Home>Finance>The Sales Forecast Is The Cornerstone For Budgeting. Why?


Finance
The Sales Forecast Is The Cornerstone For Budgeting. Why?
Published: October 11, 2023
Learn why the sales forecast is vital for budgeting in finance. Discover how accurate projections help optimize financial planning
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Importance of Sales Forecasting
- Relationship between Sales Forecasting and Budgeting
- Factors Affecting Sales Forecasting
- Methods of Sales Forecasting
- Key Components of a Sales Forecast
- Benefits of Using Sales Forecast for Budgeting
- Challenges in Sales Forecasting for Budgeting
- Best Practices for Effective Sales Forecasting
- Conclusion
Introduction
Sales forecasting plays a pivotal role in the financial planning and decision-making process for businesses. It is an essential tool that enables organizations to anticipate future revenue and plan their budget accordingly. By estimating future sales, companies can determine their financial resources, allocate funds to different departments, and make informed strategic decisions.
In the ever-evolving and highly competitive business landscape, accurate sales forecasting is crucial for effective budgeting. It provides valuable insights into market trends, customer behavior, and the overall performance of a company. By understanding the potential demand for their products or services, businesses can align their resources and ensure optimal utilization.
Without a solid sales forecast, businesses may face numerous challenges in their budgeting process. They may overestimate or underestimate their revenue, leading to financial instability and inadequate resource allocation.
This article aims to highlight the importance of sales forecasting in the budgeting process and explore the relationship between the two. It will delve into the various factors that affect sales forecasting, the methods used to forecast sales, and the key components of a sales forecast. Additionally, it will discuss the benefits of using sales forecasts for budgeting, the challenges involved, and best practices for effective sales forecasting.
Whether you are a small business owner or a financial professional, understanding the significance of sales forecasting and its impact on budgeting can help you make better financial decisions, mitigate risks, and maximize profitability.
Importance of Sales Forecasting
