Home>Finance>Where Are Shares Outstanding On Financial Statements

Finance
Where Are Shares Outstanding On Financial Statements
Published: December 22, 2023
Learn where shares outstanding appear on financial statements and how it impacts the overall financial health of a company. Discover the key aspects of finance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Shares Outstanding
- Importance of Shares Outstanding
- Calculation and Reporting of Shares Outstanding
- Where Shares Outstanding is Shown on Financial Statements
- Shares Outstanding on Balance Sheet
- Shares Outstanding on Income Statement
- Shares Outstanding on Statement of Cash Flows
- Analysis and Interpretation of Shares Outstanding
- Conclusion
Introduction
When analyzing a company’s financial health and performance, there are several key metrics and indicators to consider. One important factor to examine is the number of shares outstanding. Shares outstanding is a fundamental concept in the world of finance that provides valuable insights into a company’s structure and ownership distribution.
Shares outstanding refers to the total number of shares issued by a company and held by its shareholders, including both common and preferred stock. This metric plays a crucial role in determining a company’s market value and can have a significant impact on its financial statements and overall performance.
Understanding the concept of shares outstanding is essential for investors, financial analysts, and other stakeholders as it helps in evaluating a company’s market capitalization, calculating financial ratios, and making informed investment decisions. By examining changes in shares outstanding over time, analysts can gain insights into a company’s growth, dilution potential, and ownership structure.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the concept of shares outstanding, its importance, calculation, and reporting methods, as well as where this information is typically shown on financial statements. We will also explore how shares outstanding can be analyzed and interpreted to gain meaningful insights into a company’s financial standing and potential future prospects.
Definition of Shares Outstanding
Shares outstanding, also referred to as outstanding shares or issued shares, represents the total number of shares that a company has issued to investors and is currently held by shareholders. It includes both the shares held by institutional investors, individual shareholders, and the company’s insiders, such as executives and employees.
Shares outstanding is an important metric because it determines the ownership distribution of a company and affects its market capitalization. Market capitalization is calculated by multiplying the current stock price by the number of shares outstanding. This metric provides an estimate of the total value of a company as perceived by the market.
It’s important to note that shares outstanding do not include shares that are authorized but not yet issued or shares that have been repurchased by the company through buyback programs. These shares are typically held as treasury stock and are not considered to be outstanding shares.
Shares outstanding can be categorized into two main types: common shares and preferred shares. Common shares represent ownership in a company and provide shareholders with voting rights in corporate decision-making. Preferred shares, on the other hand, offer a fixed dividend payment but usually do not provide voting rights. The total number of common shares and preferred shares outstanding determines a company’s overall shares outstanding.
The concept of shares outstanding is crucial for investors and analysts as it helps in assessing a company’s ownership structure, potential dilution, and overall market value. It provides insight into how the company’s ownership is distributed among shareholders and can have implications for dividend payments and voting rights.
Now that we have established the definition of shares outstanding, let us explore its significance and why it is an essential metric to consider when analyzing a company’s financial statements.
Importance of Shares Outstanding
The number of shares outstanding is a critical component for investors and analysts when evaluating a company’s financial health and performance. Here are some key reasons why shares outstanding is important:
- Market Capitalization: Shares outstanding plays a crucial role in determining a company’s market capitalization. Market cap is calculated by multiplying the current market price per share by the total number of shares outstanding. This metric provides an estimate of the company’s total value as perceived by the market, and is a key factor in comparing companies within the same industry.
- Ownership Structure: Shares outstanding provides insights into a company’s ownership structure. It shows the distribution of ownership among different shareholders, including institutional investors, insiders, and individual investors. Analyzing the ownership distribution can help investors understand the level of control and influence certain stakeholders may have on the company’s decision-making processes.
- Market Value per Share: By dividing a company’s market capitalization by the number of shares outstanding, analysts can determine the market value per share. This measure can be used to assess the relative value of a company’s stock and compare it to industry peers. It is an important factor for investors looking to make informed decisions regarding buying or selling shares.
- Earnings per Share (EPS): Shares outstanding is a key factor in calculating earnings per share (EPS), which is a profitability measure widely used by investors. EPS is calculated by dividing a company’s net income by the weighted average number of shares outstanding during a specific period. It provides insights into the company’s profitability on a per-share basis, allowing for meaningful comparisons across different companies.
