
Finance
What Is ACH Credit In Banking
Modified: January 15, 2024
Learn what ACH credits are in the world of banking and how they can impact your finances. Explore the benefits and potential risks of ACH credits in this informative guide.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to conducting financial transactions, it’s important to have a clear understanding of the various methods available. One such method that is commonly used in the banking industry is ACH Credit. But what exactly is ACH Credit and how does it work?
ACH stands for Automated Clearing House and it is a network that enables the electronic transfer of funds between banks and financial institutions. ACH Credit refers to a type of transaction in which funds are electronically deposited into a recipient’s account. This can be done for various purposes, such as direct deposits, payroll payments, tax refunds, or vendor payments.
The ACH Credit system facilitates seamless and efficient money transfers, eliminating the need for physical checks or manual processing. With just a few clicks, businesses and individuals can initiate ACH Credit payments, saving time and resources.
In this article, we will dive deeper into the world of ACH Credit, exploring how it works, its benefits and drawbacks, examples of transactions, and how to set up ACH Credit payments. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of this common banking practice and how it can benefit your financial transactions.
Definition of ACH Credit
ACH Credit is a method of electronic funds transfer that allows money to be deposited directly into a recipient’s bank account. The term “ACH” stands for Automated Clearing House, which is a network that facilitates the secure and efficient transfer of funds between financial institutions.
In an ACH Credit transaction, the sender initiates the payment electronically, providing the recipient’s bank account information, such as the routing number and account number. The sender’s bank then uses the ACH network to transmit the funds to the recipient’s bank, which credits the funds to the recipient’s account.
This method offers a convenient and cost-effective alternative to traditional paper checks or cash transfers. ACH Credit transactions can be used for a wide range of purposes, including direct deposits, vendor payments, tax refunds, and salary payments.
It is important to note that ACH Credit transactions require the recipient’s consent and authorization to receive funds. This ensures that the money is being transferred to the correct recipient and helps to prevent unauthorized or fraudulent transactions.
Overall, ACH Credit provides a secure and efficient way to transfer funds electronically, streamlining financial transactions and reducing the reliance on paper-based payment methods.