Sales forecasting is vital for businesses of all sizes and across various industries. It serves as a compass that guides decision-making and provides insight into future revenue potential. Here are some key reasons why sales forecasting is important.
- Strategic Planning: Sales forecasting enables businesses to develop effective strategies to achieve their goals. By analyzing market trends and customer behavior, organizations can identify opportunities, set realistic targets, and align their resources accordingly. Having a clear sales forecast helps in determining marketing strategies, product development, and resource allocation.
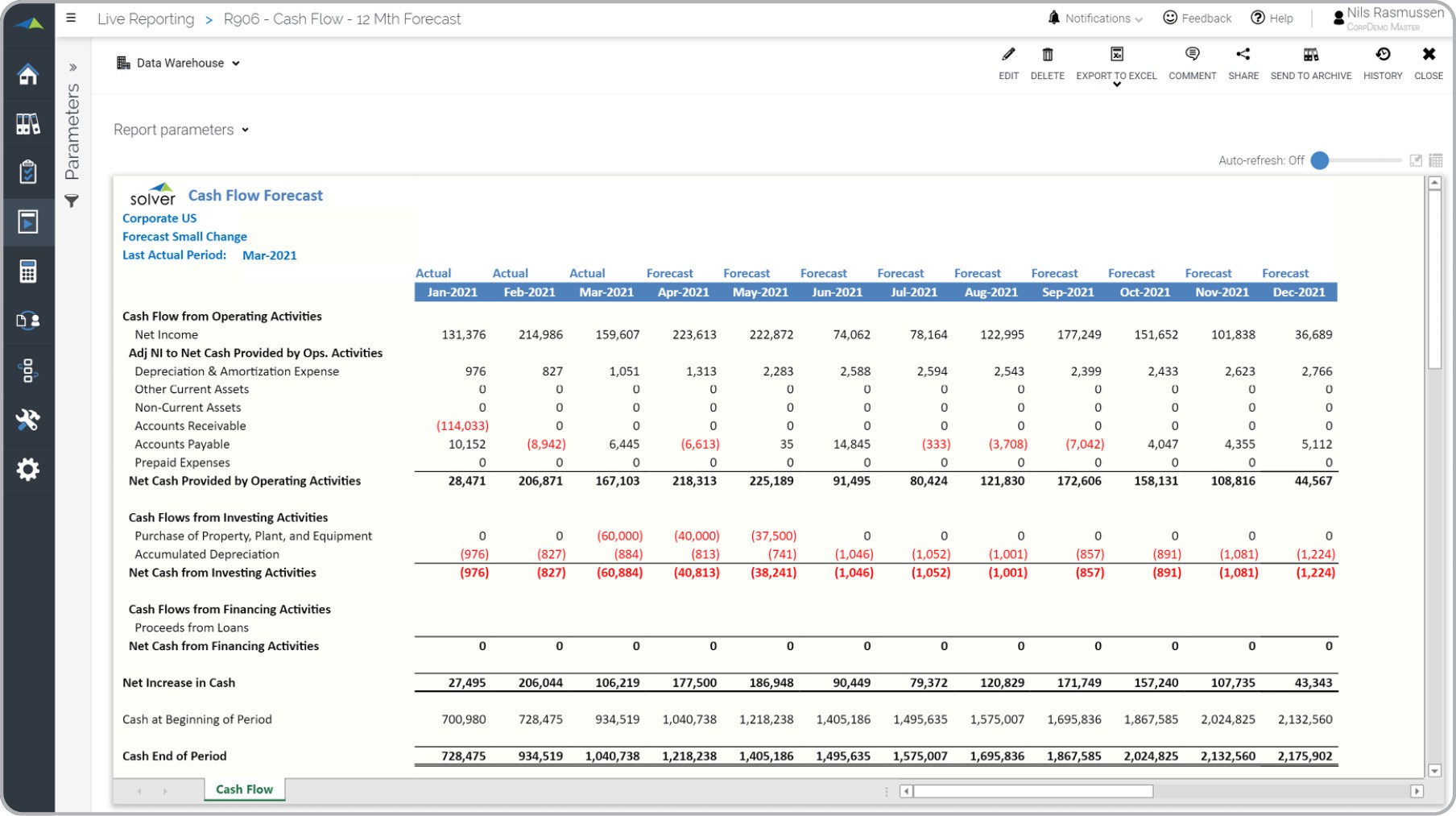
- Financial Planning: Sales forecast plays a central role in the budgeting process. It provides the foundation for determining the financial resources needed and the allocation of funds across different departments. By accurately predicting sales, businesses can plan their expenses, manage cash flow, and make informed decisions about investments and cost reductions.
- Resource Allocation: Sales forecasting helps businesses allocate their resources effectively. It allows for the optimization of production capacity, staffing levels, inventory management, and raw material procurement. By aligning resources with projected sales, companies can avoid overstocking or understocking, reduce wastage, and improve overall operational efficiency.
- Performance Evaluation: Sales forecasting enables businesses to assess their performance against set targets. By comparing actual sales with forecasted sales, organizations can identify areas of improvement, evaluate the effectiveness of their strategies, and take corrective actions if necessary. It also helps in setting realistic sales goals for sales teams and evaluating their performance based on the forecasted figures.
- Decision Making: Sales forecasting provides valuable insights for making informed business decisions. It helps in determining pricing strategies, launching new products, expanding into new markets, and identifying potential risks and opportunities. Having accurate sales forecasts reduces the uncertainty associated with decision making and increases the likelihood of success.
Overall, sales forecasting is crucial as it enables businesses to plan, allocate resources effectively, evaluate performance, and make sound strategic decisions. By incorporating accurate sales forecasts into their budgeting process, organizations can enhance their financial stability, optimize their operations, and achieve their business objectives.
