Finance
What Is A Credit Authorization
Published: January 10, 2024
Learn about the credit authorization process and its importance in managing your finances. Explore how it impacts your financial decisions and protects your personal information.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Credit Authorization
- Purpose of Credit Authorization
- Importance of Credit Authorization
- Process of Credit Authorization
- Factors Considered in Credit Authorization
- Benefits of Credit Authorization
- Challenges in Credit Authorization
- Role of Technology in Credit Authorization
- Conclusion
Introduction
When it comes to managing personal or business finances, it’s important to have a solid understanding of credit authorization. Whether you’re applying for a loan, opening a new credit card, or making a significant purchase, credit authorization plays a crucial role in the process.
Credit authorization refers to the process that financial institutions and lenders follow to evaluate and approve or decline a request for credit. It involves assessing the creditworthiness of individuals or businesses to determine if they have the ability to repay the borrowed funds. This process is essential for maintaining financial stability and mitigating risks for both lenders and borrowers.
The purpose of credit authorization is to ensure responsible lending practices and enable individuals and businesses to access the financial resources they need to achieve their goals. By conducting a thorough evaluation of creditworthiness, lenders can make informed decisions, protect their interests, and maintain the overall integrity of the financial system.
Credit authorization encompasses various factors that lenders consider when evaluating credit applications. These factors include an individual’s credit history, income level, employment status, debt-to-income ratio, and other relevant financial information. By looking at these aspects, lenders can assess the level of risk they face in extending credit.
Understanding the importance of credit authorization is crucial for individuals who want to build and maintain a positive credit profile. A good credit history can open doors to better interest rates, higher credit limits, and increased access to financial opportunities. On the other hand, a poor credit history may result in higher interest rates, lower credit limits, and limited borrowing options.
Definition of Credit Authorization
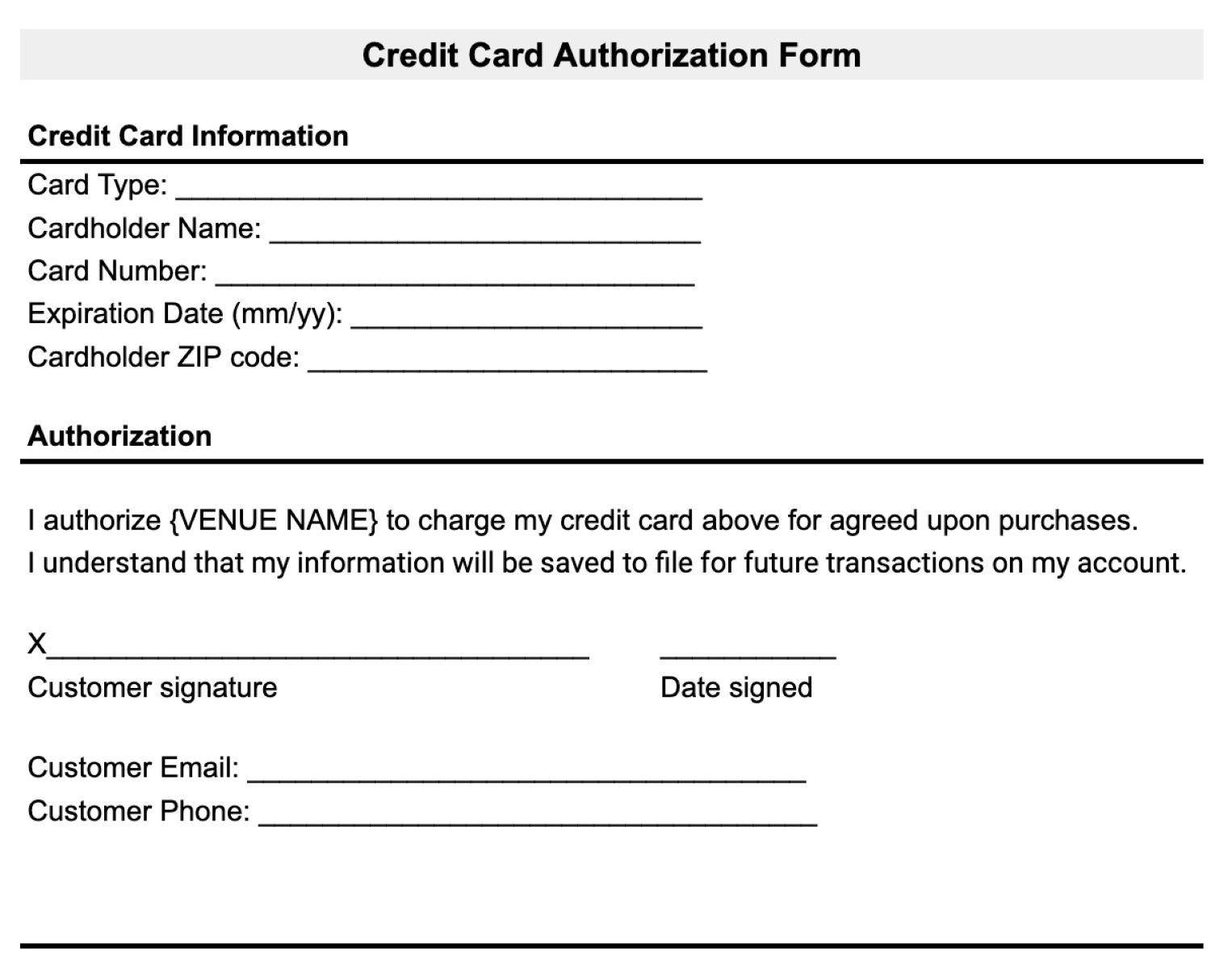
Credit authorization refers to the process by which financial institutions and lenders evaluate and approve or decline a request for credit, such as a loan or credit card. It involves assessing the creditworthiness of individuals or businesses to determine if they have the ability to repay the borrowed funds.
