Finance
What Is Capital Markets Investment Banking
Modified: December 30, 2023
Discover the world of capital markets investment banking and its role in finance. Explore opportunities for growth and financial success in this dynamic field.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Capital Markets Investment Banking
- Role of Investment Banks in Capital Markets
- Services Offered by Capital Markets Investment Banks
- Functions of Capital Markets Investment Banks
- Key Players in Capital Markets Investment Banking
- Benefits and Risks of Capital Markets Investment Banking
- Trends in Capital Markets Investment Banking
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to the world of capital markets investment banking, where finance meets strategy and opportunity. In this dynamic sector, investment banks play a vital role in assisting corporations, governments, and other entities in raising capital and managing financial transactions. Whether it’s issuing stocks or bonds, providing advisory services, or facilitating mergers and acquisitions, capital markets investment banking is the engine that drives the global economy.
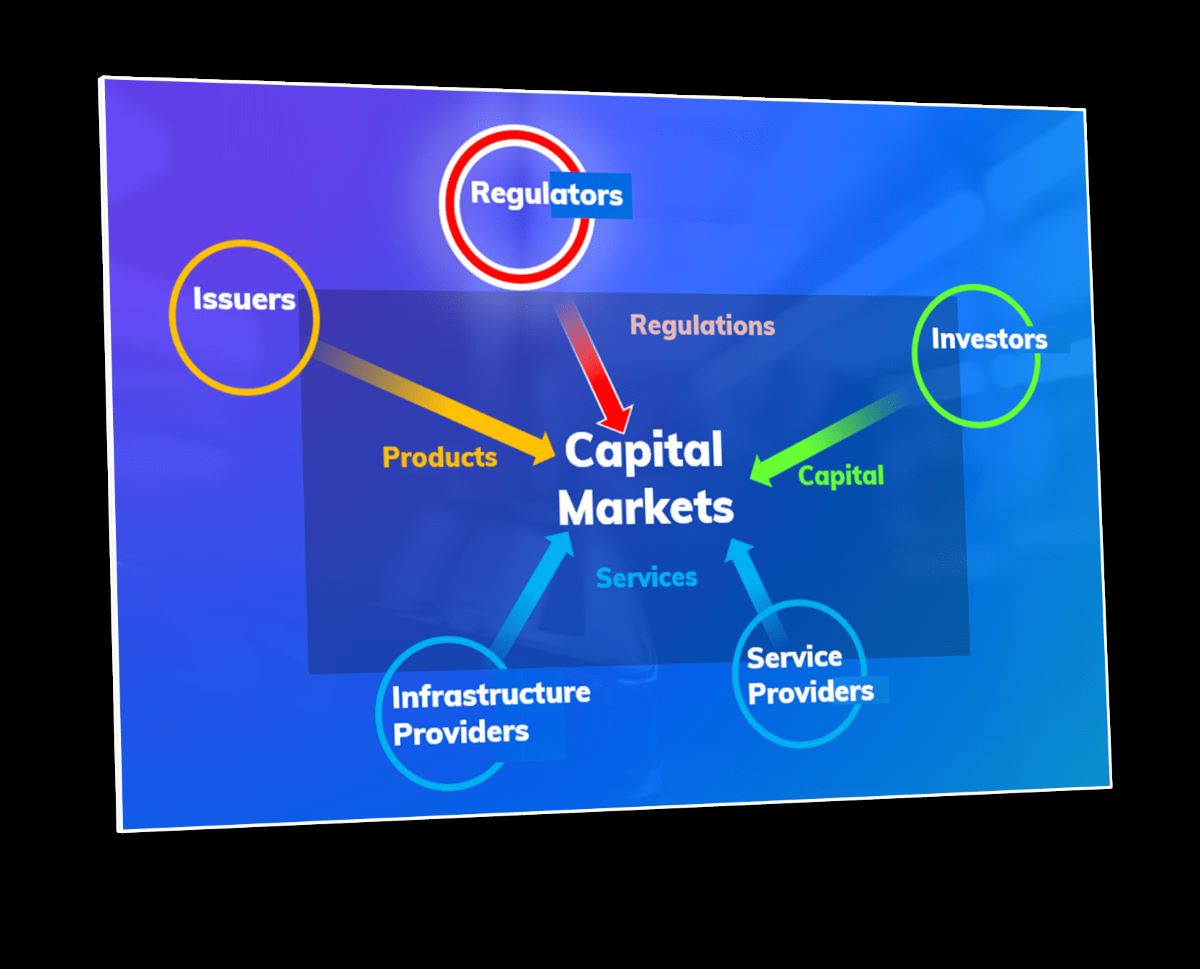
At its core, capital markets investment banking refers to the activities of financial institutions that help clients raise capital by underwriting securities and offering financial advisory services. Investment banks act as intermediaries between issuers and investors, using their expertise and networks to bridge the gap and facilitate transactions. This branch of banking is critical for companies seeking funding to fuel growth, governments looking to finance public projects, and investors seeking opportunities to deploy their capital.