Relationship between Sales Forecasting and Budgeting
Sales forecasting and budgeting have a symbiotic relationship, as they are closely intertwined in the financial planning process of a business. Sales forecasts provide the foundation upon which budgets are built, serving as a guide for revenue projections and resource allocation. The relationship between sales forecasting and budgeting can be understood through the following aspects:
- Revenue Projections: Sales forecasting provides the basis for revenue projections in the budgeting process. By estimating future sales volumes and prices, businesses can forecast their total revenue for a given period. This revenue projection forms a key component of the budget, influencing decisions related to expenses, investments, and profit margins.
- Expense Allocation: Sales forecasts help in determining how expenses should be allocated across different departments or cost centers. If sales are projected to grow significantly, businesses may need to allocate additional resources to areas such as marketing, production, or customer service. On the other hand, if sales forecasts indicate slower growth, cost control measures may be implemented, and resources may be reallocated to more profitable areas.
- Working Capital Management: Sales forecasts play a crucial role in determining the working capital requirements of a business. By estimating future sales and their impact on inventory levels, accounts receivable, and accounts payable, businesses can plan their cash flow needs. This information is essential for budgeting purposes as it helps in optimizing inventory levels, managing credit terms with suppliers, and ensuring sufficient cash reserves for day-to-day operations.
- Investment Decisions: Sales forecasts provide valuable insights for making investment decisions in the budgeting process. By projecting future sales, businesses can assess the potential return on investment (ROI) for various initiatives such as new product development, market expansion, or technology upgrades. This information helps in prioritizing investments and allocating funds to projects that are expected to yield the highest returns.
- Performance Evaluation: Sales forecasts serve as benchmarks for evaluating the performance of a business. By comparing actual sales with forecasted sales, businesses can assess their performance against set targets and identify any gaps or deviations. This analysis helps in identifying areas of improvement, adjusting budgets, and taking corrective actions if necessary.
In summary, sales forecasting and budgeting are closely intertwined processes that rely on each other for effective financial planning. Sales forecasts provide the foundation for revenue projections, resource allocation, working capital management, investment decisions, and performance evaluation. By incorporating accurate sales forecasts into the budgeting process, businesses can improve financial stability, optimize resource utilization, and make informed decisions to drive growth and profitability.
Factors Affecting Sales Forecasting
Sales forecasting is a complex process that can be influenced by various internal and external factors. Understanding these factors is essential for accurate and realistic sales forecasts. Here are some key factors that can affect sales forecasting:
- Market Conditions: The overall market conditions, including economic factors, industry trends, and competitive landscape, can impact sales forecasts. Changes in consumer purchasing power, market demand, or the entry of new competitors can all have an effect on sales projections. Sales forecasters need to closely monitor market conditions and incorporate them into their analysis.
- Historical Data: Past sales performance is a critical factor in sales forecasting. By analyzing historical sales data, businesses can identify patterns, seasonality, and trends that can help predict future sales. However, it is important to consider any factors that may have influenced historical sales but may not be present in the future, such as one-time events or market anomalies.
- Product Lifecycle: The stage of the product lifecycle can impact sales forecasting. For new products, it can be challenging to accurately forecast sales as there is limited historical data and the market reception is uncertain. For mature products, sales forecasting may be more predictable based on historical trends, market saturation, and customer loyalty. Understanding where a product stands in its lifecycle is crucial for accurate sales forecasting.
- Seasonality and Trends: Many industries experience seasonal fluctuations in demand. Sales forecasts must consider these seasonal patterns and adjust accordingly. Additionally, identifying and incorporating trends in customer behavior, such as changing preferences or shifts in buying habits, can help improve the accuracy of sales forecasts.
- Marketing and Promotion: The effectiveness of marketing and promotional activities can impact sales forecasts. A well-executed marketing campaign can drive sales beyond expectations, while a lackluster effort can result in lower-than-projected sales. Sales forecasters should consider the anticipated impact of marketing and promotion when estimating future sales.
- Internal Factors: Factors within the organization, such as changes in pricing strategies, product quality, distribution channels, or sales force effectiveness, can affect sales forecasts. Any changes in these factors need to be taken into account when forecasting future sales. Additionally, the availability and accuracy of internal data systems and sales tracking tools can impact the reliability of sales forecasts.
