Finance
What Is An Option Credit Spread
Modified: January 15, 2024
Learn the ins and outs of finance with this comprehensive guide on option credit spreads. Discover how to maximize your returns in the stock market.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Options trading can be a lucrative and exciting venture for investors, offering a wide range of strategies to take advantage of market movements. One such strategy is the option credit spread, which allows traders to generate income or reduce risk by simultaneously selling and buying options contracts.
An option credit spread involves combining two options contracts of the same type (either both calls or both puts) on the same underlying asset. The trader sells one option with a higher strike price and buys another option with a lower strike price, creating a “spread” between the two. The difference in premium received from selling the higher strike option and the premium paid for buying the lower strike option represents the net credit received.
Option credit spreads are popular among traders because they provide opportunities to profit in various market conditions, including bullish, bearish, and neutral scenarios. This strategy also offers a limited risk profile, making it attractive for risk-averse investors. However, it is essential to understand the different types of option credit spreads, strategies involved, and the associated risks before incorporating them into your trading arsenal.
Definition of an Option Credit Spread
An option credit spread is a trading strategy that involves simultaneously selling and buying options contracts on the same underlying asset. This strategy creates a spread between the strike prices of the two options, resulting in a net credit to the trader.
When executing an option credit spread, traders sell one option contract with a higher strike price and buy another option contract with a lower strike price. The options can be either calls or puts, depending on the trader’s market outlook and strategy. The premium received from selling the higher strike option is greater than the premium paid for buying the lower strike option, resulting in a net credit.
The primary objective of employing an option credit spread is to generate income or reduce risk. By receiving a net credit upfront, traders can enjoy immediate profits if the options expire worthless. The maximum profit potential is limited to the net credit received, while the maximum loss is capped at the difference between the strike prices minus the net credit.
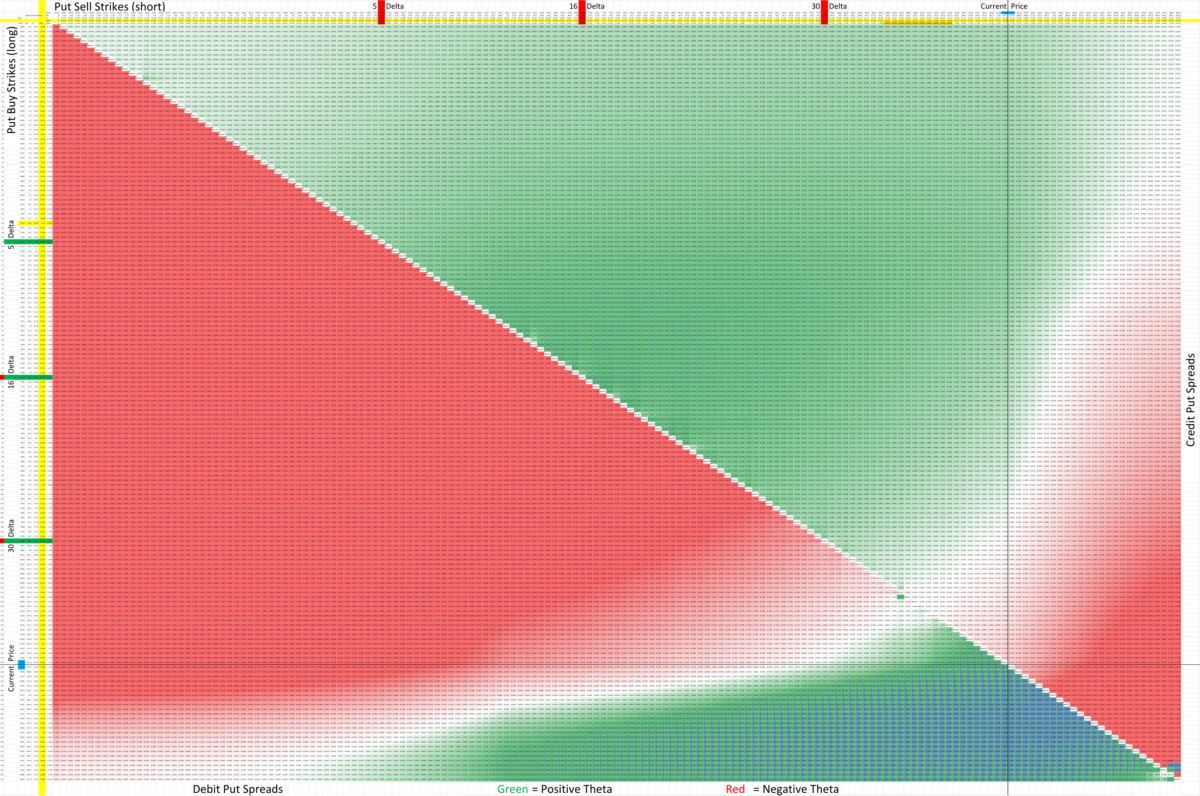
Option credit spreads can be categorized into two main types: bull put spreads and bear call spreads. These spreads allow traders to profit from bullish, bearish, or neutral market conditions, making them versatile strategies for both experienced and novice options traders.
