Home>Finance>Why Do Insurance Companies Use Letters Of Credit


Finance
Why Do Insurance Companies Use Letters Of Credit
Modified: January 15, 2024
Discover why insurance companies utilize letters of credit in their financial operations and the role they play in the world of finance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Letters of Credit
- Overview of Insurance Companies
- Reasons for Insurance Companies to Use Letters of Credit
- Risk Mitigation through Letters of Credit
- Benefits of Letters of Credit for Insurance Companies
- Challenges and Limitations of Letters of Credit
- Examples of Insurance Companies Using Letters of Credit
- Conclusion
Introduction
In the world of finance, insurance companies play a crucial role in protecting individuals, businesses, and assets against various risks. These companies assess and evaluate risks, provide coverage, and offer financial compensation in the event of an insured loss. However, to ensure they can meet their financial obligations, insurance companies often utilize different risk management tools and strategies, one of which is the use of Letters of Credit (LCs).
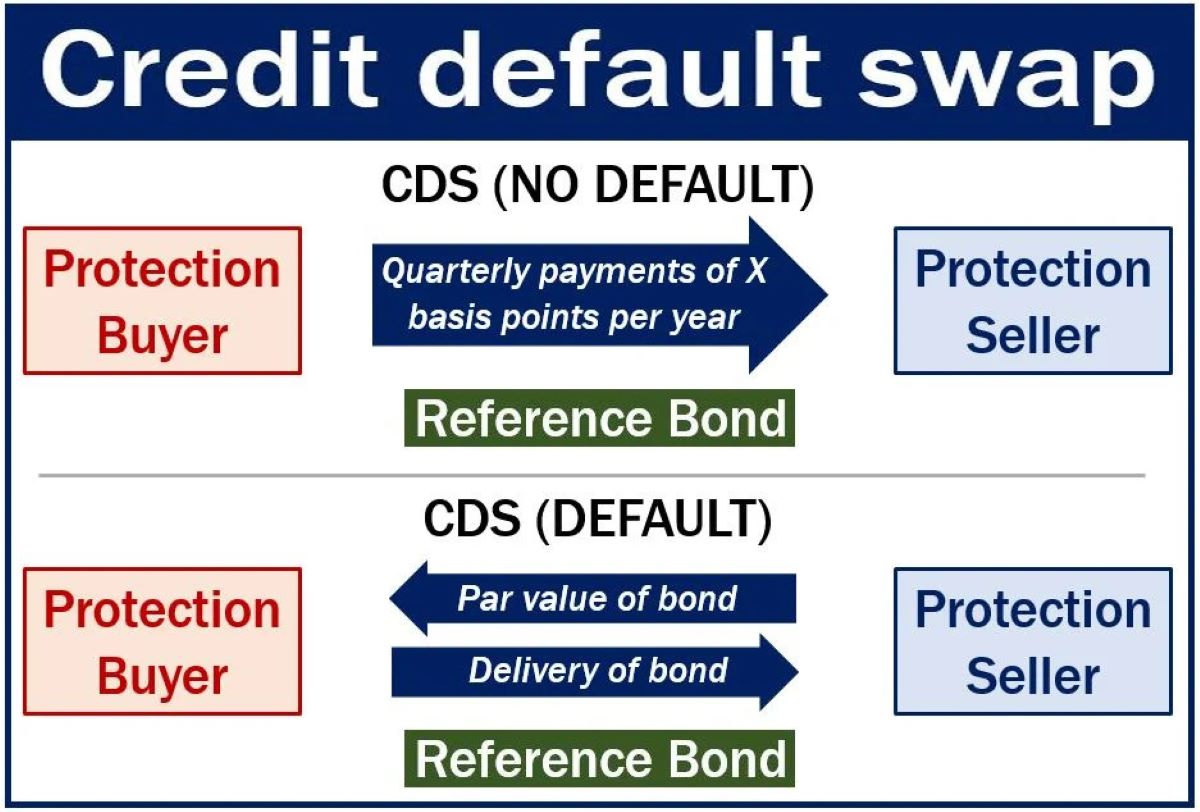
A Letter of Credit is a financial instrument commonly used in international trade transactions. It is a written commitment from a bank on behalf of a buyer that guarantees payment to a seller, provided that the seller fulfills certain pre-established conditions. In the case of insurance companies, these LCs serve as a form of collateral, ensuring that they have the necessary funds to honor their financial obligations to policyholders.
