Home>Finance>What Is Considered The Collateral On A Life Insurance Policy Loan?


Finance
What Is Considered The Collateral On A Life Insurance Policy Loan?
Published: October 15, 2023
Learn about the collateral accepted for life insurance policy loans, an important aspect of personal finance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Life insurance policy loans can provide individuals with a way to access cash quickly while still keeping their coverage in place. However, when obtaining a loan against a life insurance policy, lenders typically require collateral to secure the loan. This collateral serves as a guarantee that the lender will be repaid, even if the borrower defaults on the loan. Understanding what is considered collateral in a life insurance policy loan is crucial for borrowers to make informed decisions.
In this article, we will explore the concept of collateral in life insurance policy loans, the types of collateral that may be accepted, and the risks and considerations associated with borrowing against a policy.
It’s important to note that the specific collateral requirements may vary depending on the insurance company and the terms of the policy, so it’s essential for individuals to consult with their insurance provider and thoroughly review their policy documents.
Now, let’s delve deeper into the world of collateral in life insurance policy loans and discover what assets can be used to secure these loans.
Understanding Collateral in Life Insurance Policy Loans
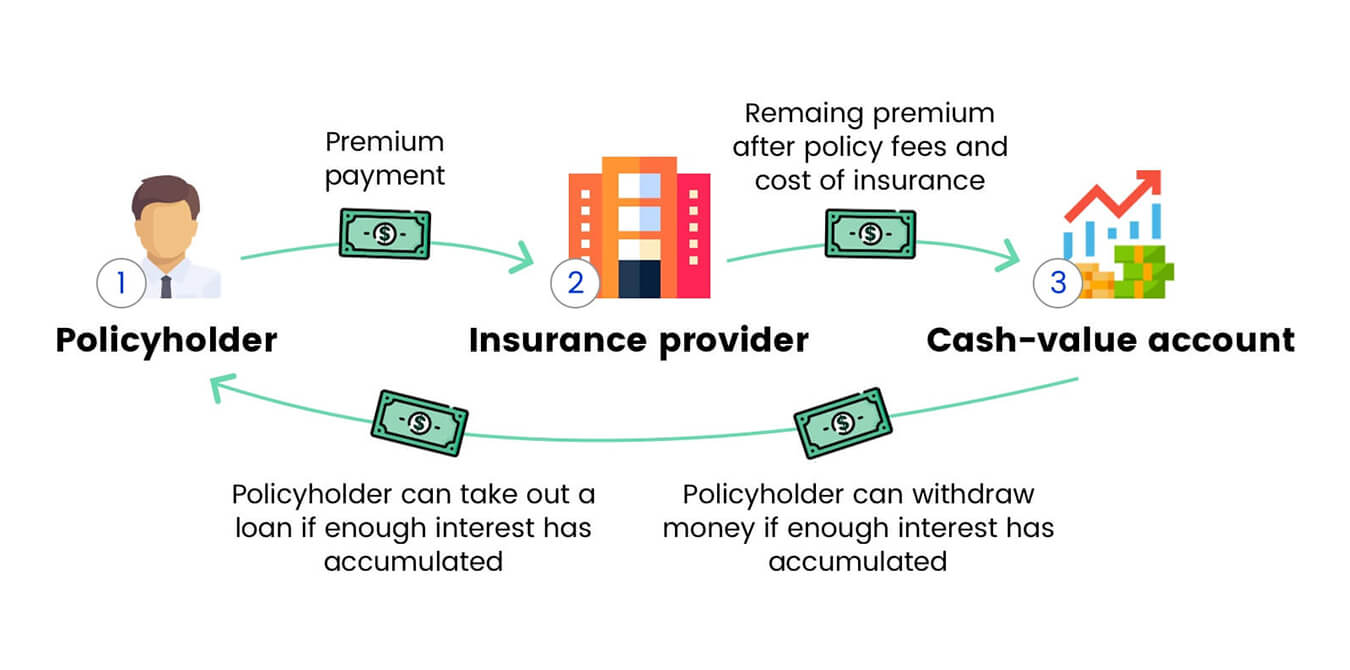
Collateral in a life insurance policy loan refers to the assets or resources that borrowers pledge to secure the loan. It acts as a form of security for the lender, providing assurance that they will be able to recover the loan amount if the borrower defaults. When obtaining a life insurance policy loan, the value of the collateral is typically equal to or greater than the loan amount.
Unlike traditional loans, life insurance policy loans do not require a credit check or an extensive application process. Instead, the loan is secured by the policy’s cash value, surrender value, death benefit assignment, or even policy dividends. This means that borrowers can access funds quickly without going through the rigorous approval procedures associated with other types of loans.