During the credit authorization process, lenders review an applicant’s financial information, credit history, income level, employment status, and other relevant factors to make an informed decision. This evaluation helps them assess the level of risk associated with extending credit to the applicant.
When an individual or business seeks credit, they submit an application containing personal and financial details to the lender. The lender then verifies the information provided and conducts a thorough analysis of the applicant’s creditworthiness. This evaluation helps determine if the applicant meets the lender’s criteria for credit approval.
If the credit authorization process results in an approval, the lender sets the terms and conditions of the credit agreement, such as the interest rate, repayment period, and any associated fees. The borrower then has the opportunity to accept the terms and proceed with the credit agreement.
If the credit authorization process leads to a decline, the lender provides a clear explanation as to why the request was not approved. This information can be valuable for the applicant to understand any areas of improvement needed for future credit applications.
Overall, credit authorization is a crucial aspect of the financial industry as it helps manage risk, protect lenders’ interests, and ensure responsible lending practices. It also plays a significant role for individuals and businesses in accessing the necessary financial resources to meet their goals and objectives.
Purpose of Credit Authorization
The purpose of credit authorization is to ensure responsible lending practices and enable individuals and businesses to access the financial resources they need. It serves several important objectives for both lenders and borrowers:
- Risk Assessment: Credit authorization allows lenders to assess the creditworthiness of applicants and evaluate the level of risk associated with extending credit. By analyzing an applicant’s financial information, credit history, income, and employment status, lenders can make informed decisions to protect their interests.
- Financial Stability: The credit authorization process helps maintain the overall stability of the financial system. By carefully evaluating credit applications, lenders can identify potential risks and prevent excessive borrowing, which could lead to financial instability for both the borrower and the lender.
- Responsible Lending: Credit authorization ensures that lenders engage in responsible lending practices. By evaluating an individual’s ability to repay the borrowed funds, lenders can offer appropriate credit limits and terms that align with the borrower’s financial capacity. This helps prevent borrowers from taking on excessive debt that they may struggle to repay.
