Home>Finance>Where Do I Report 1099-Misc Income On My Tax Return?


Finance
Where Do I Report 1099-Misc Income On My Tax Return?
Published: October 28, 2023
Learn where to report 1099-Misc income on your tax return and maximize your finance. Ensure you don't miss any deductions or penalties.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of tax reporting! If you’ve received a 1099-MISC form, it means you’ve earned income that wasn’t subject to traditional employer withholding. As a result, it’s your responsibility to report this income accurately when filing your tax return. But where exactly does this income go?
In this article, we’ll dive into the details of reporting 1099-MISC income on your tax return. Whether you’re a freelancer, independent contractor, or receive miscellaneous income for services rendered, we’ll guide you through the process step by step.
Understanding the ins and outs of tax reporting can be intimidating, but rest assured, we’re here to simplify it for you. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of where to report your 1099-MISC income, so you can file your tax return accurately and with confidence.
Keep in mind that this guide is intended for informational purposes only and should not substitute professional tax advice. Every individual’s financial situation and tax obligations are unique, so it’s always a good idea to consult with a tax professional or CPA for personalized guidance.
Understanding 1099-MISC Income
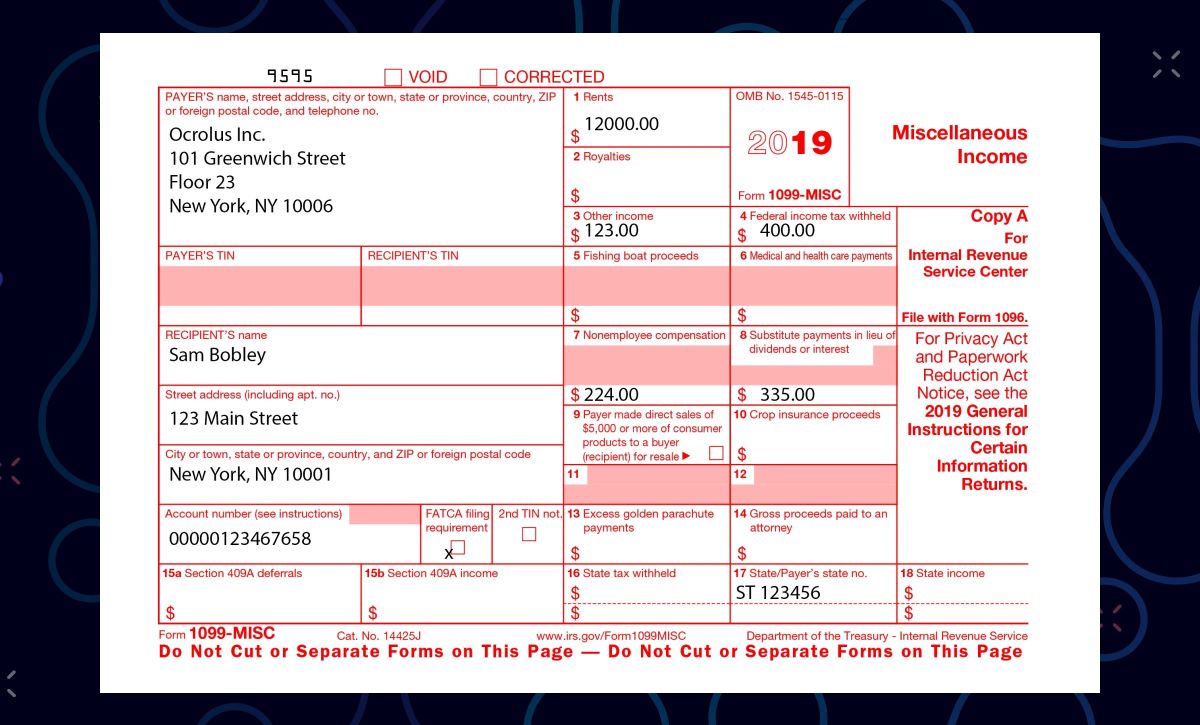
Before we jump into the reporting process, let’s first ensure we have a clear understanding of what 1099-MISC income entails. The 1099-MISC form is used to report income received as a non-employee or for miscellaneous services rendered. This can include various types of income, such as:
- Payments for freelance work
- Compensation for independent contractor services
- Prize winnings or awards
- Rental income
- Royalty payments
- Income from partnerships or joint ventures
It’s important to note that the person or entity paying you, referred to as the payer, is responsible for issuing the 1099-MISC form if they paid you $600 or more in a tax year. If you received less than $600, they are not required to issue a 1099-MISC form, but it is still your responsibility to report the income.
When you receive a 1099-MISC form, it will show the total amount of income you received from that payer. You must report this amount on your tax return, regardless of whether you received a physical copy of the form or not. The IRS receives a copy of the 1099-MISC form as well, so it’s crucial to ensure accurate reporting to avoid any discrepancies.
