Finance
What Is ACH Credit
Published: January 14, 2024
Learn about ACH credit and its role in finance. Understand the benefits and process behind this electronic payment system.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of ACH Credit! In the realm of finance and banking, ACH Credit plays a crucial role in facilitating electronic money transfers. Whether you’re a business owner, an employee, or an individual looking to make secure and convenient payments, understanding how ACH Credit works can greatly benefit you. From seamless transactions to improved cash flow, ACH Credit offers a plethora of advantages in today’s digital age.
ACH, which stands for Automated Clearing House, is a nationwide electronic payment network that enables the transfer of funds between financial institutions. ACH Credit is a method of payment where the sender authorizes their bank to transfer funds to the recipient’s account. This type of transaction is commonly used for recurring payments, such as direct deposits of paychecks, vendor payments, and even tax refunds.
With the advancement of technology, ACH Credit has become a popular alternative to traditional paper checks. It provides a more efficient, cost-effective, and secure way of transferring funds, eliminating the need for physical checks and the associated risks of loss or theft. Additionally, ACH Credit allows for faster processing times, ensuring that payments are delivered promptly to the intended recipients.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the intricacies of ACH Credit, from its inner workings to the numerous benefits it offers. We will delve into the different use cases of ACH Credit and discuss the security measures in place to safeguard these electronic transactions. Furthermore, we will compare ACH Credit to its counterpart, ACH Debit, to highlight their distinctive features and functions.
Whether you’re a business owner seeking efficient payment solutions or an individual looking for hassle-free money transfers, understanding the power of ACH Credit can transform the way you conduct transactions. So, let’s dive in and explore the world of ACH Credit!
What is ACH Credit?
ACH Credit refers to a method of electronic funds transfer where funds are initiated by the sender to be deposited into the recipient’s account through the Automated Clearing House (ACH) network. It offers a secure, convenient, and cost-effective way of conducting financial transactions.
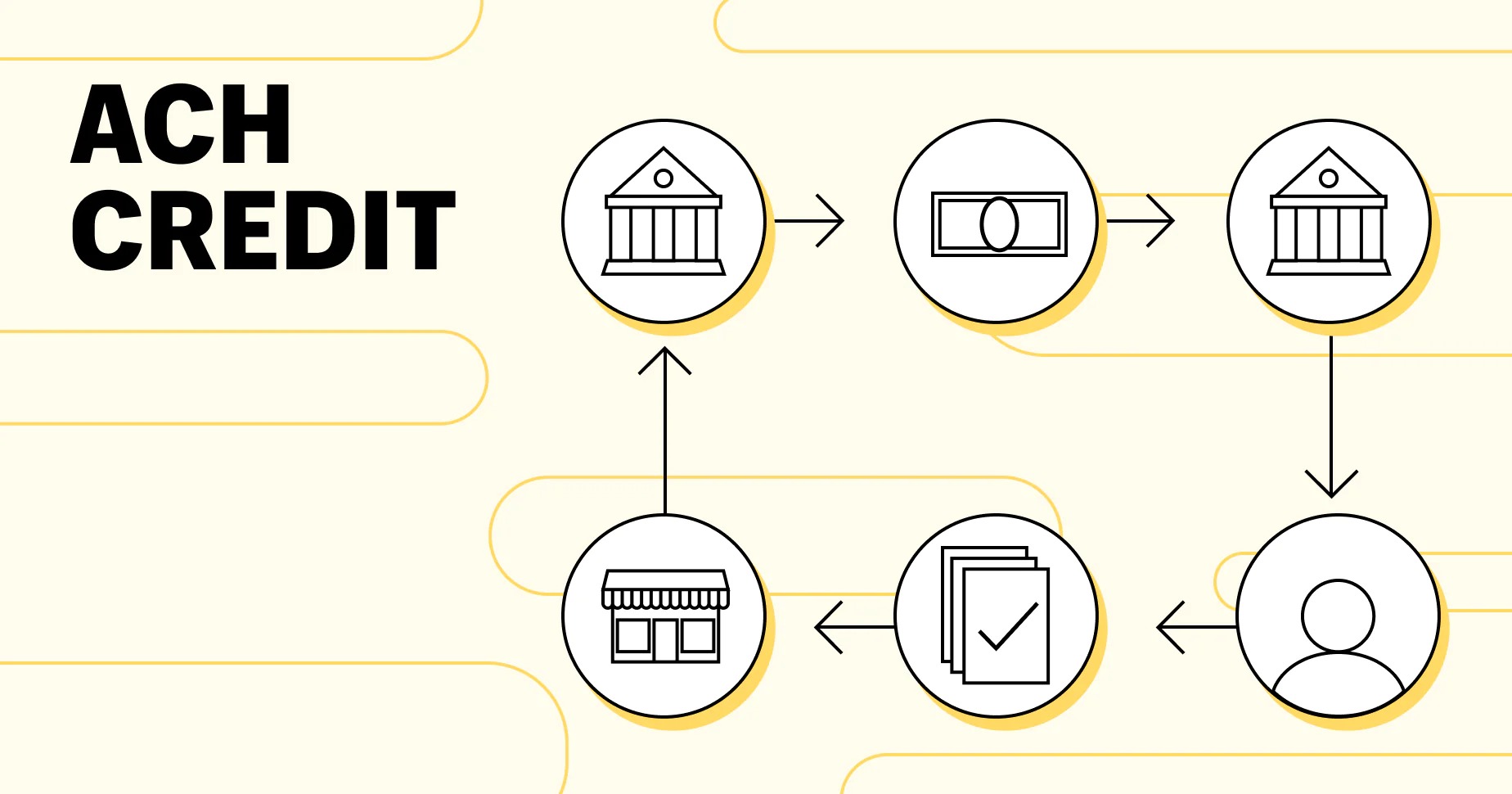
