Finance
How To Do Bookkeeping For A Small Business
Modified: March 1, 2024
Learn how to do bookkeeping for a small business and master the finance. Discover essential tips and tools to streamline your financial management.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Determine Your Accounting Method
- Set Up Your Chart of Accounts
- Record and Organize Financial Transactions
- Track Income and Expenses
- Reconcile Bank Statements
- Prepare Financial Statements
- Payroll Accounting
- Cash Flow Management
- Budgeting and Forecasting
- Sales Tax Reporting
- Tax Preparation and Filing
- Audit and Financial Compliance
- Closing Thoughts
Introduction
Welcome to the world of small business bookkeeping! As a small business owner, it is crucial to have a solid understanding of bookkeeping practices to effectively manage your finances. Bookkeeping is the process of recording, organizing, and tracking all financial transactions of your business. It not only helps you keep track of your income and expenses but also provides valuable insights into the financial health and performance of your business.
Proper bookkeeping ensures that you have accurate and up-to-date financial records, which are essential for making informed business decisions, securing loans, filing taxes, and complying with financial regulations. It helps you monitor your cash flow, track your profitability, and identify areas for improvement.
In this article, we will provide you with a comprehensive guide on how to do bookkeeping for your small business. We will walk you through the essential steps and best practices to help you establish a strong foundation for financial success. From choosing the right accounting method to preparing financial statements and handling payroll, we’ve got you covered.
Whether you are a solopreneur or have a small team, understanding the basics of bookkeeping will empower you to take control of your company’s financials. It will allow you to make informed decisions, spot potential issues early on, and ultimately drive the growth and profitability of your business.
So let’s dive in and demystify the world of small business bookkeeping!
Determine Your Accounting Method
Before diving into the intricacies of bookkeeping, it’s crucial to determine which accounting method you will use for your small business. The two most common methods are cash basis accounting and accrual basis accounting.
- Cash Basis Accounting: This method records transactions when cash is received or paid out. It’s a straightforward approach that is often used by small businesses with simple financial operations. With cash basis accounting, you record income when you receive payments from customers and record expenses when you pay bills. This method provides a clear picture of your immediate cash flow and is relatively easier to maintain.
- Accrual Basis Accounting: This method records transactions when they occur, regardless of when the cash is received or paid out. It considers accounts receivable and accounts payable and provides a more comprehensive view of your business’s financial position. With accrual accounting, you record revenue when it’s earned, even if the payment hasn’t been received yet, and record expenses when they are incurred, even if the payment hasn’t been made yet. This method provides a more accurate representation of the profitability and financial health of your business.
Choosing the right accounting method depends on the nature of your business, industry requirements, and your reporting needs. Some businesses may be required to use accrual accounting by tax regulations or if they have inventory. Consult with a certified public accountant (CPA) or tax professional to determine the accounting method that best suits your business.
Once you’ve determined the accounting method, it’s important to stick with it consistently. Changing your accounting method can be complex and may require adjusted financial statements from previous periods.
By identifying and adopting the appropriate accounting method for your small business, you lay the foundation for accurate financial reporting and analysis. It sets the stage for managing your cash flow, tracking income and expenses, and making informed business decisions based on solid financial data.
Set Up Your Chart of Accounts
When it comes to organizing your financial transactions, having a well-structured chart of accounts is essential. A chart of accounts is a list of specific categories or “accounts” that you use to classify and track different types of transactions.
The chart of accounts typically consists of several main account categories, including assets, liabilities, equity, income, and expenses. Each category is further broken down into subaccounts that provide more detailed information about the specific transactions within that category.
For example, under the “Assets” category, you might have subaccounts for cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and equipment. Under the “Expenses” category, you might have subaccounts for rent, utilities, salaries, and advertising expenses.
Setting up your chart of accounts will depend on several factors, including the nature of your business, industry-specific requirements, and the level of detail you want to track. It’s important to strike a balance between having enough accounts to provide valuable insights and not overwhelming the system with unnecessary complexity.
Consider consulting with a CPA or bookkeeping professional to help you design a chart of accounts that aligns with your business needs. They can provide guidance on best practices, industry-specific accounts, and help ensure that your chart of accounts follows generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP).
Once your chart of accounts is set up, it’s crucial to consistently record and categorize your transactions using the designated accounts. This will ensure accurate and organized financial records and make it easier to generate reports for analysis and decision-making.
Investing time and effort in setting up and maintaining a well-structured chart of accounts will pay off in the long run. It will streamline your bookkeeping process, provide transparency into your financial performance, and enable you to effectively manage your business’s finances.
