if applicable), and the name of the primary insured (if different from the patient). Insurance information should be collected at the initial visit and updated as needed.
If a patient has multiple insurance policies, it is crucial to determine which one is primary and which is secondary. Understanding the coordination of benefits and ensuring proper sequencing of claims is essential for accurate reimbursement. You may need to ask the patient to provide a copy of their insurance card for verification purposes.
Another vital aspect of gathering patient information is obtaining a signed consent form that authorizes the healthcare provider to bill their insurance and release relevant medical information. This consent form ensures compliance with privacy regulations and protects patient confidentiality.
In some cases, patients may be covered by government-sponsored programs such as Medicare or Medicaid. It is essential to gather the necessary documentation to confirm eligibility and establish the proper billing procedures for these programs.
Having a streamlined process for collecting and verifying patient information is crucial for accurate and efficient insurance billing. Utilizing electronic health record (EHR) systems and practice management software can help automate this process, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
Remember, timely and accurate patient information is the backbone of the insurance billing process. Gathering complete and up-to-date information at the outset ensures a smooth billing workflow and increases the chances of successful claim submission and reimbursement.
Verifying Insurance Coverage
Verifying insurance coverage is a crucial step in the insurance billing process. It involves confirming the patient’s insurance eligibility, coverage details, and any specific requirements or limitations that may impact the claim submission.
Before providing any medical services, it is important to verify the patient’s insurance coverage. This can be done by contacting the insurance company directly, using online portals or electronic eligibility systems, or outsourcing verification services to a third-party company. The goal is to ensure that the patient is active and covered by insurance on the date of service.
During the verification process, healthcare providers should gather important information such as the effective date of coverage, coverage limitations (such as pre-existing conditions or max benefit allowances), co-pay or deductible amounts, and any specific requirements, such as prior authorizations or referrals.
Verifying insurance coverage helps prevent claim denials and reduces the risk of non-payment. It allows providers to determine if a patient’s insurance will cover the services being rendered and if any out-of-pocket costs will be incurred by the patient.
It is important to note that insurance coverage can change, so it is good practice to re-verify insurance before subsequent visits or when there are significant gaps in treatment. This helps ensure that the most accurate and up-to-date information is used for claim submission.
Verifying insurance coverage is especially crucial when dealing with new patients or when there are changes in insurance plans. It helps avoid surprises and improves the financial transparency of the healthcare encounter for both the provider and the patient.
Utilizing electronic eligibility systems or software can simplify the verification process by automating the retrieval of insurance information. These systems can streamline the verification process and save valuable time and resources.
Remember, verifying insurance coverage is an integral part of the insurance billing process. It helps determine the patient’s financial responsibility, ensures accurate claim submission, and improves the overall revenue cycle management.
Coding Properly
Coding plays a crucial role in insurance billing, as accurate coding ensures proper reimbursement and minimizes the risk of claim denials. Proper coding involves assigning the correct diagnosis and procedure codes based on the services provided during a patient’s visit.
The two main coding systems used in healthcare are the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) and the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code sets. The ICD codes are used to capture the patient’s diagnosis, while the CPT codes describe the procedures or services performed.
To code properly, healthcare providers should document the patient’s medical conditions, symptoms, and any relevant tests or treatments performed during the visit. It is crucial to document all services rendered adequately and in sufficient detail to support the assigned codes.
Medical coding professionals or billing specialists are responsible for translating the medical documentation into the appropriate codes. They must have a solid understanding of the coding guidelines and conventions to ensure accurate coding.
Healthcare providers should also stay updated with the latest coding changes and updates. The coding guidelines and rules can change annually, so it is essential to use the most current code sets and documentation requirements.
Inaccurate coding can result in claim denials or delayed payments. Common coding errors include coding for services not performed, using incorrect codes, or failing to provide sufficient documentation to support the codes assigned.
Proper coding also helps avoid fraudulent activities and ensures compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. It is imperative to code and bill only for services that were medically necessary and provided to the patient.
As part of the documentation process, healthcare providers should maintain a standardized approach to coding by establishing coding protocols and ensuring consistent training for coding staff. Regular audits and reviews of coding practices can identify areas for improvement and help maintain accuracy.
