
Finance
What Is Budgeting And Forecasting
Published: October 11, 2023
Learn the importance of budgeting and forecasting in finance, and how these essential tools can help you make informed financial decisions and achieve your financial goals.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Budgeting
- Purpose of Budgeting and Forecasting
- Benefits of Budgeting and Forecasting
- Key Components of Budgeting and Forecasting
- Types of Budgeting Methods
- Steps in the Budgeting and Forecasting Process
- Challenges in Budgeting and Forecasting
- Best Practices for Budgeting and Forecasting
- Conclusion
Introduction
When it comes to managing finances, there are several important tools and techniques that can help individuals and businesses make informed decisions. Two crucial techniques in the realm of finance are budgeting and forecasting. These processes provide a roadmap to effectively allocate resources, plan for the future, and achieve financial goals.
Budgeting involves creating a detailed plan for how money will be spent and saved over a specific period of time. It serves as a financial blueprint that helps individuals and businesses track income, control expenses, and allocate resources efficiently. On the other hand, forecasting is the process of predicting future financial outcomes based on historical data and market trends.
Both budgeting and forecasting play a vital role in financial planning and decision-making by providing insights into cash flow, identifying potential risks and opportunities, and facilitating effective resource allocation. This article will delve into the intricacies of budgeting and forecasting, exploring their definitions, purposes, benefits, key components, methods, process steps, challenges, and best practices.
Whether you are an individual striving to manage your personal finances or a business owner looking to optimize your company’s financial performance, understanding the concepts of budgeting and forecasting is essential. By honing your skills in these areas, you can gain greater control over your financial situation, make informed decisions, and ultimately achieve your financial objectives.
Definition of Budgeting
Budgeting is the process of creating a financial plan that outlines expected income and expenses over a specific period of time. It provides a systematic and organized approach to managing finances, allowing individuals and businesses to effectively allocate resources and track their financial activities.
At its core, budgeting involves estimating and allocating funds for various categories such as income, expenses, savings, and investments. It enables individuals to prioritize their financial goals and make informed decisions about how to allocate their money based on their income level and financial priorities.
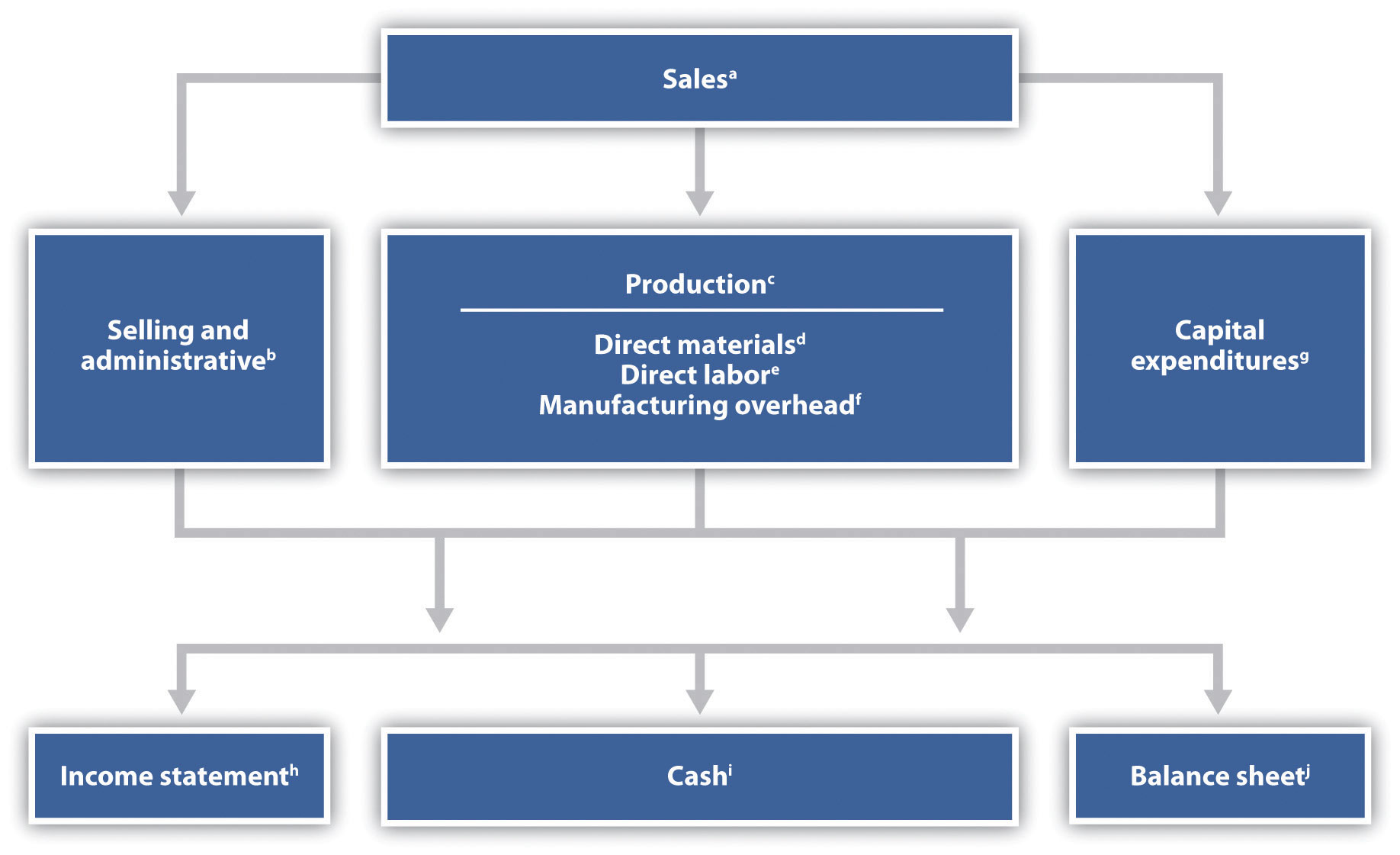
For businesses, budgeting serves as a strategic tool for planning and controlling financial operations. It helps to set achievable targets, monitor performance, and make necessary adjustments to achieve financial objectives. Business budgets typically encompass revenue projections, operating expenses, capital expenditures, and other financial aspects specific to the organization.
