Finance
What Is Dynamic Hedging
Published: January 15, 2024
Discover the concept of dynamic hedging and its significance in finance. Learn how it helps investors manage risk and optimize their portfolios.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
In the world of finance, managing risk is a crucial aspect of any investment strategy. Whether you are a trader, investor, or financial institution, it is important to understand and implement various risk management techniques to mitigate potential losses and protect your portfolio. One such technique is dynamic hedging, a strategy that has gained significant popularity in recent years.
Dynamic hedging is a risk management approach that involves adjusting the composition of a portfolio to offset potential losses due to changing market conditions. Unlike traditional static hedging, which involves using derivatives to hedge against specific risks, dynamic hedging focuses on continuously monitoring and adjusting the hedge to align with market movements.
The purpose of dynamic hedging is to minimize the impact of market fluctuations on the value of a portfolio. By actively managing the hedge, investors can potentially limit downside risk and capture upside potential. This strategy is particularly beneficial in highly volatile markets, where prices can rapidly change, leading to substantial gains or losses.
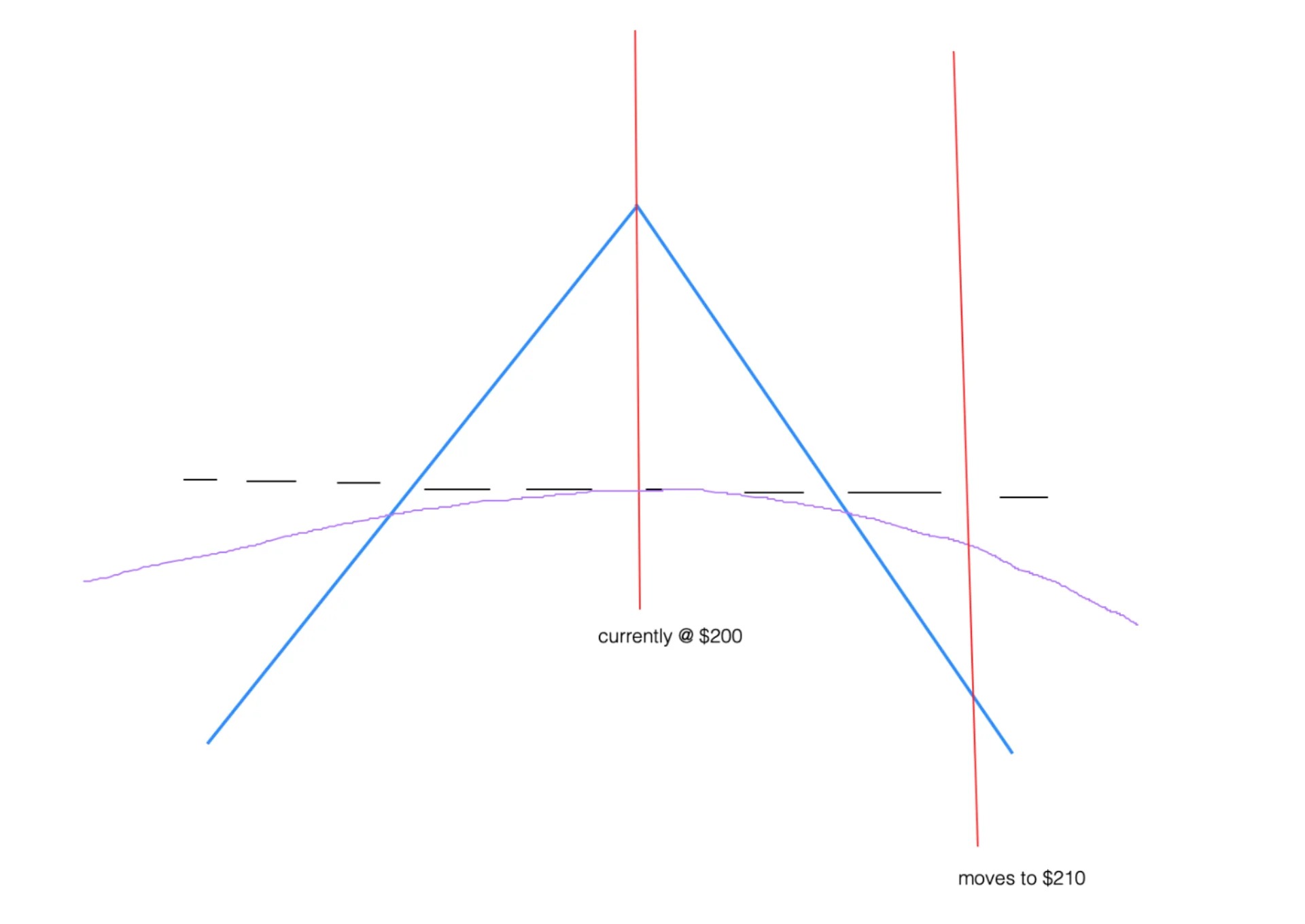
The principles of dynamic hedging are based on the concept of delta hedging. Delta is a measure of the sensitivity of an option’s price to changes in the price of the underlying asset. By dynamically adjusting the hedge based on changes in delta, investors can ensure that the value of the hedge closely mirrors the changes in the value of the underlying asset.
