Finance
When Are 1099s Due To The IRS?
Published: November 1, 2023
Stay on top of your finance and tax obligations with this guide. Find out when 1099 forms are due to the IRS and avoid penalties.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to tax season, individuals and businesses alike are faced with numerous forms and deadlines. One such form that can often cause confusion is the 1099 form. If you’re unsure about when 1099s are due to the IRS, you’re not alone. Understanding the deadlines for filing these forms is essential to ensure compliance and avoid penalties.
The 1099 form is a tax form used to report income received that is not subject to withholding. It is typically issued by businesses to individuals or other businesses that they have paid throughout the year. The form serves to notify both the recipient and the IRS of the income earned, enabling the government to track and tax the appropriate amounts.
Knowing the due date for filing 1099 forms is crucial as it allows sufficient time to gather the necessary information and complete the required documentation. Failure to file the forms on time can result in penalties and interest charges. Therefore, it is important to familiarize yourself with the filing deadlines for various types of 1099 forms to avoid any unnecessary complications.
In this article, we will explore the due dates for filing 1099 forms, the penalties for late filing, and the possible extensions available for those who need more time to file. By understanding these key aspects, you can better navigate the tax season and fulfill your obligations to the IRS.
Understanding 1099 Forms
Before diving into the specific due dates for filing 1099 forms, let’s first understand the purpose and types of 1099 forms. The 1099 form series consists of various types of forms, each used to report different types of income transactions. Here are some common types of 1099 forms:
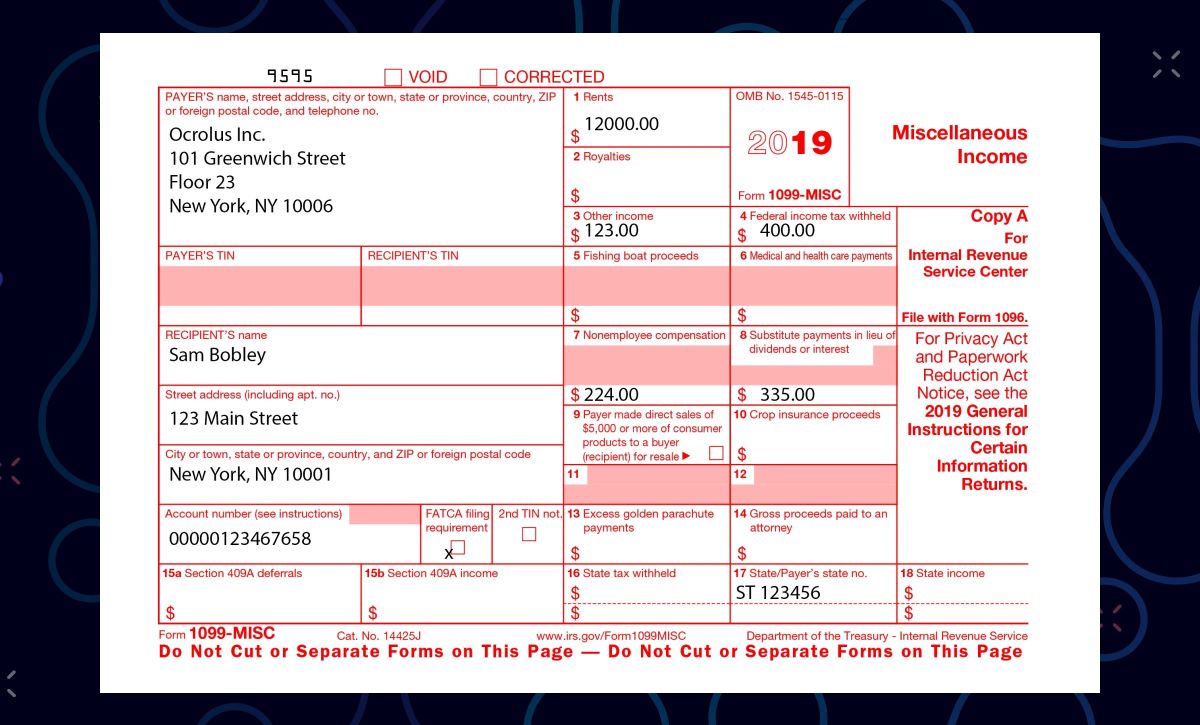
- 1099-MISC: Used to report miscellaneous income, such as freelance earnings, rental income, and payments made to independent contractors.