- Access to Financial Resources: Credit authorization enables individuals and businesses to access the financial resources they need to achieve their goals. By providing credit opportunities to creditworthy borrowers, lenders contribute to the growth and development of the economy by supporting investments, business expansions, and personal financial endeavors.
- Discouraging Fraud: The credit authorization process helps detect and deter fraudulent activities. By carefully examining an applicant’s financial information and verifying their identity, lenders can minimize the risk of fraud and protect themselves and their customers from potential financial losses.
Overall, the purpose of credit authorization is to strike a balance between providing individuals and businesses with access to credit while ensuring responsible lending practices and mitigating risks for both borrowers and lenders. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability and integrity of the financial system while enabling economic growth and individual financial success.
Importance of Credit Authorization
Credit authorization is of utmost importance in the financial industry. It plays a significant role in maintaining the integrity of the lending process and has several key benefits for both lenders and borrowers:
- Responsible Lending: Credit authorization ensures that lenders engage in responsible lending practices by evaluating an applicant’s creditworthiness. This helps prevent borrowers from taking on excessive debt and reduces the risk of default, protecting both parties involved in the credit transaction.
- Risk Mitigation: By assessing an individual’s financial information and credit history, credit authorization helps lenders evaluate the level of risk associated with extending credit. This enables them to make informed decisions regarding interest rates, loan terms, and credit limits, safeguarding their financial interests and reducing the likelihood of default.
- Access to Financial Opportunities: Credit authorization allows individuals and businesses to access the financial resources they need to achieve their goals. Whether it is purchasing a home, starting a new business, or funding an education, credit authorization provides opportunities to obtain necessary funds, enabling growth and progress.
- Building Credit History: Establishing a positive credit history is essential for individuals to access future credit opportunities. Credit authorization provides individuals with the chance to demonstrate their creditworthiness and build a strong credit profile, which can lead to better interest rates, higher credit limits, and more favorable borrowing terms in the future.
- Economic Growth: The availability of credit plays a crucial role in driving economic growth. By extending credit to creditworthy borrowers, financial institutions and lenders provide the necessary capital for investments, business expansions, and other economic activities. This fuels economic development and contributes to overall prosperity.
Furthermore, credit authorization is essential for maintaining the stability of the financial system. By ensuring responsible lending practices, it helps prevent excessive borrowing, reduces the risk of financial crises, and protects the overall integrity of the banking and lending sectors.
Overall, the importance of credit authorization cannot be overstated. It promotes responsible lending practices, mitigates risk, enables financial opportunities, and fuels economic growth. It is a critical component of the lending process that benefits both lenders and borrowers, fostering a healthy and sustainable financial ecosystem.
Process of Credit Authorization
The process of credit authorization involves several steps that lenders follow to evaluate credit applications and make informed decisions. While the exact process may vary depending on the lending institution, the following steps are commonly involved:
- Application Submission: The credit authorization process begins with the applicant submitting a credit application to the lender. This application typically includes personal and financial information, such as income details, employment history, and credit references.
- Verification of Information: The lender verifies the information provided by the applicant to ensure its accuracy. This may involve contacting employers, reviewing pay stubs, and requesting documentation such as bank statements or tax returns.
- Credit History Evaluation: Lenders assess the applicant’s credit history to gauge their past credit performance. This involves reviewing the applicant’s credit report, which includes information about credit accounts, payment history, and any negative credit events such as defaults or bankruptcies.
- Assessment of Income and Financial Capacity: Lenders evaluate the applicant’s income level and financial capacity to repay the borrowed funds. This includes considering factors such as debt-to-income ratio, existing financial obligations, and stability of employment or business income.
- Review of Collateral (if applicable): In certain cases, such as secured loans, lenders may evaluate the value and condition of collateral that the applicant intends to pledge as security for the credit. This provides an additional layer of security for the lender in case of default.
- Risk Analysis: Based on the information gathered, lenders assess the level of risk associated with extending credit to the applicant. This involves considering factors such as the applicant’s creditworthiness, financial stability, and likelihood of repayment.
