Home>Finance>What Is The Minimum Payment On A $300 Credit Card


Finance
What Is The Minimum Payment On A $300 Credit Card
Published: February 25, 2024
Learn about the minimum payment for a $300 credit card and its impact on your finances. Find out how to manage your credit card payments effectively. Gain insights on finance and credit management.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Understanding Minimum Payments on Credit Cards
When you receive your credit card statement, you may notice a section that outlines the minimum payment due. This is the smallest amount you are required to pay by the due date to keep your account in good standing. While it may be tempting to only pay the minimum, it’s essential to understand how this payment is calculated and the potential long-term implications of only making minimum payments.
Minimum payments are typically calculated as a percentage of your total balance, often around 1-3% of the outstanding amount, or a fixed dollar amount, whichever is higher. This means that the minimum payment can fluctuate based on your balance. It’s crucial to review your credit card agreement to understand the specific formula used by your issuer to calculate the minimum payment.
It’s important to recognize that while making the minimum payment can help you avoid late fees and maintain a positive payment history, it can also lead to significant interest charges. Credit card companies apply interest to the remaining balance after the minimum payment is made, which can result in a cycle of debt if only minimum payments are consistently made.
Understanding the concept of minimum payments is vital for responsible credit card management. By comprehending how they are calculated and the potential financial consequences, cardholders can make informed decisions about their payment strategy and overall credit card usage.
Factors Affecting Minimum Payments
Several factors influence the calculation of minimum payments on credit cards, and understanding these elements is crucial for managing your credit card debt effectively.
- Outstanding Balance: The most significant factor in determining the minimum payment is the outstanding balance on your credit card. Minimum payments are often calculated as a percentage of the total balance, meaning that a higher balance will result in a larger minimum payment.
- Interest Rate: The interest rate on your credit card directly impacts the minimum payment. Higher interest rates lead to greater interest charges on the outstanding balance, which, in turn, increases the minimum payment amount.
- Minimum Payment Formula: Each credit card issuer has its own formula for calculating minimum payments. This formula can include a percentage of the total balance, a fixed dollar amount, or a combination of both. Understanding your card issuer’s specific calculation method is essential for managing your payments effectively.
- Payment History: Your payment history, including any late or missed payments, can also affect the minimum payment amount. If you have a history of late payments, your card issuer may increase the minimum payment to mitigate the perceived risk of potential delinquency.
- Credit Score: While not a direct factor in minimum payment calculations, your credit score can influence the interest rate on your credit card. A lower credit score may result in a higher interest rate, leading to increased minimum payments due to higher interest charges.
By understanding these factors, credit card holders can make informed decisions about their repayment strategy, budgeting, and overall credit card usage. Being aware of how minimum payments are calculated empowers individuals to take control of their financial well-being and avoid potential pitfalls associated with credit card debt.
Calculating the Minimum Payment on a $300 Credit Card
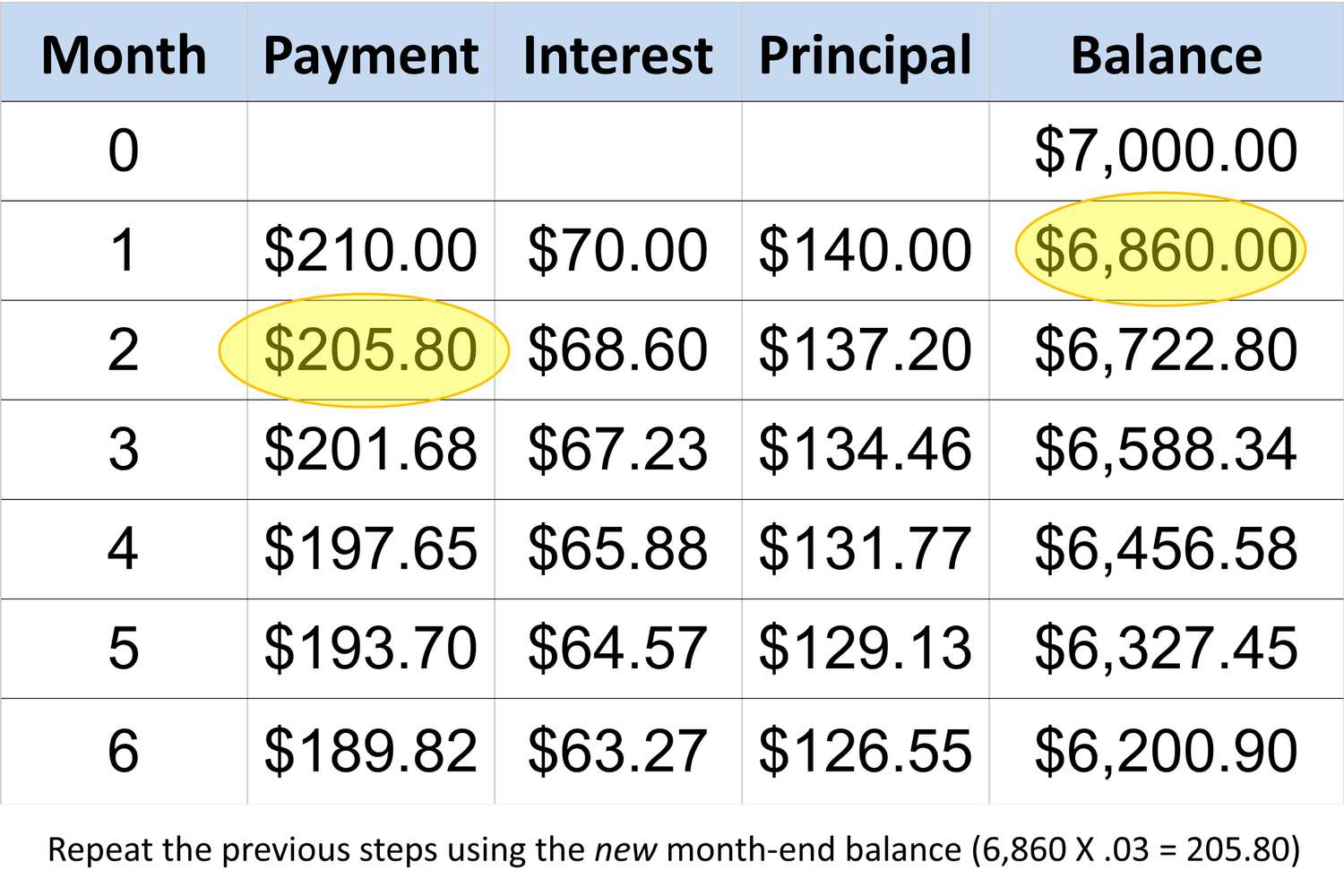