When an ACH Credit transaction takes place, the sender initiates the transfer by providing their financial institution with the necessary information, such as the recipient’s bank account number and routing number. The sender’s bank then sends the funds to the ACH operator, who processes and transfers the funds to the recipient’s bank. Finally, the recipient’s bank deposits the funds into the recipient’s account.
ACH Credit is commonly used for various types of payments, including direct deposits of paychecks, vendor payments, pension and retirement contributions, tax refunds, and more. It allows businesses and individuals to automate regular payments, ensuring timely and accurate transactions without the need for physical checks.
One of the key advantages of ACH Credit is its efficiency. Unlike paper checks that require manual processing and can take days to clear, ACH Credit transactions are typically processed electronically, resulting in faster fund transfers. This not only saves time for both the sender and recipient but also improves cash flow for businesses.
ACH Credit also offers cost savings. Compared to traditional payment methods, such as wire transfers or issuing and mailing physical checks, ACH Credit is a more cost-effective option. It eliminates the need for paper, postage, and administrative tasks associated with manual payment processing, reducing transaction costs for businesses.
In addition to its efficiency and cost-effectiveness, ACH Credit provides enhanced security. With ACH transactions, sensitive financial information is transmitted securely through encrypted channels, minimizing the risk of fraud and unauthorized access. The ACH network also adheres to strict regulations and guidelines to protect the integrity of electronic fund transfers.
Overall, ACH Credit is a powerful tool that simplifies payment processes, improves efficiency, and offers a secure means of transferring funds. Whether it’s paying employees, vendors, or receiving recurring income, ACH Credit streamlines financial transactions and provides peace of mind for businesses and individuals alike.
How Does ACH Credit Work?
Understanding how ACH Credit works is essential in navigating the world of electronic funds transfers. Let’s dive into the step-by-step process of how ACH Credit transactions take place:
- The Sender Initiates the Transfer: The ACH Credit process begins when the sender, either an individual or a business, authorizes their financial institution to initiate a funds transfer. The sender provides relevant information, such as the recipient’s bank account number and routing number, along with the amount to be transferred.