- Credit Decision: After completing the evaluation process, the lender makes a credit decision. If approved, the lender sets the terms and conditions of the credit agreement, including the interest rate, repayment period, and any associated fees. If declined, the lender provides a clear explanation of the reasons for the denial.
- Notification to the Applicant: The lender communicates the credit decision to the applicant. In the case of an approval, the applicant is provided with the details of the credit agreement and has the option to accept the terms. If declined, the applicant receives information about the reasons for the denial.
- Monitoring and Management: Once a credit agreement is established, the lender monitors the borrower’s repayment behavior and manages the credit account accordingly. This includes periodic review and assessment of the borrower’s creditworthiness and financial circumstances.
The process of credit authorization aims to ensure responsible lending practices, protect the interests of both lenders and borrowers, and maintain the overall integrity of the financial system. It provides a systematic evaluation of credit applications, allowing lenders to make informed decisions and borrowers to access the financial resources they need to fulfill their goals and aspirations.
Factors Considered in Credit Authorization
When evaluating credit applications, lenders take various factors into consideration to make informed decisions about credit authorization. These factors help lenders assess an individual’s creditworthiness and ability to repay the borrowed funds. While the specific weight assigned to each factor may differ among lenders, the following are commonly considered:
- Credit History: Lenders review an applicant’s credit history to assess their past credit performance. This includes examining payment history, outstanding debts, and the presence of any negative information such as late payments, defaults, or bankruptcies.
- Income and Employment: Lenders evaluate the applicant’s income level and stability of employment or business income. This helps assess the borrower’s ability to make timely repayments and manage new credit obligations.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio: The debt-to-income ratio is calculated by comparing an individual’s monthly debt payments to their gross monthly income. Lenders consider this ratio to determine if the applicant can comfortably manage additional debt obligations.
- Financial Obligations: Lenders review the applicant’s existing financial obligations, such as outstanding loans, credit card balances, or other monthly payments. This information helps assess the borrower’s capacity to take on additional credit.
- Collateral (if applicable): In cases where the credit is secured by collateral, lenders evaluate the value and condition of the asset being used as security. Collateral provides an additional layer of security for the lender in case of default.
- Length of Credit History: The length of an applicant’s credit history is taken into account. Lenders consider a longer credit history as an indicator of the borrower’s ability to handle credit responsibly over an extended period.
- Payment History: Lenders assess an individual’s history of making timely payments on previous credit obligations. Consistently making on-time payments indicates responsible credit management.
- Credit Utilization: The credit utilization ratio reflects the amount of available credit that an individual is using. Lenders consider lower credit utilization ratios as a positive indication of responsible credit management.
- Public Records: Lenders may review public records, such as tax liens, judgments, or legal actions, to evaluate the applicant’s financial stability and assess any potential risks associated with extending credit.
- Other Relevant Factors: Depending on the lending institution and the specific circumstances, other factors such as educational background, stability of residential address, and industry-specific considerations may also be taken into account.
By considering these factors, lenders are able to make well-informed credit authorization decisions. It allows them to mitigate risks, ensure responsible lending practices, and provide individuals and businesses with appropriate access to the financial resources they need.
Benefits of Credit Authorization
Credit authorization offers a range of benefits for both lenders and borrowers. The following are some key advantages of credit authorization:
- Access to Funds: Credit authorization enables individuals and businesses to access the funds they need for various purposes, such as purchasing a home, starting a business, or funding education. It provides opportunities for financial growth and allows borrowers to fulfill their goals and aspirations.
- Better Interest Rates: A positive credit authorization outcome can lead to better interest rates for borrowers. Lenders assess the creditworthiness of individuals and businesses and offer favorable terms to those with strong credit histories, allowing borrowers to save money on interest payments.
- Higher Credit Limits: Successfully obtaining credit authorization can result in higher credit limits for borrowers. This allows individuals and businesses to have greater purchasing power and flexibility when it comes to making significant investments or managing cash flow.
- Improved Credit Profile: Credit authorization plays a significant role in building and improving an individual’s credit profile. Timely repayments and responsible credit management contribute to positive credit history, which leads to a stronger credit profile over time.