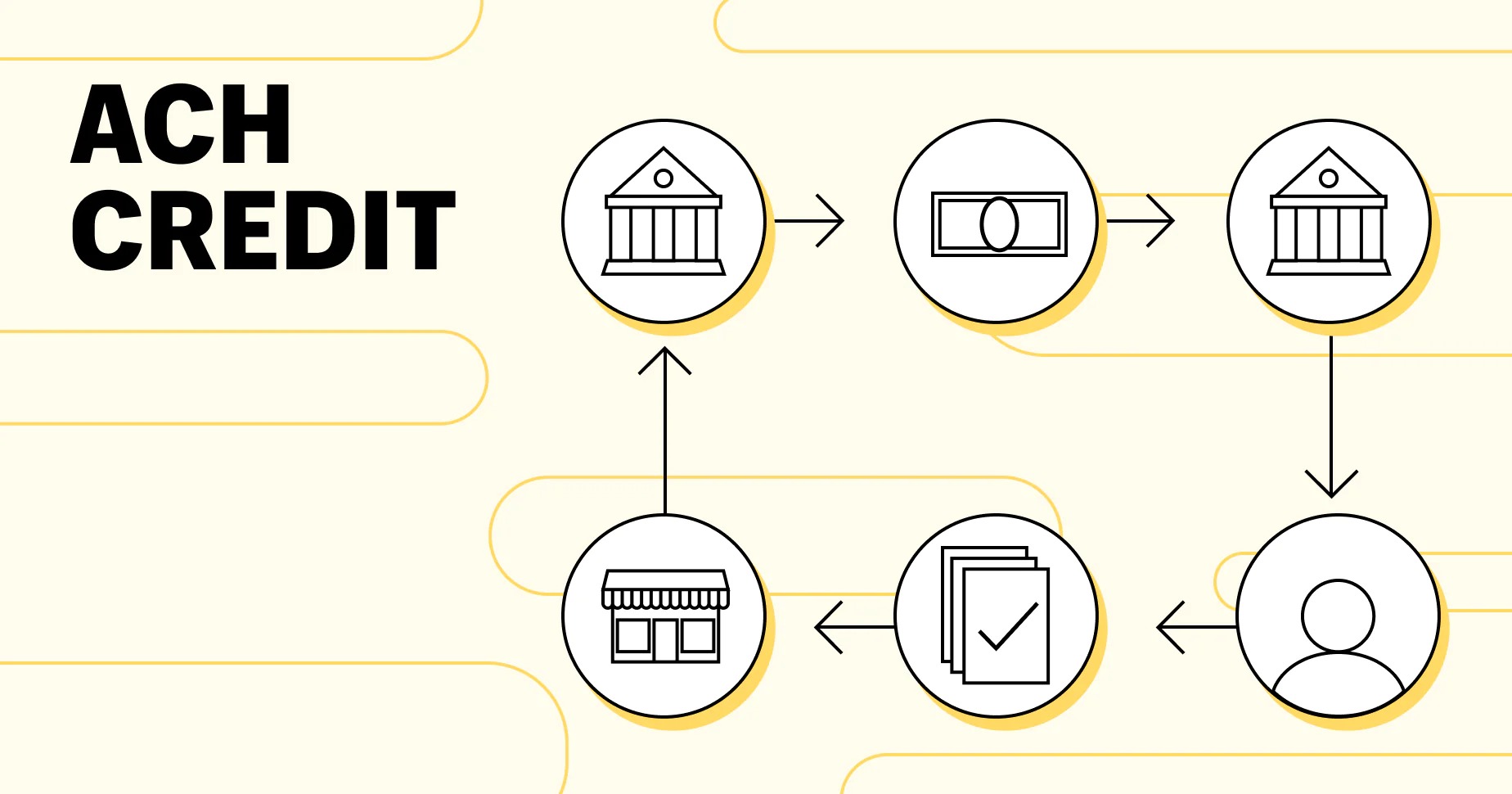
How ACH Credit Works
ACH Credit transactions involve a series of steps to transfer funds from the sender to the recipient’s account. Here is a breakdown of how ACH Credit works:
- The sender initiates the transaction: The sender, who can be an individual or a business, starts the ACH Credit transaction by instructing their bank to transfer a specific amount of money to the recipient’s bank account.
- The sender’s bank validates the request: Once the sender submits the transaction, their bank verifies their account and available funds to ensure that the transfer can be fulfilled. This step is crucial for preventing insufficient funds or fraudulent transactions.
- The transaction is sent through the ACH network: After validation, the sender’s bank uses the ACH network to transmit the transaction details to the recipient’s bank. The information includes the recipient’s bank account number, routing number, and the amount to be transferred.
- The recipient’s bank receives the transaction: The recipient’s bank, upon receiving the transaction details, verifies the information and confirms the recipient’s account. If all the details match, the bank credits the funds to the recipient’s account.
- The recipient can access the funds: Once the funds are credited to the recipient’s account, they can access the money through their bank account. They can withdraw the funds, use them for payments, or leave them in the account for future use.
It’s important to note that the speed of ACH Credit transactions may vary depending on the banks involved and the ACH network’s processing time. Typically, ACH Credit transactions can take one to three business days to complete.
A key advantage of ACH Credit is its automated nature, which eliminates the need for physical checks and manual processing. This results in faster and more efficient transactions, reducing the risk of errors and delays that can occur with traditional payment methods.
Overall, ACH Credit simplifies the process of transferring funds electronically, providing a secure and streamlined method for individuals and businesses to initiate payments to recipients’ bank accounts.
Benefits of ACH Credit
ACH Credit offers numerous benefits for both senders and recipients of funds. Here are some key advantages of using ACH Credit as a payment method:
- Speed and Efficiency: ACH Credit transactions are typically faster than traditional paper-based methods. Instead of waiting for physical checks to be sent and processed, funds can be electronically transferred between accounts, reducing the time it takes to receive payments.