- External Factors: External factors, such as changes in government regulations, industry regulations, or geopolitical events, can have a significant impact on sales forecasts. Unforeseen events like natural disasters, economic downturns, or global pandemics can disrupt sales projections. Sales forecasters need to stay attuned to these external factors and adjust their forecasts accordingly.
Accurate sales forecasting requires a comprehensive analysis of these factors and a continuous monitoring of the market and business environment. By considering these factors, businesses can improve the accuracy of their sales forecasts and make more informed decisions about resource allocation, budgeting, and strategic planning.
Methods of Sales Forecasting
Sales forecasting involves predicting future sales volumes and revenue based on various data and analytical techniques. There are several methods and approaches that businesses can use to forecast sales. Here are some common methods of sales forecasting:
- Historical Sales Data: This method involves analyzing past sales data to identify patterns, trends, and seasonality. By extrapolating historical sales trends, businesses can estimate future sales. However, this method relies on the assumption that historical patterns will continue in the future, which may not always be the case.
- Market Research: Market research involves gathering information about the target market, customer preferences, buying behavior, and market trends. This data is used to make informed estimates about future sales. Market research methods include surveys, interviews, focus groups, and data analysis from secondary sources. Market research can provide valuable insights for sales forecasting, especially for new products or markets.
- Expert Opinions: This method involves seeking inputs and opinions from industry experts, sales managers, and professionals who have knowledge and experience in the specific market. These experts provide their insights and estimates based on their expertise and market knowledge. While expert opinions can be subjective, they can provide valuable qualitative insights to complement quantitative forecasting methods.
- Lead/opportunity-based Forecasting: This method is commonly used in sales-driven organizations. It involves evaluating the pipeline of leads and opportunities and assigning probabilities of closing deals. By quantifying the value of potential opportunities and the likelihood of conversion, businesses can forecast their future sales based on the sales pipeline.
- Econometric Models: Econometric models use statistical techniques to analyze historical sales data along with other economic indicators, such as GDP, inflation rates, or consumer sentiment. These models help identify the relationships between these variables and sales. They are useful when there is a strong correlation between economic indicators and sales performance.
- Time-Series Analysis: Time-series analysis involves analyzing historical sales data to identify patterns and seasonality. Various statistical techniques, such as moving averages, trend analysis, and exponential smoothing, are used to forecast future sales based on these patterns. It is a quantitative forecasting method that relies on historical data to predict future sales.
- Regression Analysis: Regression analysis involves identifying the relationship between sales and other independent variables, such as marketing expenditure, price, or customer demographics. By analyzing historical data and applying regression models, businesses can estimate the impact of these variables on future sales and forecast accordingly.
No single method is universally applicable, and businesses often combine multiple methods to generate more accurate sales forecasts. The choice of method depends on the industry, product/service characteristics, available data, and business goals. It is important to regularly review and update sales forecasts based on actual sales performance and adjust the forecasting method as needed.
Key Components of a Sales Forecast
A comprehensive sales forecast comprises several key components that collectively provide a clear picture of future sales projections. These components help businesses analyze and plan their revenue streams effectively. Here are the key components of a sales forecast:
- Sales Units: This component represents the quantity of products or services that are projected to be sold within a given time period. It is an important metric that helps businesses estimate their production or service capacity requirements and evaluate the demand for their offerings.
- Sales Revenue: Sales revenue is the total monetary value generated from the sale of products or services. It is calculated by multiplying the number of units sold by the selling price per unit. Sales revenue is a crucial component as it directly impacts the financial performance and profitability of a business.
- Pricing: Pricing is a critical component of a sales forecast. It involves determining the sale price for each unit of a product or service. Pricing decisions should consider factors such as market demand, competition, production costs, and customer willingness to pay. Accurately estimating pricing is essential for realistic revenue projections.
