Home>Finance>An Accrual Of Wages Expense Would Have What Effect On The Balance Sheet?

Finance
An Accrual Of Wages Expense Would Have What Effect On The Balance Sheet?
Modified: February 21, 2024
Learn how the accrual of wages expense impacts the balance sheet in finance. Understand its effect on financial statements and reporting.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
In the world of finance, accurately recording and categorizing expenses is crucial for maintaining an accurate representation of a company’s financial position. One such expense that plays a vital role in financial statements is wages expense. Wages expense represents the compensation paid to employees for the services they provide to the company.
Accurate and timely recording of wages expense is essential for financial reporting and ensuring compliance with accounting principles such as accrual accounting. Accrual accounting recognizes revenue and expenses when they are incurred, regardless of when the actual cash transactions occur.
In some cases, a company may need to accrue wages expense at the end of an accounting period to accurately reflect the financial obligations it has incurred but has not yet paid. This accrual adjustment affects the balance sheet, one of the three primary financial statements that provide an overview of a company’s financial position.
Understanding the effect of accruing wages expense on the balance sheet is crucial for both financial analysts and decision-makers, as it provides insight into the overall liabilities and financial health of a company.
Definition of wages expense
Wages expense refers to the monetary compensation that a company pays to its employees in exchange for their services during a specific period. It encompasses the salaries, wages, bonuses, commissions, and other forms of compensation that employees receive from the company.
Wages expense is a significant component of a company’s operating expenses and is typically reported on the income statement as part of the operating costs. It is important to accurately track and record wages expense to determine the true cost of labor and assess the company’s profitability.
Wages expense can vary based on factors such as employee compensation agreements, overtime pay, and additional benefits. The company’s human resources department is responsible for calculating and ensuring the accurate payment of wages to employees.
