Finance
What Is A Sequence Number In Banking
Published: October 13, 2023
Discover the importance of sequence numbers in banking and how they contribute to the efficient processing of financial transactions. Explore the role of finance in maintaining accurate records and ensuring secure transactions.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Sequence Number in Banking
- Importance of Sequence Numbers in Banking Processes
- How Sequence Numbers Are Generated
- Benefits of Using Sequence Numbers in Banking
- Common Uses of Sequence Numbers in Banking
- Sequence Numbers and Transaction Tracking
- Sequence Numbers in Online Banking
- Sequence Numbers and Fraud Prevention
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to the world of banking, where numbers play a crucial role in ensuring smooth and efficient processes. One such number that holds immense significance in the banking industry is the sequence number. Whether you’re making a transaction, tracking your account activity, or even safeguarding against fraud, sequence numbers are an indispensable part of the banking system.
In simple terms, a sequence number in banking is a unique identifier assigned to each transaction or event that occurs within a banking system. This number allows banks to keep track of the order in which transactions take place and ensure accurate recordkeeping. From depositing funds to making withdrawals, from online transfers to paper checks, every action is assigned a sequence number to facilitate organization and provide a reliable trail of banking activities.
The importance of sequence numbers in banking cannot be overstated. They serve as a vital component in ensuring the integrity and efficiency of banking processes. Not only do they help customers keep track of their transactions, but they also assist banks in managing their operations and maintaining accurate records. Whether you’re a frequent user of online banking or prefer the traditional branch experience, sequence numbers are an integral part of the behind-the-scenes framework that keeps the banking system running seamlessly.
In the following sections, we will explore the definition and generation of sequence numbers, as well as their significance in various aspects of banking. We will also explore how sequence numbers are utilized in transaction tracking, online banking, and fraud prevention. By understanding the role and purpose of sequence numbers, you will gain a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of the banking industry and the measures put in place to ensure secure and efficient financial transactions.
Definition of Sequence Number in Banking
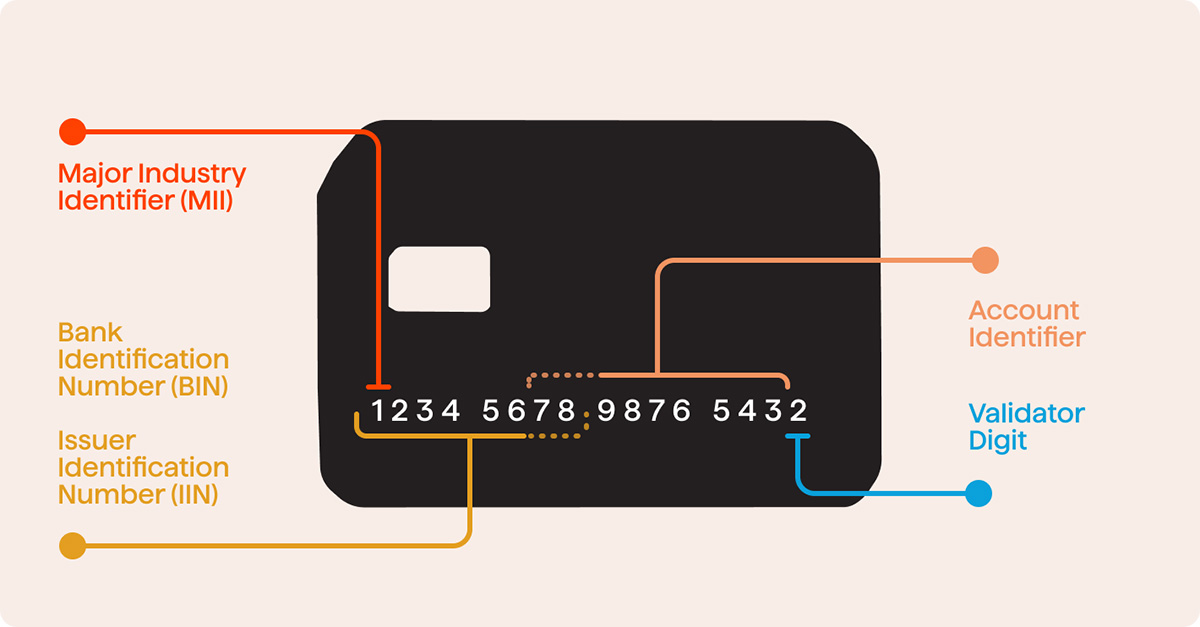
A sequence number in banking refers to a unique identifier assigned to each transaction or event that takes place within a banking system. It serves as a chronological record of banking activities, allowing banks to track the order in which transactions occur and maintain accurate records.