Utilizing electronic health record (EHR) systems with integrated coding functionality can enhance the coding process by providing prompts and suggestions based on the documented clinical information. These systems can help streamline coding workflows and improve accuracy.
Remember, accurate coding is crucial for successful insurance billing. By capturing the right diagnosis and procedure codes, healthcare providers can maximize reimbursement, ensure compliance, and maintain a healthy revenue cycle.
Submitting Claims
Submitting claims is a critical step in the insurance billing process, as it involves sending the necessary documentation to the insurance company for reimbursement. Properly submitting claims ensures timely payment and reduces the risk of claim denials or rejections.
Before submitting a claim, it is important to ensure that all required information is accurate and complete. This includes the patient’s demographics, insurance information, diagnosis codes, procedure codes, and any supporting documentation such as medical records or test results.
The method of claim submission can vary depending on the insurance company and their preferred submission process. Most insurance companies now encourage electronic claim submission, which allows for faster processing and reduces the chance of errors.
Electronic claim submission involves using designated billing software or clearinghouses to send claims electronically to the insurance company. The software or clearinghouse validates the data before transmitting it, flagging any potential errors or missing information that may cause the claim to be rejected.
If electronic claim submission is not possible, paper claims can be utilized. Paper claims require the completion of the appropriate claim forms, including the CMS-1500 form for professional services or the UB-04 form for institutional services. It is essential to ensure that the forms are filled out correctly and legibly to avoid delays or rejections.
Prior to submitting the claim, it is also important to verify that the correct insurance company address or electronic claim submission address is used. Sending the claim to the wrong address or using an outdated address can result in claim delays or non-payment.
Once the claim is submitted, it is important to track and monitor its progress. This can be done by using billing software or online portals provided by the insurance company. Tracking the claim allows for proactive follow-up in case of delays or rejections.
Keep in mind that each insurance company may have different timelines for claim processing. Some claims may be processed and paid within a few weeks, while others may take several weeks or even months.
In some cases, insurance companies may request additional information or clarification through a process called a “claim review” or “adjudication.” It is important to respond promptly to these requests to avoid delays in payment.
Remember, submitting claims accurately and in a timely manner is crucial for ensuring proper reimbursement. Utilizing electronic claim submission, double-checking the claim information, and tracking the progress of claims can help streamline the process and improve the revenue cycle.
Following Up on Claims
Following up on submitted claims is a crucial part of the insurance billing process. It involves tracking the progress of claims and proactively addressing any issues or delays to ensure timely reimbursement.
After submitting a claim, it is important to monitor its status regularly. Most insurance companies provide online portals or automated phone systems that allow healthcare providers to check the status of their claims. These tools provide real-time updates on whether the claim has been received, processed, or paid.
As part of the follow-up process, it is essential to verify that the claim has been received by the insurance company. Sometimes, claims may get lost in transit or misrouted, leading to unnecessary delays. If a claim has not been received within the expected timeframe, contacting the insurance company to inquire about its status is recommended.
In cases where a claim is denied or rejected, it is important to follow up promptly to resolve the issue. Common reasons for claim denials or rejections include incomplete or inaccurate information, eligibility issues, coding errors, or missing documentation. Understanding the reason for the denial and taking appropriate action, such as providing additional information or appealing the decision, is crucial for obtaining payment.
When following up on claims, it is important to document all communication and maintain accurate records of the dates, times, and individuals spoken to. This information can be useful in case of disputes or further inquiries.
To effectively follow up on claims, establishing clear and efficient communication channels with insurance company representatives is essential. This may involve designated contacts or account representatives who can provide support and assist in resolving issues related to claim processing.
Automation and technology can also play a key role in streamlining the follow-up process. Utilizing practice management software or revenue cycle management systems can help track claims, send automated reminders, and generate reports for analysis. These tools can improve efficiency and reduce the likelihood of overlooked or neglected claims.
In addition to monitoring the status of claims, it is important to keep track of reimbursement amounts. This includes comparing the expected payment to the actual reimbursement received and identifying any discrepancies or underpayments. Promptly addressing any issues with reimbursement can help ensure accurate financial reporting and maximize revenue.
Remember, following up on claims is crucial for effective insurance billing. Proactively tracking the progress of claims, resolving denials or rejections promptly, and maintaining accurate records can help ensure timely reimbursement and a healthy revenue cycle.