Record and Organize Financial Transactions
Recording and organizing financial transactions is a fundamental aspect of bookkeeping. It involves systematically documenting every financial activity that occurs within your business, whether it’s income received from sales, expenses paid to suppliers, or investments made into the company.
To effectively record and organize financial transactions, follow these steps:
- Create a system: Establish a reliable bookkeeping system that suits your business’s needs. This can be a computerized accounting software or manual record keeping using spreadsheets or ledgers.
- Document all transactions: Record all financial transactions promptly and accurately. This includes invoices, receipts, bank statements, payroll records, and any other relevant documents. Ensure that you include details such as dates, amounts, descriptions, and the accounts affected.
- Categorize transactions: Assign the appropriate account codes to each transaction to categorize them correctly in your chart of accounts. This ensures that transactions are accurately classified and can be easily analyzed and reported on in the future.
- Organize documentation: Keep all financial documentation well-organized and easily accessible. This includes filing physical copies in a structured filing system or using digital document management tools.
- Implement internal controls: Put in place internal controls to safeguard against errors, fraud, and unauthorized access to financial records. This can include separating duties, conducting regular audits, and implementing approval processes.
Consistency and attention to detail are key when recording and organizing financial transactions. By doing so, you establish a strong foundation for accurate financial reporting, tax compliance, and decision-making.
Consider leveraging accounting software to automate and streamline the record-keeping process. These tools can provide features such as bank feed integration, which automatically imports transactions, reducing the manual entry required.
Remember to regularly review, reconcile, and validate your recorded transactions to ensure accuracy and identify any discrepancies or errors. This will help maintain the integrity of your financial records and improve the reliability of your reporting.
Recording and organizing financial transactions is not just a compliance requirement; it is essential for understanding the financial health of your business and making informed decisions. It provides valuable insights into your cash flow, profitability, and overall financial performance.
Track Income and Expenses
Tracking income and expenses is a vital part of small business bookkeeping. It allows you to monitor your revenue and costs, analyze profitability, and make informed financial decisions. By accurately tracking your income and expenses, you gain visibility into the financial health of your business and can identify areas for improvement.
Here are some steps to effectively track your income and expenses:
- Record Sales and Revenue: Record all sources of income, including sales, service fees, and any other revenue streams specific to your business. Categorize them based on the nature of the income (e.g., product sales, consulting fees) to track performance and analyze trends.
- Track Expenses: Document all business expenses, such as rent, utilities, inventory purchases, payroll expenses, and marketing costs. Organize your expenses by category to understand your spending patterns and identify opportunities to reduce costs.
- Reconcile Bank and Credit Card Statements: Regularly reconcile your bank and credit card statements with your recorded transactions to ensure accuracy. This process helps identify any discrepancies, missing transactions, or errors.
- Use Accounting Software: Consider using accounting software to streamline the tracking process. Software solutions allow you to input income and expenses, generate reports, and integrate with other financial systems to automate tasks and save time.
- Track Accounts Receivable and Payable: Keep a close eye on outstanding customer invoices and vendor bills. Monitor accounts receivable to ensure timely payments, and stay on top of accounts payable to avoid late fees or penalties.
- Perform Regular Financial Analysis: Analyze your income and expense data periodically to gain insights into your business’s financial performance. Look for patterns, identify areas of high spending, and evaluate the profitability of different products or services.
Consistently tracking income and expenses provides a clear picture of your cash flow, profit margins, and overall financial viability. It also helps you prepare accurate financial statements, such as profit and loss statements and balance sheets, which are essential for tax preparation, securing financing, and evaluating business growth.
Remember, accurate tracking requires attention to detail and consistency. Make it a regular habit to update your financial records, review financial reports, and reconcile accounts. This ensures that your income and expenses are accurately reflected in your bookkeeping system and provides you with the financial information needed to drive your business forward.