- Dividend Payments: The number of shares outstanding is also important for analyzing dividend payments. Companies often distribute dividends to shareholders based on the number of shares they hold. By considering shares outstanding, investors can assess the company’s ability to sustain dividend payments and the potential yield on their investment.
Overall, shares outstanding is a crucial metric that serves as a foundational element for understanding a company’s financial structure, market value, and potential for growth. By analyzing this metric in conjunction with other financial indicators, investors and analysts can make informed decisions about investment opportunities and better evaluate a company’s performance in the market.
Calculation and Reporting of Shares Outstanding
To calculate shares outstanding, we need to consider the initial issuance of shares, any subsequent issuances, and any repurchases or retirements of shares. Let’s explore how shares outstanding are calculated and reported:
1. Initial Issuance: When a company initially goes public or issues shares, the number of shares issued becomes the starting point for calculating shares outstanding. This information is disclosed in the company’s initial public offering (IPO) prospectus or the registration statement filed with the regulatory authorities.
2. Subsequent Issuances: Companies may issue additional shares over time to raise capital for various purposes, such as expansion or acquisitions. These subsequent issuances increase the total number of shares outstanding. The details of these issuances are typically disclosed in the company’s financial statements, notes to the financial statements, or in separate filings with the regulatory authorities.
3. Retirements or Repurchases: In some cases, companies may decide to repurchase their own shares from the open market or from existing shareholders. These repurchased shares are considered treasury stock and are no longer considered as outstanding shares. This reduces the total number of shares outstanding. Companies usually disclose buyback programs or share repurchases in their financial statements or in separate filings.
4. Stock Splits and Reverse Splits: A stock split involves dividing existing shares into multiple shares, while a reverse split consolidates shares into a smaller number. These actions do not change the ownership structure or the total value of shares outstanding. However, they do impact the number of shares outstanding and the price per share. Companies notify shareholders about these actions through press releases and filings with regulatory authorities.