Handling Insurance Denials
Dealing with insurance claim denials can be frustrating, but it is a common challenge in the insurance billing process. Understanding how to handle denials effectively is essential for optimizing reimbursement and minimizing financial losses.
When a claim is denied, the first step is to review the denial explanation provided by the insurance company. This explanation will outline the reason for the denial, such as coding errors, lack of medical necessity, missing information, or non-covered services. Understanding the specific reason for the denial is crucial for taking appropriate action.
Once the reason for the denial is identified, healthcare providers can begin the process of appealing the decision. This involves gathering any additional documentation or information that supports the medical necessity of the services rendered. This may include medical records, test results, or letters of medical necessity.
When preparing an appeal, it is important to ensure that all necessary information is included and clearly communicated. Clearly state the reasons why the denial is being contested and provide any supporting evidence that demonstrates the validity of the claim.
It is also essential to pay attention to the timelines for filing an appeal. Insurance companies typically have specific deadlines for submitting appeals, and missing these deadlines may result in a loss of opportunity to appeal the denial.
Keep track of all correspondence and communication related to the appeal, including dates, individuals spoken to, and any reference numbers provided. This documentation will serve as a record of the appeal process and may be useful in case of further inquiries or escalation.
When submitting the appeal, it is recommended to do so through a traceable method, such as certified mail or email with a delivery receipt. This ensures that the appeal is received by the insurance company and can be tracked if needed.
In some cases, it may be necessary to engage in discussions or negotiations with the insurance company’s representatives to resolve the denial. Utilize clear and professional communication to explain the situation and advocate for the validity of the claim.
If the appeal is unsuccessful or the insurance company continues to deny the claim, further options may include mediation or arbitration, which involve third-party intervention to facilitate resolution. Consulting with legal counsel or professional billing experts may be advisable in complex or prolonged denial situations.
Remember, handling insurance denials requires persistence and attention to detail. Understanding the reason for the denial, gathering supporting documentation, and following the appeal process diligently can increase the chances of a successful resolution and maximize reimbursement.
Appealing Denied Claims
When an insurance company denies a claim, it is not the end of the road. Healthcare providers have the option to appeal the decision and contest the denial. Appealing denied claims is an important step in the insurance billing process, as it allows providers to advocate for the validity of the services rendered and increase the chances of reimbursement.
The first step in appealing a denied claim is understanding the reason provided by the insurance company for the denial. This information is typically included in the denial explanation or the Explanation of Benefits (EOB) received from the insurance company. It is crucial to review the denial reason thoroughly to identify the specific errors or issues that need to be addressed in the appeal.
Once the denial reason is identified, healthcare providers can begin preparing the appeal. This involves gathering all necessary documentation and supporting evidence to demonstrate the medical necessity and appropriateness of the services provided. This may include medical records, test results, treatment plans, or letters of medical necessity.
The appeal should clearly and concisely explain why the claim should be reconsidered and provide a strong argument supported by the gathered evidence. It is important to address the specific concerns raised by the insurance company and provide counterarguments or clarifications to support the claim’s validity.
When drafting the appeal letter, it is crucial to maintain a professional and assertive tone. Clearly state the reasons for the appeal, reference any relevant policy provisions or guidelines, and include any necessary forms or documentation requested by the insurance company.
Timeliness is key when appealing denied claims. Many insurance companies have strict deadlines for submitting appeals, so it is important to adhere to these timelines. Start the appeal process as soon as possible to allow ample time for review and consideration by the insurance company.
It is recommended to keep copies of all appeal documents, including the appeal letter, supporting documentation, and any correspondence or proof of submission. This documentation will serve as a record of the appeal process and may be crucial in case of further inquiries or escalations.
When submitting the appeal, choose a traceable method such as certified mail or email with a delivery receipt to ensure proof of submission. This allows for tracking and confirmation of receipt by the insurance company.
In cases where an appeal is denied again or the insurance company does not respond within a reasonable timeframe, further options may include seeking legal advice or engaging in alternative dispute resolution methods such as mediation or arbitration.
Remember, appealing denied claims requires thorough preparation, clear communication, and a strong argument supported by evidence. Understanding the denial reason, addressing the concerns raised, and submitting a compelling appeal can increase the chances of overturning the denial and receiving the reimbursement rightfully due.
