
Finance
Why Do People Use Credit Default Swaps
Published: March 4, 2024
Discover the reasons behind the widespread use of credit default swaps in the world of finance and gain insights into their impact on the financial market. Learn how these instruments provide risk management and investment opportunities.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Role of Credit Default Swaps in Financial Markets
- Deciphering the Mechanics and Purpose of Credit Default Swaps
- Harnessing Credit Default Swaps for Speculative Purposes
- Utilizing Credit Default Swaps for Risk Mitigation and Portfolio Protection
- Exploring the Regulatory Implications and Strategic Applications of Credit Default Swaps
- Embracing a Comprehensive Perspective on Credit Default Swaps
Introduction
Understanding the Role of Credit Default Swaps in Financial Markets
In the intricate web of financial instruments and investment strategies, credit default swaps (CDS) have emerged as a controversial yet integral component. These derivatives, often shrouded in complexity, play a pivotal role in the world of finance. Understanding why people use credit default swaps requires delving into the multifaceted purposes they serve, ranging from speculative trading to risk hedging and regulatory arbitrage.
The utilization of credit default swaps has been a subject of intense scrutiny and debate, especially in the aftermath of the 2008 financial crisis. Despite their notoriety, CDS are widely employed by a diverse array of market participants, including institutional investors, hedge funds, and financial institutions. Their appeal lies in the potential to generate substantial profits, mitigate risk exposure, and exploit regulatory loopholes.
This article aims to unravel the enigma surrounding credit default swaps, shedding light on the motivations behind their usage and the implications for financial markets. By examining the various roles that CDS play, from speculative instruments to risk management tools, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of their impact on the global financial landscape.
Understanding Credit Default Swaps
Deciphering the Mechanics and Purpose of Credit Default Swaps