There are several strategies that can be employed for dynamic hedging, depending on the specific assets and market conditions. These strategies can include using options, futures contracts, or other derivatives to offset potential losses. The goal is to create a hedge that mirrors the movements of the underlying asset or portfolio, thereby reducing the risk of losses.
Dynamic hedging offers several advantages for investors. First and foremost, it allows for more precise risk management by actively adjusting the hedge to align with market conditions. This can help investors avoid large losses and preserve capital. Additionally, dynamic hedging can provide opportunities for profit by capturing potential gains during market upswings.
However, dynamic hedging is not without its limitations. One of the main challenges is the constant monitoring and adjustment required. This strategy requires active involvement and expertise in tracking market movements and making timely decisions. Additionally, transaction costs and the availability of suitable derivatives can impact the effectiveness of dynamic hedging.
Throughout this article, we will explore the principles, strategies, advantages, limitations, and real-world case studies of dynamic hedging. By understanding and incorporating this risk management technique into their investment approach, investors can enhance their ability to navigate changing market conditions and protect their portfolios.
Definition of Dynamic Hedging
Dynamic hedging is a risk management strategy that involves continuously adjusting the composition of a portfolio to mitigate potential losses caused by fluctuations in market conditions. Unlike traditional static hedging, which involves using derivatives to hedge against specific risks, dynamic hedging focuses on actively managing the hedge to align with changes in the market.
At its core, dynamic hedging is based on the concept of delta hedging. Delta is a measure of the sensitivity of an option’s price to changes in the price of the underlying asset. By dynamically adjusting the hedge based on changes in delta, investors can ensure that the value of the hedge closely mirrors the changes in the value of the underlying asset.
The primary objective of dynamic hedging is to minimize the impact of market fluctuations on the value of a portfolio. This strategy is particularly beneficial in volatile markets, where prices can rapidly change, exposing investors to potential losses. By actively managing the hedge, investors aim to reduce downside risk and capture upside potential.
Dynamic hedging strategies typically involve the use of derivatives, such as options, futures contracts, or swaps, to offset potential losses. The choice of derivatives depends on the specific assets being hedged and the market conditions. These derivatives are used in conjunction with the underlying assets in the portfolio to create a hedge that mirrors the movements of the portfolio.
One key aspect of dynamic hedging is the continuous monitoring and adjustment of the hedge. Market conditions can change rapidly, and as a result, the delta of the portfolio’s assets may fluctuate. To maintain an effective hedge, investors need to regularly assess the delta and make the necessary adjustments to ensure that the hedge remains aligned with the underlying assets.
It’s important to note that dynamic hedging is not an entirely risk-free strategy. While it aims to minimize downside risk, there is still a possibility of losses depending on market conditions. Additionally, transaction costs and the availability of suitable derivatives can impact the effectiveness of dynamic hedging.
Overall, dynamic hedging is a dynamic and proactive approach to risk management in the world of finance. By continuously adjusting the composition of a portfolio to align with market conditions, investors can enhance their ability to mitigate potential losses and protect their investments.
Purpose of Dynamic Hedging
The purpose of dynamic hedging is to minimize the impact of market fluctuations on the value of a portfolio and protect against potential losses. By actively managing the hedge, investors aim to reduce downside risk and capture upside potential. Dynamic hedging is particularly beneficial in volatile markets where prices can rapidly change, exposing investors to significant losses.
The primary goal of dynamic hedging is to maintain the value of the portfolio as closely as possible to the changes in the underlying assets. This is achieved by continuously adjusting the hedge based on changes in market conditions. By doing so, investors can offset potential losses that may arise due to market fluctuations.