Accurate recording of wages expense is not only essential for financial reporting but also for compliance with tax regulations and labor laws. In many jurisdictions, companies are required to maintain detailed records of wages paid to employees for statutory purposes, such as reporting to tax authorities and providing employee income statements.
Neglecting to properly record and report wages expense can lead to legal and financial consequences, including penalties, tax audits, and damage to the company’s reputation.
Accrual of wages expense
Accrual accounting requires expenses to be recognized when they are incurred, rather than when they are paid. In the case of wages expense, this means that if employees have worked during a certain accounting period but have not been paid by the end of that period, the company needs to accrue the wages expense.
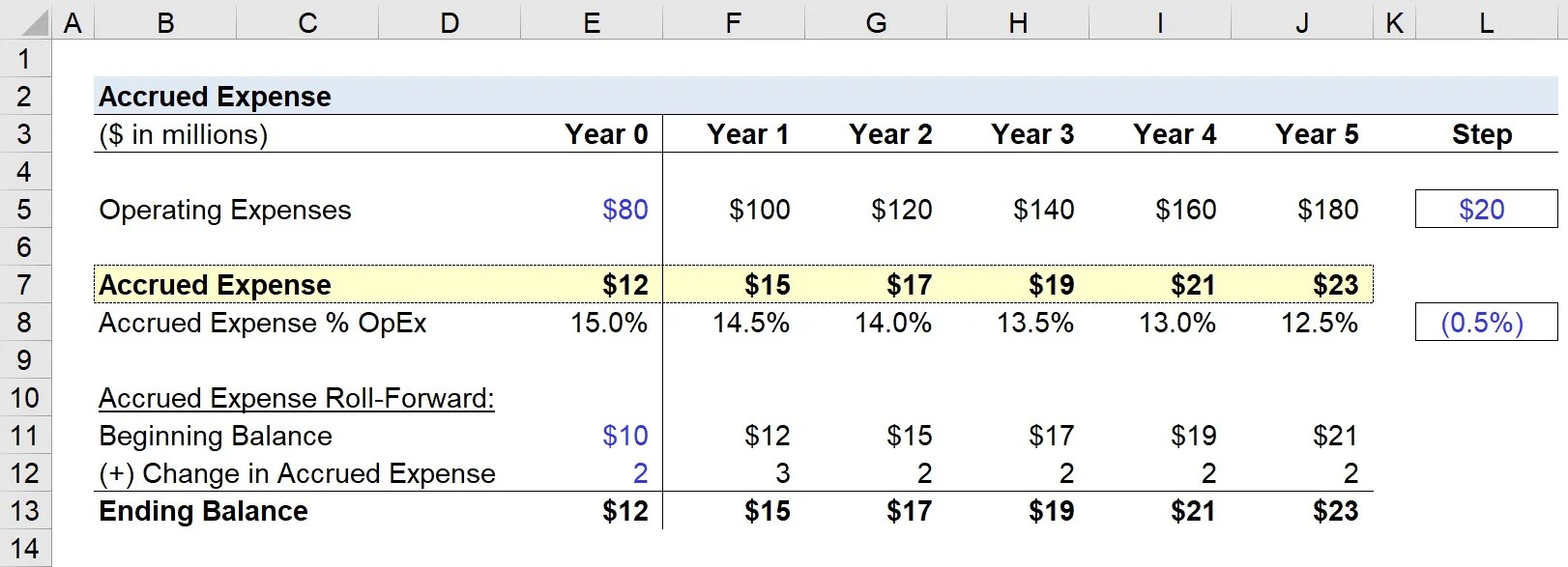
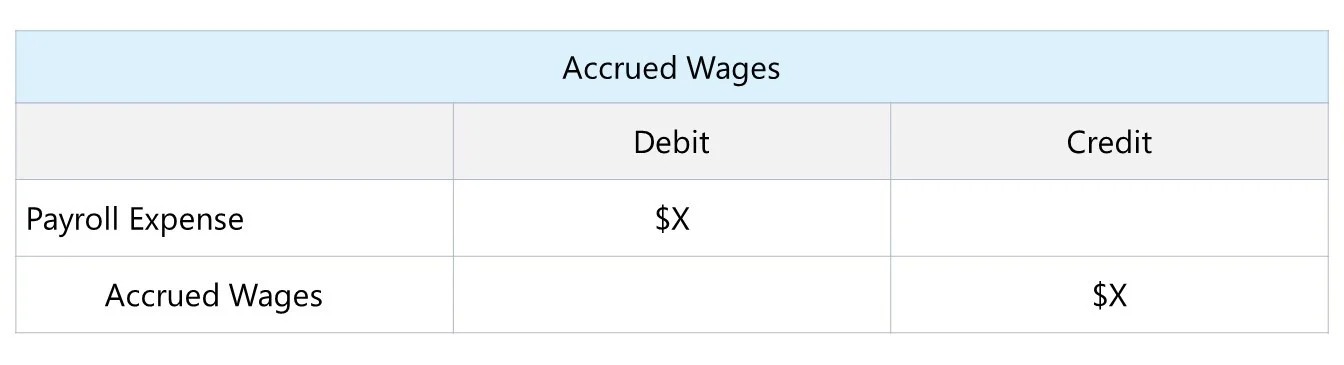
To accrue wages expense, the company estimates the amount of wages owed to employees based on the number of hours worked or the agreed-upon compensation. This accrual is recorded as a liability known as “accrued wages payable” or “wages payable” on the balance sheet.
The accrual of wages expense ensures that financial statements reflect the financial obligations the company has incurred, even if the actual cash payment to employees will take place in the following accounting period.
The accrual process involves adjusting the accounting records to reflect the wages expense for the period. This usually happens at the end of the accounting period, during the closing process. The specific method and timing of the accrual will depend on the company’s accounting policies and the regulations governing financial reporting.
Accruing wages expense not only ensures accurate financial reporting but also provides a more realistic representation of the company’s financial position. It recognizes the true cost of labor associated with the period, even if the cash outflow occurs later.
It is important to note that once the accrued wages payable is recorded, it is necessary to reverse the accrual in the following accounting period when the actual payment is made to employees. This ensures that the expense is not double-counted, and the financial statements accurately represent the cash flow and financial position of the company.