Capital markets investment banking plays a crucial role in enabling economic growth and development by facilitating the efficient allocation of capital. By connecting investors with issuers, investment banks help to channel funds from those who have surplus capital to those who need it to fund their projects and initiatives. This process not only fosters economic expansion but also helps create employment opportunities and drive innovation.
In the following sections, we will explore the various aspects of capital markets investment banking, including its definition, roles, services, functions, key players, benefits, risks, and emerging trends. By gaining an understanding of this fascinating field, you will be better equipped to navigate the complexities of the financial world and make informed decisions regarding your investments and business ventures.
Definition of Capital Markets Investment Banking
Capital markets investment banking can be defined as the specialized branch of banking that focuses on raising capital for businesses and governments through the issuance of securities, as well as providing strategic financial advice and transactional support. It encompasses a wide range of activities aimed at facilitating the buying and selling of financial instruments in the global marketplace.
Investment banks operating in the capital markets play a crucial role in assisting companies and governments in raising funds by underwriting and distributing securities in the primary market. This involves managing initial public offerings (IPOs), where a private company becomes publicly traded, or bond offerings, where fixed-income securities are issued, among other types of transactions.
In addition to underwriting securities, capital markets investment banking also involves providing other financial services such as mergers and acquisitions (M&A) advisory, corporate and debt restructuring, and asset securitization. Investment banks act as trusted advisors to their clients, offering strategic guidance and in-depth analysis to ensure that their financial decisions align with their objectives and market conditions.
Furthermore, capital markets investment banking includes trading and brokerage activities in the secondary market, where previously issued securities are bought and sold among investors. Investment banks often have dedicated trading desks that facilitate the trading of equities, bonds, derivatives, and other financial instruments on behalf of their clients, providing liquidity and market access.
Overall, capital markets investment banking serves as a crucial link between issuers and investors, providing expertise, infrastructure, and financial solutions to meet the complex needs of both parties. Its core objective is to optimize the flow of capital in the economy, enabling businesses to grow, governments to fund public projects, and investors to deploy their resources in a diversified and profitable manner.
The next sections will delve deeper into the specific roles, services, and functions performed by investment banks in capital markets, shedding light on the intricate workings of this fascinating sector.
Role of Investment Banks in Capital Markets
Investment banks play a crucial role in capital markets by acting as intermediaries between issuers of securities and investors. Their primary function is to facilitate the raising of capital for businesses and governments, while also providing a range of financial services to ensure efficient and effective transactions. Let’s explore the key roles investment banks play in the capital markets.
Underwriting and Issuance: One of the primary roles of investment banks is to underwrite securities and facilitate their issuance in the primary market. This involves assessing the creditworthiness of issuers, pricing the securities, and managing the distribution process. Investment banks find buyers for the securities and guarantee a certain level of purchase, helping issuers raise the necessary funds required for their projects or operations.
Financial Advisory: Investment banks provide strategic financial advice to corporations and governments regarding a range of financial transactions. This includes mergers and acquisitions, where investment banks assist in identifying potential targets, conducting due diligence, and negotiating deals. They also offer advice on corporate restructuring, debt financing, and other financial matters that require specialized knowledge and expertise.
Market Making and Trading: Investment banks play a crucial role in providing liquidity and market access by acting as market makers. They facilitate the buying and selling of securities in the secondary market by offering bid and ask prices, ensuring ongoing market activity. Investment banks also engage in proprietary trading, leveraging their expertise and resources to generate profits from trading activities for their own accounts.