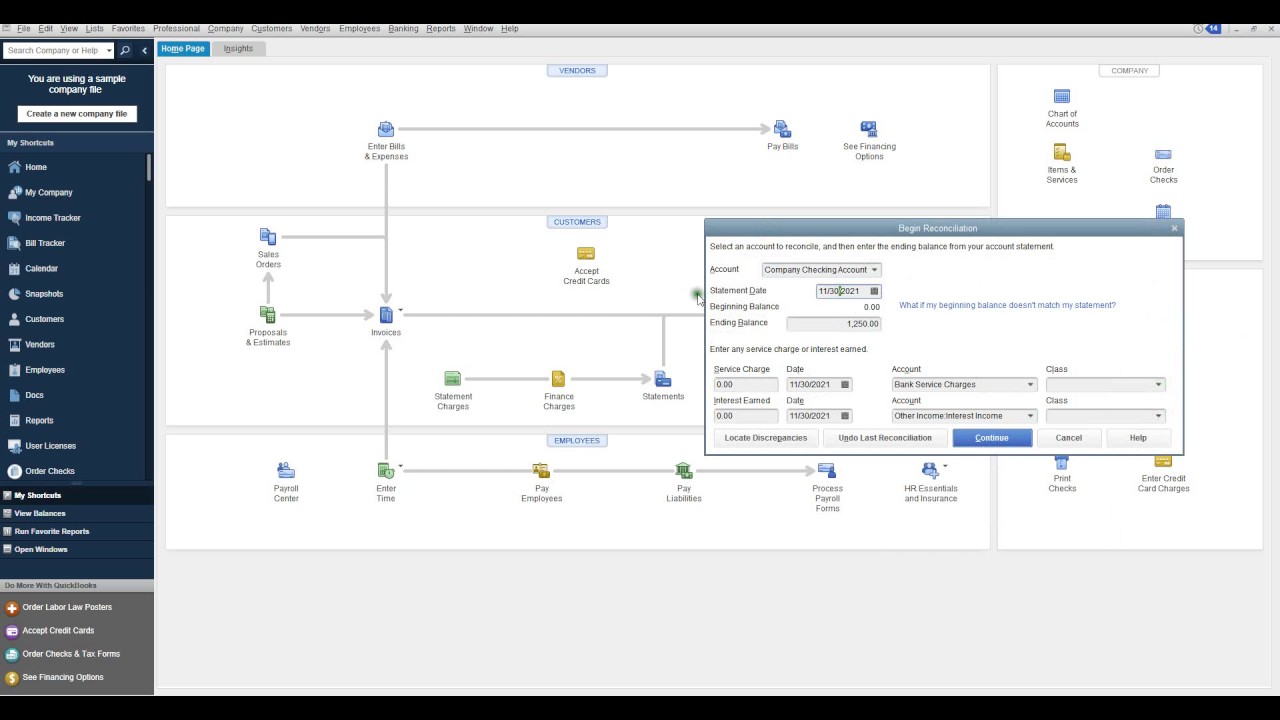
Reconcile Bank Statements
Reconciling your bank statements is a crucial step in the bookkeeping process. It involves comparing your recorded transactions with the bank’s records to ensure that they match up and reconcile any discrepancies. This process helps you maintain accurate financial records, identify errors or fraudulent activity, and ensure the integrity of your financial data.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to reconcile your bank statements:
- Gather Documents: Collect your bank statements for the period you wish to reconcile, as well as any supporting documentation such as check registers, deposit slips, and receipts.
- Compare Deposits: Start by comparing the deposits recorded in your bookkeeping system with those on the bank statement. Check for any discrepancies in the amounts or dates and make note of any missing deposits.
- Verify Withdrawals: Next, compare the withdrawals or checks recorded in your bookkeeping system with those on the bank statement. Look for any errors or unauthorized transactions that might indicate fraudulent activity.
- Reconcile Differences: If there are differences between your records and the bank statement, investigate each discrepancy. Common reasons for discrepancies include timing differences, bank fees, and errors in recording transactions. Make any necessary adjustments in your records to reconcile the differences.
- Update Records: Once you have reconciled all discrepancies, update your bookkeeping records to reflect the accurate and reconciled bank statement balances.
- Document Reconciliation: Keep a record of the bank statement reconciliation process, including any adjustments made, for future reference and audit purposes.
Reconciling your bank statements on a regular basis, such as monthly or quarterly, is important for several reasons:
- Accuracy: Reconciling ensures that your recorded transactions match the actual transactions processed by the bank, providing you with accurate financial data.
- Fraud Detection: The reconciliation process helps identify any unauthorized transactions or fraudulent activity that may have occurred, allowing you to take appropriate action.
- Identification of Errors: Reconciling helps uncover any errors made in recording transactions, allowing you to correct them promptly and maintain accurate financial records.
- Financial Insights: By reconciling your bank statements, you gain a clearer understanding of your business’s cash flow, identify any outstanding checks or deposits, and ensure that your financial reports are reliable.
Using accounting software can streamline the bank reconciliation process, as it can automatically import bank transactions, match them with your recorded transactions, and highlight any discrepancies. This can save time and reduce the likelihood of errors.
By regularly reconciling your bank statements, you maintain the accuracy and integrity of your financial records, giving you a solid foundation for making informed financial decisions and ensuring the financial health of your small business.
