Finance
What Is The Meaning Of ACH Credit?
Modified: January 15, 2024
Learn the Meaning of ACH Credit in Finance and how it impacts your financial transactions. Discover the benefits and usage of ACH Credit in just a few sentences.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
In today’s digital age, financial transactions have become increasingly convenient and efficient. One such method is the Automated Clearing House (ACH) system, which allows for secure and swift electronic transfers of funds between banks in the United States. Within the ACH system, there are two primary types of transactions: ACH credits and ACH debits.
This article will focus on ACH credits, exploring their meaning, how they work, their benefits, common uses, and the differences between ACH credits and ACH debits. Additionally, we’ll delve into the ACH credit process and the importance of security and safety when utilizing ACH credits.
Understanding the concept of ACH credits is essential for individuals and businesses alike, as it can simplify the payment process, increase efficiency, and save valuable time and resources. Whether you are an entrepreneur, a finance professional, or simply someone curious about improving their financial knowledge, gaining a comprehensive understanding of ACH credits will prove invaluable.
So, let’s dive deeper into the world of ACH credits and uncover their significance in modern-day banking.
Understanding ACH
Before delving into the specifics of ACH credits, it’s important to have a clear understanding of the Automated Clearing House (ACH) system itself. The ACH system is an electronic network that facilitates the movement of funds between financial institutions in the United States. It serves as a secure and efficient alternative to paper checks, allowing for the quick and seamless transfer of funds.
The ACH system operates under the governance and regulations set forth by the National Automated Clearing House Association (NACHA). NACHA establishes the rules and guidelines that financial institutions must follow when processing ACH transactions, ensuring the security and reliability of the system.
ACH transactions encompass various types of electronic transfers, including ACH credits and ACH debits. ACH credits involve the electronic transfer of funds from one bank account to another, while ACH debits involve the withdrawal of funds from a bank account.
Transacting through the ACH system offers numerous benefits. It eliminates the need for physical checks, reducing the risk of fraud and errors associated with manual processing. ACH transactions are typically faster, with funds being transferred within one to two business days. Moreover, the ACH system provides a cost-effective solution, as compared to other payment methods that may incur processing fees.
While ACH transactions are predominantly used by businesses for payroll deposits, bill payments, and vendor payments, individuals can also utilize the ACH system for various purposes, such as paying for goods and services, transferring funds between personal accounts, and making charitable donations.
With an understanding of the ACH system as a foundation, let’s delve deeper into the meaning and mechanics of ACH credits.
What is ACH Credit?
ACH Credit is a type of electronic payment where funds are initiated by the sender to be deposited into the recipient’s bank account. It is a convenient and secure method of transferring funds, commonly used for direct deposits, online bill payments, and business-to-business transactions.
When an ACH credit is initiated, the sender provides their bank with the necessary information, including the recipient’s bank account number and routing number. Using this information, the sender’s bank initiates the transfer of funds to the recipient’s bank account.
ACH credits are versatile and can be used for various types of transactions. For example, employers use ACH credits to deposit employees’ salaries directly into their bank accounts, eliminating the need for paper checks or cash. Similarly, businesses use ACH credits to pay vendors, suppliers, and contractors, streamlining the payment process and reducing paperwork.
ACH credits are also commonly used for online bill payments and recurring payments. By providing the necessary bank account information, individuals can set up automatic payments for their utility bills, mortgage payments, subscription services, and more. This eliminates the need for manual bill payments and ensures timely payments without the risk of forgetting or incurring late fees.
Furthermore, ACH credits are a popular choice for charitable donations, as they offer a secure and convenient way for individuals to contribute to their favorite organizations. Donors can provide their bank account information to the charity, which uses ACH credits to collect the donations efficiently.
ACH credits provide numerous benefits for both the sender and the recipient. For the sender, ACH credits eliminate the need for physical checks, reducing the cost and time associated with printing, mailing, and reconciling paper transactions. Additionally, the sender has the convenience of initiating the transfer from their own bank account, whether through online banking or mobile banking applications.
For the recipient, ACH credits offer a reliable and efficient method of receiving funds. The funds are deposited directly into their bank account, eliminating the need to visit a physical bank or handle paper checks. This ensures faster access to the funds, as they are typically available within one to two business days.
Overall, ACH credits provide a secure, convenient, and cost-effective solution for transferring funds electronically. They have revolutionized the way payments are made, offering a streamlined alternative to traditional paper-based transactions.