Research and Analysis: Investment banks employ teams of analysts who conduct in-depth research and analysis on companies, industries, and market trends. Their research reports provide valuable insights to investors, helping them make informed investment decisions. Investment banks also organize investor conferences and roadshows, where they present their research and connect companies with potential investors.
Risk Management: Investment banks are involved in managing and mitigating various types of financial risks. They offer risk management solutions to clients, including hedging strategies, derivatives, and other risk mitigation products. Investment banks also assess the creditworthiness of issuers and provide credit ratings to help investors evaluate the risk associated with investing in specific securities.
Capital Allocation: Investment banks play a crucial role in allocating capital efficiently in the economy. By connecting investors with issuers, they help channel funds to productive projects and businesses, fostering economic growth. Investment banks evaluate investment opportunities, conduct due diligence, and provide advice to investors on allocating their capital across different asset classes and geographies.
Overall, investment banks act as trusted advisors, catalysts, and intermediaries in the capital markets. Their expertise, networks, and financial services help drive economic growth, create market liquidity, and enable efficient capital allocation, benefiting both issuers and investors.
Services Offered by Capital Markets Investment Banks
Capital markets investment banks offer a wide range of financial services to clients, assisting them in raising capital, executing transactions, and managing their financial needs. These services are designed to meet the complex and evolving demands of companies, governments, and institutional investors. Let’s explore some of the key services provided by capital markets investment banks.
Underwriting and Capital Raising: Investment banks serve as intermediaries between issuers and investors, underwriting and facilitating the issuance of securities in the primary market. They assess the creditworthiness of issuers, determine an appropriate pricing model, and help structure the offering to ensure a successful issuance. Investment banks leverage their distribution networks and market expertise to find investors and raise capital on behalf of clients.
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) Advisory: Investment banks offer strategic advice and guidance to clients involved in mergers, acquisitions, and other corporate transactions. They provide valuation services, conduct due diligence, facilitate negotiations, and help structure deals to maximize value for their clients. Investment banks assist in identifying potential targets or buyers, and they play a crucial role in facilitating the execution of M&A transactions.
Corporate Restructuring: In times of financial distress or strategic realignment, investment banks provide expertise in corporate restructuring. They assist clients in evaluating different restructuring options, including debt refinancing, asset divestitures, and operational reorganization. Investment banks help develop and implement restructuring plans to optimize the financial position and operations of distressed companies.
Equity and Debt Capital Markets: Investment banks offer comprehensive services in equity and debt capital markets. For equity capital markets, they help companies raise funds through initial public offerings (IPOs) and follow-on offerings. In debt capital markets, investment banks facilitate the issuance of corporate bonds, government bonds, and other debt instruments. They provide pricing advice, manage the offering process, and tap into their investor networks to ensure successful placements.
Derivatives and Risk Management: Investment banks offer customized derivative products to clients for hedging and risk management purposes. They provide expertise in options, futures, swaps, and other derivative instruments to help clients manage exposure to interest rates, exchange rates, commodities, and other market risks. Investment banks work with clients to design hedging strategies tailored to their specific risk profiles.
Research and Market Insights: Investment banks employ dedicated research teams that provide in-depth analysis, forecasts, and insights on various companies, industries, and market trends. Research reports help investors make informed investment decisions, and investment banks organize conferences and events to showcase their research and connect clients with potential investors. They also offer market insights and advisory services to clients based on their research and analysis.
Asset Management and Wealth Advisory: Investment banks may offer asset management services to institutional and individual clients. They manage investment portfolios, provide investment advice, and offer tailored wealth management solutions to high-net-worth individuals. Investment banks leverage their expertise in financial markets to help clients achieve their investment objectives and grow their wealth over time.
These are just a few examples of the many services offered by capital markets investment banks. Their primary goal is to provide comprehensive financial solutions and expertise to clients in navigating the complex world of capital markets, driving economic growth, and fostering financial success.