- Product Mix: The product mix component considers the proportion of different products or service offerings in the overall sales forecast. It analyzes the contribution of each product or service to the total sales revenue. Understanding the product mix helps businesses identify their most profitable offerings and allocate resources accordingly.
- Sales Channels: Sales channels refer to the various channels or platforms through which products or services are sold to customers. This component takes into account different sales channels such as direct sales, online sales, distribution partners, or third-party retailers. Evaluating sales channels helps businesses assess their distribution strategies and optimize sales efforts.
- Customer Segments: Customer segmentation involves categorizing customers into groups based on specific characteristics such as demographics, buying behavior, or preferences. This component enables businesses to tailor their sales and marketing strategies to different customer segments. By understanding customer segments, businesses can forecast sales more accurately and customize their approach for each group.
- Geographical Considerations: Geographical considerations involve analyzing sales forecasts based on different regions or markets. This component takes into account factors such as regional demand variations, market potential, and cultural differences. By considering geographical aspects, businesses can develop localized strategies and adapt their sales forecasts accordingly.
- Time Period: The time period component refers to the specific duration for which the sales forecast is being made. It could be a monthly, quarterly, or annual forecast. The choice of time period depends on the business’s needs and goals. Accurately defining the time period helps in setting realistic targets and evaluating performance against those targets.
These key components form the building blocks of a sales forecast, allowing businesses to estimate future sales volume and revenue. By analyzing these components, businesses gain insights into their market potential, profit margins, pricing strategies, and resource allocation. Regularly reviewing and updating sales forecasts based on these components is crucial for effective decision-making and financial planning.
Benefits of Using Sales Forecast for Budgeting
Integrating sales forecasts into the budgeting process offers numerous benefits to businesses. It not only provides a clear picture of expected revenue but also drives informed financial decision-making. Here are the key benefits of using sales forecasts for budgeting:
- Accurate Resource Allocation: Sales forecasts allow businesses to allocate their resources effectively. By aligning anticipated sales volumes with production capacity, staffing levels, and inventory management, businesses can optimize resource utilization and minimize waste. This ensures that the right resources are allocated to meet sales demands, leading to improved operational efficiency and cost control.
- Financial Stability: Incorporating sales forecasts into budgeting promotes financial stability. By estimating future sales and revenue, businesses can develop realistic budgets and align their expenses accordingly. This prevents overcommitting or overspending, ensuring that resources are managed prudently. Accurate sales forecasts enable businesses to avoid financial strain and maintain a stable financial position.
- Informed Decision-Making: Sales forecasts provide valuable insights for making informed business decisions. By anticipating future sales, businesses can assess the financial viability of new initiatives, such as product development, market expansion, or capital investments. Sales forecasts guide decision-making by providing a clear understanding of market potential, customer demand, and revenue projections.
- Budgetary Control: Sales forecasts aid in budgetary control by establishing benchmarks for performance evaluation. By comparing actual sales with forecasted sales, businesses can identify performance gaps and take corrective actions. This helps in monitoring budget adherence, identifying areas of improvement, and implementing necessary adjustments to ensure financial goals are met.
- Risk Mitigation: Sales forecasts help businesses identify potential risks and mitigate them proactively. By forecasting sales, businesses can anticipate market fluctuations, changing customer preferences, or competitive pressures. This aids in developing contingency plans and implementing risk management strategies to minimize the potential impact on financial performance.
- Effective Resource Planning: Sales forecasts assist in long-term resource planning. By anticipating future sales, businesses can plan for expansion, capacity upgrades, or hiring additional staff in advance. This allows for smoother resource acquisition and allocation, ensuring that the resources needed to meet sales demands are readily available.
- Performance Evaluation: Sales forecasts enable businesses to evaluate their performance and track progress towards their sales targets. By comparing actual results with forecasted figures, businesses gain insights into their sales performance, uncover areas of strength and weakness, and identify opportunities for improvement. This information helps in setting realistic goals for sales teams and evaluating their performance effectively.