One of the fundamental aspects of budgeting is the concept of tracking and comparing actual financial results against the budgeted amounts. This process allows individuals and businesses to evaluate their financial performance, identify variances, and take corrective actions if necessary. By regularly monitoring their budget, individuals and organizations can gain visibility into their financial health and make more informed decisions.
Overall, budgeting provides a structured framework for financial planning and management. It helps individuals and businesses establish financial discipline, allocate resources effectively, and ensure that financial decisions align with their long-term goals and priorities.
Purpose of Budgeting and Forecasting
Budgeting and forecasting serve several important purposes in personal and business financial management. These processes provide a roadmap for financial planning, decision-making, and achieving financial goals. Let’s explore the key purposes of budgeting and forecasting:
- Financial Planning: One of the primary purposes of budgeting and forecasting is to facilitate effective financial planning. By creating a budget and making financial projections, individuals and businesses can set financial goals, allocate resources, and develop strategies to achieve them. This enables proactive decision-making and helps in identifying potential financial challenges in advance.
- Resource Allocation: Budgeting and forecasting play a vital role in resource allocation. They provide insights into available funds, allowing individuals and businesses to allocate resources effectively across different categories such as expenses, savings, and investments. By aligning resources with financial priorities, budgeting and forecasting optimize the utilization of financial resources.
- Performance Evaluation: Budgeting and forecasting enable individuals and businesses to evaluate their financial performance. By comparing actual results with budgeted amounts and projections, they can assess their financial health and identify areas of improvement. This process helps in measuring progress towards financial goals and making necessary adjustments to optimize performance.
- Risk Management: Budgeting and forecasting assist in identifying and managing financial risks. By anticipating future financial outcomes and potential challenges, individuals and businesses can develop contingency plans and take preventive measures. This helps in mitigating risks, minimizing financial losses, and ensuring financial stability.
- Decision-Making: Budgeting and forecasting provide a data-driven foundation for decision-making. They offer insights into the financial implications of different choices and scenarios, enabling individuals and businesses to make informed decisions. Budgeting and forecasting also help in prioritizing financial goals and allocating resources accordingly.