Dynamic hedging serves several purposes in the realm of risk management:
- Minimizing downside risk: One of the key purposes of dynamic hedging is to minimize the potential losses that a portfolio may incur. By actively managing the hedge, investors can offset losses that may arise due to adverse market movements. This proactive approach helps to protect the portfolio from significant downturns and preserve capital.
- Limiting exposure to market fluctuations: Dynamic hedging allows investors to limit their exposure to market fluctuations by adjusting the hedge in response to changes in market conditions. This can be particularly beneficial in volatile markets, where prices can rapidly change and lead to substantial gains or losses. By continuously monitoring the market and adjusting the hedge accordingly, investors can mitigate the risks associated with market volatility.
- Preserving capital: Dynamic hedging helps investors preserve their capital by minimizing losses during adverse market conditions. By actively managing the hedge, investors aim to protect their investments and reduce the impact of market downturns. This capital preservation is crucial for long-term financial stability and growth.
- Capturing upside potential: Dynamic hedging not only aims to protect against downside risk but also seeks to capture upside potential. By adjusting the hedge in response to positive market movements, investors can benefit from favorable market conditions and potentially generate additional returns. This allows investors to take advantage of market upswings and enhance their overall portfolio performance.
Overall, the purpose of dynamic hedging is to effectively manage risk and protect portfolios from adverse market conditions. By continuously adjusting the hedge to align with changing market conditions, investors can minimize potential losses, preserve capital, and potentially capture upside potential.
Principles of Dynamic Hedging
The principles of dynamic hedging are rooted in the concept of delta hedging, which involves continuously adjusting the hedge to align with changes in the underlying asset’s price. Here are the key principles that guide dynamic hedging:
- Delta neutrality: The fundamental principle of dynamic hedging is to maintain a delta-neutral position. Delta is the measure of an option’s sensitivity to changes in the price of the underlying asset. By ensuring that the overall delta of the portfolio is close to zero, investors can minimize the impact of market movements on the value of the portfolio. This is achieved by adjusting the hedge as the delta of the underlying assets fluctuates.
- Continuous monitoring: Dynamic hedging requires continuous monitoring of market conditions and the delta of the underlying assets. Investors need to stay vigilant and track any changes in the market that may impact the delta of the portfolio. By consistently monitoring the market, investors can make timely adjustments to the hedge and maintain its effectiveness.
- Timely adjustments: Timing is crucial in dynamic hedging. Investors must make timely adjustments to the hedge to ensure that it remains aligned with market movements. This involves buying or selling derivatives to offset changes in the value of the underlying assets. The goal is to maintain a hedging strategy that closely mirrors the movements of the portfolio, reducing the risk of losses.
- Risk management: Risk management is a core principle of dynamic hedging. The objective is to mitigate potential losses by actively managing the hedge based on market conditions. By adjusting the hedge in response to changes in the delta of the underlying assets, investors aim to reduce downside risk and protect the value of the portfolio.
- Adaptability: Dynamic hedging requires adaptability to changing market conditions. Investors must be flexible and willing to adjust their strategies as needed. This involves assessing the effectiveness of the current hedge and making necessary changes to maintain alignment with market movements.
By adhering to these principles, investors can effectively implement dynamic hedging strategies to manage risk and protect their portfolios. The continuous monitoring, timely adjustments, and focus on delta neutrality enable investors to navigate changing market conditions and mitigate potential losses.
Strategies for Dynamic Hedging
Dynamic hedging involves the implementation of various strategies to continuously adjust the composition of a portfolio in response to changes in market conditions. These strategies aim to maintain a delta-neutral position and effectively hedge against potential losses. Here are some common strategies used in dynamic hedging:
- Options-based hedging: One strategy for dynamic hedging involves the use of options to offset potential losses. For example, investors can use put options to protect against downside risk by purchasing the right to sell a specific asset at a predetermined price. By adjusting the number and strike prices of put options based on changes in the delta, investors can maintain a delta-neutral position and minimize losses.
- Futures-based hedging: Another strategy for dynamic hedging is using futures contracts to offset potential losses. Futures contracts are agreements to buy or sell an asset at a future date and a predetermined price. By entering into futures contracts, investors can hedge against price fluctuations of the underlying asset. Adjustments to the number and expiration dates of futures contracts can be made to maintain a delta-neutral position.
- Combination hedging: Combination hedging involves using a mix of options, futures contracts, and other derivatives to create a dynamic hedge. Investors can combine different derivatives to offset potential losses and maintain a delta-neutral position. The specific combination of derivatives depends on the assets being hedged and the market conditions.