Effect of accruing wages expense on the balance sheet
The accrual of wages expense has a direct impact on the balance sheet, which is a financial statement that provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. Specifically, accruing wages expense affects both the liabilities and equity sections of the balance sheet.
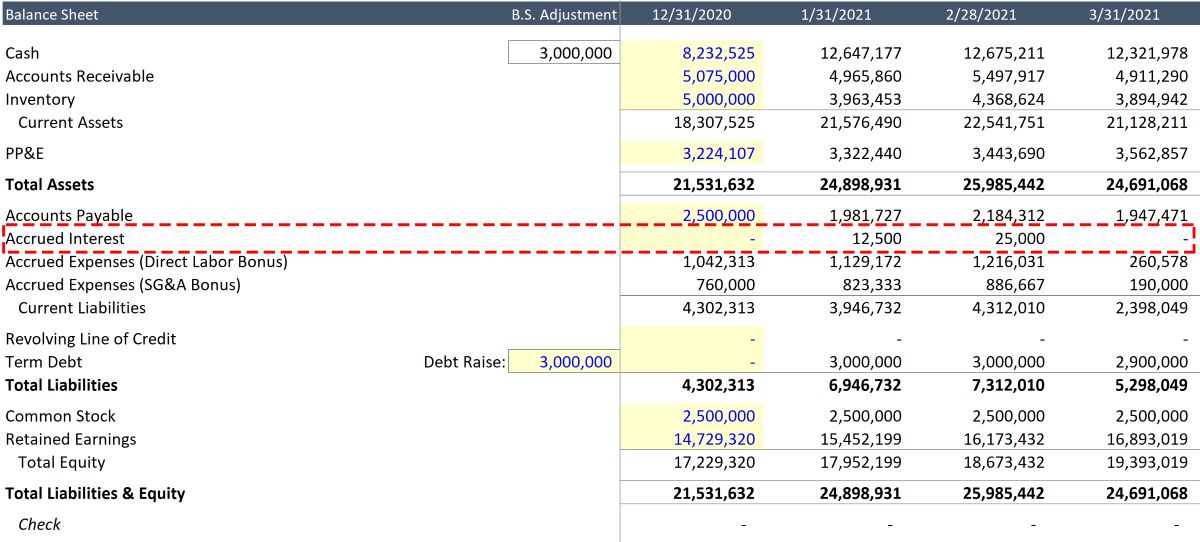
When the company accrues wages expense, it increases the liability account known as “accrued wages payable” or “wages payable.” This reflects the amount of wages that the company owes to its employees for the services they have rendered but have not yet been paid. Accrued wages payable is classified as a current liability, as it is expected to be settled within one year.
The increase in accrued wages payable represents an outstanding financial obligation and highlights the company’s liability to fulfill its payment obligations to employees. This accrued liability is reported under the current liabilities section of the balance sheet.
On the other hand, the accrual of wages expense does not directly impact the equity section of the balance sheet. However, it indirectly affects the retained earnings, which is a component of shareholder’s equity.
Accrued wages expense reduces the company’s net income for the period. This reduction in net income leads to a decrease in retained earnings, as net income is one of the factors that contribute to the calculation of retained earnings. Retained earnings represent the accumulated profits of the company that have not been distributed to shareholders as dividends.
Therefore, the accrual of wages expense reduces the amount of accumulated earnings that shareholders have invested in the company, ultimately impacting the overall equity position.
It’s important to note that the effect of accruing wages expense on the balance sheet is temporary. Once the actual payment is made to employees in the subsequent accounting period, the accrued wages payable is reduced, and the corresponding cash outflow is reflected in the cash or cash equivalents section of the balance sheet.
In summary, the accrual of wages expense increases the accrued wages payable liability on the balance sheet and decreases the retained earnings in the equity section. It accurately reflects the company’s financial obligations to employees and provides a comprehensive view of its financial position.