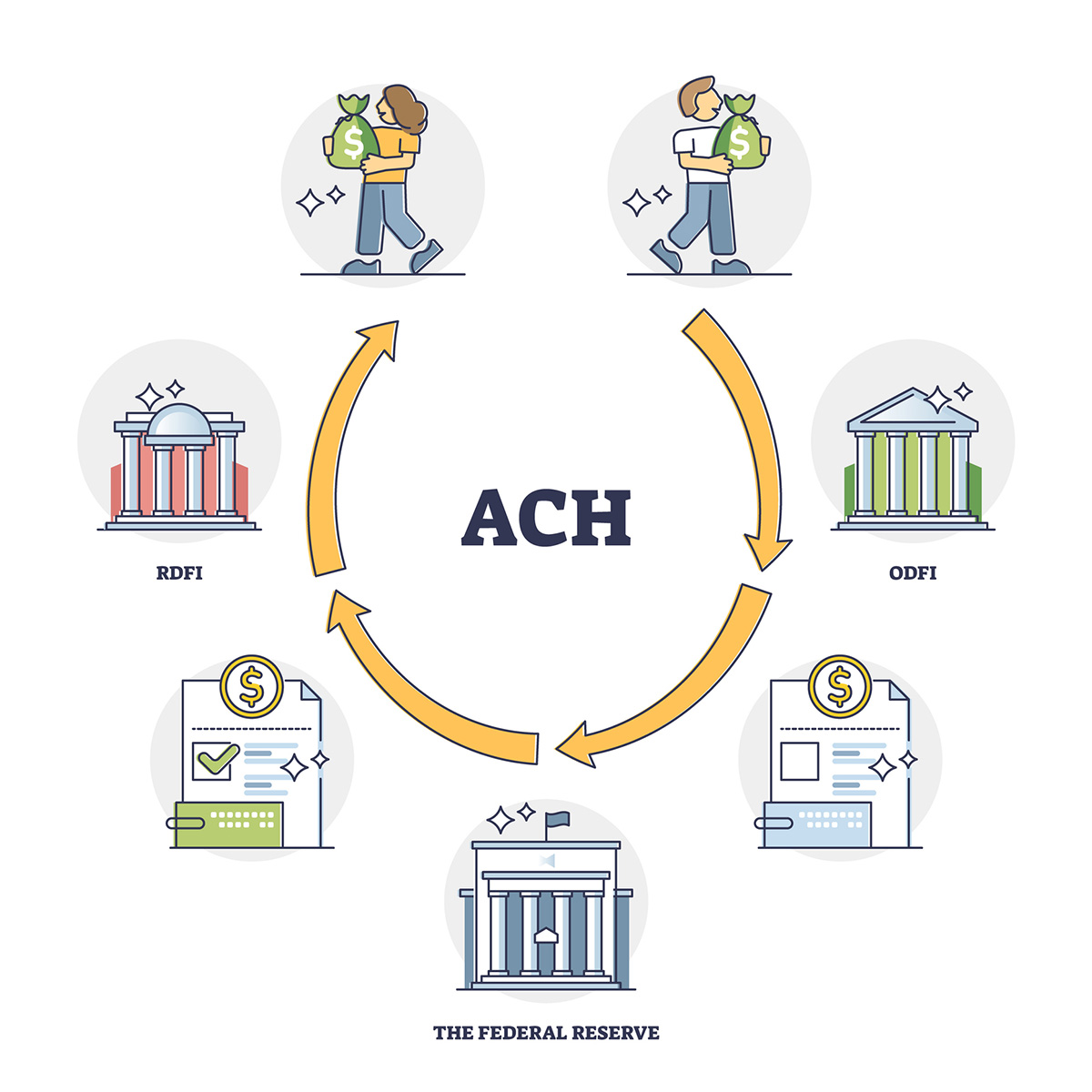
How ACH Credits Work
ACH credits utilize a standardized process to transfer funds electronically between bank accounts. Here’s a step-by-step overview of how ACH credits work:
- The sender initiates the ACH credit by providing their bank with the necessary information, including the recipient’s bank account number and routing number. This information ensures that the funds are deposited into the correct bank account.
- The sender’s bank verifies the account information and debits the sender’s account for the amount to be transferred. They then initiate the ACH credit transaction and forward it to the Automated Clearing House (ACH) network.