Types of Option Credit Spreads
Option credit spreads come in different forms, each designed to cater to specific market scenarios and trading objectives. The two main types of option credit spreads are the bull put spread and the bear call spread.
Bull Put Spread
A bull put spread is a bullish options strategy that involves selling a put option with a higher strike price and simultaneously buying a put option with a lower strike price. The trader executes this strategy when they anticipate the underlying asset’s price to increase or remain stable.
With a bull put spread, the trader receives a credit upfront by selling the higher strike put option, while the purchased put option acts as downside protection. If the underlying asset’s price remains above the higher strike price at expiration, both options will expire worthless, allowing the trader to keep the initial credit received. The maximum profit is limited to the net credit received, while the maximum loss is capped at the difference between the strike prices minus the net credit.
Bear Call Spread
On the other hand, a bear call spread is a bearish options strategy. Traders employ this strategy when they anticipate a downward movement or a range-bound market for the underlying asset.
In a bear call spread, the trader sells a call option with a lower strike price and simultaneously buys a call option with a higher strike price. The premium received from selling the lower strike call helps offset the cost of buying the higher strike call, resulting in a net credit. The maximum profit is limited to the net credit received, while the maximum loss is capped at the difference between the strike prices minus the net credit.
Both the bull put spread and the bear call spread are defined risk strategies, as the maximum loss is known upfront. Traders can choose the appropriate spread based on their market outlook and risk tolerance.
Bull Put Spread
A bull put spread is an options strategy used by traders to profit from a bullish or neutral outlook on a particular underlying asset. It involves selling a put option with a higher strike price and simultaneously buying a put option with a lower strike price. The strategy is implemented to generate income while limiting downside risk.
When executing a bull put spread, the trader receives a premium by selling a put option at a higher strike price. This put option is considered “naked”, meaning it is not offset by any other position. To limit the potential downside risk, the trader simultaneously buys a put option at a lower strike price. This lower strike put option acts as insurance, providing protection in case the price of the underlying asset depreciates significantly.
The main objective of a bull put spread is for both options to expire worthless, allowing the trader to keep the premium received from the higher strike put option. If the price of the underlying asset remains above the higher strike price at expiration, both options will expire out of the money, and the trader will realize their maximum profit, which is equal to the initial premium received.
However, if the price of the underlying asset falls below the lower strike price, the trader may face potential losses. The maximum loss is limited to the difference between the strike prices minus the premium received, as the lower strike put option provides a hedge against significant losses.
Traders may choose to implement a bull put spread when they anticipate the price of the underlying asset to either remain stable or increase moderately. This strategy allows them to generate income while controlling their downside risk. Furthermore, the risk is known upfront and limited, making it a popular strategy for risk-averse traders.
It is important for traders to carefully consider the strike prices and expiration dates when implementing a bull put spread. The strike prices should be chosen based on the trader’s desired risk-reward profile and their expectation of the underlying asset’s price movement. Additionally, selecting appropriate expiration dates is crucial to ensure sufficient time for the underlying asset to move in the desired direction.
