
Finance
What Is A Qualitative Risk Assessment
Published: January 15, 2024
Learn how qualitative risk assessments in finance can help identify potential risks, evaluate their impact, and develop effective risk mitigation strategies.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of risk assessment! In today’s ever-changing and unpredictable business landscape, it has become essential for organizations to identify and manage potential risks that could impact their operations and financial stability. One of the key methods used in this process is qualitative risk assessment.
Qualitative risk assessment involves evaluating risks based on subjective measures such as likelihood and impact, rather than relying on quantitative data. While quantitative risk assessment uses numerical values and statistical models, qualitative risk assessment focuses on understanding the nature and characteristics of risks.
This article aims to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of qualitative risk assessment, its importance, steps involved, benefits, limitations, and examples of methods used in this process. Whether you are a business owner, risk manager, or simply interested in understanding how organizations assess risks, this article will serve as a valuable resource to help you navigate the fascinating world of qualitative risk assessment.
So, let’s dive in and explore the exciting realm of qualitative risk assessment!
Definition of Qualitative Risk Assessment
Qualitative risk assessment is a method used to evaluate and analyze risks based on subjective measures and expert judgment rather than numerical data and mathematical models. It focuses on understanding the qualitative aspects of risks, such as their likelihood, impact, and potential consequences, rather than quantifying them with precise numbers.
Unlike quantitative risk assessment, which relies on statistical analysis and probability calculations, qualitative risk assessment takes a more qualitative and descriptive approach. It is often used when there is a lack of reliable data or when the risks are difficult to quantify due to their complex and subjective nature.
In qualitative risk assessment, risks are typically categorized and prioritized based on their severity, likelihood, and potential impact on various aspects of the organization, such as financial performance, reputation, operational efficiency, and legal compliance. The assessment is usually conducted by a team of experts and stakeholders who bring their knowledge and expertise to the table.
The output of a qualitative risk assessment is usually a qualitative risk register or risk matrix, which provides an overview of identified risks, their potential impact, and potential mitigation strategies. This helps organizations in developing risk management plans and making informed decisions regarding risk treatment and mitigation.
Overall, qualitative risk assessment provides a valuable framework for organizations to identify and understand risks, prioritize them based on their potential impact, and develop appropriate risk management strategies to minimize or mitigate their potential negative effects.
Importance of Qualitative Risk Assessment
Qualitative risk assessment plays a vital role in the overall risk management process and is crucial for organizations across various industries. Here are some key reasons why qualitative risk assessment is important:
- Identifying and understanding risks: Qualitative risk assessment helps organizations identify and understand potential risks that could impact their operations, projects, or objectives. By evaluating risks qualitatively, organizations can gain insights into the nature, characteristics, and potential consequences of each risk, allowing them to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions.
- Prioritizing risks: With qualitative risk assessment, organizations can prioritize risks based on their severity, potential impact, and likelihood of occurrence. This allows management to prioritize their resources and efforts in addressing the most critical and high-impact risks, ensuring that risk mitigation and management efforts are focused where they matter most.
- Developing risk management strategies: Qualitative risk assessment provides the foundation for designing effective and targeted risk management strategies. By understanding the qualitative aspects of risks, organizations can develop appropriate risk treatment plans, implement control measures, and establish contingency plans to minimize the potential negative impacts of identified risks.
- Enhancing decision-making: A thorough qualitative risk assessment enables organizations to make better-informed decisions. By evaluating risks qualitatively, decision-makers can assess the potential impacts and likelihood of various scenarios, helping them weigh the associated risks and benefits before making critical decisions. This ensures that decisions are made with a clear understanding of the potential risks and their potential consequences.
- Improving stakeholder communication: Qualitative risk assessment aids in effective communication with stakeholders. By using a qualitative approach, organizations can explain risks in a language that is easily understood by stakeholders who may not be familiar with complex quantitative analysis. This promotes transparency, facilitates meaningful discussions, and builds trust with stakeholders.
In summary, qualitative risk assessment is essential for organizations to identify, prioritize, and manage risks effectively. It helps organizations gain a comprehensive understanding of risks, prioritize resources, develop targeted risk management strategies, make informed decisions, and communicate effectively with stakeholders. By incorporating qualitative risk assessment into their risk management processes, organizations can proactively address potential risks and uncertainties and minimize potential negative impacts on their operations and objectives.
Steps in Qualitative Risk Assessment
The process of qualitative risk assessment involves several key steps that help organizations systematically evaluate and analyze risks. While the specific steps may vary based on the organization’s needs and industry, here is a general framework for conducting qualitative risk assessment:
- Identify and define risks: The first step is to identify potential risks that could impact the organization. This involves brainstorming and gathering input from stakeholders, subject matter experts, and relevant sources. Each risk should be clearly defined, describing its nature, source, and potential consequences.