- The ACH network receives the transaction and processes it according to the rules and regulations set forth by the National Automated Clearing House Association (NACHA). The ACH network acts as an intermediary between the sender’s bank and the recipient’s bank.
- The ACH network forwards the ACH credit transaction to the recipient’s bank through a secure and encrypted channel. The recipient’s bank receives the transaction and verifies the account information.
- Once the account information is verified, the recipient’s bank credits the funds to the recipient’s bank account. The recipient can then access the funds, usually within one to two business days.
It’s important to note that ACH credits are typically processed in batches, rather than individually. This means that multiple ACH credit transactions are grouped together and processed at specific intervals throughout the day. The batch processing allows for efficient handling of a large volume of transactions and reduces processing costs for financial institutions.
Another key aspect of how ACH credits work is the settlement process. Settlement refers to the actual movement of funds between the banks involved in the ACH transaction. While the sender’s bank debits the sender’s account at the time of initiating the ACH credit, the actual transfer of funds between banks occurs during the settlement process.
Settlement typically occurs through the Federal Reserve or a private clearinghouse, depending on the financial institution. During the settlement, the sender’s bank reimburses the recipient’s bank for the funds transferred in the ACH credit transaction.
Overall, the process of ACH credits involves the sender initiating the transaction, the sender’s bank debiting their account, the ACH network facilitating the transfer, the recipient’s bank crediting the funds, and the settlement process ensuring the movement of funds between banks. This standardized process ensures the secure and efficient transfer of funds through the ACH system.
Benefits of ACH Credit
ACH credits offer several advantages for both senders and recipients compared to traditional payment methods. Let’s explore some of the key benefits:
- Efficiency and Speed: ACH credits allow for faster and more efficient fund transfers compared to other payment methods. With ACH credits, funds are typically available in the recipient’s account within one to two business days, ensuring timely access to the transferred funds.
- Cost-Effectiveness: ACH credits are a cost-effective payment solution, especially for businesses that regularly make payments to employees, vendors, or suppliers. ACH transactions usually involve lower transaction fees compared to alternatives such as wire transfers or paper checks, resulting in cost savings over time.
- Convenience: ACH credits offer convenience for both senders and recipients. Senders can initiate ACH credits from the comfort of their own banking platform, whether it’s through online banking or mobile apps. Recipients benefit from direct deposits, eliminating the need to physically deposit or handle paper checks.
- Increased Security: ACH credits enhance security by reducing the risk of lost or stolen checks. Unlike traditional checks that can be intercepted or misplaced, ACH credits are electronically initiated and securely transferred between banks, minimizing the chances of fraud or identity theft.
- Automation and Streamlining: ACH credits offer automation and streamlining benefits for recurring payments. Individuals and businesses can set up automatic ACH credits for regular bill payments or payroll deposits. This eliminates the need for manual intervention, reduces paperwork, and ensures that payments are made on time.
- Environmental Friendliness: ACH credits contribute positively to the environment by reducing paper waste. With no need for physical checks, ACH credits help minimize the consumption of paper, ultimately lowering the carbon footprint associated with traditional payment methods.
It is important to note that while ACH credits offer numerous benefits, there may be limits on transaction amounts and processing times imposed by financial institutions or specific ACH network regulations. It’s essential to familiarize yourself with these limitations and consult with your bank to ensure that ACH credits align with your specific needs.
Overall, the benefits of ACH credits make them an attractive payment solution for individuals and businesses alike. They provide efficient, cost-effective, and secure transfers, while also offering convenience, automation, and environmental advantages.
Common Uses of ACH Credit
ACH credits offer a wide range of applications, both personal and business-related. Let’s explore some of the most common uses of ACH credits:
- Direct Deposit: Direct deposit is one of the most widely used applications of ACH credits. Employers use ACH credits to deposit employees’ salaries directly into their bank accounts. This eliminates the need for paper checks, offers convenience, and ensures timely access to funds.
- Online Bill Payments: ACH credits are popularly used for online bill payments. Individuals can set up automatic ACH credits to pay their utility bills, mortgage payments, credit card bills, subscriptions, and more. This provides convenience, reduces the risk of late payments, and minimizes time spent on manual bill payments.
- Vendor and Supplier Payments: Businesses frequently use ACH credits to make payments to vendors, suppliers, and contractors. Instead of writing and mailing checks, businesses can initiate ACH credits to transfer funds directly into the recipient’s bank account. This streamlines payment processes, reduces paperwork, and fosters stronger business relationships.