- Cost Savings: ACH Credit transactions are generally more cost-effective compared to paper checks and wire transfers. Banks often charge lower fees for ACH Credit transactions, making it a cost-efficient option, especially for businesses that have frequent payment needs.
- Security: ACH Credit transactions offer enhanced security compared to physical checks, where there is a risk of loss or theft. With electronic transfers, the funds are securely transmitted within the ACH network, reducing the chances of fraudulent activity.
- Convenience: ACH Credit eliminates the need for manual handling and processing of physical checks. Both senders and recipients can enjoy the convenience of initiating and receiving payments electronically, reducing paperwork and administrative tasks.
- Automation: ACH Credit allows for automated and recurring payments, which is particularly beneficial for businesses that need to make regular salary payments, vendor payments, or subscription renewals. This automation saves time and reduces the likelihood of missing payment due dates.
- Accuracy: ACH Credit transactions reduce the risk of errors that can occur with manual data entry. By electronically transferring funds, the chances of misinterpreting or misplacing information are minimized, resulting in more accurate transactions.
These benefits make ACH Credit an attractive option for businesses, organizations, and individuals who seek a secure, efficient, and cost-effective way to transfer funds electronically.
Drawbacks of ACH Credit
While ACH Credit offers many advantages, it is important to be aware of the potential drawbacks associated with this payment method. Here are some of the key drawbacks of ACH Credit:
- Transaction Time: ACH Credit transactions may not be as immediate as other payment methods. Depending on the involved banks and the ACH network’s processing time, it can take one to three business days for the funds to be transferred. This could be a disadvantage if quick access to funds is needed.
- Transaction Limits: Some banks and financial institutions may impose transaction limits or caps on ACH Credit transfers. This means that there could be limitations on the maximum amount that can be sent or received through ACH Credit. It’s important to check with your bank to understand the transaction limits that apply to your account.
- Risk of Insufficient Funds: While ACH Credit transactions require validation of sender’s funds, there is still a risk of insufficient funds. If a sender’s account does not have enough money to cover the ACH Credit transfer, it could result in rejected or failed transactions, causing inconvenience and potential fees.
- Authorization and Consent: ACH Credit transactions require the recipient’s consent and authorization to receive funds. This means that a sender cannot initiate an ACH Credit transfer without the recipient’s permission. While this is intended for security purposes, it can cause delays if the recipient does not promptly provide authorization.
- Security Concerns: While ACH Credit transactions are generally secure, there is still a risk of unauthorized access or breaches. It is important to ensure that proper security measures are in place, such as using secure networks and safeguarding account information, to minimize the risk of fraudulent activities.
- Limited International Use: ACH Credit is primarily used within the domestic banking system of a country. It may not be suitable for international transactions, as it may not be supported by all countries or foreign banks. In such cases, alternative payment methods like wire transfers may be necessary.
Despite these drawbacks, ACH Credit remains a widely used and preferred payment method for many individuals and businesses due to its efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and convenience. Understanding the limitations and potential challenges can help users better manage their expectations and make informed decisions when using ACH Credit for their financial transactions.
Examples of ACH Credit Transactions
ACH Credit transactions are commonly used for various types of financial transactions. Here are some examples of how ACH Credit can be utilized:
- Direct Deposits: ACH Credit is frequently used for direct deposit of salaries, wages, or benefits. Employers can automatically deposit funds into their employees’ bank accounts, ensuring timely and convenient payment.
- Vendor Payments: Businesses often use ACH Credit to make payments to vendors and suppliers. Instead of writing and mailing checks or using other payment methods, businesses can transfer funds directly to the vendor’s bank account, streamlining the payment process.
- Bill Payments: Many individuals and businesses use ACH Credit to pay bills electronically. Whether it’s utility bills, credit card payments, or mortgage payments, ACH Credit allows for automated and recurring payments, ensuring timely and hassle-free transactions.