Resubmitting Claims
Resubmitting claims is a crucial step in the insurance billing process when initial claims are denied or rejected by the insurance company. It provides an opportunity to correct any errors, provide additional documentation, or address any issues that led to the claim denial.
When a claim is denied or rejected, it is important to review the denial explanation or the Explanation of Benefits (EOB) received from the insurance company. This will help identify the specific reason for the denial or rejection, allowing for targeted corrections or additions in the resubmission.
Before resubmitting a claim, it is important to understand the insurance company’s policies and guidelines for resubmissions. Some insurance companies have specific procedures, forms, or timeframes for resubmitting claims, and it is important to follow these instructions to ensure the claim is considered for review.
When resubmitting a claim, it is crucial to address the reason for the denial or rejection explicitly. This may involve correcting coding errors, providing additional documentation to support medical necessity, or clarifying any incomplete or missing information from the initial submission.
Ensure that all necessary information is provided in the resubmission, including the patient’s demographics, insurance information, updated coding, and any additional supporting documentation. Utilize clear and concise language to explain the changes made and why the resubmitted claim should be reconsidered.
When resubmitting claims, it is important to keep track of all documentation and correspondence related to the resubmission. This includes maintaining copies of the resubmitted claim, any supporting documentation, and any proof of submission or delivery confirmation.
Monitor the progress of the resubmitted claim and follow up with the insurance company if necessary. Keep a record of the dates and individuals spoken to during the follow-up process, as well as any reference numbers or case identifiers provided by the insurance company.
If a resubmitted claim is once again denied or rejected, it may be necessary to escalate the matter by filing an appeal or seeking professional advice. The specific steps to take will depend on the policies and procedures of the insurance company, as well as the complexity of the denial.
Remember, resubmitting claims provides an opportunity to address errors and rectify issues that led to the initial denial or rejection. Understanding the reason for the denial, providing the necessary information or documentation, and closely following the insurance company’s guidelines will improve the chances of a successful resubmission and reimbursement.
Understanding Reimbursement
Understanding the process of reimbursement is vital in the insurance billing cycle as it determines the amount of payment that healthcare providers receive for the services rendered. Reimbursement can vary based on several factors, including insurance policies, contractual agreements, and fee schedules.
Healthcare providers negotiate contracts with insurance companies to establish reimbursement rates for their services. These rates can be based on a variety of factors, such as the type of service provided, the location of the practice, and the specific insurance plan. It is important for providers to be aware of the reimbursement rates established in their contracts to ensure fair compensation for their services.
Reimbursement can be made through different methods. The most common methods include fee-for-service, where providers are paid a set fee for each service rendered, and capitation, where providers receive a fixed monthly payment per patient regardless of the services provided. Other methods, such as bundled payments or value-based reimbursement, may also be used depending on the insurance plan and healthcare organization.
When it comes to reimbursement, it’s important to understand that the amount paid by the insurance company may not always cover the full cost of the services provided. Patient responsibility in the form of deductibles, co-pays, or co-insurance may be applied, and it is crucial to communicate these financial responsibilities to patients accurately.
Ensuring accurate documentation and coding is essential for maximizing reimbursement. Properly documenting the medical necessity of services, assigning accurate diagnosis codes, and using appropriate procedure codes will help justify the reimbursement amount sought. Consistent and accurate documentation can also support the provider’s position in case of audits or reviews.
It is also important to understand the role of insurance claims processing in the reimbursement process. Insurance companies review the submitted claims, process them based on the patient’s benefits and coverage, and determine the amount of reimbursement based on the contracted rates. The reimbursement process can take time, and providers should track the progress of their claims to ensure timely payment.
Additionally, healthcare providers should stay updated with insurance industry trends and changes. Ongoing education and staying current with changes in reimbursement policies, coding guidelines, and regulatory requirements will help providers navigate the evolving landscape of healthcare reimbursement.
Remember, understanding reimbursement is essential for healthcare providers to ensure fair compensation for their services. By familiarizing themselves with reimbursement rates, documentation and coding requirements, and the claims processing process, providers can optimize their revenue cycle and maintain financial stability.
Tracking Payments
Tracking payments is a crucial aspect of the insurance billing process, as it allows healthcare providers to ensure accurate and timely reimbursement for the services they provide. Effective payment tracking helps maintain financial stability and enables providers to identify and address any potential issues or discrepancies that may arise.