- Loan Repayments: ACH credits are commonly used for loan repayments. Lenders can set up automatic ACH credits to collect loan payments from borrowers’ bank accounts. This ensures timely payments, reduces the risk of missed payments, and simplifies the loan repayment process for both borrowers and lenders.
- Charitable Donations: ACH credits provide a secure and convenient method for individuals to make charitable donations. Charities can collect donations by allowing donors to provide their bank account information for recurring or one-time ACH credits. This eliminates the need for writing and mailing checks, making the donation process hassle-free.
- Business-to-Business Transactions: ACH credits are widely used for business-to-business (B2B) transactions. For example, businesses can pay their suppliers for goods or services using ACH credits. This simplifies the payment process, improves cash flow management, and reduces administrative overhead.
- Government Payments: ACH credits are utilized for various government payments, including tax refunds, social security benefits, and unemployment benefits. These payments can be electronically deposited into individuals’ bank accounts, providing a secure and convenient method of receipt.
The versatility of ACH credits allows them to be used in a wide range of scenarios, making them a preferred payment method for individuals, businesses, and government entities. By leveraging ACH credits, users can streamline processes, reduce costs, and ensure efficient and timely fund transfers.
ACH Credit vs ACH Debit
While both ACH credit and ACH debit are types of electronic payments processed through the Automated Clearing House (ACH) system, they differ in terms of the direction of funds and the entities involved. Let’s explore the differences between ACH credit and ACH debit:
ACH Credit:
ACH credit refers to the electronic transfer of funds initiated by the sender to be deposited into the recipient’s bank account. The sender authorizes their bank to transfer funds to the recipient’s bank account using the ACH network. ACH credits are commonly used for direct deposits, bill payments, business-to-business transactions, and charitable donations. The sender’s bank debits the sender’s account for the amount to be transferred, initiates the ACH credit transaction, and forwards it to the ACH network. Once the recipient’s bank receives the transaction, they credit the funds to the recipient’s bank account. ACH credits are convenient, secure, and offer benefits such as efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and automation.
ACH Debit:
ACH debit, on the other hand, involves the withdrawal of funds from a bank account. In this case, the sender (also known as the originator) initiates the transaction, authorizing the recipient to withdraw funds from their bank account. ACH debit transactions are commonly used for recurring payments such as mortgage payments, utility bills, and subscriptions. For example, an individual may authorize their electricity provider to withdraw funds directly from their bank account each month for bill payment. Similar to ACH credits, ACH debits are processed through the ACH network, but they involve the movement of funds from the sender’s account to the recipient’s account.