Think of a sequence number as a way to label and organize transactions. Just like a serial number, each transaction is given a specific sequence number which can be used to identify and distinguish it from other transactions. This number helps banks keep track of the flow of funds and ensures that all transactions are processed in the correct order.
Sequence numbers are typically generated automatically by the banking system and are usually a combination of numbers and alphabets. They are designed to be unique, ensuring that no two transactions have the same sequence number. This uniqueness is crucial for accurate recordkeeping, as it eliminates confusion and allows easy retrieval of transaction information when needed.
When a customer conducts a transaction, such as making a deposit or transferring funds, the banking system assigns a sequence number to that specific transaction. This sequence number is then associated with the customer’s account, making it easy to track and refer to in the future. Whether it’s checking your account balance, reviewing transaction history, or resolving disputes, sequence numbers play a crucial role in providing accurate and reliable banking information.
It’s important to note that sequence numbers can be used for various types of banking activities, not just limited to transactions. They can also be assigned to events such as account openings, loan applications, and even customer service interactions. This allows banks to maintain a comprehensive record of all customer interactions, contributing to a complete and transparent banking experience.
Importance of Sequence Numbers in Banking Processes
Sequence numbers play a vital role in ensuring the smooth and efficient functioning of banking processes. They help maintain order, accuracy, and accountability in various aspects of the banking system. Here are some reasons why sequence numbers are crucial in banking:
1. Transaction Tracking: Sequence numbers allow banks to track and organize the flow of transactions. By assigning a unique identifier to each transaction, banks can easily locate and retrieve specific information when needed. This is particularly helpful for customers who want to review their transaction history or reconcile their accounts.
2. Accurate Recordkeeping: With sequence numbers, banks can maintain accurate and detailed records of all banking activities. This level of recordkeeping is essential for regulatory compliance, audit purposes, and resolving any disputes or discrepancies that may arise. Sequence numbers provide an indisputable trail of every transaction, ensuring transparency and accountability.
3. Orderly Processing: Sequence numbers help banks ensure that transactions are processed in the correct order. This is especially important in scenarios where multiple transactions occur simultaneously. By assigning a unique sequence number to each transaction, banks can prioritize and process them in the sequence they were received, reducing the chances of errors or mismanagement.
4. Efficient Dispute Resolution: In the unfortunate event of a dispute or discrepancy, sequence numbers can be invaluable in resolving the issue quickly and accurately. With a clear sequence of events provided by the sequence numbers, banks can easily trace the origin of the problem, identify any errors or fraudulent activities, and take the necessary steps to rectify the situation.
5. Streamlined Operations: Sequence numbers help banks streamline their operations by providing a systematic way to track and manage transactions. By organizing transactions in a chronological order, banks can easily identify any bottlenecks or inefficiencies in their processes and take corrective measures to enhance the overall efficiency and customer experience.
Overall, sequence numbers are an essential component of the banking system. They ensure accuracy, transparency, and efficiency in various banking processes, from transaction tracking to recordkeeping and dispute resolution. By utilizing sequence numbers, banks can provide their customers with a secure and reliable banking experience while maintaining the integrity of their operations.
How Sequence Numbers Are Generated
Sequence numbers in banking are typically generated automatically by the banking system. The process of generating sequence numbers involves a combination of algorithmic calculations and unique identifiers to ensure the uniqueness and integrity of each number.
Here are the steps involved in generating sequence numbers:
- System Configuration: Banks configure their systems to generate sequence numbers based on their specific requirements and business rules. This includes defining the length and format of the sequence numbers and determining the starting point.
- Unique Identifiers: To ensure the uniqueness of each sequence number, the banking system incorporates unique identifiers. These identifiers can be a combination of information such as the account number, branch code, transaction type, timestamp, and a random element. By combining these elements, the system can generate a unique sequence number for each transaction.
- Algorithmic Calculations: The banking system utilizes algorithms to calculate and generate the sequence numbers based on the predefined configuration and unique identifiers. These algorithms ensure that each sequence number is generated in a systematic and predictable manner, allowing for easy tracking and retrieval of transaction information.
- Sequencing Logic: To maintain the correct order of transactions, the banking system incorporates sequencing logic. This logic ensures that each transaction is assigned the next available sequence number in the correct sequence. By adhering to this logic, banks can accurately track the chronological order of transactions and avoid any confusion or mismanagement.