By serving these purposes, budgeting and forecasting empower individuals and businesses to take control of their finances, make informed decisions, and navigate the complexities of the financial landscape effectively.
Benefits of Budgeting and Forecasting
Budgeting and forecasting offer numerous benefits to individuals and businesses alike. These processes provide insights, structure, and informed decision-making capabilities, enabling better financial management. Let’s explore some of the key benefits of budgeting and forecasting:
- Financial Control: Budgeting and forecasting provide a framework for financial control. By setting budgets and making projections, individuals and businesses gain a better understanding of their income, expenses, and overall financial situation. This helps in managing cash flow, controlling spending, and avoiding financial pitfalls.
- Goal Setting and Achievement: Budgeting and forecasting assist in setting financial goals and tracking progress towards their achievement. By creating a budget and making projections, individuals and businesses can outline specific targets and milestones. This provides motivation and a roadmap for achieving financial objectives.
- Improved Decision-Making: Budgeting and forecasting enhance decision-making by providing valuable financial insights. They enable individuals and businesses to evaluate the financial impact of different choices and scenarios, helping in making informed decisions. Budgeting and forecasting guide resource allocation, investment decisions, and financial planning strategies.
- Financial Discipline: Budgeting and forecasting foster financial discipline and responsibility. By following a budget and making projections, individuals and businesses develop habits of accountability and financial management. These processes encourage mindful spending, saving, and investing, ultimately leading to long-term financial stability.
- Strategic Planning: Budgeting and forecasting serve as strategic tools for planning and growth. They allow individuals and businesses to align financial decisions with long-term objectives. Budgeting and forecasting help in identifying opportunities for expansion, optimizing resource allocation, and ensuring financial sustainability.
- Risk Management: Budgeting and forecasting aid in identifying and managing financial risks. By making projections and evaluating potential scenarios, individuals and businesses can anticipate challenges and take proactive steps to mitigate them. This helps in avoiding financial crises and maintaining stability.
- Financial Visibility: Budgeting and forecasting provide visibility into financial health and performance. They allow individuals and businesses to track income, expenses, savings, and investments. Budgeting and forecasting enable proactive monitoring and timely adjustments to achieve financial goals.
By reaping these benefits, individuals and businesses can optimize their financial management, make strategic decisions, and achieve long-term financial success.
Key Components of Budgeting and Forecasting
Budgeting and forecasting consist of several key components that contribute to their effectiveness. These components provide structure and guidance for creating comprehensive financial plans and projections. Let’s explore the key components of budgeting and forecasting:
- Revenue Projections: Revenue projections involve estimating the amount of income or revenue that individuals or businesses expect to generate during a specific period. This component considers factors such as sales volume, pricing strategies, market trends, and customer demand. Accurate revenue projections are essential for creating a realistic and effective budget and forecast.
- Expense Planning: Expense planning involves determining and categorizing the various types of expenses that individuals or businesses will incur during a specific period. This component includes fixed expenses (such as rent and utilities) and variable expenses (such as inventory, marketing, and employee salaries). Effective expense planning helps in managing cash flow, controlling costs, and optimizing resource allocation.
- Savings and Investments: Budgeting includes provisions for savings and investments. This component focuses on setting aside a portion of income for future financial goals and securing long-term financial stability. It involves determining the amount to save or invest and selecting appropriate savings or investment vehicles based on risk tolerance and financial objectives.