Insurance companies face various risks, including underwriting risk (the risk that claims would exceed premiums collected), investment risk, and credit risk. By using Letters of Credit, insurance companies can mitigate these risks and provide policyholders with a greater sense of security.
In this article, we will delve into the reasons why insurance companies use Letters of Credit, explore the benefits of this risk management tool, and discuss some examples of insurance companies utilizing Letters of Credit to enhance their financial stability.
Definition of Letters of Credit
A Letter of Credit (LC) is a financial instrument that serves as a guarantee of payment between two parties involved in a transaction, typically a buyer and a seller. It provides assurance to the seller that payment will be received, and to the buyer that the goods or services purchased will be delivered as agreed. Letters of Credit are commonly used in international trade, where the parties may be located in different countries and may not have an established relationship or trust.
The process of using a Letter of Credit involves a series of steps. First, the buyer and seller agree to use an LC as the method of payment. The buyer then applies to their bank for the issuance of the LC, providing the necessary details of the transaction, such as the amount and terms of payment, shipping documents, and any other specific conditions. The bank, acting as the issuing bank, undertakes to make the payment to the seller upon the receipt of the required documents.
Once the LC is issued, the seller has the assurance that if they fulfill their obligations as outlined in the LC, such as shipping the goods or providing the agreed-upon services, they will receive payment from the issuing bank. The seller can present the required documents to the designated bank, known as the confirming bank, which then verifies the documents and releases the payment to the seller.
Letters of Credit provide several advantages to both buyers and sellers in international trade transactions. For buyers, they offer protection by ensuring that payment will only be made if the seller fulfills their responsibilities as agreed. On the other hand, sellers benefit from the financial security provided by the issuing bank, reducing the risk of non-payment or default by the buyer.
It is important to note that Letters of Credit are governed by internationally recognized rules and standards, such as the Uniform Customs and Practice for Documentary Credits (UCP 600), which provide a framework for the issuance and management of LCs. These rules aim to create a standardized and transparent system for parties involved in international trade, promoting trust and reducing disputes.
Overview of Insurance Companies
Insurance companies are financial institutions that provide coverage and assume the risk of potential losses for individuals, businesses, and other entities in exchange for premium payments. They operate by pooling risks from policyholders and utilize actuarial analysis to determine the price of insurance policies based on the probability of risks occurring and the potential costs of claims.
Insurance companies offer a wide range of insurance products, including life insurance, health insurance, property insurance, auto insurance, and liability insurance. These products provide individuals and businesses with financial protection and peace of mind in the face of unexpected events such as accidents, natural disasters, illnesses, or death.
Insurance companies generate revenue primarily from premiums paid by policyholders. These premiums are carefully calculated based on various factors such as the insured’s age, health condition, occupation, location, and the level of coverage desired. The premiums collected are invested by insurance companies to generate returns and build reserves to meet their future financial obligations.
The operations of insurance companies involve assessing and underwriting risks, managing investments, and administering claims. Risk assessment involves evaluating the probability and potential severity of losses based on historical data, statistical models, and actuarial analysis. Underwriting involves determining the terms and conditions of insurance policies, including coverage limits, deductibles, and premiums.
Insurance companies also play a crucial role in managing investments to grow their assets and generate sufficient returns to cover their liabilities. They invest in various asset classes such as bonds, stocks, real estate, and other financial instruments to diversify their portfolio and balance risk and return.
Additionally, insurance companies have claims departments responsible for evaluating and processing claims made by policyholders. This involves investigating the circumstances of the claim, assessing the extent of the loss, and determining the appropriate amount of compensation to be paid to the insured.
Overall, insurance companies serve as vital intermediaries in the financial landscape, providing individuals and businesses with financial protection against unforeseen events and making significant contributions to economic stability and resilience.