- 1099-INT: Used to report interest income earned on investments, such as bank accounts or bonds.
- 1099-DIV: Used to report dividend income received from investments in stocks or mutual funds.
- 1099-B: Used to report proceeds from the sale of stocks, bonds, or other financial assets.
- 1099-K: Used to report income received from payment processors like PayPal or credit card companies.
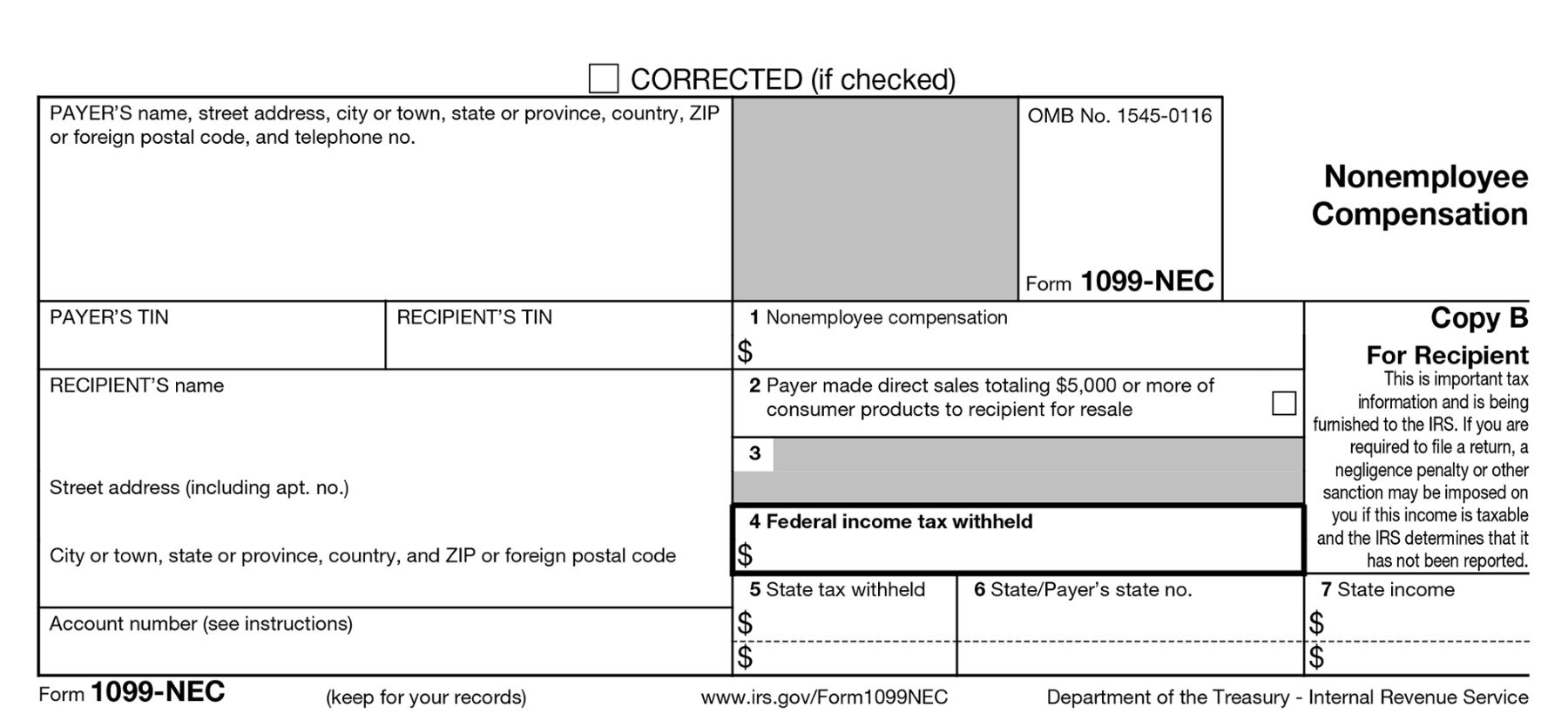
It’s important to note that not all individuals or businesses are required to file 1099 forms. Generally, if you have made payments of $600 or more to an individual or unincorporated business entity during the tax year, you are required to issue a 1099 form to them and report it to the IRS.