- Tax Refunds: ACH Credit is commonly utilized by tax authorities to issue tax refunds directly to taxpayers’ bank accounts. Rather than waiting for a physical refund check in the mail, taxpayers can receive their refunds quickly and securely through ACH Credit.
- Insurance Claims: Insurance companies often use ACH Credit to reimburse policyholders for claims. Instead of issuing paper checks, insurance companies can transfer claim payments directly into the policyholder’s bank account, expediting the reimbursement process.
- Online Payments: ACH Credit is a popular payment option for e-commerce businesses. Customers can provide their bank account information for payment processing, allowing for seamless and secure transactions without the need for credit cards.
- Government Benefits: ACH Credit is widely used for distributing government benefits, such as social security payments or unemployment benefits. This ensures efficient and reliable delivery of funds to recipients.
These examples showcase the versatility and convenience of ACH Credit for a wide range of financial transactions, making it a preferred method for both individuals and businesses.
ACH Credit vs. ACH Debit
ACH Credit and ACH Debit are two different types of electronic fund transfer methods used within the ACH system. While both involve the transfer of funds between bank accounts, there are distinct differences between the two:
ACH Credit: In an ACH Credit transaction, funds are electronically deposited into a recipient’s bank account. This type of transaction is typically initiated by the sender to make a payment or transfer funds to another party. Examples of ACH Credit include direct deposits, payroll payments, and vendor payments. ACH Credit transactions require the recipient’s consent and authorization to receive funds.
ACH Debit: On the other hand, in an ACH Debit transaction, funds are electronically withdrawn from the sender’s bank account to pay for goods or services. This type of transaction is initiated by the receiver or the receiver’s bank, typically to collect payments from the sender. Examples of ACH Debit include utility bill payments, loan repayments, and subscription fees. ACH Debit transactions require the sender’s consent and authorization for the funds to be deducted from their account.
Key Differences:
- Initiator of Transaction: In ACH Credit, the sender initiates the payment, while in ACH Debit, the receiver or receiver’s bank initiates the payment.
- Direction of Funds: ACH Credit involves depositing funds into the recipient’s account, while ACH Debit involves withdrawing funds from the sender’s account.
- Consent and Authorization: ACH Credit requires the recipient’s consent and authorization to receive funds, while ACH Debit requires the sender’s consent and authorization for the funds to be deducted from their account.
- Use Cases: ACH Credit is commonly used for direct deposits, vendor payments, and online payments, while ACH Debit is utilized for bill payments, loan repayments, and subscription fees.
It is important to note that both ACH Credit and ACH Debit transactions are processed through the ACH network, offering secure and efficient electronic transfer of funds. Understanding the differences between the two methods can help individuals and businesses determine the most appropriate option for their specific payment needs.
Security Measures for ACH Credit Transactions
ACH Credit transactions offer a secure means of electronic fund transfer. However, it is important to implement and follow certain security measures to ensure the protection of sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access. Here are some key security measures for ACH Credit transactions:
- Encryption: Utilize encryption technology to secure data during the electronic transmission of ACH Credit transactions. Encryption scrambles the data, making it unreadable to unauthorized individuals.
- Secure Networks: Ensure the use of secure and trusted networks when initiating ACH Credit transactions. Avoid using public Wi-Fi networks or insecure connections that may be susceptible to hacking or interception.
- Authentication and Authorization: Implement strong authentication and authorization protocols to verify the identity of individuals initiating ACH Credit transactions. This may include the use of secure login credentials, multi-factor authentication, and transaction authorization codes.
- Secure Account Information: Safeguard your bank account information from potential breaches. Avoid sharing sensitive details such as account numbers or routing numbers through insecure channels, such as email or unsecured websites.
- Frequent Account Monitoring: Regularly monitor your bank account for any suspicious activity or unauthorized transactions. Promptly report any potential fraudulent activity to your bank or financial institution to take appropriate measures.