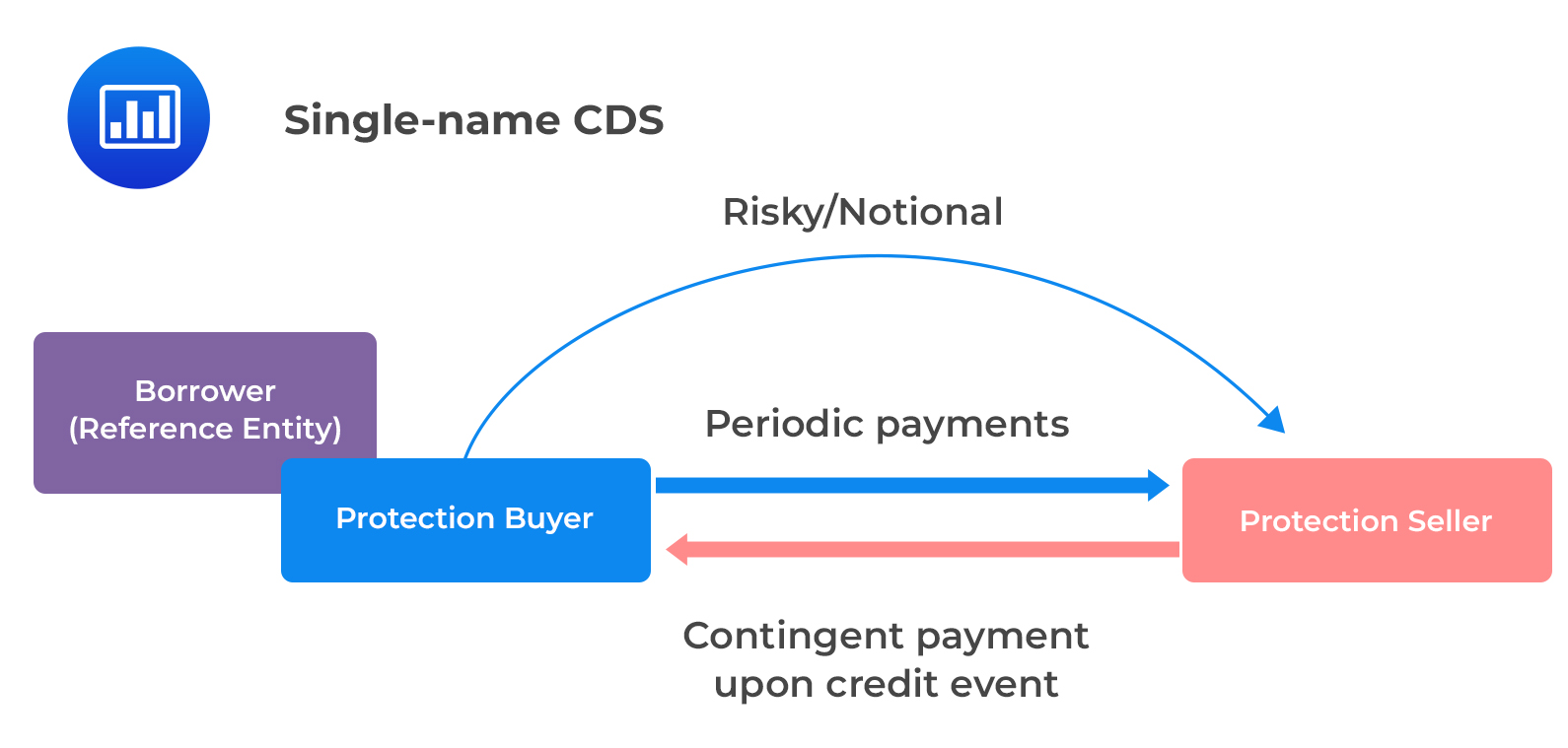
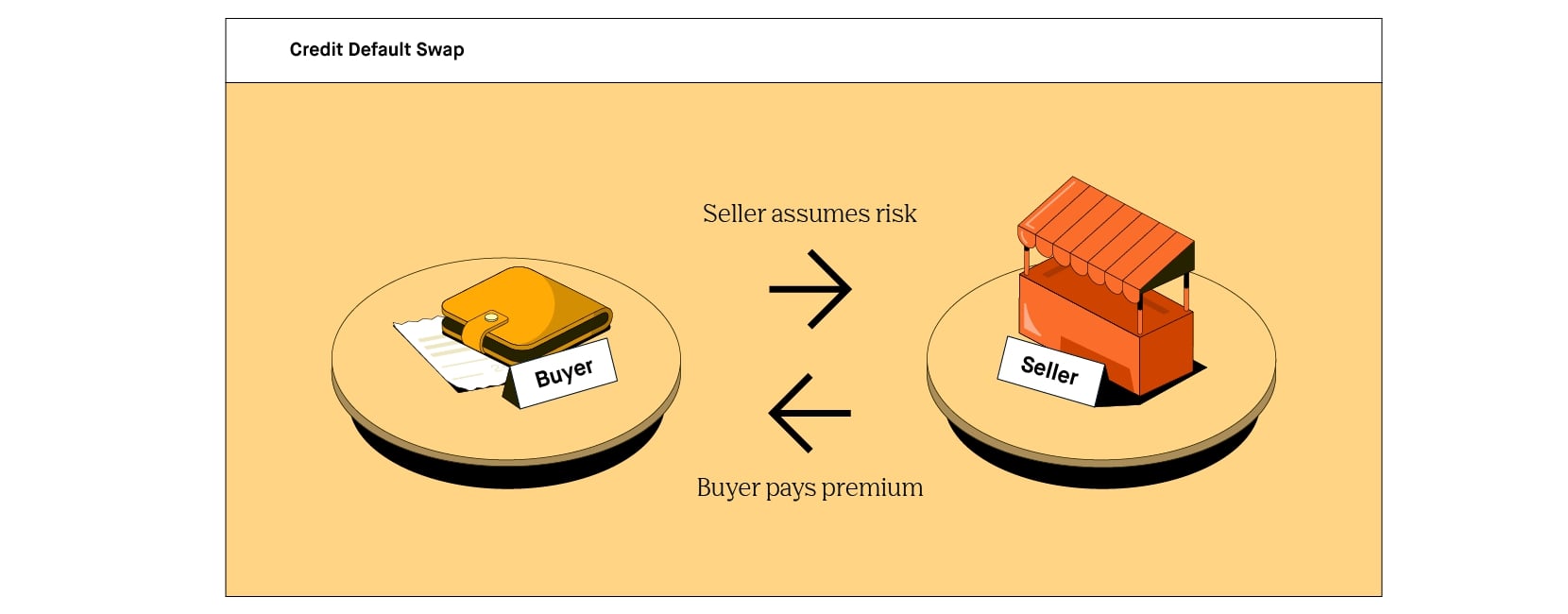
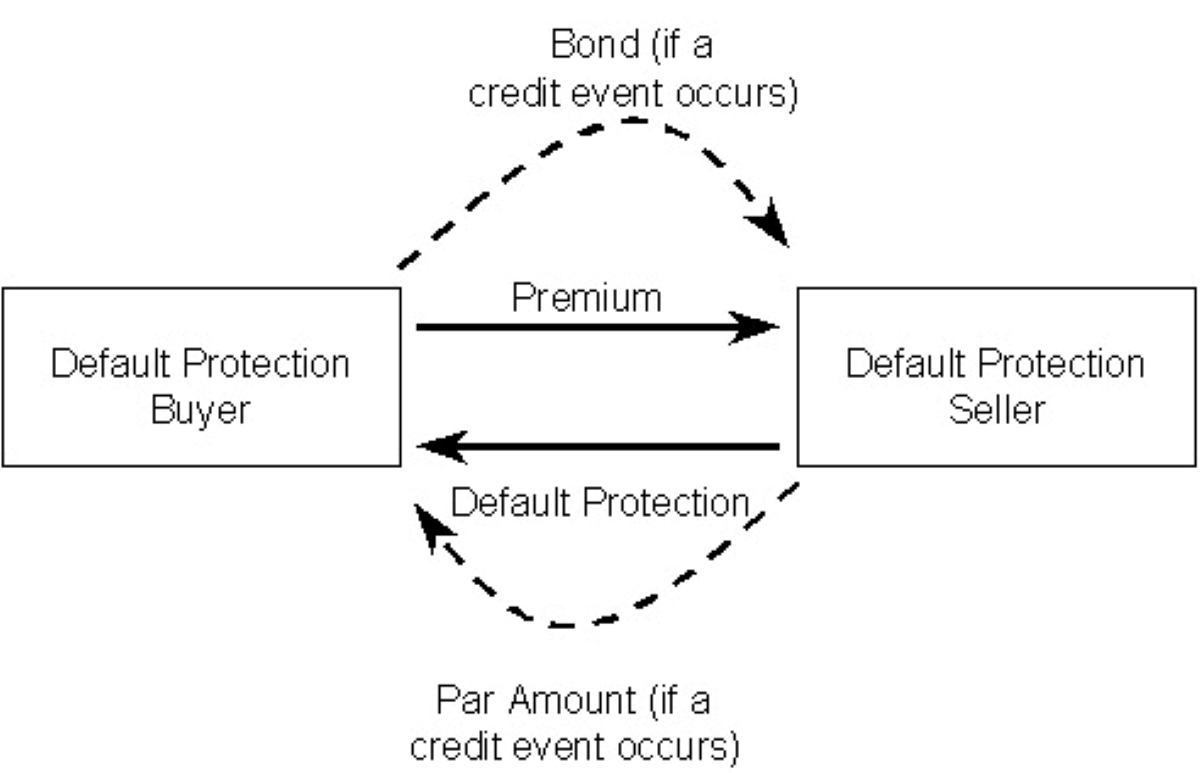
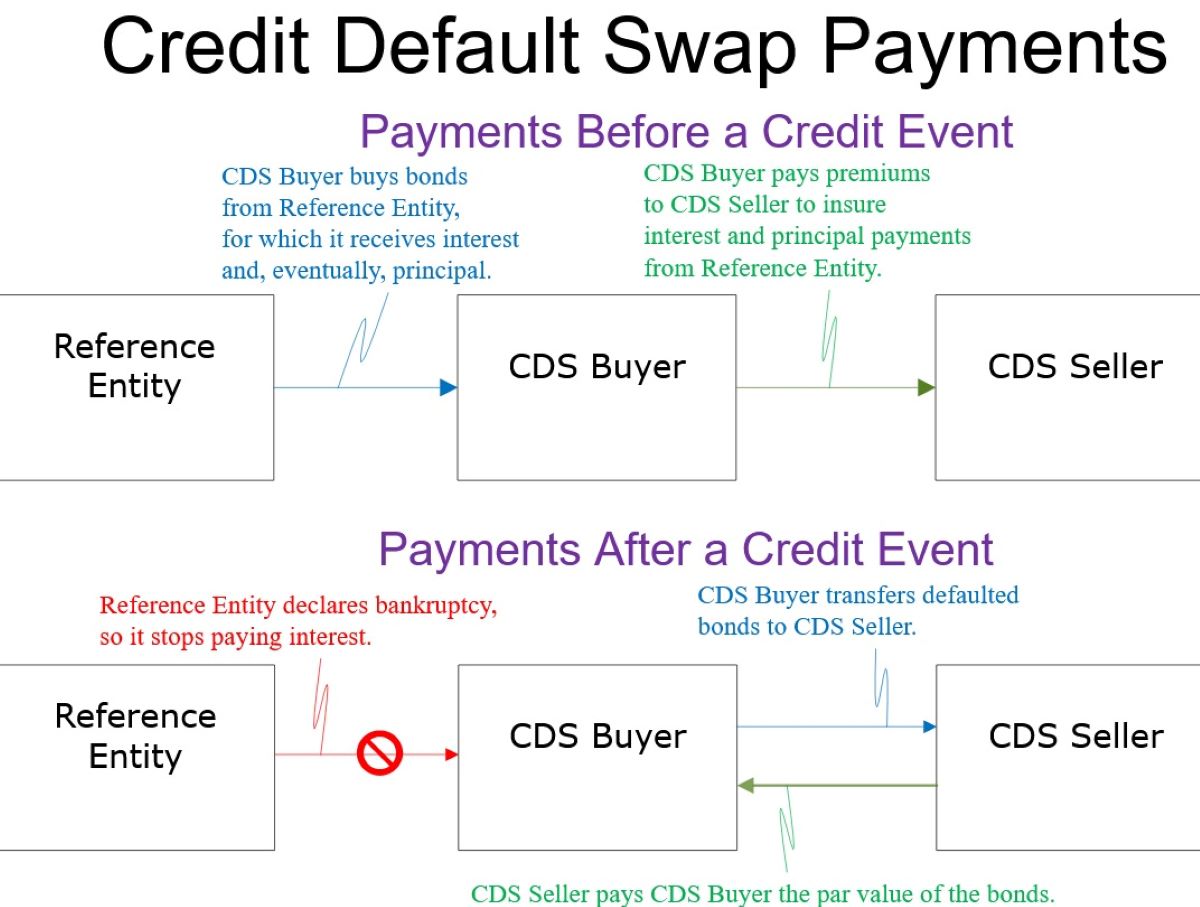
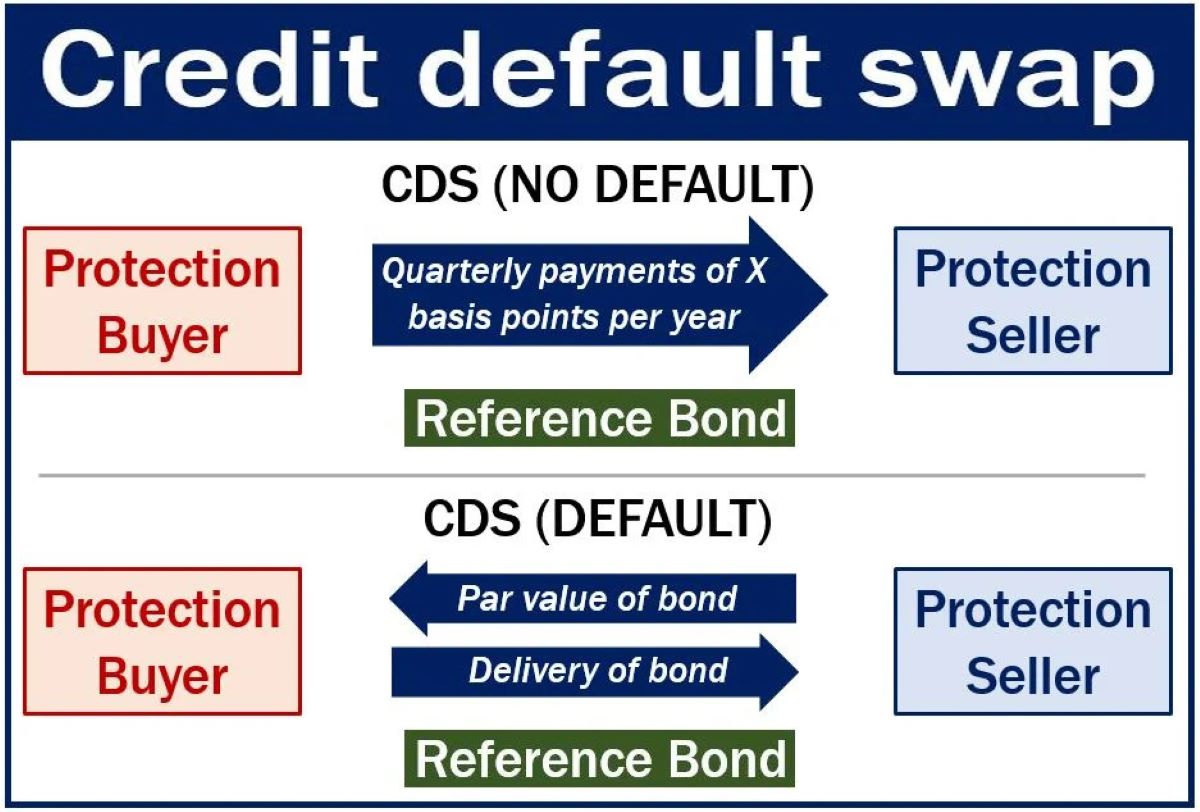
Credit default swaps (CDS) are financial derivatives that enable investors to protect against the risk of default on debt obligations or speculate on the creditworthiness of entities. In essence, a CDS functions as a form of insurance against the possibility of a borrower failing to meet their debt obligations. This insurance-like contract involves two parties: the protection buyer, who pays a periodic fee to the protection seller in exchange for coverage against potential credit events, such as default or restructuring.