Functions of Capital Markets Investment Banks
Capital markets investment banks perform a variety of functions that are essential to the smooth operation of financial markets and the efficient allocation of capital. These functions involve both key operational roles and strategic advisory services that ensure the successful execution of financial transactions. Let’s explore some of the key functions performed by capital markets investment banks.
Capital Raising: One of the primary functions of investment banks is to facilitate the raising of capital for businesses and governments. Investment banks assist companies in issuing equity and debt securities, such as stocks and bonds, to raise funds for various purposes, including expansion, refinancing, or funding specific projects. They work closely with issuers to structure the offerings, determine pricing, and find suitable investors to meet their capital requirements.
Underwriting: Investment banks act as underwriters for securities offerings, taking on the risk of buying the securities from the issuer and reselling them to investors. This provides issuers with the assurance of a guaranteed sale and helps them raise the necessary capital. Investment banks evaluate the creditworthiness of the issuer, estimate the demand for the securities, and set an offer price to attract investors.
Mergers and Acquisitions Advisory: Investment banks play a critical role in advising clients on mergers, acquisitions, and other corporate transactions. They provide strategic advice on deal structure, valuation, and negotiation tactics. Investment banks conduct thorough due diligence to assess the financial, legal, and operational aspects of the transaction. They also coordinate activities between buyers, sellers, legal advisors, and other parties involved in the deal to ensure a smooth and successful transaction.
Market Making: Investment banks engage in market making activities, providing liquidity in various financial markets, such as equity, bond, and derivative markets. Market makers facilitate the buying and selling of securities by providing bid and ask prices and ensuring that there is a continuous flow of transactions. By acting as intermediaries between buyers and sellers, investment banks contribute to the overall efficiency and stability of financial markets.
Research and Analysis: Investment banks have dedicated research teams that analyze companies, industries, and market trends. They provide research reports to clients, offering insights and recommendations on investment opportunities. Research analysts assess the financial performance of companies, conduct competitive analyses, and forecast industry trends. Their research helps investors make well-informed investment decisions and assists investment bankers in providing accurate and relevant advice to clients.
Risk Management: Investment banks assist clients in managing various types of financial risks. They provide risk management solutions, such as hedging strategies and derivative products, to help clients mitigate their exposure to market fluctuations, interest rate changes, and currency fluctuations. Investment banks assess and analyze risks associated with financial transactions and provide recommendations on risk management strategies to protect the interests of their clients.
Advisory Services: Investment banks offer a range of strategic advisory services to clients, including capital structure planning, debt restructuring, and corporate governance advice. They assist clients in optimizing their capital structure by advising on the appropriate mix of equity and debt financing. Investment banks also provide guidance on restructuring activities, such as refinancing or reorganizing debt, to improve financial stability and operational efficiency.
These functions are crucial to the operation and growth of capital markets. Investment banks play a vital role in facilitating capital raising, providing strategic advice, ensuring market liquidity, conducting research, managing risk, and offering advisory services. By performing these functions, investment banks contribute to the stability, efficiency, and growth of the overall financial system.
Key Players in Capital Markets Investment Banking
The field of capital markets investment banking is characterized by the presence of key players who contribute to the industry’s growth and success. These players include investment banks, commercial banks, institutional investors, and regulatory bodies. Let’s take a closer look at each of these key players and their roles in capital markets investment banking.
Investment Banks: Investment banks are at the heart of capital markets investment banking. They specialize in providing financial services such as underwriting, mergers and acquisitions advisory, and capital raising for clients. Investment banks have extensive networks and expertise in capital markets and often play a crucial role in facilitating the issuance and trading of securities.
Commercial Banks: Commercial banks also play a significant role in capital markets investment banking. They offer a wide range of financial services, including corporate lending, advisory services, and trade finance. Commercial banks often have integrated investment banking divisions that provide capital markets services to clients, leveraging their client relationships and balance sheet capabilities.
Institutional Investors: Institutional investors, such as pension funds, mutual funds, and insurance companies, are key players in capital markets investment banking. They are large-scale investors who deploy capital on behalf of their clients or policyholders. Institutional investors often participate in capital raising activities, invest in securities offered by investment banks, and are key buyers in secondary market transactions.