When tracking payments, one of the first steps is to establish a reliable system for recording and organizing payment information. This may include utilizing practice management software, electronic health record systems, or dedicated accounting software. These tools can streamline the payment tracking process and provide a centralized platform for managing financial transactions.
Each time a payment is received from an insurance company, it is important to record the transaction details. This includes the date of payment, the insurance company or payer responsible for the payment, the patient for whom the payment is made, and the amount received. Maintaining clear and accurate payment records ensures proper tracking and transparency.
Insurance companies typically provide an Explanation of Benefits (EOB) or remittance advice that accompanies the payment. This document outlines the specific services billed, the dollar amounts paid, and any adjustments or denials. Reviewing the EOB or remittance advice helps verify that the payment received aligns with the expected reimbursement.
Reconciliation is an important step in payment tracking. This involves comparing the payment received and recorded with the expected reimbursement based on the contracted rates and payment schedules. Discrepancies or underpayments should be promptly identified and addressed with the insurance company to ensure accurate payment.
Tracking payments also involves monitoring outstanding balances and following up on any overdue or unpaid claims. This may include sending regular statements or reminders to patients for their portion of the payment, or contacting insurance companies to inquire about the status of pending reimbursements. Consistent follow-up helps prevent delayed or missed payments.
Utilizing automated reports or financial analytics can provide valuable insights into payment trends and patterns. These tools can help identify any potential issues with particular insurance companies, specific procedures, or recurring denials. Armed with this information, providers can take proactive steps to address these issues and optimize their revenue cycle.
Regularly analyzing payment data and financial reports can also assist providers in identifying areas for improvement, such as streamlining billing processes, negotiating better reimbursement rates, or implementing strategies to reduce claim denials.
Remember, tracking payments is essential for maintaining financial stability and maximizing revenue. By establishing a reliable system for recording payments, reconciling reimbursements, following up on outstanding balances, and utilizing payment analytics, healthcare providers can ensure accurate and timely payment and optimize their revenue cycle management.
Dealing with Insurance Audits
Insurance audits are a regular part of the insurance billing process. They are conducted by insurance companies or third-party auditors to ensure that healthcare providers are properly documenting and billing for the services rendered. Dealing with insurance audits effectively is crucial for maintaining compliance and minimizing the risk of financial penalties or reputational damage.
When notified of an audit, it is important to respond promptly and cooperatively. This involves gathering all requested documentation, such as medical records, coding records, claim forms, and any other relevant documentation. Organizing the requested information in an easily accessible and well-documented manner will facilitate the audit process.
Thoroughly review the audit request to understand the scope and specific requirements. This will help ensure that all necessary documents and information are provided, reducing the likelihood of the audit being extended or repeated due to missing or incomplete information.
During the audit, it is important to maintain open lines of communication with the auditor. Answer any questions or provide clarifications to the best of your ability. If there are concerns or disagreements with the auditor’s findings or interpretations, it is essential to address them respectfully and professionally.
Engaging with legal counsel or consulting with professional billing experts can be beneficial in navigating complex or large-scale audits. They can provide guidance on compliance requirements, offer advice on how to present information effectively during an audit, and help develop strategies to respond to audit findings, if necessary.
It is important to note that even with meticulous documentation, occasional errors or discrepancies may be identified during an audit. In such cases, it is important to take responsibility for any identified errors and work towards resolving them. This may involve implementing corrective action plans, providing additional training for staff, or adopting new billing processes to prevent similar issues in the future.
Audit findings may lead to financial recoupments, where the insurance company seeks reimbursement for overpaid claims, or penalties, depending on the nature and severity of the audit findings. If recoupments or penalties are imposed, providers should carefully review the audit findings and consult with legal counsel to determine the appropriate course of action.
Regular internal audits and self-assessments can be an effective proactive measure to identify and address potential compliance issues before an official audit occurs. By conducting periodic audits internally, healthcare providers can ensure compliance, identify areas for improvement, and minimize the impact of external audits.
Remember, dealing with insurance audits requires attention to detail, thorough documentation, and proactive compliance measures. By responding promptly, providing requested information accurately, and addressing any identified issues, healthcare providers can navigate audits successfully, maintain compliance, and protect their financial well-being.