Additionally, it’s worth mentioning that there are specific situations where you may receive other types of 1099 forms, such as a 1099-INT for interest income or a 1099-DIV for dividend income. These forms are used to report income from specific sources, so be mindful of the specific type of income you received and the appropriate form to use when reporting.
Now that we have a solid understanding of what 1099-MISC income encompasses, let’s move on to the next step: reporting this income on your tax return.
Reporting 1099-MISC Income on Form 1040
When it comes to reporting your 1099-MISC income on your tax return, the key form to focus on is Form 1040, also known as the U.S. Individual Income Tax Return. There are different sections of Form 1040 that you may need to utilize, depending on your particular tax situation.
If you received a 1099-MISC for income that is unrelated to self-employment or if you don’t have any self-employment expenses to deduct, you’ll report this income on Line 1 of your Form 1040. This is the line for “Wages, salaries, tips, etc.” Simply enter the total amount of income from your 1099-MISC form on this line.
However, if the income you received on your 1099-MISC is related to self-employment, things get a bit more complex. In this case, you’ll need to fill out additional forms to accurately report your income and related expenses.
If you’re not sure whether your 1099-MISC income qualifies as self-employment income, here are a few factors to consider:
- Did you perform services as an independent contractor?
- Were you engaged in a trade or business for profit?
- Did you have control over how the work was performed?
- Were you responsible for providing your own tools and equipment?
If you answered yes to one or more of these questions, chances are your 1099-MISC income is considered self-employment income, and you’ll need to proceed with the next steps.
To report self-employment income from your 1099-MISC, you’ll utilize Schedule C, also known as the Profit or Loss from Business form. On Schedule C, you’ll provide detailed information about your business or self-employment activity, including your income, expenses, and deductions relevant to that particular source of income.
On Line 1 of Schedule C, you’ll report the total amount of income you received from your 1099-MISC. Additionally, you’ll have the opportunity to deduct any eligible business expenses related to earning that income. It’s important to keep organized records of your expenses throughout the year to ensure accurate reporting.
Once you’ve filled out Schedule C, you’ll transfer the resulting net profit or loss amount to Line 3 of Form 1040. This represents your total business income or loss for the tax year. From there, you’ll proceed with the rest of your Form 1040, taking into consideration any other sources of income, deductions, and credits applicable to your situation.
Armed with this understanding of how to report your 1099-MISC income on Form 1040, you’ll be well on your way to accurately filing your taxes. However, the process doesn’t end here. In the next section, we’ll delve into the intricacies of reporting self-employment tax.
Schedule C: Reporting 1099-MISC Income for Self-Employed Individuals
For self-employed individuals who received 1099-MISC income, Schedule C is the crucial form for accurately reporting your income and expenses. This form allows you to calculate your net profit or loss from your self-employment activities.
When filling out Schedule C, you’ll need to provide detailed information about your business or self-employment activity. This includes the nature of your business, the type of services you provided, and any expenses directly related to generating the income reported on your 1099-MISC.
Here are the key steps to follow when reporting your 1099-MISC income on Schedule C:
- Enter your personal information, such as your name and Social Security number, at the top of Schedule C.
- Describe your business or self-employment activity using the appropriate code from the IRS’s list of business codes. This helps the IRS categorize your business correctly.
- On Line 1, enter the total income you received from your 1099-MISC form. This should match the amount reported on your 1099-MISC form.
- If you received income from multiple sources, you can break it down into separate lines to provide a clear breakdown of your income sources.
- Proceed to deduct your business expenses on the relevant lines. This includes expenses such as supplies, equipment, advertising, insurance, and professional fees.
- Remember to keep accurate records and receipts of your expenses throughout the year to support your deductions.
- Complete the rest of Schedule C, providing additional information about your business, if required.
Once you have finished completing Schedule C, you will calculate your net profit or loss for your self-employment activity by subtracting your total expenses from your total income. This net profit or loss amount will then be transferred to Line 3 of Form 1040.
It’s essential to report your self-employment income accurately and claim all eligible deductions to minimize your taxable income and potentially reduce your overall tax liability. However, be sure to consult with a tax professional or CPA to ensure compliance with all applicable tax laws and regulations.
Now that you have a solid understanding of reporting 1099-MISC income on Schedule C, let’s move on to the next step: calculating your self-employment tax.
Schedule SE: Calculating Self-Employment Tax
As a self-employed individual reporting 1099-MISC income, one important aspect to consider is the calculation of your self-employment tax. While employees have Social Security and Medicare taxes withheld from their paychecks, self-employed individuals are responsible for paying these taxes on their own.
The process of calculating self-employment tax is done using Schedule SE, also known as the Self-Employment Tax form. Schedule SE is used to determine and report your self-employment tax liability, which consists of the Social Security and Medicare taxes for self-employed individuals.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to calculating your self-employment tax using Schedule SE:
- Start by transferring the net profit or loss amount from Schedule C, Line 31, to Line 2 of Schedule SE.