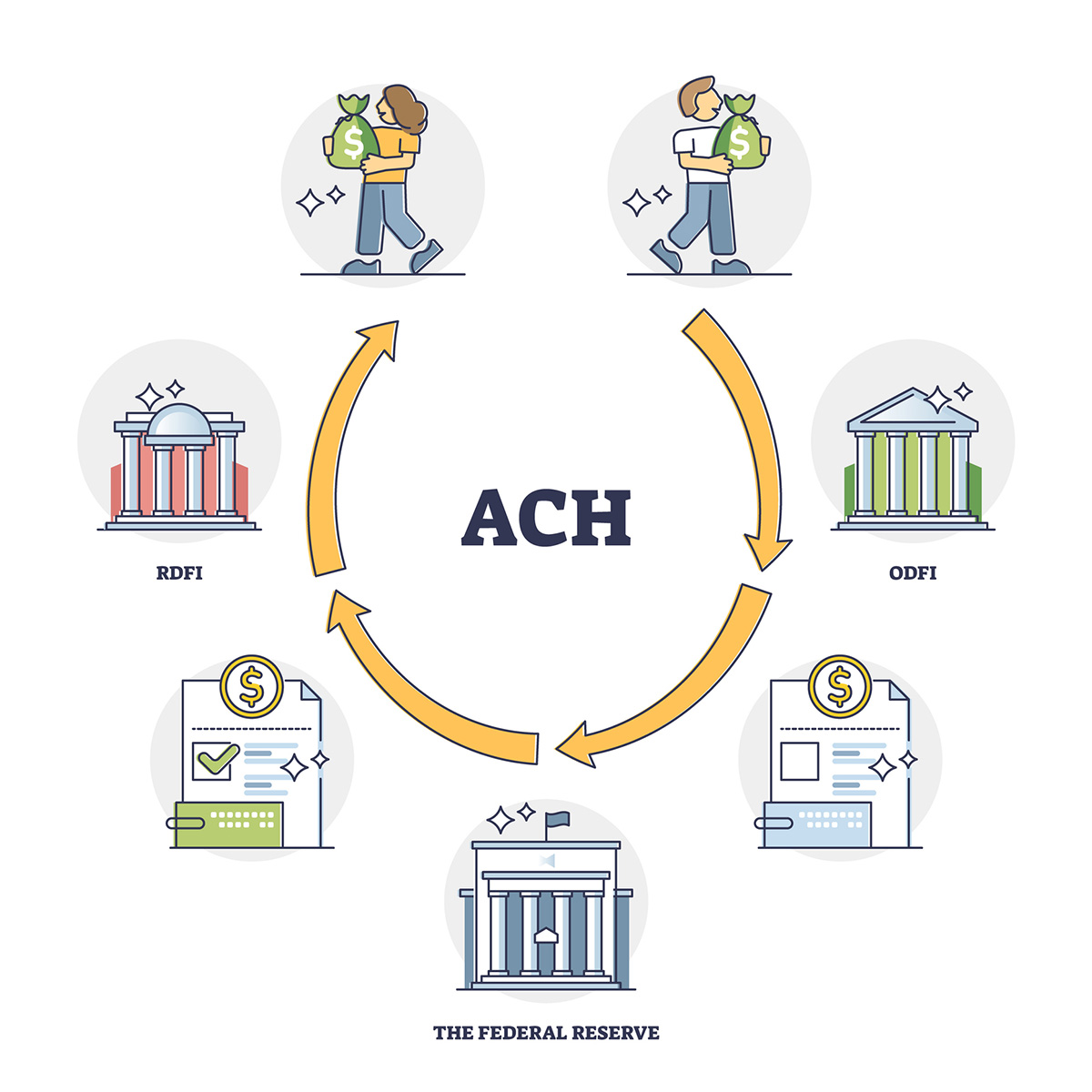
- Sender’s Bank Sends the Funds: Once the sender initiates the transfer, their financial institution, also known as the originating depository financial institution (ODFI), transmits the funds to the Automated Clearing House (ACH) network. The sender’s bank electronically sends the payment instructions, including the necessary details, to the ACH operator.
- ACH Operator Processes the Transaction: The ACH operator plays a vital role in facilitating the transaction. They receive the payment instructions from the sender’s bank and process the ACH Credit transaction. This involves verifying the routing and account numbers, ensuring that the sender has sufficient funds, and confirming that the transaction complies with ACH network rules.