- Assess the likelihood: Once the risks are identified, the next step is to assess their likelihood or probability of occurring. This can be done through expert judgment, historical data analysis, or industry benchmarks. The goal is to determine how likely each risk is to happen, ranging from low to high likelihood.
- Evaluate the impact: After assessing the likelihood, the impact of each risk needs to be evaluated. This involves considering the potential consequences on different aspects of the organization, such as financial performance, reputation, operations, and compliance. The impact can be categorized based on severity, ranging from low to high impact.
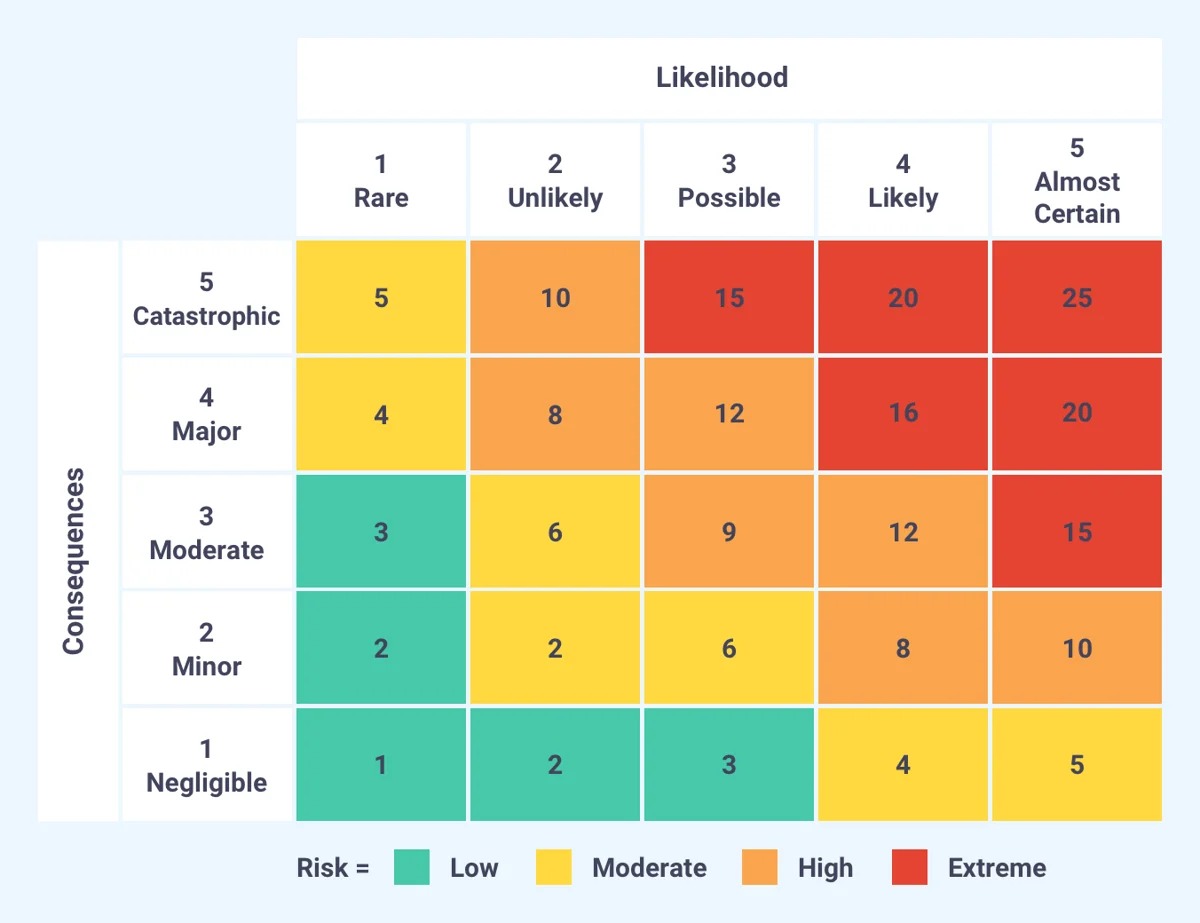
- Assign risk ratings: To prioritize risks, assign risk ratings based on the combination of likelihood and impact. This can be done using a qualitative risk matrix, where risks are plotted based on their likelihood and impact ratings, resulting in risk ratings such as low, medium, and high. The risk ratings help in prioritizing risks for further analysis and management.