- Financial Stability: By evaluating an individual’s creditworthiness and ability to repay borrowed funds, credit authorization supports financial stability. Lenders assess an individual’s financial situation and ensure that credit obligations are manageable, reducing the risk of default and financial distress.
- Opportunities for Business Growth: For businesses, credit authorization provides the opportunity to access working capital for expansion, investment in inventory, or the financing of new projects. It allows businesses to take advantage of growth opportunities and increase their competitiveness in the market.
- Protection for Lenders: Credit authorization helps lenders protect their interests by evaluating the creditworthiness of borrowers. By assessing an applicant’s financial information and credit history, lenders can make informed decisions and reduce the risk of defaults or non-payment.
- Responsible Lending Practices: Credit authorization ensures that lenders engage in responsible lending practices. By evaluating an individual’s financial capacity and creditworthiness, lenders can offer credit limits and terms that align with the borrower’s ability to repay, promoting responsible borrowing and reducing the risk of over-indebtedness.
- Economic Growth: The availability of credit fosters economic growth by providing individuals and businesses with the necessary resources to invest, expand, and thrive. Credit authorization encourages entrepreneurship, job creation, and overall economic development.
Overall, credit authorization benefits both lenders and borrowers by enabling access to funds, promoting financial stability, fostering responsible borrowing, and contributing to economic growth and prosperity.
Challenges in Credit Authorization
Credit authorization is a complex process that comes with its own set of challenges. Lenders face various obstacles and considerations when evaluating credit applications. Here are some of the common challenges involved in credit authorization:
- Risk Assessment: Assessing the creditworthiness of applicants can be challenging, especially when dealing with limited or incomplete financial information. Lenders must rely on available data and make informed judgments to assess the level of risk associated with extending credit.
- Changing Economic Conditions: Economic conditions, such as recessions or fluctuations in interest rates, can pose challenges in credit authorization. Lenders need to monitor and adjust their lending criteria to adapt to changing economic circumstances and mitigate potential risks.
- Verification of Information: Verifying the accuracy of the information provided by applicants can be a challenge. Lenders must carefully validate the data provided, such as income and employment details, to ensure its authenticity and minimize the risk of fraudulent applications.
- Assessing Self-Employed or Freelance Applicants: Evaluating the creditworthiness of self-employed individuals or those with variable income can be more complex. Lenders may require additional documentation or specialized methods for assessing their financial capacity and stability.
- Dealing with Thin Credit Files: Some applicants may have limited credit history or no credit history at all, making it challenging for lenders to assess their creditworthiness. Lenders may need to rely on alternative data sources or employ different approaches to evaluate these individuals.
- Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with various regulations and legal requirements adds complexity to the credit authorization process. Lenders must stay up-to-date with changing regulations, such as data protection laws and anti-money laundering measures, to ensure compliance and protect customer data and privacy.
- Balancing Risk and Access to Credit: Lenders face the challenge of striking a balance between managing risk and providing access to credit. They must assess the creditworthiness of applicants but also fulfill their role in supporting economic growth and providing financial opportunities to individuals and businesses.
- Managing Portfolio Risk: Lenders need to maintain a balanced and diverse portfolio of credit to minimize the risk of concentrated exposure to a particular sector or type of borrower. This requires careful risk management and monitoring of the overall credit portfolio.
- Keeping Pace with Technological Advancements: The rapid advancement of technology presents both opportunities and challenges in credit authorization. Lenders must adapt to new digital platforms and tools to streamline the credit authorization process, while also ensuring data security and privacy.
Overcoming these challenges requires a combination of industry expertise, advanced analytics, and continuous adaptation to changing market dynamics. By addressing these challenges, lenders can enhance their credit authorization processes and make informed decisions that benefit both lenders and borrowers.
