
Finance
What Is IRS Form 2848?
Published: October 31, 2023
Learn all about IRS Form 2848, required for granting power of attorney in finance matters. Find out how to navigate this important tax document and get your financial affairs in order.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to navigating the complex and intricate world of taxes, it’s not uncommon to find yourself in need of assistance. Whether you’re an individual taxpayer or a business owner, there may be times when you need someone else to represent your interests before the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). This is where IRS Form 2848, also known as the Power of Attorney and Declaration of Representative, comes into play.
IRS Form 2848 acts as a crucial tool for granting authority to another individual or entity to act on your behalf in tax-related matters. By completing this form, you empower your designated representative to communicate with the IRS, receive confidential tax information, and handle various tax-related transactions on your behalf.
Understanding the purpose and appropriate use of IRS Form 2848 is essential when it comes to managing your tax affairs effectively. In this article, we will explore the different aspects of IRS Form 2848, from its intended purpose to the proper procedures for completing and submitting the form. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how this powerful document can streamline your interactions with the IRS and provide the support you need.
Purpose of IRS Form 2848
The primary purpose of IRS Form 2848 is to authorize someone else to act as your representative before the IRS. This form establishes a legal power of attorney relationship, granting your chosen representative the authority to handle tax-related matters on your behalf. By filing Form 2848, you are essentially designating someone to represent your interests and interact directly with the IRS.
There are several specific tasks that your designated representative can perform with the power of attorney granted through Form 2848:
- Receive and inspect confidential tax information related to your tax account
- Respond to IRS notices or communication on your behalf
- Make inquiries about your tax account and request adjustments if necessary
- Provide or request additional documentation or records to support your tax position
- Participate in conferences, meetings, or hearings with the IRS on matters related to your tax account
- Sign and execute agreements, consents, waivers, or other documents on your behalf
It’s important to note that while Form 2848 grants your representative the authority to act on your behalf, it does not relieve you of your own responsibilities as a taxpayer. You remain ultimately responsible for the accuracy and completeness of your tax returns and any associated liabilities.
By using IRS Form 2848, you can ensure that you have someone qualified and knowledgeable representing your interests during interactions with the IRS. Whether you are unable to handle your tax affairs personally or simply want the expertise of a tax professional or attorney, this form provides a convenient and secure way to delegate authority.
Who Can Use IRS Form 2848
IRS Form 2848 can be utilized by a variety of individuals or entities seeking representation before the IRS. Here are some examples of who can use this form:
- Individual Taxpayers: If you are an individual taxpayer and need someone to handle your tax matters, you can use Form 2848 to designate a representative. This could be a tax professional, such as an enrolled agent, certified public accountant (CPA), or attorney.
- Business Owners: Business owners, including sole proprietors, partners, or corporate officers, can also complete Form 2848 to authorize a representative to handle their tax affairs. This is especially useful for navigating complex tax issues or addressing disputes with the IRS.
- Estate Executors or Administrators: If you are managing the tax affairs of a deceased individual’s estate as an executor or administrator, you can use Form 2848 to appoint someone to act on the estate’s behalf. This is commonly done by estate attorneys or tax professionals.
- Nonresident Aliens: Nonresident aliens who have U.S. tax filing obligations may need to designate a representative to handle these matters. Form 2848 allows nonresident aliens to authorize someone to communicate with the IRS and handle their tax affairs in the United States.
- Tax Professionals: Tax professionals themselves, such as tax practitioners or accounting firms, may complete Form 2848 to designate another individual within their organization to represent clients before the IRS. This form consolidates the authority to act on behalf of multiple taxpayers.
It’s important to remember that not just anyone can be designated as a representative using Form 2848. The individual or entity you choose must meet certain qualifications and be eligible to practice before the IRS. This includes enrolled agents, CPAs, attorneys, and individuals who are authorized to practice under special provisions.
Before designating a representative, it’s crucial to ensure they have the necessary experience, knowledge, and understanding of tax laws and procedures to effectively handle your tax matters. Conducting due diligence and selecting a qualified representative will help ensure a smooth and successful experience when interacting with the IRS.