Reporting: Companies are required to disclose the number of shares outstanding in their financial statements. This information is typically found in the notes to the financial statements or in a separate section specifically addressing share capital and ownership structure. Additionally, companies are required to report any significant changes in shares outstanding in their periodic filings with regulatory authorities, such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States.
It is important for investors and analysts to carefully review the company’s financial statements and regulatory filings to access accurate and up-to-date information regarding shares outstanding. By understanding how shares outstanding are calculated and reported, stakeholders can make more informed investment decisions and evaluate a company’s ownership structure.
Where Shares Outstanding is Shown on Financial Statements
Shares outstanding information is typically disclosed in a company’s financial statements, allowing investors and analysts to easily access and evaluate this important metric. Let’s explore where shares outstanding is shown on the main financial statements:
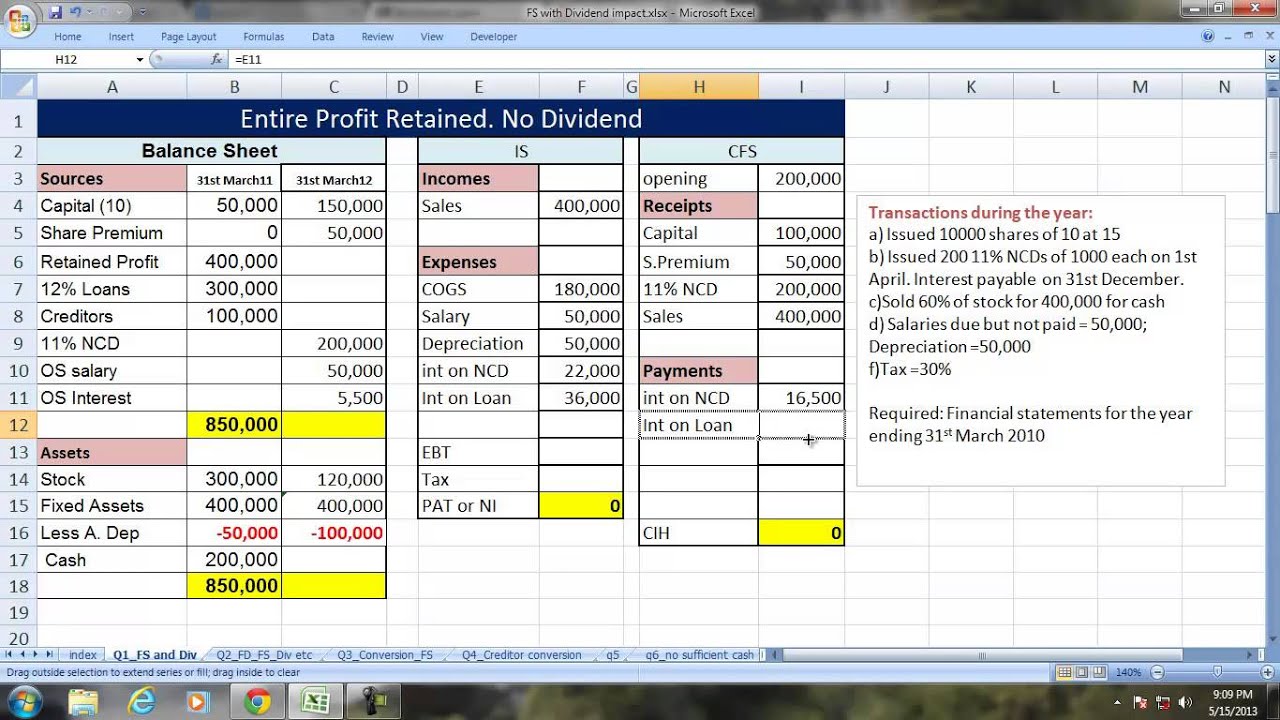
1. Balance Sheet: The total number of shares outstanding is commonly reported on the balance sheet under the shareholders’ equity section. It is typically listed as “Common Stock” or “Capital Stock” and may be further categorized into different classes or series of stock if applicable. This section provides an overview of the company’s ownership structure and the number of shares available in the market.
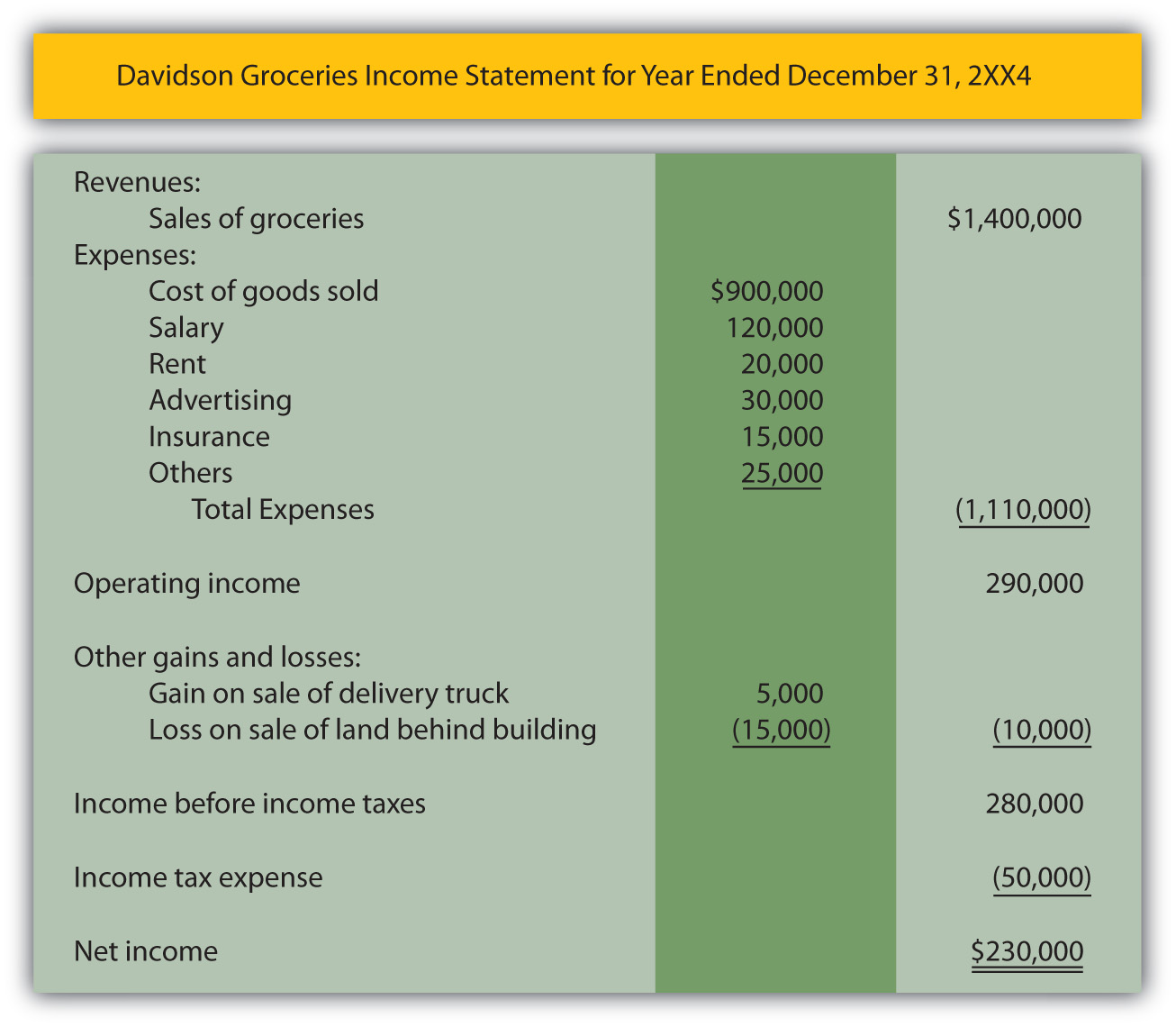
2. Income Statement: The income statement does not directly include shares outstanding information. However, the number of shares outstanding is a crucial factor in calculating earnings per share (EPS), which is reported on the income statement. EPS is calculated by dividing the company’s net income by the weighted average number of shares outstanding during a specific period.
3. Statement of Cash Flows: Similar to the income statement, the statement of cash flows does not directly display shares outstanding. However, it may indirectly provide information related to shares outstanding through financing activities. For example, if a company issues additional shares or repurchases existing shares, these transactions are reflected in the statement of cash flows under the financing activities section.
In addition to the financial statements, shares outstanding information may also be found in the footnotes to the financial statements. These footnotes provide detailed explanations, disclosures, and additional information about the company’s shares and ownership structure. Footnotes may include information about any stock splits, reverse splits, or stock repurchase programs that have occurred.