- Improved Cash Flow Management: Sales forecasts aid in cash flow management by projecting future revenue streams. Businesses can estimate cash inflows based on anticipated sales and plan their cash outflows accordingly. This helps in avoiding cash shortages, managing working capital effectively, and ensuring that sufficient funds are available for day-to-day operations.
By incorporating sales forecasts into the budgeting process, businesses can make informed financial decisions, optimize resource allocation, mitigate risks, and maintain financial stability. Sales forecasts provide the necessary foundation for aligning budgets with revenue expectations, enabling businesses to navigate the competitive landscape and achieve their financial goals.
Challenges in Sales Forecasting for Budgeting
Sales forecasting for budgeting purposes can pose various challenges for businesses. These challenges arise from the uncertainty and complexity of the business environment, market dynamics, and internal factors. It is important to be aware of these challenges to develop effective strategies and mitigate potential risks. Here are some common challenges in sales forecasting for budgeting:
- Market Volatility: The ever-changing market conditions can make sales forecasting challenging. Factors such as economic fluctuations, changes in consumer behavior, and emerging trends can significantly impact sales predictions. Businesses need to adapt quickly and adjust their forecasts to effectively respond to market volatility.
- Limited Data: Insufficient and unreliable historical data can hinder accurate sales forecasting. This may occur when businesses are launching new products, entering new markets, or experiencing rapid growth. Without a solid foundation of historical data, sales projections may lack accuracy and increase the risk of overestimation or underestimation.
- Uncertain Customer Behavior: Customers’ buying behavior can be unpredictable, making it challenging to forecast sales accurately. Factors such as changing preferences, new market entrants, or disruptive technologies can significantly impact customer behavior. Anticipating and incorporating these changes into sales forecasting requires a deep understanding of the target market and continuous monitoring of customer trends.
- Competitive Pressures: Intense competition within the industry can add complexity to sales forecasting. Competitors’ actions, pricing strategies, and market share fluctuations can directly influence sales projections. Failing to account for these competitive pressures can lead to inaccurate sales forecasts and potential revenue shortfalls.
- External Factors: External factors such as government regulations, natural disasters, or geopolitical events can impact sales forecasting. Unforeseen events, such as economic recessions or global pandemics, can disrupt market conditions and customer demand. Adapting sales forecasts to account for these external factors can be challenging but necessary for accurate budgeting.
- Internal Challenges: Internal challenges, such as changes in management, sales team turnover, or shifts in company strategy, can affect sales forecasting. These changes can lead to variations in sales performance and make it difficult to establish consistent sales patterns. Maintaining open communication and an accurate flow of information within the organization can help address internal challenges in sales forecasting.
- Lack of Alignment: Lack of alignment between sales teams, marketing departments, and finance functions can hinder sales forecasting for budgeting purposes. Collaborative efforts and effective communication are essential to ensure that sales projections are based on accurate market insights, sales data, and financial considerations.
- Forecasting Errors: Sales forecasts are subject to human error, biases, and judgmental inaccuracies. Overoptimistic or conservative sales projections can affect budgeting decisions and lead to suboptimal resource allocation. Regular evaluation and validation of forecasting methodologies can help address these errors and improve the accuracy of sales forecasts.
Despite the challenges, businesses can overcome these obstacles by employing robust data analysis techniques, leveraging technology and analytics tools, and continuously monitoring market trends. Regularly reviewing and refining sales forecasting techniques can help businesses improve the accuracy of sales forecasts and enhance the effectiveness of budgeting processes.
Best Practices for Effective Sales Forecasting
Accurate and reliable sales forecasting is crucial for effective budgeting and financial planning. Here are some best practices that businesses can follow to enhance the accuracy and effectiveness of their sales forecasting:
- Collect and Analyze Data: Gather relevant data from multiple sources, including historical sales data, market research, customer insights, and industry reports. Analyze this data to identify patterns, trends, and factors that influence sales performance.