Prepare Financial Statements
Preparing financial statements is a crucial step in small business bookkeeping. Financial statements provide a comprehensive snapshot of your business’s financial performance, position, and cash flow. They help you evaluate profitability, assess liquidity, and make informed decisions based on accurate and up-to-date financial data.
Here are the key financial statements that you should prepare:
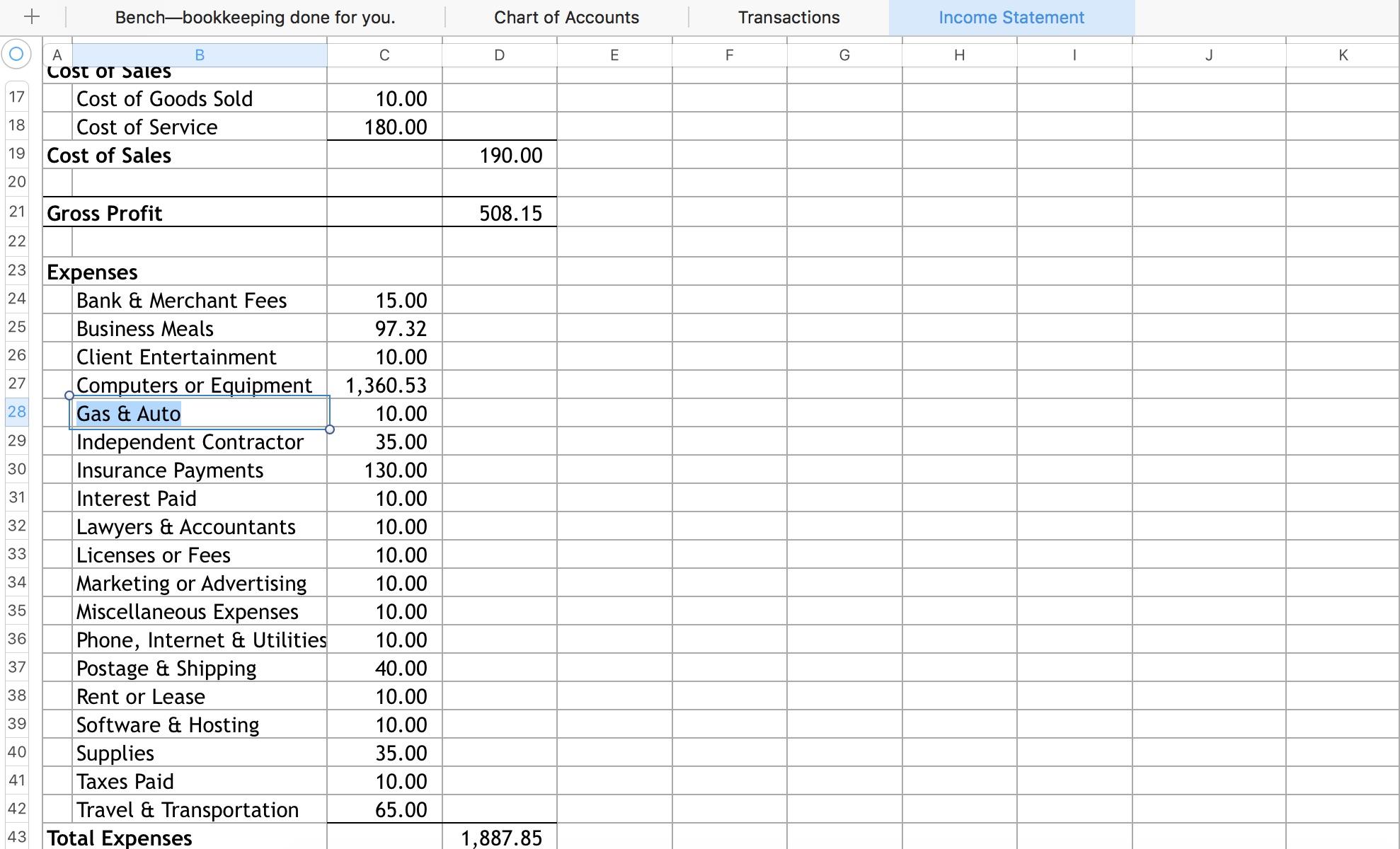
- Income Statement: Also known as the profit and loss statement, the income statement summarizes the revenue, expenses, and net income or loss of your business during a specific period. It helps you evaluate your business’s profitability and identify trends in revenue and expenses.
- Balance Sheet: The balance sheet provides a snapshot of your business’s financial position at a specific point in time. It presents your assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity. The balance sheet helps you understand the financial strength, liquidity, and solvency of your business.