In summary, ACH credit involves the sender initiating the transfer of funds to be deposited into the recipient’s account, while ACH debit involves the sender authorizing the recipient to withdraw funds from their account. ACH credit is often used for direct deposits, payments, and transfers, while ACH debit is commonly used for recurring payments. Both ACH credit and ACH debit offer convenience, security, and efficiency, making them popular choices in the electronic payment landscape.
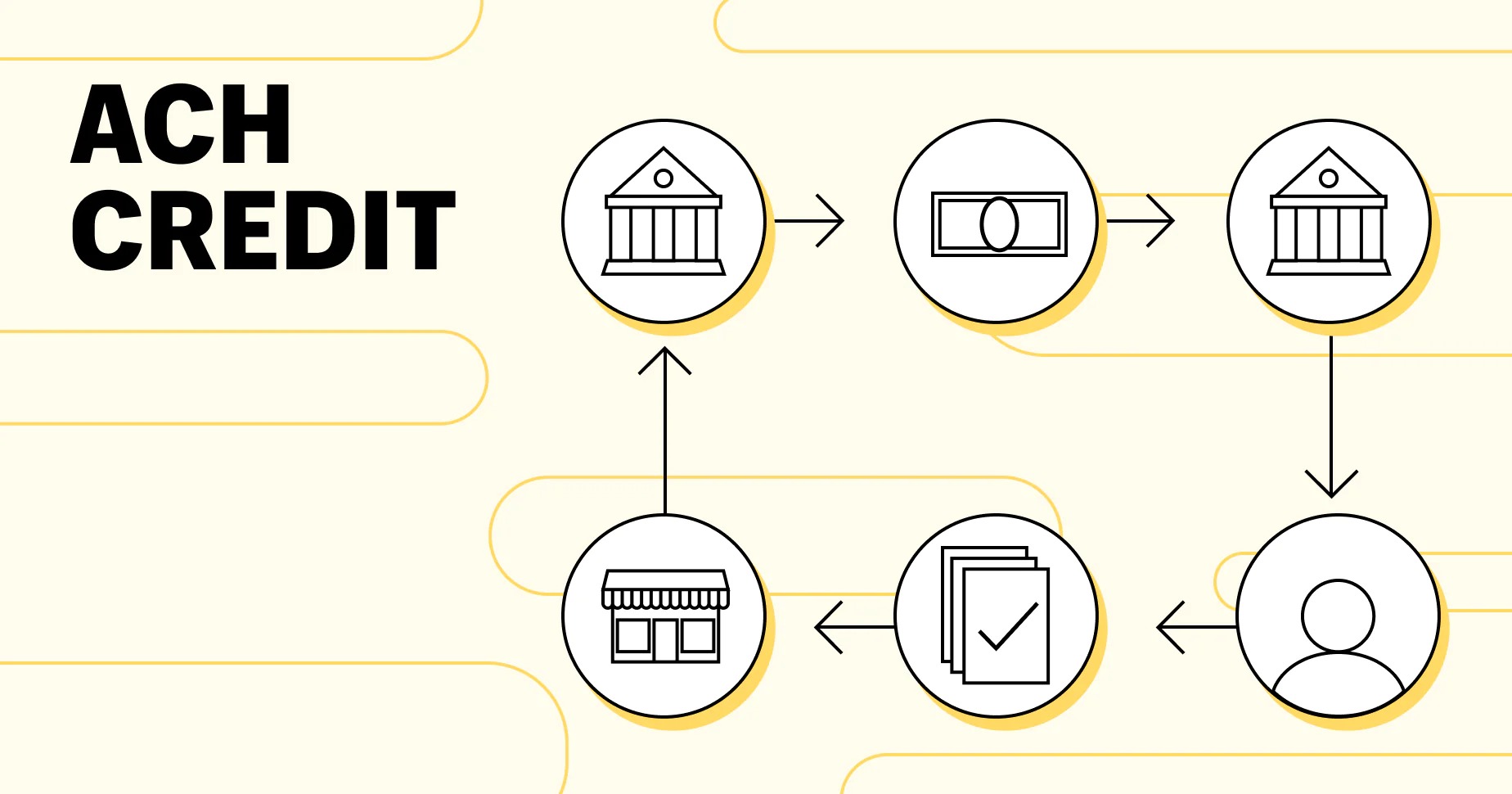
ACH Credit Process
The ACH credit process follows a set of steps to ensure the secure and efficient transfer of funds between banks. Let’s explore the key stages involved in the ACH credit process:
- Initiation: The ACH credit process begins when the sender (also known as the originator) initiates the transaction. The sender provides their bank with the necessary information, including the recipient’s bank account number and routing number. They may also specify the amount to be transferred and any additional details regarding the transaction.
- Sender’s Bank Verification: Upon receiving the instruction, the sender’s bank verifies the account information provided by the sender. They ensure that the account and routing numbers are accurate and correspond to the intended recipient’s bank. This verification step is crucial to prevent any errors in processing or funds being transferred to the wrong account.
- Debit the Sender’s Account: Once the account information is verified, the sender’s bank debits the sender’s account for the amount specified in the ACH credit transaction. This ensures that the funds are available for transfer and covers the transfer fees associated with the transaction.
- ACH Network Processing: After debiting the sender’s account, the sender’s bank forwards the ACH credit transaction to the Automated Clearing House (ACH) network. The ACH network acts as an intermediary between the sender’s bank and the recipient’s bank, coordinating the secure transfer of funds.
- Recipient’s Bank Verification and Credit: The ACH network forwards the ACH credit transaction to the recipient’s bank, which then verifies the account information and ensures that the recipient’s bank account is active and able to receive the funds. Once verified, the recipient’s bank credits the funds to the recipient’s bank account.
- Recipient’s Access to Funds: Once the funds are credited to the recipient’s bank account, the recipient can access the funds. The availability of funds may vary, but typically, they are available within one to two business days.
The ACH credit process involves coordination between the sender’s bank, the ACH network, and the recipient’s bank. This standardized process ensures the secure and efficient transfer of funds, reducing the risk of errors and providing a reliable payment method.