Role of Technology in Credit Authorization
Technology plays a vital role in the credit authorization process, transforming the way lenders evaluate creditworthiness and make informed decisions. Here are some key ways technology impacts credit authorization:
- Efficiency and Speed: Technology automates many aspects of the credit authorization process, allowing for faster and more efficient evaluation of credit applications. Advanced algorithms and machine learning algorithms can quickly analyze large amounts of data, reducing manual effort and enhancing the speed of decision-making.
- Data Analysis and Risk Assessment: Technology enables lenders to access and analyze vast amounts of data to assess creditworthiness more accurately. Advanced analytics and data mining techniques can identify patterns and trends, providing lenders with insights into an applicant’s financial behavior and credit risk.
- Alternative Data Sources: Technology allows lenders to tap into non-traditional data sources for credit evaluation. This includes analyzing data from social media accounts, online purchasing history, or rent payments to supplement traditional credit information. Incorporating alternative data sources helps assess creditworthiness for individuals with limited credit history or unconventional income sources.
- Fraud Detection and Prevention: Advanced technology provides robust tools for fraud detection and prevention in credit authorization. Powerful algorithms can flag suspicious activities, identify patterns of fraudulent behavior, and detect identity theft, protecting lenders and borrowers from financial loss and maintaining the integrity of the credit process.
- Enhanced Decision Making: Technology provides lenders with data-driven insights and risk models to make more informed credit decisions. By leveraging predictive analytics, lenders can better assess credit risk, determine suitable terms, and optimize credit allocation to minimize defaults and maximize profitability.
- Online and Mobile Application: Technology enables borrowers to apply for credit conveniently through online and mobile platforms. This streamlines the application process, allowing applicants to provide necessary information and upload supporting documents digitally, saving time and effort for both lenders and borrowers.
- Customer Experience: Technology enhances the overall customer experience throughout the credit authorization process. Online portals, interactive interfaces, and real-time updates provide borrowers with transparency and convenience, allowing them to track the status of their applications and communicate effectively with lenders.
- Compliance and Security: Technology facilitates compliance with regulatory requirements and data security measures. Automated systems can ensure adherence to data protection laws, anti-money laundering regulations, and other industry-specific guidelines, safeguarding customer information and maintaining confidentiality.
- Continuous Improvement: Technology allows lenders to collect and analyze data on credit performance, enabling continuous improvement in credit authorization processes. By monitoring key metrics and outcomes, lenders can refine their risk models, adjust lending criteria, and enhance decision-making frameworks for more accurate credit assessments.
In summary, technology revolutionizes the credit authorization process by improving efficiency, enabling sophisticated risk assessment, enhancing decision-making, and ensuring compliance and security. It empowers lenders to make data-driven decisions, provide a seamless customer experience, and navigate potential risks effectively.
Conclusion
Credit authorization is a critical process that ensures responsible lending practices and enables individuals and businesses to access the financial resources they need. By evaluating an applicant’s creditworthiness and ability to repay borrowed funds, lenders can make informed decisions that protect their interests and maintain the integrity of the financial system.
The credit authorization process involves assessing various factors such as credit history, income level, employment status, and financial obligations. These factors help lenders evaluate the level of risk associated with extending credit and determine appropriate credit limits and terms.
Credit authorization offers numerous benefits for lenders and borrowers alike. It provides access to funds, allows for better interest rates and higher credit limits, and contributes to the building of a positive credit profile. It promotes financial stability, responsible lending practices, and supports economic growth and development.
However, credit authorization is not without its challenges. Lenders face obstacles in assessing risk, verifying information, and managing changing economic conditions. Compliance with regulations and balancing risk with access to credit are ongoing considerations in the credit authorization process.
Technology plays a crucial role in credit authorization, enhancing efficiency, data analysis, risk assessment, fraud detection, and customer experience. It enables lenders to make data-driven decisions, streamline processes, and ensure compliance and security.
In conclusion, credit authorization is a fundamental process in the financial industry that enables responsible lending and supports the financial goals of individuals and businesses. By addressing challenges, leveraging technology, and maintaining a balanced and customer-centric approach, lenders can make informed credit decisions that benefit both lenders and borrowers, fostering economic growth and stability.