- Cash Flow Statement: The cash flow statement shows the inflow and outflow of cash during a specific period. It categorizes cash flows into operating, investing, and financing activities. The cash flow statement helps track the sources and uses of cash and assesses your business’s ability to generate and manage cash.
- Statement of Changes in Equity: This statement records the changes in equity during a specific period, including contributions, distributions, and retained earnings. It helps you track the impact of changes in ownership and equity on your business’s financial position.
To prepare financial statements effectively, follow these steps:
- Review and Organize Transactions: Ensure that your financial records are complete, accurate, and up-to-date. Organize them by categories such as income, expenses, assets, and liabilities.
- Generate Trial Balance: Create a trial balance to ensure that all debits and credits in your records are in balance. This acts as a preliminary check before preparing financial statements.
- Use Accounting Software: Utilize accounting software to streamline the process. Most accounting software solutions provide built-in financial statement templates that automatically generate statements based on your recorded transactions.
- Calculate Key Financial Ratios: Analyze your financial statements by calculating important ratios such as gross profit margin, current ratio, and return on investment. These ratios provide insights into your business’s financial health and performance.
- Seek Professional Help if Needed: If you’re unsure about preparing financial statements or need assistance, consult with a certified public accountant (CPA) or bookkeeping professional. They can ensure accuracy, provide insights, and assist with any complex accounting requirements.
Regularly reviewing and analyzing your financial statements will help you make informed decisions, identify areas for improvement, and track your business’s financial progress over time. Stay proactive and update your financial statements regularly to reflect any changes in your business’s financial position.
Remember, financial statements are essential for tax reporting, securing loans or investments, attracting investors, and understanding the overall financial health of your small business. By preparing accurate and comprehensive financial statements, you gain valuable insights that drive the success and growth of your business.
Payroll Accounting
Payroll accounting involves managing your employees’ compensation, deductions, and benefits. It is a critical aspect of small business bookkeeping as it ensures accurate payroll processing, complies with legal requirements, and maintains employee satisfaction. Effective payroll accounting helps you manage your labor costs, track payroll expenses, and meet your tax obligations.
Here are the key steps to handle payroll accounting:
- Register with Tax Authorities: Before running payroll, ensure that you have registered with the appropriate tax authorities, such as the IRS in the United States. This ensures that you comply with payroll tax obligations and file required reports.
- Classify Employees Correctly: Determine whether your workers are employees or independent contractors. Different tax and labor laws apply to each classification, so it’s important to correctly categorize your workforce.
- Record Employee Information: Maintain accurate records of each employee, including their personal details, employment contracts, tax withholding forms (such as W-4 in the U.S.), and other relevant information.
- Calculate Gross Pay: Determine each employee’s gross pay based on their hourly rate, salary, commission, or any other agreed-upon compensation structure. Consider any overtime, bonuses, or other additional payments.
- Deduct Taxes and Withholdings: Calculate and withhold the necessary income tax, social security contributions, Medicare, and any other employee deductions. Ensure compliance with federal, state, and local tax regulations.
- Account for Employee Benefits: Account for employee benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off. Deduct the necessary employee contributions or accrue for employer-provided benefits.
- Process Payroll: Based on the calculated amounts, process payroll by issuing paychecks or initiating direct deposits. Ensure accuracy and timely payments to employees.
- File Payroll Taxes: Regularly file payroll tax returns, such as Form 941 in the U.S., and remit the appropriate payroll taxes to the taxing authorities. Meet all deadlines to avoid penalties.
- Reconcile Payroll Accounts: Regularly reconcile payroll accounts to ensure that the recorded payroll expenses match the actual amounts paid. This helps identify discrepancies and errors.
Using payroll software can simplify the payroll accounting process by automating calculations, generating paychecks, and providing comprehensive payroll reports. It helps ensure accuracy, streamline processes, and save time.
Payroll accounting requires adherence to complex regulations, accurate record-keeping, and attention to detail. If you’re unfamiliar with payroll accounting, consider consulting a payroll professional or utilizing the services of a payroll provider to ensure compliance and accuracy.
By effectively managing payroll accounting, you maintain employee satisfaction, comply with tax laws, and keep accurate track of your labor costs. Taking care of your employees’ compensation in a systematic and organized manner is essential for the financial well-being and success of your small business.
Cash Flow Management
Cash flow management is the process of monitoring, analyzing, and optimizing the flow of cash into and out of your business. It is a critical component of small business bookkeeping as it ensures that you have enough cash to cover your expenses, seize growth opportunities, and weather financial challenges.
Effective cash flow management involves the following key steps:
- Create a Cash Flow Budget: Start by creating a cash flow budget that outlines your expected cash inflows and outflows over a specific period. This helps you plan and forecast your cash needs and identify any potential cash gaps.