- Analyze risk causes and controls: For each identified risk, analyze the potential causes and existing controls or mitigation measures in place. This step helps in understanding the factors that contribute to the risk and identifies any gaps or weaknesses in the existing control mechanisms.
- Develop risk mitigation strategies: Based on the analysis of risks and their causes, develop risk mitigation strategies to minimize or eliminate the potential negative impacts. This can involve implementing additional control measures, creating contingency plans, or transferring the risk through insurance or contracts.
- Monitor and review: Regularly monitor and review the effectiveness of the risk mitigation strategies and controls. As the business and external environment evolves, new risks may emerge, and existing risks may change in their likelihood or impact. By continuously monitoring and reviewing the risks, organizations can ensure that their risk management efforts remain up to date and effective.
By following these steps, organizations can systematically evaluate and manage risks using a qualitative approach. The process allows for a structured and comprehensive analysis of risks, enabling effective decision-making, prioritization of resources, and implementation of appropriate risk management strategies.
Benefits of Qualitative Risk Assessment
Qualitative risk assessment offers organizations several key benefits in effectively managing risks. Here are some of the significant advantages of using a qualitative approach:
- Quick identification of risks: Qualitative risk assessment allows for a rapid identification of potential risks. By relying on expert judgment and subjective measures, the process can uncover risks based on the collective knowledge and experience of the risk management team. This helps organizations proactively address risks before they escalate and cause significant damage.
- Flexibility and adaptability: Unlike quantitative risk assessment that requires precise data and metrics, qualitative risk assessment provides flexibility and adaptability. It can be used in situations where data is limited, uncertain, or difficult to quantify. This allows organizations to assess and manage risks even in complex and dynamic environments.
- Improved risk awareness: Through qualitative risk assessment, organizations gain a deeper understanding of the nature, characteristics, and potential consequences of risks. This enhances risk awareness among employees and stakeholders, promoting a risk-conscious culture within the organization. Increased awareness enables individuals to identify risks and take appropriate actions, contributing to a proactive risk management approach.
- Focus on high-impact risks: Qualitative risk assessment helps organizations focus their resources and efforts on high-impact risks. By considering the potential consequences and impact of each risk, organizations can prioritize their risk management efforts, ensuring that resources are allocated to address the risks that pose the greatest threat to their objectives and operations.
- Enhanced decision-making: The qualitative approach provides a clearer picture of risks, allowing for more informed decision-making. Decision-makers can consider the qualitative evaluations of risks, including their likelihood and impact, when evaluating different courses of action. This enables organizations to make well-informed decisions that take into account the potential risks and their potential consequences.
- Better communication with stakeholders: Qualitative risk assessment simplifies communication about risks with stakeholders who may not have a background in quantitative analysis. By using qualitative measures and descriptive language, organizations can effectively communicate risks, their potential impacts, and the rationale behind risk management strategies. This promotes transparency and understanding among stakeholders, fostering trust and collaboration.
Overall, qualitative risk assessment provides organizations with a flexible and adaptable approach to identify, understand, prioritize, and manage risks. It improves risk awareness, helps in resource allocation, enhances decision-making, and promotes effective communication with stakeholders. By harnessing the benefits of qualitative risk assessment, organizations can navigate uncertainties and proactively address potential risks, safeguarding their operations and achieving their objectives.
Limitations of Qualitative Risk Assessment
While qualitative risk assessment offers valuable insights and benefits, it is important to recognize its limitations. Here are some of the key limitations associated with the qualitative approach:
- Subjectivity: Qualitative risk assessment relies on subjective measures and expert judgment, which can introduce bias and variability. Different individuals may interpret risks differently, leading to inconsistencies in the assessment process. This subjectivity can limit the reliability and reproducibility of the results.
- Lack of precision: Unlike quantitative risk assessment that provides precise numerical values, qualitative risk assessment lacks precision. It does not provide quantifiable data, making it challenging to compare risks or conduct rigorous analysis. This can limit the ability to make accurate predictions or perform robust statistical evaluations.
- Limited data availability: Qualitative risk assessment relies heavily on the expertise and knowledge of individuals involved in the assessment. It can be challenging to obtain comprehensive and reliable data, particularly in situations where data is scarce or unavailable. This can lead to incomplete risk assessments or reliance on anecdotal evidence.
- Difficulty in ranking risks: The qualitative approach may face challenges in accurately ranking risks. The subjective nature of the assessment can make it difficult to assign consistent and comparable ratings to different risks. This can reduce the effectiveness of the risk prioritization process and may result in an inaccurate representation of risk severity.