One of the key reasons people use credit default swaps is to gain exposure to the credit risk of specific entities without owning the underlying debt. This allows investors to take positions on the creditworthiness of corporations or sovereign entities without the need to directly hold their bonds or loans. Moreover, CDS provide a means for market participants to express their views on credit risk and engage in speculative trading activities.
While credit default swaps offer the potential for significant profits, they also carry inherent risks and complexities. The intricate nature of CDS contracts, coupled with the interconnectedness of financial markets, has raised concerns about their impact on systemic stability. The widespread use of credit default swaps has amplified the interconnectedness of financial institutions and heightened the potential for contagion in the event of credit events.
Despite the criticisms and controversies surrounding credit default swaps, they continue to be utilized for a myriad of purposes, reflecting their versatility and significance in modern finance. From facilitating efficient risk transfer to enabling market participants to express their credit views, CDS occupy a prominent position in the financial toolkit of investors and institutions alike.
Speculative Trading
Harnessing Credit Default Swaps for Speculative Purposes
One of the primary motivations driving the use of credit default swaps is their appeal as speculative instruments. Market participants, ranging from hedge funds to proprietary trading desks, leverage CDS to capitalize on anticipated changes in the credit quality of underlying entities. By entering into CDS contracts, investors can take directional positions on the creditworthiness of corporations, sovereigns, or structured finance products, without the need to own the actual debt instruments.
Speculative trading using credit default swaps allows investors to profit from both positive and negative credit events. For instance, if an investor anticipates a deterioration in the credit profile of a specific company, they can purchase CDS protection on that entity, thereby standing to benefit if a credit event occurs. Conversely, investors may engage in the selling of CDS protection if they believe that the credit risk of a particular entity is overstated, enabling them to earn premiums as compensation for assuming the credit risk.
While speculative trading through credit default swaps presents opportunities for potential gains, it also introduces complexities and risks. The leveraged nature of CDS transactions can amplify both profits and losses, making them a double-edged sword for speculators. Moreover, the interconnectedness of CDS contracts across market participants and the potential for cascading effects in the event of credit events underscore the intricate dynamics of speculative trading using these derivatives.
Despite the inherent risks and criticisms associated with speculative trading in credit default swaps, they continue to attract a diverse array of market participants seeking to capitalize on evolving credit conditions and market dynamics. The speculative appeal of CDS lies in their capacity to offer leveraged exposure to credit risk, enabling investors to express their views on credit quality and potentially reap substantial profits in the process.
Hedging Against Risk
Utilizing Credit Default Swaps for Risk Mitigation and Portfolio Protection
Besides serving as speculative tools, credit default swaps play a crucial role in enabling market participants to hedge against credit risk and safeguard their investment portfolios. Hedging using CDS involves employing these derivatives to offset potential losses arising from adverse credit events, thereby mitigating the impact of default or credit deterioration on a portfolio of bonds or loans.
Investors and financial institutions utilize credit default swaps to hedge against the credit risk associated with their holdings of corporate bonds, sovereign debt, or structured finance products. By purchasing CDS protection, investors can effectively transfer the credit risk to the protection seller, thereby insulating their portfolios from the financial repercussions of credit events. This risk mitigation strategy provides a mechanism for market participants to safeguard their investments and enhance the overall resilience of their portfolios.
Moreover, credit default swaps offer a flexible and efficient means of managing credit exposure without the need to divest underlying assets. This ability to hedge credit risk through CDS contracts empowers investors to tailor their risk profiles and optimize the risk-return tradeoff within their investment portfolios. Whether seeking to protect against the credit risk of specific entities or diversify credit exposures, hedging with credit default swaps affords market participants a valuable risk management tool.