Regulatory Bodies: Regulatory bodies, such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States or the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the United Kingdom, play a crucial role in overseeing and regulating capital markets investment banking activities. They set and enforce rules and regulations to protect investors, maintain market integrity, and ensure fair and transparent operations in the capital markets. Regulatory bodies also play a vital role in preventing fraudulent and unethical practices.
Rating Agencies: Rating agencies are independent organizations that assess the creditworthiness and risk profile of issuers and their securities. They assign credit ratings based on their evaluation, which provide investors with an indication of the credit quality and default risk associated with a particular security. Rating agencies play a critical role in providing transparency and confidence in the capital markets, helping investors make informed investment decisions.
Exchanges and Clearinghouses: Exchanges serve as marketplaces where securities are bought and sold. They provide the infrastructure and regulatory framework for trading and are responsible for maintaining fair and orderly markets. Clearinghouses act as intermediaries in the settlement process, ensuring that securities and funds are properly transferred between buyers and sellers. Exchanges and clearinghouses play a vital role in ensuring the efficiency, transparency, and integrity of capital markets activities.
Law Firms and Legal Advisors: Law firms and legal advisors play an essential role in capital markets investment banking by providing legal counsel and support. They help navigate complex legal and regulatory frameworks, review transaction documents, ensure compliance with securities laws, and offer guidance on corporate governance matters. Law firms and legal advisors play a crucial role in structuring and executing transactions while safeguarding the legal interests of their clients.
These key players collaborate and interact within the capital markets ecosystem, working together to fuel economic growth, facilitate capital raising, and ensure the integrity of financial transactions. Their combined efforts contribute to the stability, efficiency, and vibrancy of capital markets around the world.
Benefits and Risks of Capital Markets Investment Banking
Capital markets investment banking offers various benefits and opportunities for both issuers and investors. At the same time, it entails certain risks that need to be carefully managed and considered. Let’s explore the benefits and risks associated with capital markets investment banking.
Benefits:
- Capital Raising: Capital markets investment banking provides a platform for businesses and governments to raise capital essential for growth, expansion, and financing projects. By accessing the capital markets, issuers can tap into a broader investor base and secure funding at competitive terms.
- Liquidity: Investment banks enhance market liquidity by providing a platform for buying and selling securities. This allows investors to efficiently enter or exit positions and ensures continuous trading activity, promoting price discovery and transparent markets.
- Efficient Allocation of Capital: Capital markets investment banking facilitates the efficient allocation of capital by connecting investors with issuers. This process enables funds to flow to productive projects and businesses, supporting economic growth and innovation.
- Financial Expertise: Investment banks offer a wide range of financial services and expertise, including underwriting, advice on mergers and acquisitions, risk management, and research. This specialized knowledge helps clients make informed financial decisions and optimize their strategies.
- Transparency: Capital markets operate under rules and regulations set by regulatory bodies to ensure transparency and fair practices. Disclosure requirements and reporting standards improve transparency, allowing investors to make well-informed investment decisions.
Risks:
- Market Volatility: Capital markets are subject to fluctuations in prices and volatility, influenced by various factors such as economic conditions, geopolitical events, and investor sentiment. This volatility can result in unpredictable market movements and impact investment returns.
- Liquidity Risk: While investment banks enhance liquidity in the markets, there can be instances of illiquidity, especially during times of market stress or for certain securities. Illiquidity can make it challenging to sell securities at desired prices, potentially impacting investment portfolios.
- Regulatory and Compliance Risks: The capital markets are heavily regulated to protect investors and maintain market integrity. Investment banks must comply with a range of rules and regulations, and failure to do so can result in legal and reputational risks.
- Counterparty Risk: Capital markets investment banking entails engaging with various counterparties, such as issuers, investors, and other market participants. There is a risk of default or non-performance by these counterparties, which can lead to financial losses.
- Market Manipulation and Insider Trading: Capital markets can be susceptible to market manipulation and insider trading. These unethical practices can distort prices, undermine market integrity, and disadvantage investors who are not privy to non-public information.
It is important for participants in capital markets investment banking, including investment banks, issuers, and investors, to carefully assess and manage these risks. Diligent risk management practices, adherence to regulations, and thorough due diligence can help mitigate these risks and ensure a sound and resilient investment environment.