Filing 1099 forms serves two main purposes. First, it ensures transparency and accuracy in reporting income to the IRS. It helps the government track income that might otherwise go unreported, reducing the chances of tax evasion. Second, these forms provide recipients with documentation of the income they have earned, which they can use to accurately report their income on their own tax returns.
Now that we have a better understanding of the purpose and types of 1099 forms, let’s explore the specific due dates for filing them.
Due Date for Filing 1099 Forms
The due date for filing 1099 forms with the IRS and providing copies to recipients is typically January 31st of the year following the tax year in which the income was earned. This means that if you made payments that require a 1099 form during the calendar year, they must be filed and distributed by January 31st of the following year.
It’s important to note that if the due date falls on a weekend or a federal holiday, the deadline is extended to the next business day. This allows for any unforeseen circumstances or delays that may occur.
It’s crucial to be diligent in meeting this deadline as failure to do so can result in penalties and interest charges. Late or incorrect filing of 1099 forms can lead to penalties ranging from $50 to $270 per form, depending on the length of the delay and whether it was a willful or inadvertent failure.
Additionally, timely filing of 1099 forms is important for the recipients. They rely on these forms to accurately report their income on their own tax returns, so it’s essential to provide them with the necessary documentation before the deadline.
Now that we know the general due date for filing 1099 forms, let’s explore the specific filing deadlines based on the type of 1099 form.
Filing Deadlines Based on Form Type
The specific filing deadlines for 1099 forms can vary depending on the type of form being filed. While the general due date for most 1099 forms is January 31st, there are a few exceptions. Let’s take a closer look at the filing deadlines based on form type:
- 1099-MISC: This form is used to report miscellaneous income, such as freelance earnings or payments to independent contractors. The deadline for filing Form 1099-MISC is typically January 31st.
- 1099-INT: Form 1099-INT is used to report interest income earned on investments. The deadline for filing this form is also January 31st.
- 1099-DIV: This form is used to report dividend income received from stocks or mutual funds. The deadline for filing Form 1099-DIV is generally January 31st.
- 1099-B: Form 1099-B is used to report proceeds from the sale of stocks, bonds, or other financial assets. The deadline for filing this form is typically February 15th.
- 1099-K: This form is used to report income received from payment processors like PayPal or credit card companies. The deadline for filing Form 1099-K is generally January 31st.
It’s important to check the specific instructions and guidelines provided by the IRS for each form type to ensure compliance with the correct filing deadline. Failing to meet the deadline can result in penalties and interest charges, so it’s crucial to stay organized and submit the necessary forms on time.
Now that we understand the filing deadlines based on the form type, let’s discuss the penalties for late filing.
Penalties for Late Filing
Understanding the potential penalties for late filing of 1099 forms is crucial to ensure compliance and avoid unnecessary expenses. Late or incorrect filing can result in financial penalties, which can vary depending on the length of the delay and whether the failure was intentional or unintentional.