Bear Call Spread
A bear call spread is an options strategy used by traders to profit from a bearish or neutral outlook on a particular underlying asset. It involves selling a call option with a lower strike price and simultaneously buying a call option with a higher strike price. The strategy is implemented to generate income while limiting upside risk.
When executing a bear call spread, the trader receives a premium by selling a call option at a lower strike price. This call option is considered “naked”, meaning it is not covered by owning the underlying asset. To limit the potential upside risk, the trader simultaneously buys a call option at a higher strike price. This higher strike call option acts as a hedge, providing protection in case the price of the underlying asset appreciates significantly.
The main objective of a bear call spread is for both options to expire worthless, allowing the trader to keep the premium received from the lower strike call option. If the price of the underlying asset remains below the lower strike price at expiration, both options will expire out of the money, and the trader will realize their maximum profit, which is equal to the initial premium received.
However, if the price of the underlying asset rises above the higher strike price, the trader may face potential losses. The maximum loss is limited to the difference between the strike prices minus the premium received, as the higher strike call option provides a hedge against significant losses.
Traders may choose to implement a bear call spread when they anticipate the price of the underlying asset to either remain stable or decrease moderately. This strategy allows them to generate income while controlling their upside risk. Furthermore, the risk is known upfront and limited, making it a popular strategy for risk-averse traders.
When implementing a bear call spread, traders need to carefully consider the strike prices and expiration dates. The strike prices should be chosen based on their desired risk-reward profile and their expectation of the underlying asset’s price movement. Additionally, selecting appropriate expiration dates is crucial to ensure sufficient time for the underlying asset to move in the desired bearish direction.
Strategies for Option Credit Spreads
Option credit spreads offer traders a variety of strategies to capitalize on market movements while managing risk. Here are several popular strategies used with option credit spreads:
1. Directional Strategy
In a directional strategy, traders choose a specific market direction they believe the underlying asset will move. For example, if they expect a bullish trend, they would execute a bull put spread. If they anticipate a bearish trend, they would employ a bear call spread. The goal is to profit from the price movement while limiting potential losses.
2. Range-Bound Strategy
A range-bound strategy is employed when traders expect the underlying asset to stay within a particular price range. In this case, they can use a combination of bull put and bear call spreads to take advantage of the lack of significant price movement. By implementing a range-bound strategy, traders can earn income from the premiums received without needing the asset’s price to move in a specific direction.
3. High Probability Strategy
The high probability strategy focuses on selling out-of-the-money options with low probabilities of being exercised. Traders aim to capitalize on the diminishing value of these options as they approach expiration. By conducting thorough analysis and selecting options with a low likelihood of being in-the-money, traders can increase the chances of the options expiring worthless and retaining the premium received.
4. Adjusting Strategy
Adjusting strategies involve making modifications to existing positions based on changes in market conditions. Traders may choose to roll the options to a different strike price or expiration date, close out one leg of the spread to take profits, or add additional contracts to adjust risk exposure. These adjustments allow traders to adapt to unexpected market developments and optimize their position.
It is important for traders to carefully consider their trading goals, risk tolerance, and market analysis when selecting a strategy for option credit spreads. Each strategy comes with its own unique advantages and potential risks, so it is crucial to thoroughly understand the potential outcomes and make informed decisions based on market conditions.
Advantages of Option Credit Spreads
Option credit spreads offer several advantages that make them an appealing strategy for traders. Let’s explore some of these advantages:
1. Income Generation
One of the key advantages of option credit spreads is the ability to generate income. By selling options contracts and receiving a premium upfront, traders can collect immediate income. This income can be especially attractive for traders seeking regular cash flow from their investments.
2. Limited Risk
Option credit spreads offer limited risk, making them an attractive strategy for risk-conscious traders. The maximum risk is known upfront and is limited to the difference between the strike prices minus the net credit received. This limited risk profile provides peace of mind and allows traders to better manage their overall portfolio risk.