Trends in Capital Markets Investment Banking
The field of capital markets investment banking is constantly evolving as new technologies, changing regulations, and shifting market dynamics shape the industry. Staying ahead of emerging trends is essential for investment banks to remain competitive and adapt to the changing needs of clients. Let’s explore some of the key trends in capital markets investment banking.
1. Digital Transformation: Investment banks are embracing digital technologies to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and enhance the client experience. Robotic process automation (RPA), artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) are being deployed to automate repetitive tasks and enhance data analysis capabilities. Digital platforms and mobile applications are offering clients convenient access to investment services and real-time market information.
2. Sustainable and Impact Investing: There is a growing focus on sustainable and impact investing, driven by increasing investor demand for socially responsible investment opportunities. Investment banks are developing dedicated teams and products to cater to this trend, offering green bonds, social impact funds, and sustainability-focused research. They are also integrating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors into their investment decision-making processes.
3. Alternative Investments: A shift towards alternative investments, such as private equity, venture capital, and hedge funds, is observed in capital markets investment banking. Investors are seeking diversification and higher returns beyond traditional asset classes. Investment banks are establishing alternative investment platforms and providing expertise in deal sourcing, due diligence, and fund structuring to cater to this demand.
4. Rise of Fintech: Fintech startups are disrupting the financial industry, including capital markets investment banking. Fintech firms are leveraging advanced technologies to offer innovative financial services, such as peer-to-peer lending, digital asset trading, and automated investment platforms. Investment banks are collaborating with fintech companies, investing in their ventures, or developing their own fintech solutions to improve operational efficiency and enhance client offerings.
5. Regulatory Changes: Regulatory frameworks governing capital markets are constantly evolving to enhance transparency, protect investors, and mitigate systemic risks. Investment banks are adapting to regulatory changes, such as increased reporting requirements, stricter capital adequacy standards, and enhanced compliance measures. They are investing in regulatory technology (RegTech) solutions to automate and streamline compliance processes and manage risks effectively.
6. Globalization and Emerging Markets: Capital markets investment banking is expanding beyond traditional markets as globalization and economic growth fuel demand for financial services in emerging markets. Investment banks are establishing a presence in these markets, forging partnerships with local entities, and providing advisory services to facilitate cross-border transactions and capital raising in rapidly growing economies.
7. Data Analytics and Decision Making: Investment banks are leveraging data analytics and advanced algorithms to generate insights and support informed decision-making. Big data analysis helps identify market trends, client preferences, and investment opportunities. Investment banks are building sophisticated data infrastructure and recruiting data science professionals to extract valuable insights from data that can drive investment strategies and enhance client engagement.
These trends are reshaping the landscape of capital markets investment banking, providing opportunities for innovation, efficiency improvements, and value creation. Investment banks that embrace these trends and proactively adapt to the changing industry dynamics will be well-positioned to thrive in an increasingly competitive market.
Conclusion
Capital markets investment banking plays a pivotal role in the global financial system, connecting businesses, governments, and investors in the pursuit of capital raising and efficient capital allocation. Investment banks serve as intermediaries, helping issuers raise funds, facilitating transactions, providing strategic advice, and managing financial risks. This dynamic field brings numerous benefits, including access to capital, market liquidity, financial expertise, and transparency.
However, capital markets investment banking also poses risks, such as market volatility, liquidity challenges, and regulatory compliance. It is crucial for investment banks and market participants to stay vigilant and manage these risks through robust risk management practices, adherence to regulations, and ongoing monitoring of market developments.
As the industry evolves, investment banks are embracing digital transformation, sustainable investing, alternative investments, and fintech collaborations. They are adapting to regulatory changes, expanding into emerging markets, and leveraging data analytics to enhance decision-making capabilities. Staying abreast of these trends is vital for investment banks to remain competitive and meet the evolving needs of clients in the rapidly changing financial landscape.
In conclusion, capital markets investment banking serves as a catalyst for economic growth, fostering innovation, job creation, and efficient capital allocation. By providing a wide range of financial services, investment banks play a crucial role in driving the success of businesses, governments, and investors worldwide. However, they must continue adapting, innovating, and navigating the complexities of the industry to deliver value to their clients and contribute to a resilient and vibrant capital markets ecosystem.