How to Fill Out IRS Form 2848
Completing IRS Form 2848 requires careful attention to detail to ensure accuracy and effectiveness. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to fill out the form:
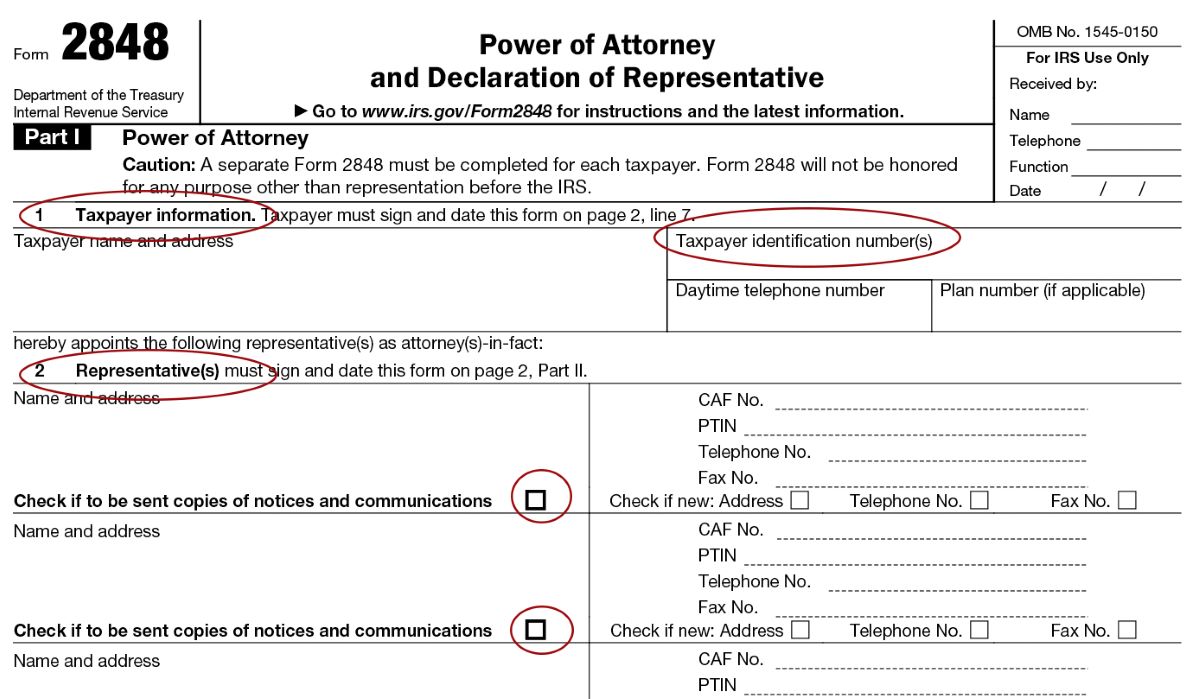
- Identify the taxpayer: Provide your personal or business information, including your name, address, taxpayer identification number (such as your Social Security Number or Employer Identification Number), and contact information. If applicable, include the contact information for your representative as well.
- Select the tax matters: Indicate the specific tax matters for which your representative is authorized to act. This can include income tax, employment tax, excise tax, estate tax, gift tax, and more. Be specific and include all relevant tax periods.
- Identify the representative: Provide the name, address, and contact information of the individual or entity you are appointing as your representative. Include their taxpayer identification number, such as their Social Security Number or Employer Identification Number.
- Specify the acts authorized: Clearly state the acts you are authorizing your representative to perform. This can include receiving and inspecting confidential tax information, signing documents on your behalf, and representing you in meetings or hearings with the IRS.
- Sign and date the form: Both you as the taxpayer and your representative must sign and date the form. Make sure the signatures are legible and match the names provided. You can use a digital or electronic signature if filing online.
- Attach supporting documentation (if required): Depending on the situation, you may need to attach additional documentation to support your request. This can include copies of other power of attorney documents, proof of representative’s eligibility, or any other relevant information.
It’s crucial to review the completed form thoroughly before submitting it to ensure accuracy and completeness. Any errors or incomplete information may delay the processing of your request or result in the form being returned for corrections.
It’s recommended to consult with a qualified tax professional or attorney when filling out Form 2848 to ensure compliance and to address any specific concerns or complexities related to your tax situation.
Understanding Power of Attorney
Power of Attorney (POA) is a legal concept that grants an individual or entity the authority to act on behalf of another person in various matters. In the context of IRS Form 2848, the Power of Attorney allows the designated representative to act on the taxpayer’s behalf in tax-related matters.
By completing Form 2848, you are essentially granting your representative the power to make decisions and take actions as if they were the taxpayer themselves. They have the authority to communicate with the IRS, access confidential tax information, and perform other specified acts on your behalf.