- Transfer to Recipient’s Bank: Once the ACH operator processes the transaction, they transfer the funds to the recipient’s bank, also known as the receiving depository financial institution (RDFI). The ACH operator sends the payment instruction along with the funds to the recipient’s bank for further processing.
- Recipient’s Bank Deposits the Funds: Finally, the recipient’s bank receives the payment instruction and deposits the funds into the recipient’s account. The recipient can then access the funds and utilize them as needed.
It’s important to note that the duration of an ACH Credit transaction can vary. While many transactions are processed within a day or two, some may take longer, depending on factors such as the sending and receiving banks’ policies, weekends, and bank holidays. It’s always advisable to check with your financial institution for specific timelines.
ACH Credit transactions are commonly used for a variety of purposes, including payroll direct deposits, vendor and supplier payments, charitable donations, and more. The automated nature of ACH Credit streamlines payment processes, reduces manual administrative tasks, and allows for easy scheduling of recurring payments.
Overall, ACH Credit simplifies the transfer of funds by leveraging electronic systems, improving efficiency, and providing a secure and reliable method for businesses and individuals to conduct transactions.
Benefits of ACH Credit
ACH Credit offers a multitude of benefits for businesses, individuals, and financial institutions alike. Let’s explore the advantages of using ACH Credit for electronic fund transfers:
- Efficiency: ACH Credit transactions are processed electronically, allowing for faster fund transfers compared to traditional paper checks. This saves time for both the sender and recipient, ensuring that payments are delivered promptly and helping to improve cash flow for businesses.
- Cost-Effectiveness: ACH Credit is a more cost-effective payment method compared to alternatives such as wire transfers or issuing physical checks. It eliminates the need for paper, postage, and administrative tasks associated with manual payment processing, resulting in significant cost savings for businesses.
- Convenience: With ACH Credit, businesses and individuals can automate regular payments, eliminating the need for repetitive manual tasks. From payroll direct deposits to recurring vendor payments, ACH Credit simplifies payment processes, reduces administrative burden, and provides convenience for managing finances.
- Enhanced Security: ACH Credit transactions are highly secure, with sensitive financial information transmitted through encrypted channels. This minimizes the risk of fraud or unauthorized access, providing peace of mind for both senders and recipients. Furthermore, the ACH network adheres to strict regulations and guidelines to protect the integrity of electronic fund transfers.
- Decreased Risk: ACH Credit reduces the risk associated with physical checks, such as the potential for loss, theft, or forgery. By eliminating the need for paper checks, ACH Credit offers a more secure and reliable alternative, ensuring that funds are transferred safely and accurately.
- Flexibility: ACH Credit allows for various types of payments, including direct deposits, vendor payments, pensions and retirement contributions, tax refunds, and more. Its versatility makes it an ideal solution for businesses of all sizes and individuals seeking efficient and flexible payment options.
- Audit Trail and Reporting: ACH Credit transactions provide a robust audit trail and detailed reporting, allowing businesses to easily track and reconcile payments. This simplifies accounting processes, improves financial record-keeping, and facilitates seamless reconciliation.
By leveraging the benefits of ACH Credit, businesses can streamline payment processes, reduce costs, and improve efficiency. Individuals can enjoy the convenience and security of automated payments, ensuring timely and accurate fund transfers. Financial institutions can enhance their service offerings and provide value-added solutions to customers.
Whether you’re a business owner looking to optimize payment systems or an individual seeking a reliable and efficient method for fund transfers, ACH Credit offers a range of benefits that can transform the way you conduct financial transactions.
Uses of ACH Credit
ACH Credit has a wide range of applications and is utilized in various financial transactions. Let’s explore some of the key uses of ACH Credit:
- Payroll Direct Deposits: ACH Credit is commonly used for payroll direct deposits, where employers transfer employees’ salaries and wages directly into their bank accounts. This eliminates the need for paper checks, reduces administrative tasks, and ensures prompt payment to employees.
- Vendor and Supplier Payments: Businesses often use ACH Credit to make payments to their vendors and suppliers. This streamlines the payment process, improves cash flow management, and reduces the reliance on paper checks and manual bill payments.