Investors and analysts should carefully review the company’s financial statements and accompanying footnotes to gather accurate and complete shares outstanding information. Additionally, periodic filings with regulatory authorities, such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States, may provide further details about shares outstanding and any changes that have occurred.
Overall, shares outstanding information is readily available in a company’s financial statements and footnotes. This allows stakeholders to assess the company’s ownership structure, calculate important financial ratios, and make informed investment decisions based on a thorough understanding of the number of shares available in the market.
Shares Outstanding on Balance Sheet
On the balance sheet, shares outstanding information is presented under the shareholders’ equity section. This section provides key details about the ownership structure of the company and the number of shares available in the market.
Typically, shares outstanding are listed as either “Common Stock” or “Capital Stock” and are reported with the corresponding number of shares. If a company has different classes or series of stock, such as preferred stock, it may provide a breakdown of shares outstanding for each class.
The information presented on the balance sheet regarding shares outstanding allows investors and analysts to assess the company’s ownership structure and understand the percentage of ownership held by shareholders. It provides insights into the distribution of ownership and the potential influence certain shareholders may have on the company’s decision-making processes.
Additionally, the balance sheet provides historical data on shares outstanding. Companies may present information about shares issued or repurchased during a specific period, allowing stakeholders to analyze the changes in shares outstanding over time. This can be valuable for understanding trends in share issuance or repurchases and their impact on the ownership structure of the company.
Changes in shares outstanding can have significant implications for a company’s financial position. For example, if a company issues additional shares, it may indicate a need for capital infusion or expansion. On the other hand, if a company repurchases shares, it may signal a belief that the stock is undervalued or a desire to consolidate ownership.
In addition to shares outstanding, the balance sheet also provides information about other components of shareholders’ equity, such as retained earnings and additional paid-in capital. These components, along with shares outstanding, contribute to the overall equity position of the company.