- Manage Accounts Receivable: Monitor and expedite the collection of outstanding customer invoices to ensure a steady flow of cash into your business. Implement clear payment terms and follow up on late payments promptly.
- Negotiate Vendor Terms: Work with your suppliers to negotiate favorable payment terms, such as extended due dates or discounts for early payments. This can help optimize cash outflows and improve your working capital.
- Control Expenses: Review your expenses regularly and identify areas for cost savings or efficiency improvements. Reduce unnecessary spending and prioritize essential expenses to ensure optimal cash flow.
- Manage Inventory: Keep a close eye on your inventory levels to avoid stockouts or excess inventory tying up valuable cash. Implement inventory management strategies such as just-in-time ordering or dropshipping to optimize cash flow.
- Monitor Debt: Manage your debts carefully, ensuring that the repayment terms align with your cash flow. Make timely payments to avoid penalties or interest charges. Consider refinancing or negotiating better loan terms if necessary.
- Build Emergency Reserves: Set aside a portion of your cash flow as an emergency reserve to handle unexpected expenses or revenue fluctuations. This buffer can help you navigate challenging times without compromising your cash flow.
- Use Cash Flow Forecasting: Regularly update and analyze your cash flow projections to anticipate potential cash shortages or surpluses. This allows you to take proactive measures to address any imbalances and make informed business decisions.
- Use Technology and Automation:
Leverage accounting software or cash flow management tools to automate cash flow tracking, invoicing, and payment reminders. These technologies can streamline processes, reduce manual errors, and improve cash flow visibility.
By effectively managing your cash flow, you can improve profitability, reduce financial stress, and ensure the long-term success of your small business. Regularly reviewing and updating your cash flow management strategies will help you adapt to changing market conditions and maintain a healthy financial position.
Remember, positive cash flow is vital for business growth, debt repayment, and reinvesting in your company. By implementing robust cash flow management practices, you can optimize your financial resources and position your business for a prosperous future.
Budgeting and Forecasting
Budgeting and forecasting are vital components of small business bookkeeping as they help you plan, track, and control your financial resources. A budget is a financial plan that outlines your projected revenues, expenses, and cash flows over a specific period, while forecasting involves estimating future financial performance based on historical data and market trends.
Here’s how you can effectively approach budgeting and forecasting:
- Create an Annual Budget: Start by developing an annual budget that aligns with your business goals. Identify your expected revenue streams and allocate funds to various expense categories based on historical data and future projections.
- Monitor and Review Actual Performance: Regularly compare your actual financial results with the budgeted figures. Analyze any variances and determine the underlying reasons for them. This process helps identify areas of improvement and informs future budgeting decisions.
- Consider Various Scenarios: Develop different scenarios based on potential market conditions, changes in customer demand, or internal factors. This allows you to assess the potential impact on your financial performance and make informed strategic decisions.
- Involve Key Stakeholders: Engage your management team and key employees in the budgeting and forecasting process. Their insights and input can help enhance the accuracy of financial projections and ensure buy-in for the budgeted goals.
- Track Performance Indicators: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) and track them regularly. KPIs can include sales targets, profit margins, customer acquisition costs, or any other metrics relevant to your business. Monitoring these indicators helps you gauge your progress towards achieving your financial goals.
- Update Forecasts: Regularly update your financial forecasts based on changes in market conditions, customer behavior, or internal factors. This enables you to adjust your budget and make data-driven decisions to maintain your financial health.
- Use Budgeting Software: Leverage budgeting and forecasting software to simplify the process. These tools provide templates, automate calculations, and offer real-time visibility into your financial performance, making budgeting and forecasting more efficient and accurate.
- Be Flexible: Recognize that budgets and forecasts may need adjustments as circumstances change. Remain flexible and willing to adapt your plans to respond to market shifts or unforeseen challenges.
- Monitor Cash Flow: Regularly review your cash flow projections in relation to your budget and forecast. Cash flow is a critical component of budgeting and forecasting as it determines the availability of funds to support your operations and growth initiatives.
Budgeting and forecasting provide a roadmap for achieving your financial goals, managing resources effectively, and guiding your business towards success. They allow you to make informed decisions, allocate resources strategically, and stay proactive in a dynamic business environment.
Remember, budgeting and forecasting are ongoing processes rather than one-time exercises. Continuously monitor and update your financial plans to reflect changes in your business and industry conditions. By doing so, you can drive your business forward with confidence and achieve long-term financial stability.