- Limited statistical analysis: Qualitative risk assessment does not lend itself well to rigorous statistical analysis. It does not provide numerical data that can be used to conduct comprehensive statistical evaluations or apply sophisticated risk modeling techniques. This limits the ability to perform quantitative comparisons or make complex risk predictions.
- Difficulty in measuring effectiveness: It can be challenging to measure the effectiveness of risk mitigation strategies and controls in qualitative risk assessment. Without clear metrics or quantitative data, it is difficult to assess the extent to which the implemented measures have reduced the risk or improved risk management. This makes it harder to gauge the impact of risk management efforts.
Despite these limitations, qualitative risk assessment remains a valuable tool in risk management. It provides a framework for understanding and addressing risks, even in situations where quantitative data is limited. By acknowledging the limitations and incorporating other risk assessment methods where applicable, organizations can enhance the overall effectiveness and reliability of their risk management processes.
Examples of Qualitative Risk Assessment Methods
Qualitative risk assessment involves various methods and techniques to evaluate and analyze risks. Here are a few examples of commonly used qualitative risk assessment methods:
- Risk Matrix: The risk matrix is a popular tool that enables organizations to assess risks on a qualitative scale. Risks are evaluated based on their likelihood and impact, and plotted on a matrix with different risk levels, such as low, medium, and high. This helps in prioritizing risks and determining appropriate risk management strategies.
- Scenario Analysis: Scenario analysis involves identifying and evaluating different plausible scenarios that could impact an organization. Each scenario represents a potential risk, and its likelihood, impact, and potential consequences are assessed qualitatively. This method helps organizations understand the range of possible risks they may face and consider their potential impacts.
- Hazard and Operability (HAZOP) Study: HAZOP is a structured brainstorming technique used primarily in the process industries to identify and assess risks associated with complex systems or operations. It involves systematically reviewing the design or operation of a system, identifying possible deviations or abnormalities, and analyzing their potential consequences.
- Delphi Technique: The Delphi technique is a consensus-based approach that involves a panel of experts providing independent assessments and feedback on risks. The experts’ responses are collected, summarized, and shared anonymously, allowing them to revise their opinions and converge towards a consensus. This method helps to mitigate biases and enhance the accuracy of risk assessments.
- Fault Tree Analysis (FTA): FTA is a deductive risk assessment technique used to identify the contributing factors that can lead to a specific event or outcome. It involves constructing a fault tree diagram that depicts various events and their interrelationships, along with the probabilities of those events occurring. By analyzing the fault tree, organizations can understand the qualitative factors contributing to a risk.
- Checklists and Surveys: Checklists and surveys involve a structured approach to evaluate risks by systematically going through a list of predefined questions or criteria. These tools facilitate the identification and assessment of risks based on expert knowledge and standardized checklists or surveys. They provide a consistent and systematic way of evaluating risks across different areas or processes.
These are just a few examples of qualitative risk assessment methods. The choice of method depends on the specific needs and context of the organization. Often, organizations combine multiple methods to gain a comprehensive understanding of risks and make informed decisions in their risk management processes.
Conclusion
Qualitative risk assessment is a valuable tool in the risk management toolkit, allowing organizations to identify, understand, and manage risks based on subjective measures and expert judgment. While it has its limitations, qualitative risk assessment offers several benefits, including quick risk identification, flexibility, improved risk awareness, and better decision-making.
The steps involved in qualitative risk assessment provide a structured framework for organizations to assess risks, prioritize resources, and develop targeted risk management strategies. From identifying and defining risks to analyzing their causes and controls, the process helps organizations gain a comprehensive understanding of the potential risks they face and implement appropriate mitigation strategies.
Examples of qualitative risk assessment methods, such as risk matrices, scenario analysis, HAZOP studies, the Delphi technique, fault tree analysis, and checklists/surveys, provide organizations with a range of tools to evaluate and analyze risks from different perspectives.
While quantitative risk assessment may provide more precise data and statistical analysis, qualitative risk assessment caters to situations where quantitative data is limited or uncertain. It allows for a more qualitative and descriptive evaluation of risks, enabling organizations to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions to manage risks effectively.
By incorporating qualitative risk assessment into their risk management processes, organizations can navigate uncertainties, prioritize resources, and minimize potential negative impacts on their objectives and operations. It promotes a proactive approach to risk management, fosters stakeholder communication, and enhances the overall resilience of the organization.
In conclusion, qualitative risk assessment is a powerful tool that complements quantitative techniques, providing a holistic view of risks and enabling organizations to make informed decisions based on expert judgment, subjective measures, and a deep understanding of potential risks. It is an essential component of a robust and effective risk management program, helping organizations navigate uncertainties and achieve their objectives in an ever-changing business environment.