Home>Finance>Liquidity Premium: Definition, Examples, And Risk


Finance
Liquidity Premium: Definition, Examples, And Risk
Published: December 19, 2023
Learn about the liquidity premium in finance, including its definition, examples, and associated risks. Discover how this concept impacts the market and investment decisions.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Understanding Liquidity Premium in Finance
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on liquidity premium in finance, where we will define what liquidity premium is, provide examples to help you understand it better, and discuss the associated risks. By the end of this article, you’ll have a solid grasp of this important concept in finance.
Key Takeaways
- Liquidity premium refers to the additional return or yield that investors demand for investing in securities or assets that have lower liquidity.
- Investors require a liquidity premium to compensate for the potential risks and challenges associated with illiquid investments.
What is Liquidity Premium?
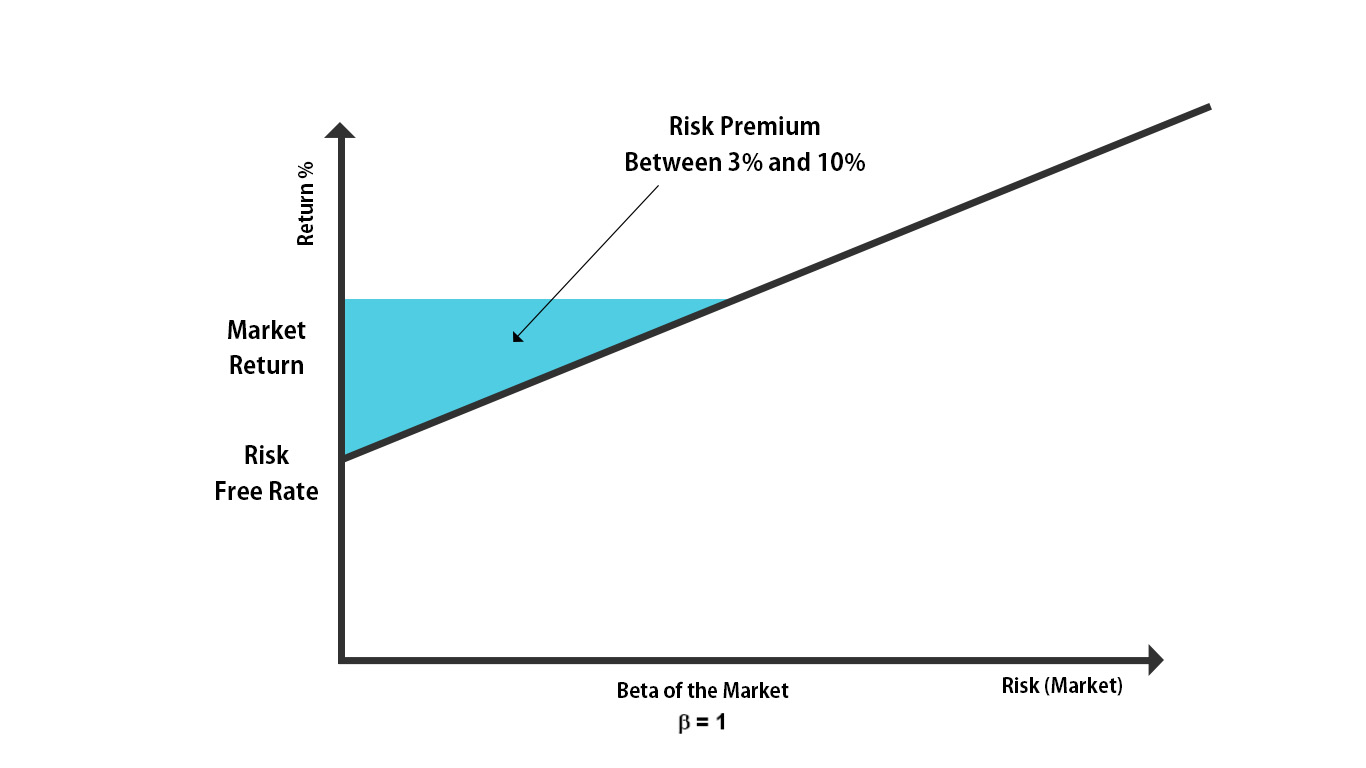
Liquidity premium is a term commonly used in the world of finance. It refers to the additional return or yield that investors demand for investing in securities or assets that have lower liquidity. In simpler terms, it is the price that investors are willing to pay to have their investment easily and quickly convertible into cash without significant impact on its market value.
To better understand liquidity premium, it’s essential to recognize that the market generally views liquidity as a desirable attribute. Investments that are easier to buy or sell without causing significant price changes are seen as more attractive. Therefore, assets with higher liquidity tend to have lower associated risks and, as a result, lower expected returns.
Examples of Liquidity Premium
Let’s explore some examples to illustrate liquidity premium in action:
- Bonds: When it comes to fixed-income investments, the level of liquidity can vary. Treasury bonds issued by the government are highly liquid due to their active secondary market and high trading volumes. As a result, they typically offer lower yields. On the other hand, corporate bonds from smaller companies with lower trading volumes may be less liquid and require a liquidity premium in the form of higher yields to attract investors.
- Real Estate: Real estate investments can also exhibit varying degrees of liquidity. Residential properties in prime locations and with high demand tend to have better liquidity, translating to lower returns. In contrast, commercial properties in less desirable areas or with limited potential buyers may require higher returns to compensate investors for the illiquidity of the asset.
These examples emphasize how liquidity premium is incorporated into different investment types to account for their associated risks and challenges.
Risks of Liquidity Premium
While liquidity premium provides potential benefits, it’s important to understand and evaluate the risks involved:
- Limited exit options: Investments with low liquidity can restrict your ability to sell or exit your position quickly. If you need to access your funds urgently, you may face challenges and potential losses due to fewer potential buyers and longer transaction times.
- Price volatility: Illiquid assets are more prone to significant price fluctuations compared to liquid investments. When fewer buyers and sellers participate in the market, the impact of each transaction is magnified, leading to potentially higher price volatility.
- Opportunity cost: By investing in illiquid assets that require a liquidity premium, you might miss out on other investment opportunities that offer better liquidity and potentially higher returns.
It’s crucial to carefully consider these risks before committing to investments with liquidity premiums.
Conclusion
Liquidity premium is an important concept in finance that refers to the additional return or yield investors demand for investing in illiquid securities or assets. By understanding liquidity premium and its associated risks, you can make more informed investment decisions and effectively manage your portfolio. Remember to assess the liquidity of different investments, evaluate potential returns, and consider the impact of liquidity premiums when constructing your investment strategy.