Overall, the shares outstanding information presented on the balance sheet is a critical component for investors and analysts. It allows them to evaluate the ownership structure, assess the impact of share issuance or repurchases, and gain insights into the company’s financial health and prospects.
Shares Outstanding on Income Statement
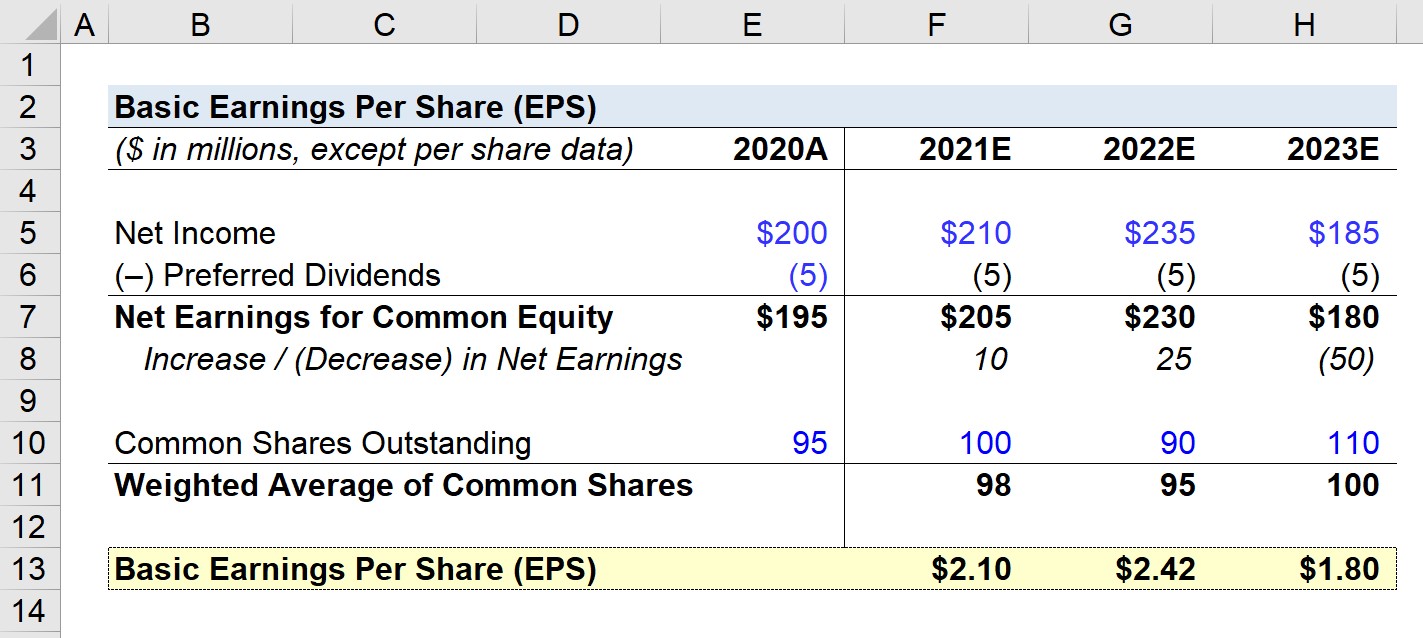
While the income statement does not directly display shares outstanding information, it plays a crucial role in calculating earnings per share (EPS), which is derived from the total number of shares outstanding during a specific period.
Earnings per share (EPS) is a commonly used profitability measure that provides insights into the company’s earnings on a per-share basis. EPS is calculated by dividing the company’s net income by the weighted average number of shares outstanding during the reporting period.