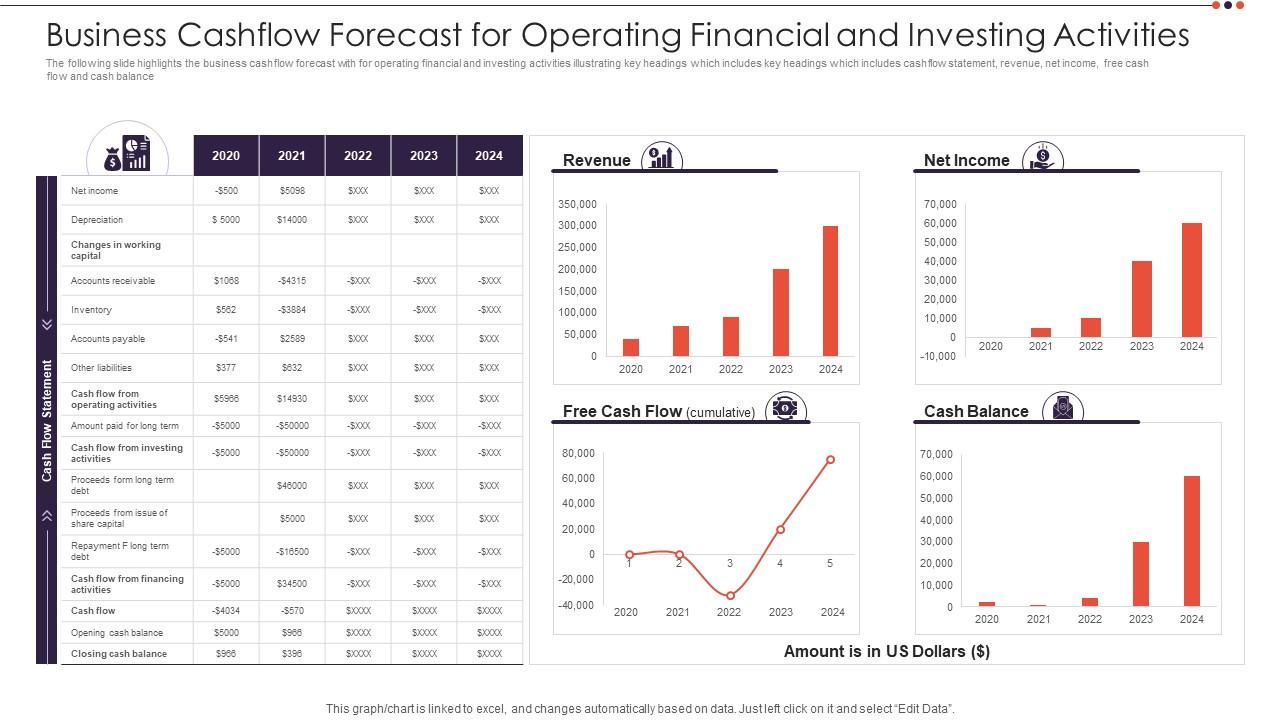
- Cash Flow Management: Cash flow management is a critical component of both budgeting and forecasting. It involves tracking the inflow and outflow of cash to ensure that there is enough liquidity to meet financial obligations. Effective cash flow management helps in avoiding cash shortages, managing debt, and optimizing financial decisions.
- Performance Measurement: Performance measurement is an essential component of budgeting and forecasting. It involves comparing actual financial results with the budgeted amounts and projections. This component helps individuals or businesses evaluate their financial performance, identify areas of improvement, and make necessary adjustments to achieve financial goals.
- Scenario Analysis: Scenario analysis is a valuable component of forecasting. It involves considering different potential scenarios and their financial implications. By assessing the impact of various factors such as changes in market conditions, consumer behavior, or internal operations, individuals or businesses can make more informed forecasts and prepare for different eventualities.
These key components of budgeting and forecasting work together to create a comprehensive financial plan and projection. They provide a detailed and holistic view of income, expenses, savings, investments, and performance, enabling individuals or businesses to make informed decisions and achieve their financial goals.
Types of Budgeting Methods
Budgeting methods vary depending on the specific needs and circumstances of individuals or businesses. Each method has its own characteristics and applicability. Let’s explore some of the common types of budgeting methods:
- Incremental Budgeting: Incremental budgeting is a traditional approach where budgets are based on the previous period’s budget or actual performance, with incremental adjustments. This method is relatively simple and quick to implement but may not account for changing circumstances or new opportunities.
- Zero-Based Budgeting: Zero-based budgeting requires individuals or businesses to justify every expense from scratch, regardless of previous budgets. This method promotes a thorough evaluation of all expenses and encourages cost control. Zero-based budgeting is time-intensive but helps prioritize expenses based on their value and align the budget with current priorities.
- Activity-Based Budgeting: Activity-based budgeting focuses on the activities or tasks that drive costs. This method involves identifying the cost drivers, estimating the expenses associated with each activity, and then budgeting accordingly. Activity-based budgeting helps in aligning budgets with specific tasks and identifying areas of cost efficiency or improvement.