- Government Benefits: ACH Credit is used for the distribution of government benefits, such as social security payments, unemployment benefits, and tax refunds. This enables efficient and direct transfer of funds to recipients, eliminating the need for paper checks and minimizing delays.
- Recurring Payments: ACH Credit allows for the automation of recurring payments for services like subscriptions, memberships, insurance premiums, and loan repayments. By setting up ACH Credit transfers, individuals and businesses can ensure timely and accurate payments without the need for manual intervention.
- Charitable Donations: Non-profit organizations often rely on ACH Credit for receiving donations. This method provides a convenient and secure way for donors to contribute funds, and it reduces administrative overhead for both the organization and the donors.
- Pension and Retirement Contributions: ACH Credit is used to transfer pension contributions and retirement plan funds to individual accounts. This ensures timely and accurate allocations of funds, facilitating retirement planning and long-term financial security.
- Business-to-Business (B2B) Payments: ACH Credit is a popular choice for B2B payments, allowing businesses to efficiently settle invoices, purchase orders, and other financial obligations. This improves payment processing, strengthens vendor relationships, and reduces transaction costs.
- Insurance Claim Payments: Insurance companies often utilize ACH Credit to disburse claim payments to policyholders. This expedites the payment process, reduces administrative tasks, and provides convenience for policyholders.
- Real Estate Transactions: ACH Credit can be used in real estate transactions for the secure transfer of funds between buyers, sellers, and financial institutions. This simplifies escrow processes, reduces the risk of fraud, and ensures timely closing of transactions.
These examples highlight the versatility and practicality of ACH Credit in a wide range of financial transactions. By leveraging ACH Credit, businesses and individuals can streamline payment processes, improve cash flow management, and enjoy the convenience and security of electronic fund transfers.
Security Measures for ACH Credit
As electronic fund transfers become increasingly prevalent, ensuring the security of ACH Credit transactions is of utmost importance. Here are some key security measures implemented to protect the integrity and confidentiality of ACH Credit:
- Encryption: ACH Credit transactions employ encryption protocols to protect sensitive financial information during transmission. Encryption converts data into a secure, coded format, making it difficult for unauthorized parties to intercept or decipher the information.
- User Authentication: Financial institutions implement robust user authentication processes to ensure that only authorized individuals can initiate ACH Credit transactions. This typically involves multi-factor authentication, where users are required to provide credentials such as passwords, PINs, and biometric verification.
- Secure Data Transmission: ACH Credit transactions utilize secure channels for data transmission, such as Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) or Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocols. These technologies create a secure connection between the sender and the ACH operator, safeguarding the confidentiality and integrity of the transmitted data.
- Network and System Security: Financial institutions maintain robust network and system security to protect against cyber threats. This includes advanced firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, regular system updates, and the implementation of industry-standard security frameworks.
- Authentication of Accounts: Financial institutions verify the authenticity of bank accounts involved in ACH Credit transactions. This helps prevent fraud by ensuring that funds are transferred to legitimate accounts and reducing the risk of erroneous or unauthorized transfers.
- Monitoring and Fraud Detection: Financial institutions continuously monitor ACH Credit transactions to detect any suspicious or fraudulent activity. Advanced fraud detection systems analyze transaction patterns, identify anomalies, and raise alerts for further investigation and mitigation.
- Regulatory Compliance: ACH Credit transactions are subject to stringent regulations to ensure compliance with industry standards and guidelines. These regulations, such as the NACHA Operating Rules, establish rules and safeguards to protect participants in the ACH network and mitigate risks associated with electronic fund transfers.
- Education and Awareness: Financial institutions and industry organizations provide education and training to customers and employees to raise awareness about security best practices and potential threats. Regular updates on security measures and emerging trends help customers stay informed and make informed decisions to protect their financial transactions.
It is important for individuals and businesses to be aware of these security measures and take precautions to safeguard their ACH Credit transactions. This includes using strong and unique passwords, keeping software and systems up to date, regularly monitoring account activity, and promptly reporting any suspicious or unauthorized transactions to the financial institution.
By implementing these security measures and maintaining high levels of vigilance, the ACH Credit system can continue to provide a secure and reliable means of electronic money transfers for businesses and individuals alike.