It’s essential to understand that the specific collateral requirements may vary depending on the insurance company and the terms of the policy. Some insurance providers may only accept certain types of collateral, while others might have more flexibility in their criteria. Additionally, the loan terms and conditions, such as interest rates and repayment schedules, may also be influenced by the collateral provided.
When considering a life insurance policy loan, it is crucial to review the policy documents and consult with the insurance provider to fully grasp the collateral requirements and any potential implications.
Now that we have a basic understanding of collateral in life insurance policy loans, let’s explore the different types of collateral that may be accepted.
Types of Collateral Accepted
When obtaining a life insurance policy loan, there are various types of collateral that lenders may accept to secure the loan. The specific collateral options available will depend on the insurance company and the terms of the policy. Here are some common types of collateral accepted in life insurance policy loans:
- Cash Value of the Policy: The most common type of collateral in a life insurance policy loan is the cash value of the policy itself. The cash value is the accumulated savings or investment portion of the policy, and it grows over time as the premiums are paid. Borrowers can pledge this cash value as collateral to secure the loan. If they fail to repay the loan, the lender can use the cash value to cover the outstanding amount.
- Surrender Value of the Policy: The surrender value is the amount that the policyholder would receive if they were to terminate the policy. This value is typically lower than the cash value but can still be used as collateral in a life insurance policy loan. If the borrower defaults on the loan, the lender can access the surrender value to recoup their losses.
- Death Benefit Assignment: In some cases, borrowers may choose to assign the death benefit of their life insurance policy as collateral. This means that if the borrower passes away before repaying the loan, the lender will be entitled to a portion or the entire death benefit to cover the outstanding loan amount. This type of collateral provides additional security for the lender but may impact the beneficiary’s payout.
- Policy Dividends: Some life insurance policies pay out annual dividends to policyholders based on the performance of the insurance company’s investments. These dividends can be used as collateral for a policy loan. If the borrower defaults on the loan, the lender can use the dividends to cover the outstanding balance.
It’s important to note that not all insurance policies allow for the assignment of policy dividends or death benefits as collateral. Individuals should review their policy documents or consult with their insurance provider to determine which collateral options are available to them.
Now that we have explored the common types of collateral accepted in life insurance policy loans, let’s discuss the risks and considerations associated with borrowing against a policy.
Cash Value of the Policy
The cash value of a life insurance policy is a crucial factor when it comes to obtaining a policy loan. The cash value represents the savings or investment portion of the policy and accumulates as premiums are paid over time. This cash value can serve as collateral for a life insurance policy loan.
When borrowers pledge the cash value of their policy as collateral, it provides security for the lender. If the borrower defaults on the loan, the lender can access the cash value to recoup their losses. However, it’s important for borrowers to consider the potential impact on their policy and coverage.
One of the key advantages of using the cash value as collateral is that it allows individuals to access funds without surrendering their policy. This means that the life insurance coverage remains in place, providing financial protection to the policyholder and their beneficiaries.
It’s essential for individuals to carefully evaluate the terms and conditions of the loan, including the interest rates and repayment schedule, to ensure that they can meet the financial obligations. Failure to repay the loan can result in a reduction of the cash value, potential policy termination, and loss of coverage.
Furthermore, utilizing the cash value as collateral may reduce the growth potential of the policy. When the cash value is pledged as collateral, it may limit the policy’s ability to earn interest or receive dividends. Policyholders should consider the long-term impact on their policy’s value and weigh it against their immediate financial needs.
Lastly, it’s important to note that the amount that can be borrowed against the cash value may not be the full cash value amount. Lenders typically allow borrowers to access a percentage of the cash value, depending on the policy terms and the loan agreement.
Before deciding to use the cash value as collateral for a life insurance policy loan, individuals should carefully review the loan terms, assess their financial situation, and consider alternative borrowing options. Consulting with a financial advisor or insurance professional can provide valuable insights and help make informed decisions.
Now that we have explored the significance of the cash value of a life insurance policy as collateral, let’s move on to discuss the surrender value of the policy.
Surrender Value of the Policy
The surrender value of a life insurance policy refers to the amount that the policyholder would receive if they were to terminate the policy before its maturity date. This surrender value can be used as collateral in a life insurance policy loan.
When borrowers pledge the surrender value as collateral, it provides assurance to the lender that they have a form of security if the borrower defaults on the loan. However, it’s important to understand the implications of using the surrender value as collateral.