It’s important to note that each step in the ACH credit process is subject to the rules and guidelines set forth by the National Automated Clearing House Association (NACHA), which governs ACH transactions. These regulations ensure the security and integrity of the ACH network, protecting the interests of both senders and recipients.
By following the ACH credit process, individuals and businesses can leverage the benefits of electronic fund transfers, streamlining payment processes and improving overall financial efficiency.
Security and Safety of ACH Credits
The security and safety of ACH credits are paramount in ensuring the trust and reliability of electronic fund transfers. The ACH system employs various measures to protect the integrity of transactions and safeguard sensitive financial information. Let’s explore some of the key security features and practices that ensure the safety of ACH credits:
Encryption and Secure Channels: ACH credits are transmitted through encrypted channels to protect the confidentiality of the information being exchanged. Advanced encryption algorithms are utilized to prevent unauthorized access and alteration of the data during transmission.
Authentication and Verification: Financial institutions verify the identities of senders and recipients during the ACH credit process. This includes verifying account numbers, routing numbers, and other relevant information to ensure that funds are being transferred to the intended recipients. Stringent verification procedures help in preventing fraudulent activities.
NACHA Rules and Guidelines: The National Automated Clearing House Association (NACHA) establishes rules and guidelines that financial institutions must follow when processing ACH transactions. These rules ensure the secure and proper handling of ACH credits, minimizing the risk of fraud and errors.
Fraud Detection and Monitoring: Financial institutions employ sophisticated fraud detection and monitoring systems to identify any suspicious activities related to ACH credit transactions. These systems analyze transaction patterns, monitor account activity, and utilize artificial intelligence algorithms to detect potential fraudulent behavior, enhancing the security of ACH transactions.
Secure Access and Authorization: Banks implement robust security measures to ensure secure access to online banking platforms and authorization of ACH credit transactions. This may include multi-factor authentication, strong password requirements, and additional security protocols to prevent unauthorized access to accounts and unauthorized initiation of ACH credits.
Regulatory Compliance: Financial institutions adhere to regulatory requirements, such as the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). These regulations establish standards for the protection of sensitive financial information and require financial institutions to implement comprehensive security measures to safeguard customer data.
Customer Awareness and Education: Financial institutions play a crucial role in educating their customers about best practices for ACH credit transactions and raising awareness about potential risks and fraud schemes. By providing regular updates, alerts, and educational resources, customers can stay informed and take necessary precautions to protect themselves.
It is important for individuals and businesses to remain vigilant when initiating or receiving ACH credits. This includes verifying the authenticity of requests, keeping passwords and account information confidential, and promptly reporting any suspicious or unauthorized transactions to their financial institution.
By incorporating these security measures and practices, the ACH system ensures the safety of ACH credits, enhancing the overall trust and reliability of electronic fund transfers.
Conclusion
The utilization of ACH credits has revolutionized the world of electronic fund transfers, providing individuals and businesses with a secure, efficient, and convenient payment solution. Through the Automated Clearing House (ACH) system, ACH credits have become an integral part of modern financial transactions, offering a multitude of benefits.
ACH credits allow for the swift and seamless transfer of funds between bank accounts, eliminating the need for paper checks and reducing the risk of errors and fraud. They offer efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and automation, streamlining payment processes and saving valuable time and resources.
Individuals can leverage ACH credits for direct deposits, online bill payments, and charitable donations, while businesses benefit from simplified payroll processing, vendor payments, and streamlined cash flow management. ACH credits have also found applications in government payments and business-to-business transactions, further expanding their versatility.
The ACH credit process follows a standardized set of steps, ensuring the secure and reliable transfer of funds. With measures such as encryption, authentication, verification, and robust fraud detection, the safety of ACH credits is prioritized, instilling confidence in users and protecting sensitive financial information.
While ACH credits offer numerous advantages, it’s important for individuals and businesses to be aware of any transaction limits or processing times imposed by financial institutions or specific ACH network regulations. By staying informed and taking necessary precautions, users can optimize the benefits of ACH credits while mitigating potential risks.
In conclusion, ACH credits have transformed the way we conduct financial transactions, providing a modern and efficient alternative to traditional payment methods. With their speed, convenience, and security measures in place, ACH credits have become an essential tool for individuals and businesses seeking to streamline processes, enhance financial efficiency, and embrace the digital transformation of the financial industry.