Reasons for Insurance Companies to Use Letters of Credit
Insurance companies use Letters of Credit (LCs) for several reasons, primarily to mitigate risk and ensure they have the necessary funds to meet their financial obligations. Here are some key reasons why insurance companies utilize LCs:
- Risk Mitigation: Insurance companies face various risks, including underwriting risk and credit risk. By requiring their clients or policyholders to provide an LC, insurance companies can minimize the risk of non-payment or default. The bank issuing the LC guarantees payment to the insurance company, reducing the possibility of financial loss.
- Financial Stability: Insurance companies rely on a steady stream of premium payments from policyholders to meet their financial obligations, such as settling claims and maintaining reserves. By using LCs, insurance companies enhance their financial stability by ensuring the availability of funds, especially when dealing with large claims or high-risk policies.
- International Transactions: Insurance companies operating globally often deal with international clients and partners. In such cases, using LCs provides an added layer of security in cross-border transactions, where the parties may have limited knowledge or trust in each other’s financial capacities. The LC guarantees payment, creating a level of confidence and ensuring a smooth flow of international insurance operations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Insurance companies are subject to stringent regulatory requirements to protect policyholders and maintain solvency. Some regulators may require specific financial guarantees or capital reserves to be in place. Using LCs demonstrates compliance with these requirements, providing regulators and stakeholders with assurance that the company is financially secure.
- Business Relationships: Building trust and maintaining positive relationships with reinsurers and other business partners is crucial for insurance companies. Reinsurers often require insurance companies to provide collateral, such as LCs, to mitigate the risk of non-payment. Having LCs in place demonstrates financial strength and reliability, fostering long-term collaborative relationships with reinsurers and other stakeholders.
Overall, the use of LCs by insurance companies serves as a risk management tool, ensuring financial stability, facilitating international transactions, complying with regulations, and strengthening business relationships. By reducing the risk of non-payment and default, insurance companies can focus on their core operations and effectively meet policyholders’ needs.
Risk Mitigation through Letters of Credit
Letters of Credit (LCs) serve as an effective risk mitigation tool for insurance companies, providing them with a financial guarantee and reducing the risk of non-payment or default. By utilizing LCs, insurance companies can enhance their risk management strategies in the following ways:
- Payment Assurance: Insurance companies face the risk of policyholders defaulting on premium payments or being unable to fulfill their financial obligations. By requiring policyholders to provide an LC, the insurance company ensures that payment will be made by the issuing bank, mitigating the risk of non-payment and securing a steady stream of cash flow.
- Policyholder Insolvency: In the unfortunate event that a policyholder becomes insolvent or unable to meet their financial obligations, a Letter of Credit provides a layer of protection for the insurance company. The LC guarantees payment even if the policyholder’s financial situation deteriorates, reducing the potential loss for the insurance company.
- Large Loss Claims: Insurance companies often face significant claims that may exceed their immediate available funds. By utilizing LCs, insurance companies can mitigate the risk of not being able to honor large loss claims. The LC provides assurance that the necessary funds will be available, ensuring that the company can fulfill its obligations and maintain policyholder trust.
- Risk Sharing with Reinsurers: Insurance companies often have reinsurance arrangements, where they transfer a portion of the risk to a reinsurer. Reinsurers may require insurance companies to provide collateral, such as LCs, to lessen their exposure to default risk. By using LCs, insurance companies can share the risk with reinsurers while maintaining the necessary financial security.
- Protecting Investment Income: Insurance companies invest the premiums they collect to generate income and grow their assets. However, investment returns can be volatile and unpredictable. By utilizing LCs, insurance companies can protect their investment income and ensure that they have the necessary funds to cover claims and financial obligations.
Overall, the use of Letters of Credit enables insurance companies to effectively mitigate various risks, including non-payment, policyholder insolvency, large loss claims, risk sharing with reinsurers, and safeguarding investment income. It provides a financial safety net and enhances the ability of insurance companies to withstand unexpected financial challenges.
Benefits of Letters of Credit for Insurance Companies
Letters of Credit (LCs) offer several benefits to insurance companies, enhancing their financial stability, risk management capabilities, and overall operational efficiency. Here are some key benefits that insurance companies derive from utilizing LCs:
- Financial Security: Insurance companies operate in an environment of inherent financial risk, including the potential for policyholder defaults and large claims. By using LCs, insurance companies have the assurance that the necessary funds will be available from the issuing bank. This financial security enables insurance companies to effectively meet their financial obligations, including settling claims promptly, ensuring the stability and trustworthiness of their operations.