- Portfolio rebalancing: Rebalancing the portfolio is an essential strategy in dynamic hedging. Investors adjust the allocation of assets within the portfolio to ensure alignment with market movements. This may involve buying or selling assets to maintain the desired risk exposure and delta neutrality.
- Algorithmic trading: With advancements in technology, algorithmic trading has become increasingly prevalent in dynamic hedging. Algorithms are programmed to monitor market conditions, execute trades, and make adjustments to the hedge automatically. These algorithms can analyze market data and make rapid decisions based on predetermined rules and risk parameters.
The choice of strategy depends on various factors, including the underlying assets, market conditions, and risk tolerance. It is crucial for investors to carefully assess their portfolio and determine the most appropriate strategy for dynamic hedging based on their specific needs and goals.
Implementing dynamic hedging strategies requires expertise in derivatives, risk management, and market analysis. It is important for investors to stay informed, conduct thorough research, and seek professional advice when necessary to ensure the effective implementation of dynamic hedging strategies.
Advantages of Dynamic Hedging
Dynamic hedging offers several advantages for investors looking to effectively manage risk and protect their portfolios. By actively adjusting the hedge to align with market movements, dynamic hedging provides a range of benefits:
- Precise risk management: One of the key advantages of dynamic hedging is its ability to provide precise risk management. By continuously monitoring market conditions and adjusting the hedge accordingly, investors can mitigate potential losses and protect their portfolios from adverse market movements. This proactive approach allows for a more targeted and effective risk management strategy.
- Minimization of downside risk: Dynamic hedging aims to minimize downside risk by offsetting potential losses. By adjusting the hedge in response to changes in the underlying assets’ delta, investors can ensure that the value of the hedge closely mirrors the changes in the portfolio’s value. This helps to protect against substantial market downturns and limit the impact of volatile market conditions.
- Capture of upside potential: In addition to minimizing downside risk, dynamic hedging also allows investors to capture upside potential. By adjusting the hedge to align with favorable market movements, investors can benefit from price increases and potentially generate additional profits. This provides an opportunity to enhance overall portfolio performance and capitalize on market upswings.
- Flexibility: Dynamic hedging offers flexibility in managing risk and adapting to changing market conditions. Investors can adjust the composition of the hedge based on individual risk tolerance, investment objectives, and the specific assets being hedged. This allows for customization and tailoring of the hedging strategy to meet specific needs.
- Enhanced portfolio stability: By actively managing the hedge, dynamic hedging helps to enhance portfolio stability. This is achieved by reducing the impact of market fluctuations on the value of the portfolio. By minimizing potential losses, investors can maintain capital stability and long-term financial growth.
- Improved risk/reward profile: By effectively managing risk through dynamic hedging, investors can improve the risk/reward profile of their portfolios. This strategy allows for a more targeted approach to risk management, ensuring that potential losses are minimized while still providing opportunities for capturing gains. This balanced approach can lead to more consistent and favorable investment outcomes.
Overall, dynamic hedging provides investors with a proactive and flexible approach to risk management. By continuously adjusting the hedge to align with market movements, investors can minimize downside risk, capture upside potential, and enhance the stability and performance of their portfolios.
Limitations of Dynamic Hedging
While dynamic hedging offers several advantages, it is important to understand and consider its limitations. These limitations can impact the effectiveness and implementation of dynamic hedging strategies:
- Constant monitoring and adjustment: Dynamic hedging requires constant monitoring of market conditions and timely adjustments to the hedge. This can be resource-intensive and time-consuming, especially for individual investors. The need for continuous monitoring and active decision-making may pose challenges for investors who lack the expertise or time to dedicate to such activities.
- Transaction costs: Implementing dynamic hedging strategies often involves frequent trading and the use of derivatives. These transactions can accrue significant costs, including brokerage fees, bid-ask spreads, and other transaction-related expenses. High transaction costs can erode potential gains and reduce the overall effectiveness of dynamic hedging.
- Availability of suitable derivatives: The availability of suitable derivatives is essential for implementing dynamic hedging strategies effectively. Not all derivatives may be readily available or suitable for hedging specific assets or risks. Limited availability may constrain investors’ ability to execute certain dynamic hedging strategies, limiting their effectiveness.
- Potential for tracking error: Despite efforts to maintain delta neutrality, tracking error can occur in dynamic hedging. This refers to the discrepancy between the performance of the hedge and the underlying assets. Factors such as transaction costs, liquidity issues, and imperfect correlation between the hedge and the assets can contribute to tracking error. Higher tracking error can impact the accuracy and efficiency of dynamic hedging.