- Secure Storage: Once generated, the sequence numbers are securely stored in the banking system’s database. This ensures that the sequence numbers are readily available for reference and retrieval when needed, providing a reliable record of each banking activity.
It’s important to note that the specific process of generating sequence numbers can vary between different banks and their individual systems. However, the underlying principles of uniqueness, algorithmic calculations, and sequencing logic remain consistent across the banking industry.
By leveraging technology and robust systems, banks can generate sequence numbers efficiently and effectively, ensuring the accurate tracking and management of transactions throughout the banking process.
Benefits of Using Sequence Numbers in Banking
The use of sequence numbers in banking brings various benefits to both the banks and the customers. These benefits contribute to the efficiency, transparency, and security of banking processes. Here are some key advantages of using sequence numbers:
- Order and Organization: Sequence numbers bring order and organization to banking transactions. By assigning a unique identifier to each transaction, banks can easily track, sort, and retrieve information in a systematic manner. This ensures an efficient flow of transactions and helps prevent confusion or errors.
- Transaction Tracking: Sequence numbers enable customers to track their transactions accurately. Whether through online banking platforms, mobile apps, or paper statements, customers can easily locate and review specific transactions using the assigned sequence numbers. This allows for better financial management and a clearer understanding of their banking activities.
- Accurate Recordkeeping: The use of sequence numbers ensures accurate and reliable recordkeeping in the banking system. Each transaction is assigned a unique sequence number, creating a comprehensive and transparent history of all banking activities. This level of recordkeeping is valuable for regulatory compliance, audit purposes, and resolving disputes or discrepancies.
- Efficient Customer Service: Sequence numbers play a crucial role in providing efficient and effective customer service. When customers contact the bank with inquiries or support requests, customer service representatives can quickly locate and reference specific transactions using the sequence numbers. This streamlines the resolution process and enhances the overall customer experience.
- Fraud Prevention: Sequence numbers contribute to fraud prevention measures in the banking system. By assigning unique identifiers to transactions, banks can easily identify any unauthorized or fraudulent activity. The sequence numbers create an audit trail that allows banks to trace and investigate suspicious transactions, helping to protect both the bank and its customers from fraudulent activities.
The benefits of using sequence numbers extend to both the operational efficiency of banks and the convenience and security of customers. They provide a structured framework for managing transactions, tracking banking activities, and ensuring the accuracy and integrity of the financial system.
Overall, sequence numbers are a valuable tool in the banking industry, enhancing transparency, organization, and security. They contribute to a seamless banking experience for customers and help banks maintain efficient operations while meeting regulatory requirements.
Common Uses of Sequence Numbers in Banking
Sequence numbers find wide application in various aspects of banking. They serve as unique identifiers for different types of transactions and events within the banking system. Here are some common uses of sequence numbers in banking:
- Transaction Identification: Sequence numbers are used to identify and track individual transactions. For example, when a customer makes a deposit or a withdrawal, each transaction is assigned a unique sequence number. This allows banks and customers to easily locate and reference specific transactions in their records.
- Account Activity Tracking: Sequence numbers help customers track their account activity. Whether it’s monitoring incoming and outgoing funds, tracking cash withdrawals, or checking the status of online transfers, sequence numbers provide a chronological order to the account’s transaction history. This makes it easier for customers to review and reconcile their account activity.
- Check Clearing: When a paper check is processed, sequence numbers are used to track the clearing process. Each check is assigned a sequence number that helps banks keep track of the check’s journey from the depositor’s account to the payee’s account. This ensures that checks are processed in the correct order and facilitates efficient clearing and settlement.
- Loan Application and Processing: Sequence numbers are utilized in loan applications and processing. Each loan application is assigned a unique sequence number, which helps banks track and manage the loan application process. From the initial application to the approval and disbursement stages, sequence numbers provide a systematic way to monitor the progress of each loan application.
- Customer Service Interactions: Sequence numbers are employed in customer service interactions to ensure accurate records and efficient resolution of inquiries or complaints. When customers reach out to the bank for support, their interactions are assigned sequence numbers, allowing customer service representatives to easily retrieve information and provide appropriate assistance.
- Online and Mobile Banking: In the realm of online and mobile banking, sequence numbers play a crucial role. When customers perform transactions, such as transferring funds or paying bills online, each action is recorded with a sequence number. This provides customers with a history of their online activities and assists in identifying and addressing any issues or discrepancies.
These are just a few examples of how sequence numbers are commonly used in banking. They contribute to accurate recordkeeping, efficient tracking of banking activities, and streamlined processes that enhance both the customer experience and the operational efficiency of banking institutions.