- On Line 3 of Schedule SE, calculate your self-employment tax using the current tax rate. In 2021, the self-employment tax rate is 15.3% (12.4% for Social Security and 2.9% for Medicare).
- However, you only pay the Social Security portion on the first $142,800 of net earnings. Any additional income above this threshold is only subject to the Medicare portion of the self-employment tax.
- If your 1099-MISC income is subject to the Additional Medicare Tax, which applies to high-income earners, you may need to complete additional calculations. Consult the IRS instructions or a tax professional for guidance in these cases.
- Once you have calculated your self-employment tax on Line 3, you’ll transfer the total tax liability to Line 57 of Form 1040.
It’s important to note that self-employed individuals can claim a deduction for the employer-equivalent portion of the self-employment tax on Line 13 of Schedule 1. This deduction helps offset the impact of paying both the employer and employee portions of these taxes.
Calculating and paying self-employment tax is a critical part of reporting your 1099-MISC income. It’s essential to keep accurate records, report your income correctly, and fulfill your tax obligations to avoid any penalties or interest.
Finally, it’s important to remember that tax laws and regulations can change, so it’s always wise to consult with a tax professional or CPA to ensure you’re meeting all requirements and making accurate calculations.
Now that you understand how to calculate your self-employment tax, let’s move on to discussing other reporting requirements for 1099-MISC income.
Other Reporting Requirements for 1099-MISC Income
When reporting your 1099-MISC income on your tax return, it’s important to be aware of other reporting requirements that may apply. Here are a few additional considerations to keep in mind:
- State and Local Taxes: In addition to federal taxes, you may be required to report and pay state and local taxes on your 1099-MISC income. Each state has its own tax regulations, so be sure to familiarize yourself with the requirements specific to your state.
- Estimated Tax Payments: As a self-employed individual, it’s likely you’ll need to make quarterly estimated tax payments to cover your tax liability. These payments help you avoid large tax bills at the end of the year and potential penalties for underpayment. Consult with a tax professional to determine your estimated tax payment obligations.
- Deductible Business Expenses: As a self-employed individual, you may be eligible to deduct various business expenses related to earning your 1099-MISC income. Keeping accurate records of your expenses throughout the year will enable you to claim these deductions and potentially reduce your taxable income.
- Form 1099-MISC Copies: It’s crucial to retain copies of your 1099-MISC forms for your records, even after you’ve filed your tax return. The IRS may request supporting documentation to verify your reported income if you’re selected for an audit.
- State Filing Requirements: Depending on your state, you may have additional filing requirements, such as state-specific tax forms or schedules to report your self-employment income. Be sure to research and understand the regulations applicable to your state.
Complying with these additional reporting requirements ensures that you fulfill your tax obligations accurately and in accordance with the applicable laws and regulations. By staying informed and seeking professional guidance when needed, you can navigate the tax reporting process effectively and minimize your risk of errors or penalties.
Remember, tax laws and regulations can change, so it’s essential to stay updated and consult with a tax professional or CPA to ensure you’re meeting all requirements and taking advantage of any available deductions or credits.
Now that we’ve covered the various reporting requirements for 1099-MISC income, let’s conclude our discussion.
Conclusion
Navigating the reporting requirements for 1099-MISC income may seem overwhelming, but with a clear understanding of the process, you can tackle it confidently. By accurately reporting your 1099-MISC income on your tax return, you fulfill your tax obligations and avoid potential penalties or issues with the IRS.
Remember to carefully review your 1099-MISC forms, ensuring the reported income matches what you received. In cases where you didn’t receive a 1099-MISC but still earned miscellaneous income, it’s important to report that income as well.
If your 1099-MISC income is related to self-employment, be sure to utilize Schedule C to report your income and deduct eligible business expenses. Keeping organized records of your expenses throughout the year will help you accurately report and maximize your deductions.
Additionally, calculating and paying your self-employment tax using Schedule SE is a crucial step for self-employed individuals. Reviewing the instructions and consulting with a tax professional can ensure an accurate calculation and fulfillment of your tax obligations.
Lastly, stay informed about any additional reporting requirements specific to your state or locality. Understanding and complying with state and local tax laws will help you meet all your obligations and avoid surprises.
While this guide provides a comprehensive overview of reporting 1099-MISC income, it’s always a good idea to consult with a tax professional or CPA for personalized advice. They can guide you based on your specific financial situation and help you make the most of available tax deductions and credits.
By approaching the reporting process with knowledge and accuracy, you can confidently fulfill your tax obligations while optimizing your financial situation. Remember, the goal is to report your income correctly, claim all eligible deductions, and ensure compliance with tax laws and regulations.
With this guide as your reference, you’re well-equipped to navigate the complexities of reporting 1099-MISC income. Good luck with your tax filing, and may you have a stress-free and successful tax season!