Understanding how the minimum payment is calculated on a $300 credit card balance is essential for effectively managing your credit card debt. While the specific calculation may vary based on the credit card issuer’s terms and conditions, we can explore a general example to illustrate the process.
Many credit card companies use a minimum payment formula that consists of a percentage of the outstanding balance, often around 1-3%, or a fixed dollar amount, whichever is higher. For the purpose of this example, let’s assume a minimum payment calculation based on 2% of the total balance.
With a $300 credit card balance, a 2% minimum payment would amount to $6. However, it’s important to note that credit card issuers often set a minimum dollar amount for the minimum payment to ensure that it covers at least a portion of the interest and principal balance. In this scenario, if the minimum dollar amount is set at $25, the cardholder would be required to pay $25 as the minimum payment, even though 2% of $300 is $6.
It’s crucial to review your credit card agreement to understand the specific minimum payment calculation used by your card issuer. By familiarizing yourself with the terms and conditions, you can accurately determine the minimum payment on your $300 credit card balance and plan your finances accordingly.
Additionally, it’s important to recognize that while the minimum payment keeps the account in good standing, paying only the minimum can lead to long-term interest costs and extend the time it takes to pay off the balance. Therefore, it’s advisable to aim for paying more than the minimum whenever possible to reduce the overall interest and expedite the debt repayment process.
By understanding the minimum payment calculation and its implications, credit card holders can make informed decisions about their repayment strategy and work towards effectively managing their credit card debt.
Tips for Managing Credit Card Payments
Effectively managing credit card payments is essential for maintaining financial stability and avoiding unnecessary debt. Here are some valuable tips to help individuals navigate the complexities of credit card payments:
- Pay More Than the Minimum: While the minimum payment keeps the account in good standing, it’s advisable to pay more than the minimum whenever possible. By paying more, you can reduce the overall interest costs and accelerate the repayment of the outstanding balance.
- Create a Budget: Establishing a comprehensive budget that includes provisions for credit card payments can help individuals track their expenses and allocate sufficient funds towards paying off their credit card balances. A budget provides a clear overview of available resources and ensures that payments are made on time.
- Avoid Unnecessary Spending: Limiting discretionary spending and avoiding unnecessary purchases can free up additional funds to allocate towards credit card payments. By being mindful of expenses, individuals can prioritize debt repayment and work towards reducing their outstanding balances.
- Set Up Automatic Payments: Setting up automatic payments for at least the minimum amount due can help ensure that payments are made on time, reducing the risk of late fees and negative impacts on credit scores. Automatic payments provide convenience and peace of mind, especially for individuals with busy schedules.
- Monitor Your Statements: Regularly reviewing credit card statements allows individuals to track their spending, identify any unauthorized charges, and stay informed about their outstanding balances. Monitoring statements also facilitates early detection of any discrepancies or errors that may require resolution.
By implementing these tips, individuals can proactively manage their credit card payments, mitigate the risk of accumulating excessive debt, and work towards achieving financial stability. Responsible credit card usage, combined with strategic payment management, empowers individuals to take control of their financial well-being and build a solid foundation for long-term financial success.