Home>Finance>Gamma Hedging: Definition, How It Works, And Vs. Delta Hedging


Finance
Gamma Hedging: Definition, How It Works, And Vs. Delta Hedging
Modified: January 15, 2024
Learn about gamma hedging in finance, including its definition, how it works, and how it compares to delta hedging.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Gamme Hedging: Definition, How It Works, and Vs. Delta Hedging
Welcome to our “Finance” category, where we delve into the fascinating world of financial strategies and concepts! In this blog post, we will explore gamma hedging, a technique used by investors to manage risk in their portfolios. We’ll define what gamma hedging is, explain how it works, and compare it to delta hedging. So, let’s dive right in!
Key Takeaways:
- Gamme hedging is a risk management strategy used by investors to mitigate potential losses in their portfolios.
- Gamma hedging involves making adjustments to a portfolio’s positions in response to changes in the underlying asset’s price.
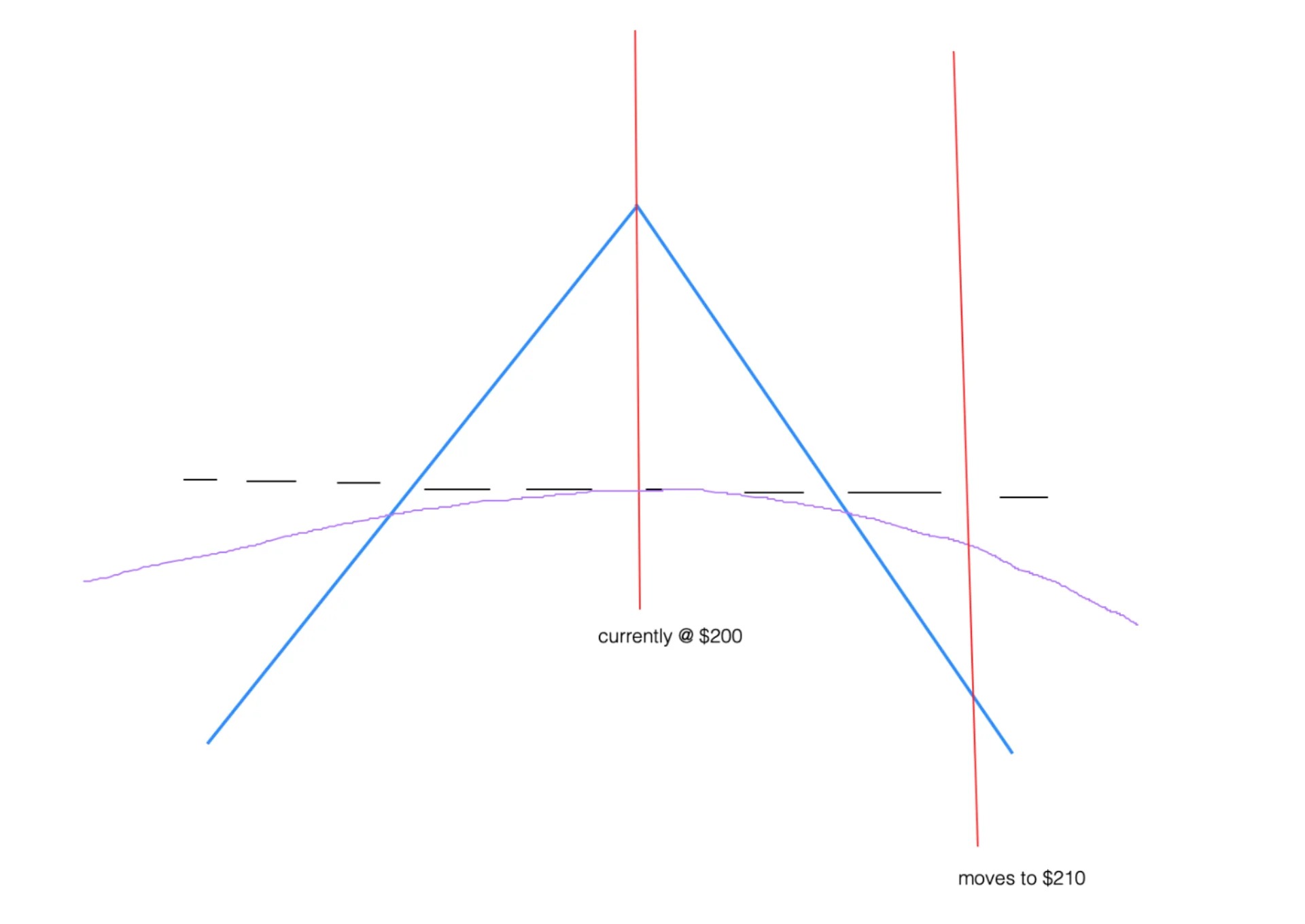
But what exactly is gamma hedging? Gamma hedging is a strategy employed by investors to protect their portfolios from adverse price movements. Unlike delta hedging, which focuses on managing changes in the portfolio’s overall value, gamma hedging specifically targets changes in the rate of change (gamma) of the portfolio’s delta, the measure of its sensitivity to the underlying asset’s price.
When an investor engages in gamma hedging, they adjust their portfolio by buying or selling additional options or underlying assets. This adjustment helps them maintain a neutral gamma position, reducing the potential impact from changes in the underlying asset’s price. By staying delta-neutral through gamma hedging, investors aim to minimize losses and potentially maximize profits in volatile market conditions.
Now, how does gamma hedging differ from delta hedging? While both strategies aim to manage risk, they do so in slightly different ways. Delta hedging primarily focuses on maintaining a neutral delta position, ensuring that the portfolio’s value remains relatively stable in response to changes in the underlying asset’s price. On the other hand, gamma hedging focuses on managing changes in the rate of change of delta.
Gamma hedging can be seen as a more proactive approach, as it involves actively adjusting the portfolio’s positions to counteract changes in the underlying asset’s price. Delta hedging, while effective in stabilizing the portfolio’s value, is more reactive and relies on periodic adjustments.
In conclusion, gamma hedging is a powerful risk management strategy that helps investors navigate market volatility. By maintaining a neutral gamma position through adjustments to their portfolio, investors can mitigate potential losses and potentially maximize gains. While similar in their objectives, gamma hedging and delta hedging employ different techniques to achieve risk mitigation. Understanding these strategies can equip investors with valuable tools to navigate the ever-changing landscape of finance.
That’s it for our exploration of gamma hedging! We hope you found this blog post informative and insightful. Stay tuned for more finance topics in our “Finance” category!