Amidst the dynamic and often unpredictable nature of credit markets, the use of credit default swaps for hedging purposes underscores their instrumental role in fortifying the resilience of investment portfolios. By mitigating the impact of credit events and potential defaults, CDS enable market participants to navigate credit risk more effectively, thereby contributing to the overall stability and risk management capabilities of the financial system.
Regulatory Arbitrage
Exploring the Regulatory Implications and Strategic Applications of Credit Default Swaps
Credit default swaps have been the subject of regulatory scrutiny and debate, particularly in the context of regulatory arbitrage. Regulatory arbitrage refers to the strategic use of financial instruments to exploit regulatory loopholes, optimize capital requirements, or circumvent regulatory constraints, thereby enhancing financial efficiency or competitive advantage.
Market participants have utilized credit default swaps as a means of achieving regulatory objectives and managing capital adequacy requirements. For instance, banks and financial institutions have employed CDS transactions to transfer credit risk off their balance sheets, thereby reducing the amount of regulatory capital reserves earmarked for covering credit exposures. This practice, known as balance sheet optimization, enables institutions to free up capital for alternative uses, potentially enhancing their profitability and capital efficiency.
Furthermore, the global nature of credit default swaps has facilitated cross-border regulatory arbitrage, allowing market participants to capitalize on regulatory disparities across jurisdictions. By leveraging the differences in regulatory frameworks and capital adequacy standards, market participants can optimize their risk management strategies and capital allocation, thereby enhancing their competitive positioning in the global financial landscape.
Despite the potential benefits of regulatory arbitrage using credit default swaps, concerns have been raised regarding the systemic implications and regulatory oversight of these practices. The strategic utilization of CDS for regulatory arbitrage purposes has underscored the need for enhanced transparency, risk monitoring, and regulatory coordination to mitigate the potential risks associated with regulatory arbitrage activities.
As regulatory authorities continue to refine and strengthen the regulatory framework governing credit default swaps, market participants are compelled to navigate the evolving landscape of regulatory requirements and compliance standards. The strategic applications of credit default swaps in regulatory arbitrage underscore the intricate interplay between financial innovation, regulatory dynamics, and the pursuit of competitive advantage within the global financial ecosystem.
Conclusion
Embracing a Comprehensive Perspective on Credit Default Swaps
The multifaceted role of credit default swaps in financial markets encompasses speculative trading, risk hedging, and regulatory arbitrage, reflecting the diverse motivations and strategic applications underlying their usage. Despite the controversies and complexities surrounding credit default swaps, these derivatives continue to wield significant influence within the global financial landscape, shaping investment strategies, risk management practices, and regulatory dynamics.
By delving into the underlying mechanisms and purposes of credit default swaps, it becomes evident that these derivatives serve as a double-edged sword, offering both opportunities and challenges for market participants. The allure of speculative trading using CDS lies in the potential for substantial profits and leveraged exposure to credit risk, albeit accompanied by inherent complexities and systemic implications. Concurrently, the utilization of credit default swaps for risk hedging purposes provides investors and financial institutions with a valuable tool for managing credit exposures and fortifying the resilience of investment portfolios in the face of credit events.
Moreover, the strategic applications of credit default swaps in regulatory arbitrage underscore the dynamic interplay between financial innovation, regulatory dynamics, and the pursuit of competitive advantage within the global financial ecosystem. While regulatory arbitrage using CDS offers potential benefits in terms of capital efficiency and risk management, it also necessitates a nuanced approach to regulatory oversight and risk monitoring to mitigate potential systemic risks and ensure financial stability.
As market participants navigate the intricate terrain of credit default swaps, it is imperative to embrace a comprehensive perspective that encompasses the opportunities, risks, and regulatory implications associated with these derivatives. By fostering transparency, risk awareness, and prudent risk management practices, market participants can harness the potential of credit default swaps while mitigating the associated complexities and systemic implications.
In essence, understanding why people use credit default swaps entails recognizing the multifaceted roles and strategic applications of these derivatives, from speculative trading to risk hedging and regulatory arbitrage. As the financial landscape continues to evolve, the dynamic interplay between credit default swaps, market dynamics, and regulatory frameworks underscores the imperative of fostering a balanced approach that aligns with the principles of financial stability, risk management, and regulatory compliance.