- Risk Mitigation: The primary benefit of LCs is risk mitigation. By requiring policyholders to provide an LC, insurance companies reduce the risk of non-payment, policyholder insolvency, and default. This risk mitigation mechanism enhances the financial stability of insurance companies and helps them navigate the challenges associated with underwriting risks and managing claims.
- Enhanced Creditworthiness: Utilizing LCs can enhance the creditworthiness of insurance companies in the eyes of policyholders, reinsurers, and other business partners. The presence of LCs indicates that insurance companies are financially secure and capable of meeting their obligations. This, in turn, fosters trust and confidence among stakeholders, leading to stronger business relationships and increased opportunities for collaboration.
- Facilitates International Operations: Insurance companies operating in the international market rely on smooth and secure transactions among various parties located in different jurisdictions. LCs provide an added layer of security and credibility in cross-border transactions, ensuring that payments will be made as agreed upon. This facilitates the expansion of insurance companies into new markets and simplifies the complexities associated with international trade.
- Regulatory Compliance: Insurance companies operate in a highly regulated industry and must comply with specific financial requirements and regulations. Some regulators may require insurance companies to maintain certain capital reserves or provide financial guarantees. LCs can serve as a form of compliance with these regulations, demonstrating the financial strength and solvency of insurance companies to regulatory authorities.
- Efficient Claims Settlement: LCs can expedite the claims settlement process for insured individuals or businesses. Insurance companies can rely on the guarantee provided by the LC, allowing them to process and settle claims promptly. This efficiency in claims settlement enhances customer satisfaction and reinforces the reputation of insurance companies in the market.
In summary, the use of Letters of Credit offers significant benefits to insurance companies, including financial security, risk mitigation, enhanced creditworthiness, facilitation of international operations, regulatory compliance, and efficient claims settlement. These benefits contribute to the overall stability and success of insurance companies in the dynamic and competitive insurance industry.
Challenges and Limitations of Letters of Credit
While Letters of Credit (LCs) provide valuable risk mitigation and financial security for insurance companies, there are certain challenges and limitations associated with their use. It is important for insurance companies to be aware of these factors to effectively manage their operations and mitigate any potential drawbacks:
- Complexity: The process of establishing and managing LCs can be complex and time-consuming. Insurance companies need to ensure that all the necessary documentation and requirements are properly fulfilled, which may involve coordination among various parties, including the buyer, issuing bank, and confirming bank. The complexity of the process can potentially lead to delays and administrative challenges.
- Costs: Obtaining and utilizing LCs entail certain costs for insurance companies. These costs may include fees associated with the issuance and management of LCs, as well as potential charges for amendments or cancellations. Insurance companies need to carefully evaluate the cost-effectiveness of using LCs compared to the risks they aim to mitigate.
- Dependence on Banks: Insurance companies rely on banks to issue and honor LCs. However, the financial stability and reputation of banks can fluctuate, potentially affecting the effectiveness and reliability of LCs. Insurance companies need to carefully select banks with a strong financial standing and establish robust relationships to mitigate these risks.
- Limited Coverage and Conditions: LCs provide financial security within the specified terms and conditions outlined in the document. However, the coverage provided by LCs may be limited to certain types of risks or specific policyholders. Insurance companies need to carefully assess the coverage and ensure that the terms of the LC align with their specific risk management needs.
- Disputes and Legal Complexities: Disputes can arise regarding the interpretation or fulfillment of LC terms, resulting in potential legal complexities and delays. Insurance companies should be prepared to navigate these disputes and seek legal guidance when necessary, which may increase costs and administrative burdens.
- Operational Inefficiencies: The processing and management of LCs can introduce additional administrative tasks and complexities into the operational workflow of insurance companies. This may require dedicated resources and systems to handle LC-related tasks, potentially affecting overall operational efficiency.