One advantage of utilizing the surrender value as collateral is that it allows individuals to access funds from their policy without fully surrendering the coverage. This means that policyholders can still maintain some level of life insurance protection while utilizing the loan amount for their financial needs.
However, it’s crucial to note that the surrender value is typically lower than the policy’s cash value. This is because surrender charges or fees may be deducted from the cash value if the policyholder chooses to terminate the policy early. The surrender value should be carefully evaluated to ensure that it meets the borrower’s financial requirements.
If the borrowers fail to repay the loan, the lender can tap into the surrender value to recover their losses. This may result in reducing the policy’s value and coverage. Additionally, utilizing the surrender value as collateral may limit the growth potential of the policy, as it may no longer accumulate interest or receive dividends while the loan is outstanding.
Before pledging the surrender value as collateral for a life insurance policy loan, individuals should consider the repayment terms, interest rates, and the impact on their coverage. Alternative borrowing options and consulting with a financial advisor can provide valuable guidance in making an informed decision.
Now that we have discussed the surrender value of the policy, let’s move on to the concept of death benefit assignment as collateral in a life insurance policy loan.
Death Benefit Assignment
In certain cases, borrowers may choose to assign the death benefit of their life insurance policy as collateral when obtaining a policy loan. This means that if the borrower passes away before repaying the loan, the lender will be entitled to a portion or the entire death benefit to cover the outstanding loan amount.
Assigning the death benefit as collateral offers added security for the lender, as they have a guarantee that they will be repaid even in the event of the borrower’s death. However, it’s essential to understand the potential consequences and considerations associated with this type of collateral.
One significant consideration is the impact on the policy’s intended beneficiaries. By assigning the death benefit as collateral, the beneficiaries may receive a reduced payout or no payout at all if the loan amount is not fully repaid. This can be a significant financial burden for the policyholder’s loved ones, especially if the death benefit was intended to provide financial support.
Furthermore, assigning the death benefit as collateral may limit the policyholder’s ability to make changes to the beneficiaries. Depending on the policy terms, the lender may need to be involved in any beneficiary changes or updates.
It’s also important to note that the amount of the death benefit assigned as collateral may not be the full death benefit amount. The lender may require a percentage of the death benefit to be assigned to cover the loan. This means that the remaining portion of the death benefit would still be available to the beneficiaries upon the policyholder’s death.
Before deciding to assign the death benefit as collateral for a life insurance policy loan, individuals should thoroughly review the loan terms, consider the impact on their beneficiaries, and assess alternative borrowing options.
Consulting with an insurance professional or financial advisor can provide valuable guidance in understanding the implications of assigning the death benefit as collateral and making an informed decision that aligns with individual financial goals and priorities.
Now, let’s explore another type of collateral used in life insurance policy loans – policy dividends.
Policy Dividends
Some life insurance policies provide policyholders with dividends, which are a share of the insurance company’s profits. These dividends can be used as collateral in a life insurance policy loan.
Policy dividends are typically paid annually or at regular intervals to policyholders who have participating policies. These dividends can be received in the form of cash, a reduction in premiums, additional coverage, or the option to accumulate with interest.
When policyholders choose to use policy dividends as collateral, they allow the lender to access the dividend payments to cover the outstanding loan amount if the borrower defaults. This provides additional security for the lender and may offer borrowers an alternative source of collateral.
It’s important to note that not all life insurance policies provide dividends, and even if they do, the dividends are not guaranteed. The dividend amounts can vary based on the insurance company’s performance and the policy’s terms and conditions.
Individuals considering using policy dividends as collateral should carefully evaluate the loan terms and the impact on their policy. If the dividends are essential for maintaining the policy’s value, coverage, or long-term goals, using them as collateral might not be the best option. It’s essential to weigh the immediate financial needs against the potential long-term consequences.
In some cases, borrowers may have the option to assign a portion of the future policy dividends as collateral, allowing them to maintain some of the dividend payments while securing the loan. This can provide a balance between accessing funds and still benefiting from the policy’s potential dividends.
Before pledging policy dividends as collateral for a life insurance policy loan, individuals should review their policy documents, consult with their insurance provider, and carefully consider the impact on their financial goals and long-term policy value. Seeking advice from a financial advisor can also provide valuable insights and guidance in making an informed decision.
Now that we have explored policy dividends as collateral, let’s move on to discuss other potential types of collateral accepted in life insurance policy loans.
Other Acceptable Collateral Types
In addition to the cash value, surrender value, death benefit assignment, and policy dividends, there may be other types of collateral that lenders accept in life insurance policy loans. The specific collateral options will depend on the insurance company and the terms of the policy. Here are some other potential types of collateral that may be accepted:
- Other Assets: Depending on the lender’s requirements and policies, they may accept other assets, such as real estate properties, stocks, bonds, or other investments, as additional collateral for a life insurance policy loan. These assets provide an additional layer of security for the lender and may allow borrowers to access more substantial loan amounts based on the value of these assets.