- Rolling Budgeting: Rolling budgeting involves creating budgets for a specific period (e.g., a year) and regularly revising them. As the budget period progresses, the budget “rolls” forward by adding a new month or quarter and dropping the oldest month or quarter. This method allows for flexibility and adjustment based on evolving circumstances.
- Flexible Budgeting: Flexible budgeting adapts to changes in activity levels or sales volume. It allows for adjustments in the budgeted amounts based on variations in production levels or business conditions. Flexible budgeting helps in assessing performance relative to the actual activity level and promotes better cost control.
- Cash Flow Budgeting: Cash flow budgeting focuses on managing cash inflows and outflows. It helps individuals or businesses project cash flow over a specific period, ensuring that there is sufficient liquidity to meet financial obligations. Cash flow budgeting is particularly important for maintaining financial stability and managing short-term funding needs.
It’s important to note that these budgeting methods are not mutually exclusive, and individuals or businesses can adopt a combination of different methods based on their specific needs and preferences. The choice of budgeting method should consider factors such as the nature of the business, industry dynamics, budgeting complexity, and strategic goals.
Steps in the Budgeting and Forecasting Process
The budgeting and forecasting process involves several key steps that help individuals or businesses create accurate and effective financial plans and projections. While the specific steps may vary depending on the circumstances, here are the general steps involved in the budgeting and forecasting process:
- Set Financial Goals: The first step in the process is to define financial goals. This involves identifying short-term and long-term objectives, such as increasing savings, reducing debt, or expanding the business. Clear goals provide direction and purpose for the budgeting and forecasting process.
- Gather Financial Data: Next, individuals or businesses need to gather relevant financial data. This includes historical financial statements, sales data, expense records, and market research. Accurate and comprehensive data are essential for creating realistic budgets and making precise forecasts.
- Analyze Income and Expenses: Analyzing income and expenses is a critical step. This involves analyzing sources of income, such as sales revenue, investments, or loans. It also includes categorizing and reviewing expenses to identify areas for cost reduction or reallocation of resources.
- Create a Budget: Based on the financial goals, data analysis, and income-expense assessment, individuals or businesses can create a budget. The budget should allocate funds to different categories, such as expenses, savings, and investments, in alignment with the financial goals.
- Forecast Future Financial Performance: Forecasting involves predicting future financial performance based on historical data, market trends, and assumptions. Individuals or businesses can use various techniques, such as trend analysis and scenario modeling, to create accurate projections of revenue, expenses, and cash flow.
- Review and Adjust: Once the budget and forecast are created, it is important to review and adjust them regularly. This involves comparing actual financial results with the budgeted amounts and projections and making necessary adjustments. Regular reviews ensure that the budget and forecast remain relevant and effective.
- Monitor Financial Performance: Monitoring financial performance is an ongoing process. Individuals or businesses should track and analyze actual performance against the budget and forecast on a regular basis. This helps in identifying variances, understanding the reasons behind them, and taking corrective actions if needed.
- Communicate and Engage: Effective budgeting and forecasting require clear communication and engagement with stakeholders. This includes sharing the budget and forecast with relevant parties, such as business partners, employees, or financial advisors. Regular communication facilitates understanding, alignment, and collaboration in achieving financial goals.
- Revise and Improve: Finally, individuals or businesses should continuously revise and improve the budgeting and forecasting process. This involves learning from past experiences, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing changes to enhance the accuracy and effectiveness of future budgets and forecasts.
By following these steps, individuals or businesses can navigate the budgeting and forecasting process effectively, ensure financial stability, and make well-informed decisions to achieve their financial goals.
Challenges in Budgeting and Forecasting
Budgeting and forecasting are complex processes that come with their own set of challenges. These challenges can impact the accuracy, effectiveness, and usefulness of the financial plans and projections. Here are some common challenges faced in budgeting and forecasting:
- Uncertainty: The future is inherently uncertain, making it challenging to predict and forecast accurately. Economic conditions, market trends, and external factors can significantly impact financial performance. Managing uncertainty requires individuals or businesses to incorporate flexibility and scenario analysis into their forecasts.