Maintaining Compliance
Maintaining compliance in the insurance billing process is crucial for healthcare providers to adhere to legal and regulatory requirements. Compliance helps ensure ethical practices, accurate billing, and proper documentation. By maintaining compliance, healthcare providers can reduce the risk of audits, penalties, and legal repercussions. Here are key strategies for maintaining compliance:
Stay Updated: Keep abreast of changes in healthcare laws, regulations, and coding guidelines. Regularly review updates from regulatory bodies such as the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) and professional organizations like the American Medical Association (AMA).
Educate Staff: Provide thorough training to staff members on compliance requirements, coding guidelines, proper documentation practices, and privacy regulations such as HIPAA. Ongoing education and refresher courses will help ensure that everyone stays up-to-date with compliance standards.
Develop Policies and Procedures: Establish clear policies and procedures that outline compliance expectations and processes for handling sensitive information, documenting services, and billing practices. Regularly review and update these policies to reflect changes in regulations or industry best practices.
Utilize Technology: Leverage electronic health record (EHR) systems, practice management software, and billing software that include compliance features and automate audit trails. These systems can assist in maintaining accurate and auditable records, reducing the risk of errors or oversights.
Implement Internal Audits: Conduct periodic internal audits to proactively identify potential compliance issues. These audits can help identify gaps in documentation, coding accuracy, and billing practices. Use the findings of these audits to rectify any issues and improve compliance procedures.
Document Thoroughly: Ensure documentation is complete, accurate, and supports the services billed. Document all services, medical necessity, and any communication with the patient or insurance company. Proper documentation is essential for justifying medical necessity, supporting claim submission, and demonstrating compliance during audits or reviews.
Monitor Coding and Billing: Regularly review coding and billing practices to ensure compliance with coding guidelines and fee schedules. Utilize regular coding audits to detect any coding errors or patterns that may raise compliance concerns.
Maintain Privacy and Security: Protect patient information by implementing strong privacy and security measures. Train staff on the proper handling of patient data, implement safeguards to prevent unauthorized access, and follow HIPAA guidelines for electronic transactions and privacy requirements.
Respond to Audits: Cooperate with insurance audits, respond to requests for information promptly, and provide accurate and complete documentation. Address any identified issues or discrepancies, and implement corrective measures to improve compliance moving forward.
Seek Legal or Compliance Expertise: Consult legal counsel or compliance experts to ensure compliance with complex regulations. They can provide guidance tailored to your specific situation, help interpret regulations, and offer advice on compliance policies and procedures.
By actively practicing and maintaining compliance in the insurance billing process, healthcare providers can mitigate risks, reduce errors, and demonstrate their commitment to ethical and responsible billing practices.
Conclusion
The insurance billing process is a vital aspect of healthcare administration, and understanding its intricacies is essential for healthcare providers and medical billing specialists. By following the steps outlined in this article, including gathering accurate patient information, verifying insurance coverage, coding properly, submitting claims, and tracking payments, providers can optimize their reimbursement and financial workflow.
Handling insurance denials and appeals effectively is crucial for maximizing reimbursement and resolving claim disputes. Providers should also be prepared to resubmit claims when necessary, addressing errors and providing additional documentation as required.
Understanding reimbursement methodologies and tracking payments play interrelated roles in maintaining financial stability and ensuring accurate payment. Regularly reviewing payment trends, reconciling reimbursements, and following up on outstanding balances are essential steps in optimizing revenue cycle management.
Dealing with insurance audits requires attention to detail and proactive compliance measures. Healthcare providers should be prepared to respond promptly, provide requested documentation, and address any identified issues with the utmost professionalism.
Maintaining compliance throughout the insurance billing process is essential for ethical practices, accurate documentation, and adherence to legal and regulatory requirements. Staying up-to-date with healthcare laws and regulations, educating staff, implementing internal audits, and utilizing technology can help ensure compliance and minimize the risk of audits, penalties, and legal repercussions.
In conclusion, mastering the art of insurance billing is a continual learning process. By staying informed, paying attention to detail, and employing effective strategies, healthcare providers can navigate the complexity of insurance billing, optimize their revenue cycle, and provide quality care to their patients while ensuring fair and timely reimbursement.