Sales Tax Reporting
Sales tax reporting is a crucial aspect of small business bookkeeping, especially for businesses that sell taxable goods or services. Sales tax is a consumption tax imposed by government authorities on the sale of certain goods and services, and it’s important to accurately report and remit these taxes to the appropriate tax agencies.
Here are the key steps involved in sales tax reporting:
- Determine Sales Tax Nexus: Understand the concept of sales tax nexus, which refers to the connection between your business and a particular taxing jurisdiction. Each jurisdiction has its own rules, so know where you have a sales tax obligation based on factors like physical presence, economic activity, or remote sales.
- Register for Sales Tax: Once you determine your sales tax obligations, register for a sales tax permit with the appropriate tax agency in each jurisdiction. Take note of the filing frequency, which could be monthly, quarterly, or annually.
- Collect Sales Tax: Calculate and collect sales tax from customers at the point of sale. Typically, you add the sales tax amount to the customer’s invoice and separate it from the taxable sales amount.
- Track Sales and Sales Tax: Maintain accurate records of sales transactions and the corresponding sales tax collected. Categorize sales by jurisdiction, product/service type, or any other relevant criteria for reporting and auditing purposes.
- Compile Sales Tax Reports: Generate sales tax reports that summarize your taxable sales, tax collected, and any exemptions or discounts applied. Ensure the reports align with the requirements of each tax agency you’re registered with.
- File Sales Tax Returns: File sales tax returns with the appropriate tax agencies by the due dates specified. Include the details of your taxable sales, sales tax collected, and any applicable exemptions. Some jurisdictions may require online filing, while others accept paper returns.
- Remit Sales Tax Payments: Pay the sales tax due to the tax agencies along with your filed returns. Ensure you remit the correct amount by the deadline to avoid penalties or interest charges.
- Maintain Proper Documentation: Keep copies of your sales tax permits, returns, payment confirmations, and any supporting documentation for each reporting period. These records are essential for auditing purposes or in case of tax disputes.
- Stay Updated on Tax Laws: Keep yourself informed about changes in sales tax laws, rates, and exemptions. Sales tax regulations can vary by jurisdiction and may change over time, so regularly review updates from the tax agencies or consult with tax professionals.
Utilizing accounting software or sales tax automation tools can simplify your sales tax reporting process by automating calculations, generating reports, and even assisting with filing and remittance. These tools can help you ensure accuracy, streamline compliance, and reduce the risk of errors.
Accurate sales tax reporting is crucial for maintaining compliance with tax laws, avoiding penalties, and demonstrating responsible financial management. It’s essential to understand your sales tax obligations, keep accurate records, and meet your reporting and remittance obligations in a timely manner.
Tax Preparation and Filing
Tax preparation and filing are important aspects of small business bookkeeping, ensuring compliance with tax regulations and fulfilling your tax obligations. Proper tax preparation allows you to calculate your tax liability accurately, maximize deductions and credits, and submit your tax returns on time.
Here are the key steps involved in tax preparation and filing:
- Gather Financial Documents: Collect all relevant financial documents, including income records, expense receipts, bank statements, and any other supporting documentation needed to prepare your tax return.
- Organize and Summarize Income: Review your revenue streams and classify your income into appropriate categories. This includes sales revenue, service fees, interest income, rental income, and any other sources of income relevant to your business.
- Calculate and Deduct Expenses: Determine and categorize your business expenses, keeping in mind applicable deductions and credits. Common expense categories include supplies, rent, utilities, advertising, professional fees, and employee wages.
- Consider Depreciation and Amortization: If you have acquired assets that can be depreciated or amortized, calculate and record these figures properly. Understand the rules and guidelines for determining the depreciation or amortization expense for tax purposes.
- Apply Tax Deductions and Credits: Identify eligible tax deductions and credits specific to your business. Examples include deductions for home office expenses, self-employment taxes, research and development credits, and small business health care credits.
- Review Changes in Tax Laws: Stay informed about any updates or changes in tax laws that may impact your business. Take note of new regulations, deductions, credits, or reporting requirements that apply to your filing year.
- Ensure Completeness and Accuracy: Review your tax return meticulously to ensure accuracy and completeness. Double-check all figures, calculations, and supporting documents to minimize errors and reduce the risk of audits or penalties.
- File Tax Returns: File your tax returns with the appropriate tax agencies within the designated deadlines. Determine whether you need to file federal, state, local, or other specific tax returns based on your business structure and location.
- Make Timely Tax Payments: Calculate your tax liability and pay the amount due to the tax agencies by the specified deadlines. Consider electronic payment options for convenience and to avoid potential payment delays or errors.