Increase in accrued wages payable
Accrued wages payable is a liability account on the balance sheet that reflects the amount of wages that a company owes to its employees for work performed but not yet paid.
When a company accrues wages expense, it increases the accrued wages payable account on the balance sheet. This increase represents the outstanding financial obligation of the company to its employees for the services rendered during a specific accounting period.
The increase in accrued wages payable is a result of estimating the amount of wages owed to employees based on factors such as the number of hours worked, salaries, or other compensation terms.
Accrued wages payable is classified as a current liability because it is expected to be settled within one year or the normal operating cycle of the company, whichever is longer.
An increase in accrued wages payable has several implications for a company:
- Financial Obligation: The increase in accrued wages payable signifies a financial obligation and highlights the company’s responsibility to pay its employees.
- Liquidity Management: Accruing wages expense allows the company to accurately track and plan for upcoming cash outflows related to employee compensation.
- Accurate Financial Reporting: By recording the increase in accrued wages payable, the company ensures that its financial statements accurately reflect the obligations incurred during the reporting period.
- Regulatory Compliance: Accruing wages expense is necessary for complying with accounting principles, tax regulations, and labor laws that require accurate financial reporting and record-keeping.
It is important for companies to regularly review and adjust their accrued wages payable balances to ensure accuracy. Any changes in estimates or actual payments made to employees should be reflected in the account to maintain the integrity of the financial statements.
Once the accrued wages payable is recorded, it is typically settled by making actual cash payments to employees in the subsequent accounting period. At that time, the accrued wages payable account is reduced, and the corresponding cash outflow is reflected on the balance sheet.
Overall, the increase in accrued wages payable showcases the financial responsibility of the company to its employees and provides valuable information for financial analysis and decision-making.
Decrease in retained earnings
Retained earnings is a component of shareholders’ equity on the balance sheet that represents the accumulated profits of a company that have not been distributed as dividends. When a company accrues wages expense, it indirectly impacts the retained earnings.
The accrual of wages expense reduces the net income of the company for the period. Net income is one of the factors that contribute to the calculation of retained earnings. Therefore, the decrease in net income due to the accrual of wages expense leads to a decrease in retained earnings.
Retained earnings are important for a company as they represent a source of internal financing and provide a measure of the company’s financial stability and growth over time.
The decrease in retained earnings can have several implications for a company:
- Impact on Shareholders: A decrease in retained earnings reduces the amount of accumulated earnings available to be distributed to shareholders as dividends.
- Investor Perception: A downward trend in retained earnings may signal lower profitability or less attractiveness to potential investors.
- Financial Health: Retained earnings serve as a cushion for the company, providing financial stability and flexibility for future investments, capital expenditures, or unforeseen expenses.
- Growth Opportunities: A reduction in retained earnings may limit the company’s ability to reinvest profits into the business for expansion, research and development, or strategic initiatives.
It is important for companies to strike a balance between distributing dividends to shareholders and retaining earnings for future growth and financial stability.
It’s worth mentioning that the decrease in retained earnings due to the accrual of wages expense is a temporary impact. Once the actual payment to employees is made in the subsequent accounting period, the accrued wages payable is reduced, and the corresponding cash outflow does not impact retained earnings. Instead, it is reflected in the cash or cash equivalents section of the balance sheet.
Accurate recording and management of retained earnings is crucial for financial reporting and providing insights into the financial health and long-term prospects of the company.
Impact on total assets
The accrual of wages expense has an impact on the total assets reported on the balance sheet. Total assets represent the resources owned by a company, which are categorized into current assets and non-current assets. The accrual of wages expense affects the current assets section of the balance sheet.
When a company accrues wages expense, it increases the liability account called “accrued wages payable” or “wages payable.” However, since the accrual of wages expense represents an amount owed by the company, it does not directly impact the total assets. Instead, it affects the current liabilities section of the balance sheet.