- Educate Employees and Customers: Provide training and education to employees and customers on security best practices for ACH Credit transactions. This includes awareness of phishing scams, suspicious emails, and the importance of keeping personal information confidential.
- Secure Systems and Firewalls: Employ robust firewalls and up-to-date security software to protect against malware, viruses, and other cyber threats. Regularly update systems and software to ensure the latest security patches are implemented.
- Secure Storage of Information: Store sensitive ACH Credit transaction records and customer information securely. Use password protection and access controls to limit unauthorized access to sensitive data.
By implementing these security measures, individuals and businesses can enhance the protection of their ACH Credit transactions and minimize the risk of fraudulent activity or data breaches.
How to Set Up ACH Credit Payments
Setting up ACH Credit payments involves a few steps to ensure seamless and efficient transfers of funds. Here’s a guide on how to set up ACH Credit payments:
- Confirm ACH Credit capability: Firstly, verify that your bank or financial institution supports ACH Credit transactions. Contact your bank or check their website to determine if they offer ACH services and any associated fees or requirements.
- Gather recipient’s bank account information: Collect the necessary details of the recipient’s bank account. This typically includes the recipient’s name, account number, and routing number. Ensure you have accurate and up-to-date information to avoid any transfer errors.
- Authorize ACH Credit transactions: For recipients to accept ACH Credit payments, they need to provide their consent and authorize you as the sender to initiate the transfers. This may involve signing an authorization form or providing account details through a secure online portal.
- Set up payment schedules: Determine the frequency and timing of your ACH Credit payments. Whether it’s a one-time payment or recurring transfers, set up a schedule that aligns with your payment needs and the recipient’s requirements.
- Initiate ACH Credit transactions: Use your bank’s online banking platform or contact their customer service to initiate the ACH Credit transactions. Provide the recipient’s bank account information and the amount to be transferred. Verify all details before submitting the transaction.
- Communication and notification: Notify the recipient about the upcoming ACH Credit payments, including the scheduled dates and payment details. This ensures transparency and helps both parties stay aware of the incoming funds.
- Record keeping and reconciliation: Maintain accurate records of all ACH Credit transactions, including transaction details, dates, and amounts. This will assist in budgeting, tracking payments, and reconciling accounts.
- Monitor and review: Regularly review your ACH Credit transactions and account statements to ensure accuracy and identify any discrepancies or potential issues. Promptly report and address any concerns or errors with your bank or financial institution.
Keep in mind that the process of setting up ACH Credit payments may vary slightly depending on the specific bank or financial institution you are using. It’s always recommended to consult with your bank’s customer service or visit their website for detailed instructions on how to set up ACH Credit payments.
By following these steps and understanding the process, you can easily enable ACH Credit payments for a variety of purposes, streamlining your financial transactions and benefiting from the convenience and efficiency of electronic fund transfers.
Conclusion
ACH Credit is a secure and efficient method of transferring funds electronically. Whether it’s direct deposits, vendor payments, or bill payments, ACH Credit offers numerous benefits such as speed, cost savings, and convenience for both individuals and businesses.
Throughout this article, we explored the definition and workings of ACH Credit transactions, highlighting its advantages and drawbacks. We discussed how ACH Credit differs from ACH Debit and the security measures one should take to protect sensitive information during ACH Credit transactions.
We also provided examples of common ACH Credit transactions, showcasing its versatility and wide range of applications. Lastly, we outlined the steps involved in setting up ACH Credit payments, ensuring a smooth and successful electronic fund transfer process.
By understanding the ins and outs of ACH Credit, individuals and businesses can leverage this payment method to streamline their financial transactions, improve efficiency, and save costs. However, it is crucial to remain vigilant and follow security best practices to protect against potential risks and fraudulent activities.
In conclusion, ACH Credit is a powerful tool that simplifies and accelerates the transfer of funds, making it an invaluable resource in the modern banking landscape. With its time-saving benefits, cost-effectiveness, and security features, ACH Credit continues to revolutionize the way individuals and businesses handle their financial transactions.