- Guarantors/Cosigners: In some cases, lenders may allow borrowers to provide a guarantor or a cosigner as collateral. A guarantor is an individual who agrees to be responsible for the loan repayments if the borrower defaults, while a cosigner agrees to take joint responsibility for the loan. Having a guarantor or cosigner with strong financial standing can give lenders more confidence in approving the loan.
- Cash Savings: Borrowers may also have the option to provide their cash savings as additional collateral. This can include savings accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs), or other readily available funds. By pledging their cash savings, borrowers can demonstrate their commitment to repaying the loan and provide additional security for the lender.
It’s important to note that the acceptance of these additional collateral types will depend on the individual insurance company’s policies and the loan agreement. Borrowers will need to consult with their insurance provider or the lender directly to determine which collateral options are available and meet the criteria for securing the loan.
Understanding the different collateral options and their implications is crucial for borrowers to make informed decisions when obtaining a life insurance policy loan. It’s recommended to thoroughly review the loan terms, assess the risks and considerations, and seek professional advice if needed before finalizing a loan agreement.
Now that we have explored the various collateral types that may be accepted in life insurance policy loans, let’s move on to discuss the risks and considerations associated with borrowing against a life insurance policy.
Risks and Considerations
Borrowing against a life insurance policy can provide individuals with much-needed funds in times of financial need, but it’s important to carefully consider the risks and implications before proceeding with a policy loan. Here are some key risks and considerations to keep in mind:
- Policy Termination: If the loan amount and interest are not repaid, it can lead to the termination of the policy. This means losing the insurance coverage and potentially impacting the financial protection of loved ones who depend on the policy’s death benefit.
- Reduced Cash Value and Death Benefit: Taking a loan against the policy’s cash value or assigning the death benefit as collateral can result in a reduction of the policy’s value. This can impact the growth potential and long-term benefits of the policy.
- Interest and Fees: Policy loans often come with interest rates and fees, which can increase the overall cost of borrowing. It’s important to carefully review and understand the loan terms to assess the impact on personal finances.
- Impact on Policy Performance: Using the policy’s cash value or dividends as collateral can limit the growth potential, as these funds may no longer accumulate interest or receive dividends while the loan is outstanding. It’s essential to consider the long-term impact on policy performance and potential returns.
- Alternative Borrowing Options: Before deciding on a policy loan, individuals should explore alternative borrowing options, such as traditional personal loans or lines of credit, to compare interest rates, terms, and potential impacts on insurance coverage.
- Effect on Beneficiaries: Assigning the death benefit or utilizing policy dividends as collateral can reduce or eliminate the intended payout for beneficiaries if the loan is not repaid. It’s crucial to consider the financial impact on loved ones and their future financial security.
Individuals considering a life insurance policy loan should thoroughly review the loan agreement, consult with their insurance provider or financial advisor, and carefully evaluate their financial situation and long-term goals. Understanding the risks and potential consequences can help make an informed decision that aligns with personal needs and priorities.
Now, let’s conclude our discussion on collateral in life insurance policy loans.
Conclusion
Collateral plays a crucial role in securing a life insurance policy loan. Understanding what assets can be used as collateral is essential for individuals considering this financial option. In this article, we have explored the concept of collateral in life insurance policy loans and discussed the different types of collateral that may be accepted.
These collateral options include the cash value of the policy, surrender value of the policy, death benefit assignment, and even policy dividends. Each of these collateral types comes with its own considerations and risks, including potential policy termination, reduced policy value, and the impact on beneficiaries.
It’s important for borrowers to carefully evaluate their financial situation, loan terms, and alternative borrowing options before deciding to use their life insurance policy as collateral. Consulting with an insurance professional or financial advisor can provide valuable insights and guidance throughout this decision-making process.
Remember to review the specific collateral requirements, loan terms, and potential consequences outlined in your policy documents carefully. This will help you make an informed decision that aligns with your financial goals and priorities.
Life insurance policy loans can provide individuals with a convenient way to access funds while maintaining their coverage. However, it’s crucial to understand the risks and considerations associated with borrowing against a policy. By doing so, borrowers can make well-informed decisions and ensure their financial stability and the protection of their loved ones.
Now, armed with a deeper understanding of collateral in life insurance policy loans, you can approach this financial option with confidence and make the best decision for your unique circumstances.