- Market disruptions: Dynamic hedging strategies may face challenges during periods of market disruptions or extreme volatility. Rapid and unpredictable market movements can make it challenging to adjust the hedge in real-time or find suitable derivatives that can effectively offset risks. This can potentially result in larger-than-expected losses and reduced effectiveness of the hedge.
- Complexity and expertise: Implementing dynamic hedging necessitates a solid understanding of options trading, derivatives, and risk management. It can be a complex strategy that requires expertise and experience. Lack of knowledge or experience in these areas can lead to ineffective hedging, potential losses, and other negative outcomes.
It is important for investors to carefully assess these limitations before implementing dynamic hedging strategies. Considerations such as transaction costs, availability of suitable derivatives, and the ability to actively monitor and adjust the hedge should be taken into account. Seeking professional advice and conducting thorough research can help investors navigate these limitations and optimize the effectiveness of dynamic hedging.
Case Studies on Dynamic Hedging
To better understand the practical application and effectiveness of dynamic hedging strategies, let’s explore a few case studies:
Case Study 1: Long-term Portfolio Protection:
During the financial crisis of 2008, many investors experienced significant losses as markets dove. However, some hedge funds effectively implemented dynamic hedging strategies to protect their portfolios. These funds continuously adjusted their hedges based on market conditions, using derivatives such as put options and futures contracts to offset potential losses. By actively managing their hedges, these funds were able to significantly limit their downside risk and preserve capital, providing long-term protection for their portfolios.
Case Study 2: Hedging Currency Risk:
International businesses often face currency risk due to fluctuations in exchange rates. Dynamic hedging can be employed to mitigate this risk. Let’s consider the example of a multinational company based in the U.S. that has significant revenue denominated in euros. To hedge against euro depreciation, the company can use dynamic hedging strategies by continuously adjusting its hedge with euro futures contracts or options. This allows the company to minimize losses caused by unfavorable exchange rate movements and protect its revenue in U.S. dollar terms.
Case Study 3: Commodity Price Hedging:
Commodity producers, such as oil companies, often face price volatility that can impact their profitability. Dynamic hedging can be utilized to manage commodity price risk effectively. For instance, an oil company could employ dynamic hedging strategies using futures contracts. By continuously adjusting the hedge based on changes in the oil price, the company can offset potential losses and protect its revenues. This allows the company to navigate volatile oil markets and maintain stable cash flows.
These case studies demonstrate the practical application of dynamic hedging in different scenarios. Whether it’s protecting portfolios during downturns, hedging currency risk, or managing commodity price fluctuations, dynamic hedging strategies can provide valuable risk management benefits.
However, it’s important to note that each case study and implementation of dynamic hedging will be unique to the specific circumstances and goals of the investor or organization. Factors such as risk tolerance, market conditions, and available hedging instruments will influence the effectiveness and outcomes of dynamic hedging strategies.
Conclusion
Dynamic hedging is a powerful risk management strategy that enables investors to mitigate potential losses and protect their portfolios in the face of changing market conditions. By continuously adjusting the hedge based on market movements and maintaining a delta-neutral position, dynamic hedging minimizes downside risk while capturing upside potential.
Throughout this article, we explored the principles, strategies, advantages, limitations, and case studies of dynamic hedging. We highlighted the importance of delta neutrality, continuous monitoring and adjustment, and precise risk management. We discussed various hedging strategies, including options-based and futures-based approaches, as well as the benefits of portfolio rebalancing and algorithmic trading.
Dynamic hedging offers several advantages, including precise risk management, minimization of downside risk, capture of upside potential, flexibility, enhanced portfolio stability, and improved risk/reward profile. However, it is not without limitations, such as the need for constant monitoring, transaction costs, availability of suitable derivatives, potential for tracking error, market disruptions, and the complexity that requires expertise.
Case studies showcased the practical application of dynamic hedging in protecting long-term portfolios, hedging currency risk, and managing commodity price fluctuations. These examples demonstrated how dynamic hedging can be tailored to specific situations and goals, providing effective risk management solutions.
In conclusion, dynamic hedging is a valuable tool for investors seeking to navigate volatile markets and protect against potential losses. By understanding its principles, implementing suitable strategies, and considering the limitations, investors can enhance their ability to manage risk and secure their financial well-being in an ever-changing financial landscape.