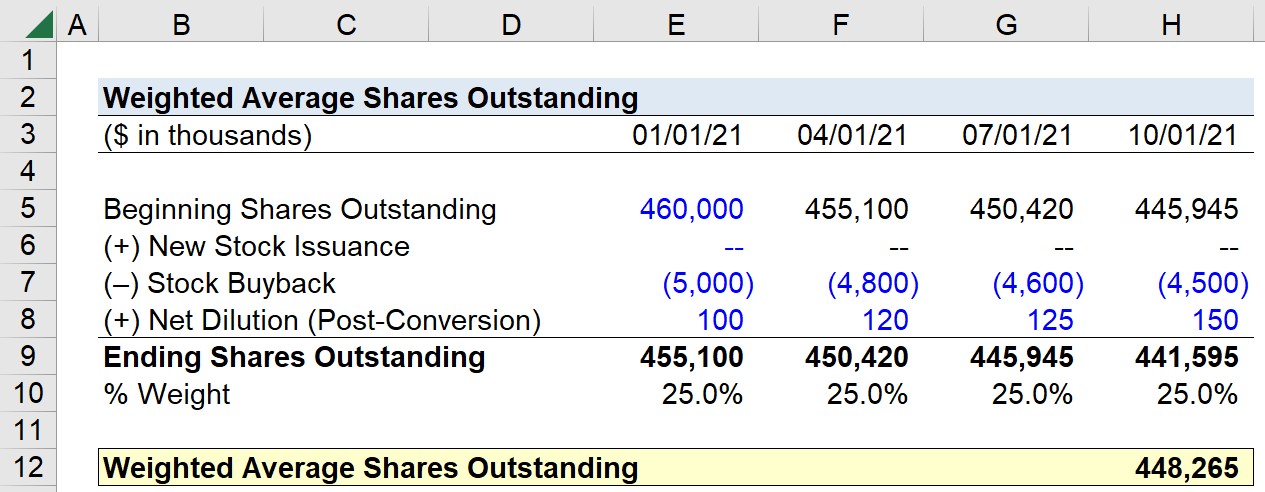
The weighted average number of shares outstanding takes into account any changes in shares outstanding that may have occurred during the period. This could include shares issued or repurchased, stock splits, or reverse splits. The purpose of using the weighted average is to provide a more accurate representation of the number of shares outstanding during the period, accounting for any changes that may have occurred.
EPS is an important metric for investors and analysts as it allows for meaningful comparisons across different companies and industries. It provides insights into the company’s profitability on a per-share basis and can help investors assess the value of the company’s stock.
Companies typically report EPS on the income statement, either as a standalone figure or as part of the earnings per share calculation. It may be presented on a per-share basis, such as “EPS (basic)” or “EPS (diluted),” indicating whether any potential dilutive securities, such as stock options or convertible bonds, were taken into consideration.
Understanding the shares outstanding information on the income statement is crucial for investors and analysts to assess a company’s profitability and to compare its performance with that of its competitors. It provides a standardized measure that takes into account the company’s net income and the number of shares outstanding, allowing for a more accurate assessment of the company’s earnings potential.
While the income statement itself does not directly provide shares outstanding information, it serves as a basis for calculating and reporting earnings per share. Investors and analysts should carefully review the income statement and related footnotes to understand the methodology used to calculate EPS and any potential dilution factors that may have been considered.
In summary, while the income statement may not display shares outstanding information directly, it is an integral part of the calculation and reporting of earnings per share, which provides valuable insights into a company’s profitability on a per-share basis.
Shares Outstanding on Statement of Cash Flows
The statement of cash flows does not directly display shares outstanding information. However, it may indirectly provide insights into shares outstanding through the financing activities section.
In the financing activities section of the statement of cash flows, companies disclose cash inflows and outflows related to their financing activities, including capital raising or share repurchases. If a company issues additional shares, the cash received from the issuance will be recorded as a cash inflow. On the other hand, if a company repurchases its own shares, the cash used for the repurchase will be recorded as a cash outflow.
By examining the financing activities section, stakeholders can infer whether there have been any significant changes in shares outstanding during the reporting period. If there are cash inflows related to the issuance of shares, it may indicate that the company sought to raise capital by issuing new shares. Conversely, cash outflows related to share repurchases may suggest that the company is buying back its shares, potentially reducing the number of shares outstanding.
It’s important to note that while the statement of cash flows may provide insights into changes in shares outstanding, the information is not directly reported. It is still necessary to refer to other financial statements, such as the balance sheet, to obtain the specific number of shares outstanding. The statement of cash flows complements this information by providing a supplementary perspective on the financing activities impacting shares outstanding.
Additionally, companies may disclose any significant share transactions in the footnotes to the financial statements. These footnotes provide further explanation and detail regarding shares issued or repurchased during the reporting period and any changes in shares outstanding.