However, indirectly, the accrual of wages expense can impact total assets. Here’s how:
- Working Capital: The increase in accrued wages payable reduces the company’s working capital, which is calculated by subtracting current liabilities from current assets. Working capital represents the company’s ability to meet its short-term financial obligations.
- Liquidity: Accruing wages expense can impact the company’s cash flow and liquidity position, as it reflects an upcoming payment obligation. This may impact the company’s ability to use its current assets effectively, potentially reducing its overall liquidity.
- Affect on Ratios: Financial ratios, such as the current ratio (current assets divided by current liabilities), may be affected by the increase in accrued wages payable. A decrease in the current ratio may indicate a tighter liquidity position and potential challenges in meeting short-term obligations.
It’s important to note that while the accrual of wages expense impacts the current liabilities section of the balance sheet, it indirectly influences the overall financial health and liquidity position of the company, and thereby, the total assets.
Ultimately, the impact of accruing wages expense on the balance sheet and total assets highlights the importance of careful financial management and accurate recording of liabilities to provide a true and comprehensive picture of a company’s financial position.
Impact on total liabilities
The accrual of wages expense directly affects the total liabilities reported on the balance sheet. Total liabilities represent the financial obligations and debts owed by a company, which are categorized into current liabilities and long-term liabilities. The accrual of wages expense impacts the current liabilities section.
When a company accrues wages expense, it increases the liability account known as “accrued wages payable” or “wages payable.” This represents the amount of wages that the company owes to its employees for work performed but not yet paid.
The increase in accrued wages payable adds to the current liabilities of the company, reflecting the short-term payment obligations that need to be settled within one year or the normal operating cycle of the company, whichever is longer.
The impact of the accrual of wages expense on total liabilities is significant for a company and has various implications:
- Financial Health: The increase in total liabilities due to the accrual of wages expense provides insight into the company’s financial obligations and its ability to meet its short-term payment commitments.
- Working Capital: The increase in accrued wages payable reduces the company’s working capital, which is calculated by subtracting current liabilities from current assets. Working capital represents the company’s ability to cover its short-term liabilities.
- Cash Flow Management: Accruing wages expense helps the company accurately track and plan for upcoming cash outflows associated with employee compensation, enabling effective cash flow management.
- Financial Reporting: Accurate recording of accrued wages payable ensures compliance with accounting principles and provides transparency in financial statements, giving stakeholders a comprehensive view of the company’s financial position.
It is essential for companies to manage and monitor their accrued wages payable balance to ensure accuracy and update the liability with actual payments made. This helps maintain the integrity of the financial statements and provides reliable information to stakeholders.
The impact of the accrual of wages expense on total liabilities reflects the company’s responsibility to its employees and highlights the importance of proper financial management in maintaining a healthy financial position.
Conclusion
The accrual of wages expense plays a crucial role in accurately representing a company’s financial position on the balance sheet. Accruing wages expense ensures that financial statements adhere to accrual accounting principles by recognizing the costs incurred during a specific period, even if the actual cash payment has not been made.
The effect of accruing wages expense on the balance sheet is twofold. It increases the accrued wages payable liability, reflecting the outstanding financial obligation to employees for services rendered. Additionally, it indirectly impacts the equity section of the balance sheet by reducing retained earnings due to the decrease in net income.
The increase in accrued wages payable and the decrease in retained earnings provide important information for financial analysis and decision-making. They highlight the financial obligations and liquidity position of the company, affecting ratios such as working capital and the current ratio.
The impact of accruing wages expense on total assets and total liabilities underscores the need for accurate financial reporting and diligent financial management. It provides insights into the company’s financial health, its ability to meet short-term obligations, and its overall liquidity position.
Ultimately, accruing wages expense ensures transparency and compliance with accounting standards and regulations. It allows for proper financial planning and tracking of employee compensation obligations, contributing to the overall financial stability and success of the company.
By understanding the effects of accruing wages expense on the balance sheet, financial analysts, stakeholders, and decision-makers can gain valuable insights into a company’s financial health and make informed decisions based on a comprehensive understanding of its financial position.