Sequence Numbers and Transaction Tracking
Sequence numbers play a crucial role in transaction tracking within the banking industry. They provide a unique identifier for each transaction, enabling banks to accurately track, record, and retrieve transaction information when needed. Here are some key aspects of how sequence numbers facilitate transaction tracking:
Order and Chronological Record: Sequence numbers help maintain the order and chronological record of transactions. Each transaction is assigned a sequence number, which represents its place in the sequential flow of banking activities. This allows banks to easily determine the order in which transactions occurred, enabling them to trace the history of financial activities accurately.
Easy Reference and Retrieval: Sequence numbers provide a convenient way to reference and retrieve specific transactions. Customers can use these numbers to track their transactions and access related details, such as the date, amount, and involved parties. This helps customers reconcile their accounts, review transaction history, and obtain necessary information for financial planning or tax purposes.
Transaction Verification and Validation: Sequence numbers also aid in transaction verification and validation. As each transaction is associated with a unique sequence number, it becomes easier to verify the authenticity of the transaction and validate its occurrence. This is particularly important for detecting and preventing unauthorized or fraudulent activities within the banking system.
Dispute Resolution: In the event of a dispute or discrepancy, sequence numbers serve as valuable evidence. Customers can provide the sequence numbers of specific transactions to their banks to investigate and resolve the issue. The sequence numbers help banks match the customer’s records with their own, facilitating a faster and more accurate resolution process.
Enhanced Transaction Monitoring: Sequence numbers enable banks to implement robust transaction monitoring systems. By monitoring sequence numbers, banks can identify unusual or suspicious patterns of transactions, which may indicate fraudulent or illegal activities. This proactive approach enhances the security of the banking system and helps protect customers from potential risks.
Audit Trail and Regulatory Compliance: Sequence numbers contribute to establishing an audit trail for financial transactions. These numbers serve as a crucial component in meeting regulatory requirements and ensuring compliance with industry standards. The ability to trace and provide a comprehensive record of transactions is essential during internal and external audits or investigations.
Overall, sequence numbers serve as a fundamental mechanism for tracking transactions in banking. They enable accurate recordkeeping, easy retrieval of transaction details, verification of transaction authenticity, and efficient dispute resolution. By leveraging sequence numbers, banks can ensure transparency, maintain customer trust, and uphold the integrity of their financial processes.
Sequence Numbers in Online Banking
Sequence numbers are integral to the functioning of online banking systems, providing a systematic way to track and manage transactions conducted through digital platforms. Here’s how sequence numbers are utilized in online banking:
Transaction Confirmation and Receipts: When customers perform transactions online, such as fund transfers or bill payments, each transaction is assigned a unique sequence number. This number serves as a confirmation and receipt for the transaction, allowing customers to verify the details and track the status of their online transactions.
Transaction History and Account Statements: Sequence numbers play a crucial role in maintaining an accurate and comprehensive transaction history for customers’ online banking activities. Each transaction is recorded with its corresponding sequence number, enabling customers to view and track their past transactions conveniently. Online banking platforms often provide account statements that include sequence numbers, allowing customers to review and reconcile their account activity.
Real-Time Transaction Monitoring: Online banking systems utilize sequence numbers to enable real-time monitoring of transactions. As transactions occur, the sequence numbers are recorded, and the system analyzes them to detect any suspicious or unauthorized activities. This ensures the security and integrity of online banking transactions, providing customers with peace of mind.
Transaction Verification and Validation: Sequence numbers are a vital tool in verifying and validating online transactions. Customers can use the assigned sequence numbers to confirm the authenticity and accuracy of their completed transactions. Should any discrepancies or concerns arise, the sequence numbers provide a reference point for investigating and resolving issues with the bank.
Secure Transaction Tracking: Sequence numbers contribute to the secure tracking of online transactions. They provide a unique identifier for each transaction, allowing customers to easily locate and review specific transactions within their online banking platforms. This helps in identifying and resolving any issues related to transaction errors, unauthorized activities, or account disputes.
Streamlined Customer Service: Sequence numbers assist customer service representatives in providing efficient and personalized support to customers. When customers reach out for assistance regarding specific transactions, the sequence numbers associated with those transactions facilitate the identification and retrieval of relevant information, enabling quicker and more effective customer service.
Regulatory Compliance: Sequence numbers in online banking systems contribute to meeting regulatory compliance requirements. They form a crucial part of audit trails and records, helping banks comply with financial regulations and provide comprehensive transaction data for internal and external audits.