Insurance companies need to weigh the benefits and challenges associated with the use of LCs and assess their specific risk management requirements. Careful consideration of these challenges and limitations can help insurance companies effectively leverage LCs as a risk mitigation tool while navigating potential drawbacks.
Examples of Insurance Companies Using Letters of Credit
Many insurance companies around the world utilize Letters of Credit (LCs) as part of their risk management and financial stability strategies. Here are a few examples of insurance companies that have incorporated LCs into their operations:
- XYZ Insurance Company: XYZ Insurance Company, a global provider of property and casualty insurance, frequently deals with large corporate clients and international transactions. To mitigate the risk of non-payment and ensure financial stability, XYZ Insurance Company requires its clients to provide LCs that guarantee payment in the event of a claim. This practice allows the company to handle high-value claims by utilizing the funds available through the LCs, ensuring prompt settlement and maintaining policyholder confidence.
- ABC Reinsurance: ABC Reinsurance is a renowned reinsurance company that offers risk management solutions to insurance companies around the world. In order to protect against potential defaults or non-payment by its clients, ABC Reinsurance often requests collateral in the form of LCs. These LCs serve as a guarantee, ensuring that ABC Reinsurance receives the agreed-upon reinsurance premiums and mitigating the risk of financial loss due to client insolvency or non-payment.
- DEF Life Insurance: DEF Life Insurance operates in a highly regulated industry and is required to maintain certain capital reserves to ensure solvency. To meet these regulatory requirements, DEF Life Insurance uses LCs as a form of financial guarantee. The LCs demonstrate to regulators that the company has the necessary financial strength and ensures the availability of funds to meet its policyholder obligations.
- GHI Insurance Corporation: GHI Insurance Corporation specializes in providing insurance coverage for international trade transactions. The company offers trade credit insurance and requires its policyholders to secure LCs as a means of guaranteeing payment for exported goods. The LCs provide assurance to GHI Insurance Corporation that payment will be received, even in the event of buyer default or non-payment, minimizing the risk of financial loss for the company.
- JKL Health Insurance: JKL Health Insurance offers comprehensive health insurance coverage to individuals and families. To enhance financial stability and secure premium payments, JKL Health Insurance requires policyholders to provide LCs as a form of collateral. The LCs act as a guarantee of payment, ensuring that the company has a consistent cash flow to cover claims and maintain the financial well-being of the organization.
These are just a few examples showcasing how insurance companies across various sectors incorporate Letters of Credit into their risk management and financial operations. The utilization of LCs enables these companies to mitigate risks, ensure financial stability, comply with regulatory requirements, and maintain positive business relationships.
Conclusion
In the dynamic and ever-evolving world of insurance, risk management and financial stability are paramount for insurance companies. The use of Letters of Credit (LCs) provides insurance companies with a powerful tool to mitigate risks, ensure financial security, and enhance operational efficiency.
By requiring policyholders to provide LCs, insurance companies can reduce the risk of non-payment, policyholder insolvency, and default. The presence of LCs offers financial security and stability, enabling insurance companies to meet their financial obligations, settle claims promptly, and maintain policyholder trust.
Moreover, the use of LCs enhances the creditworthiness of insurance companies, facilitating stronger relationships with reinsurers and other business partners. LCs also serve as a valuable risk mitigation mechanism in international transactions, fostering trust and ensuring smooth operations in the global market.
However, it is important to acknowledge the challenges and limitations associated with LCs. The complexity of the process, costs, dependence on banks, and potential disputes pose certain obstacles that should be carefully managed by insurance companies.
Examples of insurance companies utilizing LCs highlight the diverse applications and benefits of this risk management tool across different sectors and operations. From property and casualty insurance to reinsurance, health insurance, and international trade coverage, insurance companies adopt LCs to enhance financial stability, comply with regulations, and protect against risks.
In conclusion, Letters of Credit play a vital role in the risk management strategies of insurance companies. They offer financial security, mitigate risks, enhance creditworthiness, facilitate international operations, ensure regulatory compliance, and streamline claims settlement. Insurance companies that effectively leverage the potential of LCs are better positioned to navigate uncertainties, build strong partnerships, and provide reliable coverage in an ever-changing insurance landscape.