The penalties for late filing of 1099 forms can range from $50 to $270 per form, based on how long the filing is delayed and whether the failure was willful or inadvertent. Here are the penalty amounts based on the delay:
- Small Filer Penalty: If you are a small business with average annual gross receipts of $5 million or less, and you file the correct 1099 form within 30 days of the deadline, the penalty is $50 per form. If you file the correct form more than 30 days after the deadline but before August 1st, the penalty increases to $110 per form. If you file after August 1st or you do not file the required 1099 form at all, the penalty rises to $280 per form.
- Large Filer Penalty: If your business has average annual gross receipts exceeding $5 million, the penalty structure is slightly different. Filing the correct 1099 form within 30 days of the deadline incurs a penalty of $110 per form. If you file after 30 days but before August 1st, the penalty increases to $280 per form. Filing after August 1st or not filing at all results in a penalty of $560 per form.
- Intentional Disregard Penalty: If the IRS determines that your failure to file or correctly file the 1099 forms was due to intentional disregard, the penalties can increase significantly. In such cases, the penalty is at least $570 per form with no maximum limit.
It’s important to note that these penalties can add up quickly if you are responsible for filing multiple forms. Therefore, it’s crucial to stay organized and ensure timely and accurate filing of 1099 forms to avoid unnecessary expenses.
Now that we understand the penalties for late filing, let’s explore the extensions available for those who need more time to file their 1099 forms.
Extensions for Filing 1099 Forms
If you find yourself in a situation where you are unable to file your 1099 forms by the original deadline, you may be eligible for an extension. Extensions provide additional time to gather the necessary information and complete the required documentation, helping to avoid late filing penalties.
To request an extension for filing 1099 forms, you need to submit Form 8809, Application for Extension of Time to File Information Returns, to the IRS before the original deadline. This form grants an automatic 30-day extension, pushing the filing deadline to March 2nd.
It’s important to keep in mind that extensions are only granted for filing the forms, not for providing copies to the recipients. Therefore, it’s essential to communicate with the recipients and provide them with the necessary information by the original deadline, even if you have been granted an extension for filing with the IRS.
While the automatic extension is typically for 30 days, under certain circumstances, an additional 30-day extension may be granted. However, this requires filing a second extension request and providing a valid reason for needing the extra time.
It’s important to note that extensions only apply to filing the 1099 forms. If you owe taxes based on the income reported on the 1099 forms, you must still pay the taxes by the original due date to avoid any penalties or interest charges. The extension only provides additional time for filing the forms themselves.
It is worth mentioning that while extensions provide some flexibility, it’s still crucial to file the 1099 forms as soon as possible to ensure compliance and avoid any potential issues with the IRS. Late filing, even with an extension, can still result in penalties, albeit at a reduced rate compared to not filing at all.
Now that we understand the extensions available for filing 1099 forms, let’s summarize the key points discussed in this article.
Conclusion
Filing 1099 forms accurately and on time is crucial for both businesses and individuals to ensure compliance with IRS regulations. Understanding the due dates, penalties for late filing, and available extensions can help navigate the complexities of tax season and avoid unnecessary expenses.
We learned that the general due date for filing 1099 forms is January 31st of the year following the tax year in which the income was earned. The specific due dates may vary depending on the type of form being filed, with exceptions for certain forms like 1099-B having a February 15th deadline.
Penalties for late filing of 1099 forms can range from $50 to $270 per form, depending on the delay and whether the failure was willful or inadvertent. It’s important to file the forms accurately and on time to avoid these penalties and ensure accurate reporting of income to the IRS.
If you find yourself unable to meet the original filing deadline, you may be eligible for an extension of up to 30 days by filing Form 8809. However, extensions only apply to filing the forms and not providing copies to recipients. It’s crucial to communicate with recipients and provide them with the necessary information by the original deadline.
In conclusion, being aware of the due dates, penalties, and extensions for filing 1099 forms is essential for maintaining compliance and avoiding unnecessary expenses. By staying organized and following the proper procedures, businesses and individuals can navigate the tax season with confidence and fulfill their obligations to the IRS.