Overall, sequence numbers in online banking systems enhance transaction tracking, provide transaction verification and validation, improve customer service, and support regulatory compliance. They are vital in ensuring a secure and efficient online banking experience for customers while maintaining the integrity and transparency of digital financial transactions.
Sequence Numbers and Fraud Prevention
Sequence numbers play a crucial role in fraud prevention within the banking industry. By providing a unique identifier for each transaction, sequence numbers contribute to detecting and preventing fraudulent activities. Here’s how sequence numbers aid in fraud prevention:
Transaction Monitoring: Sequence numbers enable banks to establish robust transaction monitoring systems. By tracking the sequence numbers associated with transactions, banks can identify any unusual patterns or discrepancies that may indicate fraudulent activities. Unusual sequence number variations or unexpected changes in transaction patterns can trigger alerts and prompt further investigation.
Red Flags for Unauthorized Activities: Sequence numbers help identify unauthorized activities in banking systems. If a sequence number is associated with a transaction that a customer did not initiate or authorize, it can raise a red flag and alert the bank to potential fraudulent activity. Detecting such anomalies allows banks to take immediate action to mitigate the risk and protect the customer’s account.
Fraudulent Transaction Detection: Sequence numbers assist banks in detecting fraudulent transactions. If a sequence number is flagged as potentially fraudulent, additional security measures can be implemented to verify the authenticity of the transaction. This may involve contacting the customer for confirmation, conducting further investigation, or placing a hold on the transaction until its legitimacy is established.
Transaction Traceability: Sequence numbers provide a traceable trail of transactions, allowing banks to investigate and resolve suspicious activities. Banks can review the sequence numbers associated with a particular account to track the source of fraudulent transactions, identify potential vulnerabilities, and take appropriate measures to prevent further unauthorized activities.
Fraudulent Account Detection: Sequence numbers also aid in identifying fraudulent accounts. If multiple accounts are associated with suspicious or fraudulent sequence numbers, it can indicate fraudulent account creation or identity theft. By tracking these sequence numbers, banks can identify and flag such accounts to prevent further unauthorized transactions.
Enhanced Security Measures: Sequence numbers contribute to the implementation of enhanced security measures in banking systems. Banks can use sequence numbers to establish additional layers of verification or authentication for certain transactions. For example, customers may be required to provide the sequence number associated with a particular transaction when contacting customer service for additional assistance or making changes to their accounts.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Sequence numbers help banks assess and mitigate the risk of fraudulent activities. By analyzing the sequence numbers associated with transactions, banks can identify potential vulnerabilities in their systems and implement proactive measures to prevent fraudulent activities before they occur.
Overall, sequence numbers play a vital role in fraud prevention within the banking industry. By leveraging these unique identifiers, banks can enhance transaction monitoring, detect unauthorized activities, trace fraudulent transactions, detect fraudulent accounts, and implement additional security measures to safeguard customer accounts and prevent financial losses.
Conclusion
Sequence numbers are an essential component of the banking industry, providing a systematic way to track, organize, and manage transactions. These unique identifiers play a vital role in ensuring the accuracy, efficiency, and security of banking processes.
Throughout this article, we have explored the definition and generation of sequence numbers in banking, highlighting their significance in various aspects of the industry. Sequence numbers enable accurate transaction tracking, allowing customers to monitor their account activity and reconcile their records. They contribute to efficient dispute resolution, providing a chronological record of transactions that can be accessed and reviewed when needed.
Furthermore, sequence numbers enhance the security and integrity of banking systems. They serve as a tool for fraud prevention, enabling banks to detect and mitigate fraudulent activities. The traceability provided by sequence numbers aids in identifying unauthorized transactions and fraudulent accounts, protecting both banks and customers from financial losses.
Sequence numbers also contribute to the seamless operation of online banking platforms. They enable customers to track their online transactions, verify their authenticity, and access detailed transaction histories. By facilitating efficient customer service interactions and ensuring regulatory compliance, sequence numbers enhance the overall banking experience for customers.
In conclusion, sequence numbers are a fundamental element of the banking industry, contributing to accurate recordkeeping, transaction monitoring, customer service, and fraud prevention. They ensure the integrity of financial transactions and provide customers with the confidence and trust they seek in their banking relationships.
As the banking industry continues to evolve, sequence numbers will remain vital in facilitating efficient and secure financial transactions. By understanding and appreciating the role of sequence numbers in banking, we gain a deeper understanding of the intricate processes that drive the industry forward.