Investors and analysts should carefully review the statement of cash flows in conjunction with the balance sheet and related footnotes to gain a comprehensive understanding of the impact of financing activities on shares outstanding. By doing so, stakeholders can better assess the company’s capital structure, capital raising activities, and potential impact on ownership dilution.
While the statement of cash flows does not directly provide shares outstanding information, it offers important insights into the financing activities surrounding the company’s shares, providing a supplementary perspective on changes in the company’s capital structure.
Analysis and Interpretation of Shares Outstanding
The analysis and interpretation of shares outstanding provides valuable insights into a company’s ownership structure, market value, and potential dilution. Here are some key factors to consider when analyzing and interpreting shares outstanding:
1. Ownership Structure: Shares outstanding information allows investors to evaluate the distribution of ownership among shareholders. By analyzing the percentage of shares held by institutional investors, insiders, and individual shareholders, stakeholders can assess the level of control and influence certain stakeholders may have on the company’s decision-making processes.
2. Market Capitalization: Shares outstanding is a key component in calculating a company’s market capitalization. Market cap provides an estimate of the company’s total value as perceived by the market. By multiplying the current stock price by the number of shares outstanding, investors can assess the company’s market value and compare it to industry peers.
3. Dilution Potential: Changes in shares outstanding can potentially impact existing shareholders’ ownership percentage and voting rights. If a company issues additional shares, it can dilute the ownership percentage of existing shareholders. Investors should analyze the potential dilution effects when evaluating investment opportunities and the impact on their future return on investment.
4. Earnings per Share (EPS): Shares outstanding plays a crucial role in calculating earnings per share (EPS), which provides insights into a company’s profitability on a per-share basis. By dividing the company’s net income by the weighted average number of shares outstanding, investors and analysts can assess the company’s profitability and compare it to industry peers.
5. Changes Over Time: Analyzing changes in shares outstanding over time can provide valuable information about a company’s growth and capital raising activities. Significant increases in shares outstanding may indicate the issuance of new shares to finance expansion or acquisitions. Conversely, significant decreases in shares outstanding may indicate share repurchases or potential stock consolidation.
6. Industry and Peer Comparison: Comparing a company’s shares outstanding to industry averages and peer companies can provide insight into its relative market position and ownership structure. Observing how a company’s shares outstanding measure up to its peers can highlight potential strengths or weaknesses in the company’s ownership distribution and market value.
Overall, the analysis and interpretation of shares outstanding provide valuable information for investors and analysts. By evaluating the ownership structure, market capitalization, dilution potential, EPS, changes over time, and industry comparisons, stakeholders can gain a comprehensive understanding of a company’s financial standing, growth potential, and market perception. It is crucial to consider shares outstanding in conjunction with other financial metrics and qualitative factors to make informed investment decisions.
Conclusion
Shares outstanding is a fundamental concept in finance that provides crucial insights into a company’s ownership structure, market value, and potential dilution. Understanding and analyzing shares outstanding is essential for investors and analysts when evaluating a company’s financial health and making informed investment decisions.
Throughout this article, we have explored the definition of shares outstanding, its importance in assessing market capitalization and ownership structure, and its impact on financial statements such as the balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows. We have also discussed the calculation and reporting of shares outstanding and how it can be analyzed and interpreted to gain meaningful insights into a company’s performance.
By examining shares outstanding, investors can assess the distribution of ownership among different stakeholders and evaluate the potential influence certain shareholders may have on a company’s decision-making processes. It allows for the calculation of key metrics such as market capitalization, earnings per share (EPS), and provides indicators of potential dilution effects.
Furthermore, changes in shares outstanding over time can provide valuable information about a company’s growth, capital raising activities, and potential expansion plans. By comparing shares outstanding to industry averages and peer companies, stakeholders can gauge a company’s competitive position and market perception.
To accurately analyze shares outstanding, it is essential to review a company’s financial statements, including the balance sheet, income statement, statement of cash flows, and related footnotes. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of the company’s capital structure and any changes in shares outstanding.
In conclusion, shares outstanding is a vital metric that plays a key role in assessing a company’s financial standing, ownership structure, and market value. By understanding and analyzing shares outstanding, investors and analysts can make informed investment decisions and gain valuable insights into a company’s performance and potential for growth.