It is important to understand the scope and limitations of the Power of Attorney when using Form 2848. The authority granted to your representative is specific to the tax matters listed on the form. It does not give them unlimited power over your personal or financial affairs outside of those tax-related matters.
Furthermore, the Power of Attorney relationship established through Form 2848 is typically limited to matters before the IRS. It may not necessarily extend to other legal or financial matters outside of the IRS’s jurisdiction. If you want your representative to act on your behalf in other areas, you may need to establish separate Power of Attorney documents specific to those matters.
It’s crucial to select a representative whom you trust and who possesses the necessary knowledge and expertise to handle your tax affairs effectively. This ensures that the Power of Attorney is utilized in your best interests and that your representative is capable of making informed decisions on your behalf.
Remember that the Power of Attorney relationship can be revoked or terminated at any time. If you no longer wish to grant your representative the authority to act on your behalf, you can submit a written revocation to the IRS. This revocation should include your name, contact information, and the name of your representative.
Understanding the Power of Attorney and its implications is essential when completing IRS Form 2848. It empowers you to designate someone you trust to handle your tax matters and streamline your interactions with the IRS.
Importance of Accurate and Complete Information
When filling out IRS Form 2848, providing accurate and complete information is of utmost importance. The information you provide on the form directly impacts the validity and effectiveness of the Power of Attorney relationship established with your representative. Here’s why accurate and complete information matters:
1. Validity of the Form: The IRS requires accurate and complete information to ensure the form is valid. Inaccurate or incomplete information may result in the form being rejected, delaying the authorization process or requiring additional steps to rectify the issue.
2. Proper Representation: Your designated representative relies on the information provided to accurately represent your interests before the IRS. If the information is not complete or accurate, it may hinder their ability to effectively communicate, receive important notices, or advocate on your behalf.
3. Protecting Your Privacy: Form 2848 involves sharing sensitive and confidential tax information with your representative. Accurate information ensures that the right person has access to your account and protects your privacy from unauthorized individuals who may attempt to act on your behalf.
4. Avoiding Miscommunication: Clear and accurate information on the form helps avoid miscommunication between you, your representative, and the IRS. By providing specific details about the tax matters and acts authorized, you can ensure that everyone understands their roles and responsibilities.
5. Minimizing Errors and Issues: Providing accurate information reduces the likelihood of errors or issues arising during the processing of your form. This can help prevent unnecessary delays, disputes, or complications that may arise if incorrect or incomplete information is discovered later on.
6. Compliance with IRS Requirements: The IRS has specific requirements for what information must be provided on Form 2848. Failing to provide accurate and complete information may result in non-compliance with IRS regulations, potentially leading to penalties or other consequences.
Remember to review the form thoroughly before submitting it to ensure all information is accurate and complete. It’s also advisable to consult a qualified tax professional or attorney to verify the information and address any specific concerns related to your tax situation.
By providing accurate and complete information on IRS Form 2848, you can establish a reliable and effective Power of Attorney relationship, ensuring your representative can act on your behalf with confidence and competence.
Submitting IRS Form 2848
Once you have completed IRS Form 2848, it’s important to follow the proper procedures for submitting the form to ensure it is processed promptly and accurately. Here are the steps to submit Form 2848:
1. Review the Form: Before submitting the form, review it thoroughly to ensure all information is accurate and complete. Verify that the names, contact information, and tax matters listed are correct.
2. Signatures and Dates: Both you as the taxpayer and your designated representative must sign and date the form. Make sure the signatures are legible and match the names provided. If filing online, you may use a digital or electronic signature.
3. Attach Supporting Documentation: Depending on the situation, you may be required to attach supporting documentation to your Form 2848. This can include copies of other Power of Attorney documents, proof of eligibility, or additional information relevant to your tax matters.
4. Method of Submission: You have several options for submitting Form 2848 to the IRS. The most common methods include mailing the form, faxing it, or submitting it electronically through the IRS e-Services platform.
5. Mailing: If you choose to mail the form, send it to the appropriate IRS address based on your location and the type of tax matters involved. Make sure to use certified mail with a return receipt to track its delivery.
6. Faxing: If you opt to fax the form, check the IRS instructions for the correct fax number to use. Keep the fax confirmation as proof of transmission.
7. Electronic Submission: To submit the form electronically, you must be registered with the IRS e-Services platform. Follow the instructions on the website to upload the completed form and any required attachments.