ACH Credit vs. ACH Debit
Within the Automated Clearing House (ACH) network, both ACH Credit and ACH Debit play significant roles in facilitating electronic transactions. While they are similar in many ways, there are key differences between the two. Let’s explore the distinctions between ACH Credit and ACH Debit:
ACH Credit:
ACH Credit involves funds being initiated by the sender to be deposited into the recipient’s account. This type of transaction is commonly used for direct deposits, vendor payments, tax refunds, and other instances in which funds are owed to the recipient. Examples of ACH Credit transactions include a company paying their employees through direct deposit or an individual making a recurring payment to their utility company.
One of the significant advantages of ACH Credit is that it allows the sender to have more control over the transfer of funds. The sender authorizes their financial institution to initiate the payment and provides relevant information, such as the recipient’s bank account number and routing number. This control and authorization make ACH Credit a secure and reliable method for making payments.
ACH Debit:
ACH Debit, on the other hand, involves funds being withdrawn directly from the sender’s account to pay the recipient or biller. With ACH Debit, the recipient has the authorization to pull funds from the sender’s account, typically for recurring payments such as mortgage payments, utility bills, or even subscription fees. Examples of ACH Debit transactions include a utility company debiting funds from a customer’s account for monthly bill payments or a credit card company automatically withdrawing payment for a monthly statement balance.
ACH Debit provides convenience for both the sender and the recipient, as regular payments can be automated and completed without the need for manual intervention. However, it’s essential for senders to carefully monitor their accounts and have sufficient funds available to cover the authorized ACH Debit transactions.
Key Differences:
The primary difference between ACH Credit and ACH Debit lies in the direction of the funds. In ACH Credit, funds are initiated by the sender and deposited into the recipient’s account, while in ACH Debit, funds are withdrawn from the sender’s account to pay the recipient or biller.
Another distinction is the level of control and authorization. With ACH Credit, the sender has more control as they authorize the transfer of funds, whereas with ACH Debit, the recipient has the authorization to pull funds from the sender’s account.
Both ACH Credit and ACH Debit offer benefits such as improved efficiency, reduced reliance on paper checks, and enhanced convenience. They are widely used for various financial transactions and play essential roles in streamlining payment processes for businesses and individuals.
Ultimately, whether to use ACH Credit or ACH Debit depends on the nature of the transaction, the party initiating the payment, and the level of control and authorization desired by both the sender and recipient.
Conclusion
ACH Credit is a powerful tool in today’s digital age, revolutionizing the way businesses and individuals conduct financial transactions. With its efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and enhanced security measures, ACH Credit offers numerous benefits that make it an attractive choice for electronic fund transfers.
From streamlining payroll processes and vendor payments to enabling recurring transactions and receiving government benefits, ACH Credit provides a secure and convenient method for transferring funds. Its automated nature saves time, improves cash flow, and reduces administrative burden for businesses, while individuals enjoy the convenience of direct deposits and automated bill payments.
Moreover, the security measures implemented for ACH Credit, such as encryption, user authentication, and diligent fraud detection, ensure the confidentiality and integrity of transactions. This gives businesses and individuals peace of mind, knowing that their financial information is being transmitted and processed securely.
It is also important to note the distinction between ACH Credit and ACH Debit. While both play significant roles in the ACH network, ACH Credit involves funds being initiated by the sender and deposited into the recipient’s account, while ACH Debit involves funds being withdrawn from the sender’s account to pay the recipient or biller. Understanding the differences between the two can help businesses and individuals determine the most suitable method for their specific needs.
In conclusion, ACH Credit offers a multitude of advantages in terms of efficiency, cost-effectiveness, convenience, and security. Leveraging this electronic payment method empowers businesses to streamline their financial processes, optimize cash flow, and enhance customer satisfaction. Similarly, individuals can benefit from the convenience and security of automated payments, ensuring timely and accurate fund transfers.
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, ACH Credit remains a reliable and indispensable tool for businesses, individuals, and financial institutions alike. By embracing the power of ACH Credit, we can unlock new possibilities and embrace a more efficient and secure financial future.