3. Versatility in Market Conditions
Option credit spreads provide versatility in various market conditions. Traders can use different types of spreads, such as bull put spreads and bear call spreads, to profit from bullish, bearish, or even range-bound market scenarios. This flexibility allows traders to adapt their strategies based on their market outlook and potentially benefit from market movements from any direction.
4. Defined Profit and Loss
Another advantage of option credit spreads is the defined profit and loss potential. Traders know the maximum potential profit they can make from the spread, which is the net credit received. They also have a clear understanding of the maximum potential loss, which is limited to the difference between the strike prices minus the net credit. This defined risk-reward profile allows for better risk management and more precise decision-making.
5. Strategic Adjustments
Option credit spreads offer the flexibility to make strategic adjustments based on market conditions. Traders can roll their positions by closing out existing options and opening new ones with different strike prices or expiration dates. These adjustments allow traders to optimize their positions and adapt to changing market dynamics, potentially improving their risk/reward profile.
Overall, option credit spreads provide income generation, limited risk, versatility in market conditions, defined profit and loss potential, and strategic adjustment opportunities. These advantages make them an attractive strategy for traders looking to diversify their portfolio and take advantage of various market scenarios.
Risks and Limitations of Option Credit Spreads
While option credit spreads can offer several advantages, it is important to be aware of the associated risks and limitations. Understanding these risks can help traders make informed decisions and manage their positions effectively. Here are some of the key risks and limitations:
1. Limited Profit Potential
One of the limitations of option credit spreads is the limited profit potential. The maximum profit is typically capped at the net credit received when establishing the spread. This means that even if the underlying asset moves significantly in the expected direction, the potential profit is limited to the premium received.
2. Potential Losses
While option credit spreads offer limited risk, losses can still occur. If the underlying asset moves against the trader’s expectations, the spread can result in a loss. The maximum loss is usually limited to the difference between the strike prices minus the net credit received. It is important for traders to carefully manage their positions and set appropriate stop-loss orders to mitigate potential losses.
3. Market Volatility
Market volatility can impact option credit spreads. Higher levels of volatility can increase the premium received from selling options, but they can also increase the potential for wider spreads and greater risks. Traders need to be mindful of the impact of market volatility on their spreads and adjust their positions accordingly.
4. Margin Requirements
Option credit spreads typically require margin to establish the positions. Margin requirements can vary depending on the broker and the specific spread strategy. Traders need to be aware of the initial and maintenance margin requirements and ensure they have enough capital in their accounts to meet these obligations.
5. Assignment Risk
There is a risk of early assignment when trading options. Although less common, it is possible for options to be exercised or assigned prior to expiration. Traders need to understand the risk of early assignment and the potential impact on their positions.
It is crucial for traders to carefully consider these risks and limitations before implementing option credit spread strategies. They should conduct thorough market analysis, set appropriate risk management measures, and stay informed about market conditions to make informed trading decisions.
Conclusion
Option credit spreads are versatile and advantageous trading strategies that offer income generation and risk management opportunities for traders. With the ability to profit from bullish, bearish, and neutral market scenarios, option credit spreads provide flexibility and diversification to a trader’s portfolio.
By simultaneously selling and buying options contracts, traders can receive a net credit upfront while limiting their potential risk. The limited risk profile allows traders to have defined profit and loss potential, providing them with better risk management control.
It is important to note that option credit spreads also come with risks and limitations. The limited profit potential and potential for losses need to be carefully considered, along with factors such as market volatility and potential assignment risk. Traders must understand these risks and develop appropriate risk management strategies.
Despite the risks, option credit spreads remain popular due to their income generation potential, versatility in different market conditions, and opportunities for strategic adjustments. Traders can employ directional, range-bound, high probability, and adjusting strategies to customize their approach based on their market outlook and risk tolerance.
In conclusion, option credit spreads can be valuable tools for traders to generate income and manage risk in the options market. However, it is essential for traders to conduct thorough analysis, stay informed about market trends, and continually assess and adjust their positions based on changing market conditions. By doing so, traders can maximize the potential benefits of option credit spreads while minimizing the associated risks.