- Data Inaccuracies: The accuracy of budgets and forecasts heavily relies on the quality and accuracy of the data used. Incomplete or incorrect data can lead to faulty assumptions and inaccurate projections. It is crucial to ensure accurate data collection and analysis to mitigate the risk of inaccurate budgeting and forecasting.
- Changing Business Environment: Businesses operate in dynamic environments where conditions can change rapidly. New competitors, regulatory changes, and technological advancements can impact financial performance. Adapting to these changes and incorporating them into budgeting and forecasting can be challenging but necessary for accurate predictions.
- Strategic Misalignment: Budgets and forecasts need to align with strategic objectives for optimal results. However, it can be challenging to strike the right balance between short-term goals and long-term strategic plans. Failure to align budgets and forecasts with the overall strategy can hinder decision-making and hinder goal achievement.
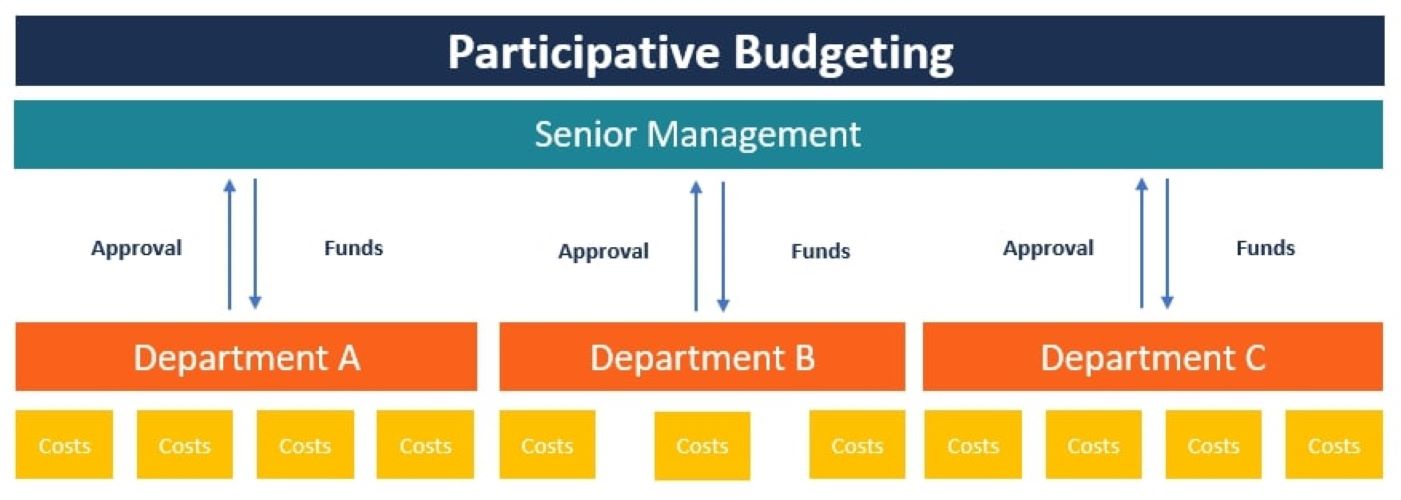
- Limited Participation: Budgeting and forecasting processes often involve multiple stakeholders who may have different perspectives and objectives. Limited participation and lack of collaboration can lead to biases, incomplete information, and resistance to change. Ensuring the involvement and buy-in of all key stakeholders is essential for accurate and effective budgeting and forecasting.
- Overemphasis on the Past: Relying too heavily on historical data can limit the ability to account for emerging trends and future developments. While historical data provides valuable insights, it does not guarantee future performance. It is important to strike a balance between historical analysis and forward-looking projections to accommodate evolving market dynamics.
- Overcomplication: Budgeting and forecasting processes can become overly complex, making it difficult to understand and implement. Complex models, excessive detail, and lack of clarity can hinder effective decision-making. Striving for simplicity and clarity while maintaining the necessary level of detail is crucial.
While budgeting and forecasting challenges exist, acknowledging and addressing them can help individuals or businesses navigate these processes more effectively. By understanding the limitations and investing in continuous improvement, individuals or businesses can overcome challenges and enhance the accuracy and reliability of their financial plans and projections.