- Segment Customers: Divide your customer base into segments based on demographics, preferences, or other relevant criteria. This helps in understanding different customer groups and tailoring sales strategies accordingly.
- Collaborate Across Departments: Foster collaboration between sales, marketing, and finance teams to gather insights from various perspectives. Regularly communicate and share information to ensure alignment and accuracy in sales forecasts.
- Use Multiple Forecasting Methods: Utilize a combination of quantitative and qualitative forecasting methods to improve forecasting accuracy. Consider historical data analysis, market research, expert opinions, and statistical modeling techniques to generate more realistic sales projections.
- Monitor Market Trends: Stay updated with market trends, industry news, and changes in customer behavior. Understand the impact that external factors may have on sales, and adjust forecasts accordingly.
- Validate and Adjust Forecasts: Regularly review and validate sales forecasts against actual performance. Adjust forecasts and assumptions based on new information or changing market conditions to improve accuracy over time.
- Leverage Technology: Use sales forecasting software and analytics tools to automate data collection, analysis, and forecasting processes. These tools can enhance accuracy, streamline workflows, and provide real-time insights for informed decision-making.
- Involve Sales Team: Engage the sales team in the forecasting process by seeking their input and incorporating their deep understanding of customers and market dynamics. This collaboration fosters buy-in, improves accuracy, and ensures that forecasts are grounded in real-world insights.
- Scenario Planning: Develop multiple scenarios to account for different market conditions and potential outcomes. By assessing best-case, worst-case, and moderate scenarios, businesses can make more informed decisions and prepare contingency plans.
- Track and Communicate Performance: Monitor and communicate sales performance regularly, comparing actual results against forecasted figures. Share performance insights with sales teams, management, and other stakeholders to facilitate learning and continuous improvement.
By implementing these best practices, businesses can enhance the accuracy, reliability, and effectiveness of their sales forecasting. This, in turn, enables more informed budgeting decisions, improved resource allocation, and better financial planning.
Conclusion
Sales forecasting is an essential component of the budgeting process, providing valuable insights into future revenue projections and guiding financial decision-making. Accurate sales forecasts enable businesses to allocate resources effectively, plan budgets, make informed strategic decisions, and navigate the complex business landscape with confidence.
Throughout this article, we explored the importance of sales forecasting in budgeting, highlighting the strong relationship between the two. Sales forecasting serves as the cornerstone for budgeting, enabling businesses to plan their financial resources, allocate funds, and set realistic targets based on anticipated sales volumes and revenue.
We discussed various factors that can affect sales forecasting, including market conditions, historical data, customer behavior, and internal and external factors. Consideration of these factors is crucial in developing accurate and reliable sales forecasts that reflect the ever-changing market dynamics.
Furthermore, we explored the different methods and key components of sales forecasting, emphasizing the need for a comprehensive approach that combines quantitative and qualitative techniques. By integrating various methods and incorporating key components such as sales units, revenue, pricing, and market segments, businesses can generate robust and meaningful sales forecasts.
Additionally, we highlighted the benefits of using sales forecasts for effective budgeting, such as improved resource allocation, financial stability, informed decision-making, and risk mitigation. Sales forecasts assist businesses in aligning their budgets with revenue expectations, optimizing resource utilization, and monitoring performance against targets.
However, we also acknowledged the challenges that businesses may face in the sales forecasting process, including market volatility, limited data, uncertain customer behavior, and internal and external complexities. By being aware of these challenges and following best practices such as data analysis, collaboration, scenario planning, and technology utilization, businesses can overcome these obstacles and enhance the accuracy of their sales forecasting.
In conclusion, sales forecasting is a vital tool for budgeting and financial planning. By incorporating accurate sales forecasts into the budgeting process, businesses can make informed decisions, allocate resources effectively, and navigate market uncertainties with confidence. Regular monitoring, analysis, and adjustment of sales forecasts based on actual performance and market dynamics are crucial for continuous improvement and maintaining a competitive edge in today’s business landscape.