- Maintain Proper Documentation: Keep copies of your filed tax returns, payment confirmations, and supporting documents for future reference. Maintain organized records to facilitate future tax audits or inquiries.
While tax preparation can be complex, using tax software or seeking the assistance of a tax professional can streamline the process and ensure compliance. These resources can assist in accurate calculations, identification of deductions and credits, and timely filing of your tax returns.
Proper tax preparation and filing demonstrate your commitment to financial responsibility and compliance. By diligently fulfilling your tax obligations, you not only avoid potential penalties and audits but also contribute to the financial stability and reputation of your small business.
Audit and Financial Compliance
Audit and financial compliance are essential elements of small business bookkeeping. They involve ensuring that your financial records are accurate, transparent, and compliant with relevant regulations and industry standards. Implementing proper controls and processes for audit and compliance helps maintain the integrity of your financial information and builds trust with stakeholders.
Here are the key aspects of audit and financial compliance:
- Internal Controls: Establish robust internal controls to safeguard your assets, prevent fraud, and ensure accurate financial reporting. This can include segregation of duties, implementing approval processes, conducting periodic internal audits, and implementing software-based controls.
- Record Keeping: Maintain organized and detailed financial records that provide transparency and support the accuracy of your financial statements. Retain documents such as receipts, invoices, bank statements, payroll records, and tax returns for the required duration.
- Compliance with Accounting Standards: Adhere to relevant accounting standards, such as Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), depending on your jurisdiction and industry. Ensure that your financial statements are prepared in accordance with the applicable standards.
- Compliance with Tax Laws: Stay updated with tax regulations and meet your tax filing and payment obligations. File accurate and timely tax returns, maintain appropriate records, and effectively manage sales tax, payroll tax, and income tax compliance.
- Financial Statement Audits: Engage external auditors to perform financial statement audits, especially if required by legal or regulatory obligations, or if you seek to provide assurance to stakeholders. External audits provide an independent assessment of your financial statements’ accuracy and compliance.
- Reporting Requirements: Understand and fulfill any reporting obligations specific to your industry or jurisdiction, such as filings with regulatory agencies or industry-specific bodies. Comply with deadlines and provide accurate information in all required reports.
- Data Security and Privacy: Take steps to protect sensitive financial information and ensure compliance with privacy laws. Implement measures to prevent data breaches, securely store financial data, and educate your employees about data security and privacy best practices.
- Regular Financial Reviews: Regularly review your financial statements and reports to identify any inconsistencies or anomalies. Conduct periodic internal reviews to assess compliance, accuracy, and effectiveness of your financial processes.
- Engage Professional Advisors: Seek the guidance of accounting professionals, auditors, and legal advisors who specialize in audit and compliance. They can help ensure that you’re following best practices, maintaining compliance, and minimizing the risk of financial errors or non-compliance.
Audit and financial compliance are ongoing processes that require diligence and attention to detail. By maintaining accurate records, implementing strong internal controls, and engaging professional support when needed, you can mitigate risks, enhance financial transparency, and maintain the trust of your stakeholders.
Remember, audit and financial compliance demonstrate your commitment to ethical business practices, transparency, and sound financial management. By prioritizing these aspects, you not only protect your business’s reputation but also provide a solid foundation for long-term success and growth.
Closing Thoughts
Effective bookkeeping is an essential component of running a successful small business. By implementing proper bookkeeping practices, you can gain valuable insights into your financial performance, make informed business decisions, and ensure compliance with tax and financial regulations.
Throughout this article, we’ve covered various aspects of bookkeeping, from determining your accounting method to preparing financial statements and managing cash flow. Each step plays a crucial role in maintaining the financial health and stability of your small business.
Remember, consistency and accuracy are key. It’s important to maintain organized records, reconcile bank statements, and track income and expenses diligently. Payroll accounting should be handled meticulously to ensure employee satisfaction and compliance with labor laws. Remaining up to date with tax laws, reporting and remitting sales tax, and properly preparing and filing tax returns are integral to your financial success.
While bookkeeping can be overwhelming, using technology such as accounting software can simplify the process and save you time. Additionally, seeking guidance from professionals, such as certified public accountants (CPAs) or bookkeeping experts, can provide valuable insights and ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations.
Ultimately, effective bookkeeping allows you to maintain a clear understanding of your business’s financial position, make informed decisions, and identify opportunities for growth and improvement. By prioritizing accurate and organized bookkeeping practices, you lay a solid foundation for long-term success and financial stability.
So, take the time to set up proper bookkeeping systems, stay proactive in tracking your financial transactions, and utilize the resources and expertise available to you. With a solid bookkeeping foundation, you can confidently navigate the financial aspects of your small business and achieve your goals.