Best Practices for Budgeting and Forecasting
Effective budgeting and forecasting require careful planning, attention to detail, and a structured approach. By implementing best practices, individuals or businesses can enhance the accuracy and usefulness of their financial plans and projections. Here are some best practices for budgeting and forecasting:
- Align Budgeting and Forecasting with Strategic Objectives: Ensure that the budgeting and forecasting processes are aligned with the overall strategic objectives of the individual or business. This involves linking financial goals to the broader mission and vision and considering long-term strategic plans when creating budgets and forecasts.
- Focus on Accuracy and Realism: Strive for accuracy and realism in budgeting and forecasting. Use reliable and up-to-date data and make reasonable assumptions. Consider both internal and external factors that may impact financial performance. Avoid overestimating revenues or underestimating expenses to ensure a realistic financial outlook.
- Involve Key Stakeholders: Generate buy-in and promote collaboration by involving key stakeholders in the budgeting and forecasting process. Seek input from various departments, executives, and financial advisors to ensure a comprehensive and well-rounded perspective. This fosters a sense of ownership and improves the overall accuracy and quality of the financial plans and projections.
- Use Multiple Scenario Analysis: To address uncertainties, incorporate multiple scenario analysis into the forecasting process. Consider a range of potential outcomes based on different assumptions and market conditions. This allows for better decision-making by understanding the potential impact of various scenarios on financial performance.
- Review and Revise Regularly: Regularly review and revise the budget and forecast. Monitor actual performance against the budget, identify variances, and adjust the projections accordingly. This enables individuals or businesses to make timely adjustments and optimize financial planning strategies based on changing circumstances.
- Implement Continuous Improvement: Strive for continuous improvement in the budgeting and forecasting processes. Learn from past experiences, gather feedback from stakeholders, and identify areas for enhancement. Evaluate the effectiveness of the processes and make necessary adjustments to streamline and optimize future budgeting and forecasting efforts.
- Invest in Technology: Leverage technology to streamline and automate the budgeting and forecasting processes. There are numerous software solutions available that can enhance accuracy, facilitate collaboration, and provide real-time data analysis. Investing in technology can improve efficiency, reduce errors, and allow for better data-driven decision-making.
- Communicate and Educate: Communicate the budget and forecast results to relevant stakeholders and provide explanations for the underlying assumptions and variances. This promotes transparency and understanding, fostering alignment and collaboration. Educate stakeholders about the importance of budgeting and forecasting and how the financial plans support the achievement of strategic goals.
By implementing these best practices, individuals or businesses can optimize their budgeting and forecasting processes, improve financial decision-making, and enhance the overall accuracy and effectiveness of their financial plans and projections.
Conclusion
Budgeting and forecasting are indispensable tools for effective financial management. They provide a roadmap to allocate resources, plan for the future, and achieve financial goals. Through the budgeting process, individuals and businesses can gain better control over their finances by tracking income, controlling expenses, and allocating resources efficiently. Forecasting, on the other hand, enables individuals and businesses to predict future financial outcomes based on historical data and market trends. The combination of budgeting and forecasting allows for informed decision-making and proactive financial planning.
Throughout this article, we have explored the definitions, purposes, benefits, key components, types, process steps, challenges, and best practices of budgeting and forecasting. By understanding these concepts, individuals and businesses can navigate the complexities of financial management and make sound financial decisions. It is important to align budgeting and forecasting with strategic objectives, focus on accuracy and realism, involve key stakeholders, and use multiple scenario analysis to address uncertainties.
Regular review and revision, along with continuous improvement, are essential for keeping budgets and forecasts up-to-date and relevant. Investing in technology tools can enhance the efficiency and accuracy of the budgeting and forecasting processes. Effective communication and education ensure transparency and understanding among stakeholders, encouraging collaboration and alignment towards financial goals.
While challenges may arise in budgeting and forecasting, acknowledging them and implementing best practices can help overcome these obstacles. By adhering to these practices, individuals and businesses can optimize their financial planning, achieve greater financial control, and make informed decisions that contribute to long-term financial success.
In conclusion, budgeting and forecasting are powerful tools that empower individuals and businesses to manage their finances effectively, allocate resources efficiently, and achieve their financial goals. By harnessing the power of budgeting and forecasting, individuals and businesses can navigate the complex financial landscape with confidence and achieve financial stability and prosperity.