8. Retain a Copy: It’s important to keep a copy of your completed Form 2848 and any supporting documentation for your records. This ensures you have a record of the authorization provided to your representative.
After submitting the form, it may take some time for the IRS to process and acknowledge the authorization. Once accepted, your designated representative will have the necessary authority to act on your behalf in the specified tax matters.
If you need to make any changes or updates to your Form 2848 after submission, you can file a new form with the updated information or submit a written revocation to the IRS.
Remember, if you have any questions or concerns about submitting Form 2848, it is always best to consult with a qualified tax professional or seek guidance from the IRS directly.
Revoking IRS Form 2848
In certain situations, you may need to revoke or cancel the authority granted to your representative through IRS Form 2848. If you no longer wish to authorize someone to act on your behalf or if your circumstances change, it’s important to follow the proper procedures to revoke the form. Here’s how to revoke IRS Form 2848:
1. Written Revocation: To effectively revoke Form 2848, you must submit a written revocation to the IRS. The revocation should include your name, contact information, and the name of the representative you wish to revoke. Be clear and specific about the intention to revoke the authority granted through Form 2848.
2. Delivery Method: You can choose to deliver the written revocation by mailing it to the appropriate IRS office or by faxing it. If mailing, use certified mail with a return receipt to track its delivery. If faxing, refer to the IRS instructions for the correct fax number to use.
3. Timely Submission: It’s important to submit the revocation in a timely manner to ensure it is processed promptly. If possible, submit the revocation as soon as your decision to revoke the authority has been made.
4. Keep a Copy: Retain a copy of the written revocation and proof of delivery (such as the certified mail receipt or fax confirmation) for your records. This serves as evidence that you have effectively revoked the authority granted through Form 2848.
It’s crucial to communicate with your representative about the revocation and ensure they are aware of the change in their authority. This helps avoid any confusion or unintended actions on their part.
Keep in mind that revoking IRS Form 2848 does not automatically resolve any ongoing tax matters or obligations. You may still be responsible for fulfilling your tax obligations, including submitting accurate and complete tax returns, even if you have revoked the authority of your representative.
If you wish to appoint a new representative after revoking the previous authority, you will need to complete a new IRS Form 2848 and follow the proper procedures for submission.
It’s always advisable to consult with a qualified tax professional or attorney if you have any doubts or concerns regarding the revocation of Form 2848 or your representation before the IRS.
By following the proper procedures and promptly submitting a written revocation, you can effectively revoke the authority granted through IRS Form 2848, ensuring that your representative is no longer authorized to act on your behalf in tax matters.
IRS Form 2848 Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about IRS Form 2848:
1. Can I authorize multiple representatives on one Form 2848?
Yes, you can authorize multiple representatives on one Form 2848. Simply provide the required information for each representative in the designated section of the form.
2. Can I revoke Form 2848 at any time?
Yes, you can revoke Form 2848 at any time by submitting a written revocation to the IRS. It’s important to follow the proper procedures for revocation to ensure it is processed accurately.
3. How long is Form 2848 valid?
IRS Form 2848 does not have an expiration date. However, the IRS may request that you provide an updated Form 2848 if a significant amount of time has passed since the original authorization was submitted.
4. Can I authorize someone to sign checks or make payments on my behalf?
No, IRS Form 2848 does not grant the authority to your representative to sign checks or make payments on your behalf. Its primary purpose is to authorize representation in tax matters before the IRS.
5. Can I authorize my spouse to represent me in tax matters?
If you file a joint tax return with your spouse, your spouse is already authorized to represent you in tax matters. In this case, you do not need to complete Form 2848 to grant them additional authority.
6. Can my representative authorize another person to act on my behalf?
No, your representative cannot further delegate the authority granted through Form 2848 to another individual or entity without your explicit consent.
7. Can I complete Form 2848 online?
Yes, the IRS provides an electronic filing option through their e-Services platform. You can complete and submit Form 2848 online, including any required attachments.
8. Can I use Form 2848 for state tax matters?
No, IRS Form 2848 is specific to federal tax matters. Each state has its own Power of Attorney forms for representation in state tax matters.
If you have further questions or concerns about IRS Form 2848 and its use, it’s recommended to consult a qualified tax professional or contact the IRS directly for assistance.
NOTE: The information provided in this article is for general informational purposes only and should not be considered as legal or tax advice. Please consult with a qualified professional for specific guidance related to your situation.