
Finance
What Is IRS Form 4797 Used For?
Published: November 1, 2023
Learn about IRS Form 4797 and its purpose in finance. Discover how this form is used to report the sale of business assets and calculate gains or losses
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Purpose of IRS Form 4797
- Who Needs to File Form 4797
- Understanding the Different Sections of Form 4797
- Reporting the Sale or Exchange of Property on Form 4797
- Reporting the Disposition of Business Assets on Form 4797
- Reporting the Sale of Depreciable Property on Form 4797
- Special Rules and Considerations for Partnerships and S Corporations
- Tips for Completing IRS Form 4797
- Common Errors to Avoid When Filing Form 4797
- Conclusion
Introduction
When it comes to navigating the complex world of finance, understanding the intricacies of the tax system is crucial. One form that both individuals and businesses may encounter is IRS Form 4797. This form plays a significant role in reporting the sale or disposition of property used in a trade or business, as well as the sale of certain depreciable assets.
Form 4797 serves as an important tool for accurately reporting gains and losses on the sale or exchange of assets, which in turn affects the tax liability of individuals and businesses. While the thought of filling out another tax form might seem daunting, having a good understanding of the purpose and requirements of Form 4797 can help streamline the process and ensure compliance with tax regulations.
In this article, we will explore the purpose of IRS Form 4797, who needs to file it, and how to properly complete the form. We will also delve into the different sections of the form, including reporting the sale or exchange of property, the disposition of business assets, and the sale of depreciable property. Additionally, we will touch on some special rules and considerations for partnerships and S corporations.
Whether you are a sole proprietor, a partner in a business, or a shareholder in an S corporation, understanding the intricacies of Form 4797 is crucial for accurately reporting your tax liability.
Before we delve into the specifics of Form 4797, let’s first take a closer look at its purpose and who needs to file it.
Purpose of IRS Form 4797
IRS Form 4797, also known as the Sales of Business Property, serves the purpose of reporting gains and losses from the sale or disposition of property used in a trade or business. It is an essential form for individuals and businesses involved in buying, selling, or exchanging property, as it allows the IRS to accurately assess tax liabilities related to these transactions.
The primary function of Form 4797 is to determine the tax treatment of the gains or losses realized from the sale or exchange of property. By reporting these transactions on Form 4797, taxpayers provide the necessary information for calculating depreciation recapture and capital gains or losses.
Depreciation recapture occurs when the sale price of a property exceeds its adjusted basis. This means that the taxpayer must “recapture” portions of the depreciation they previously claimed as deductions. The recaptured amount is treated as ordinary income and is subject to taxation at the taxpayer’s applicable tax rate.
In addition to depreciation recapture, Form 4797 is also used to report any capital gains or losses resulting from the sale or exchange of property. Capital gains or losses occur when the selling price of a property is higher or lower than its original purchase price. These gains or losses are subject to specific tax rates depending on the holding period of the property.
It is important to note that Form 4797 is not only applicable to the sale of real estate. It also encompasses the sale or exchange of other business assets, such as machinery, equipment, vehicles, and even intangible assets like patents or copyrights. Therefore, anyone engaged in a trade or business should be aware of the requirements of Form 4797 and how it may impact their tax obligations.
Now that we understand the purpose of Form 4797, let’s explore who needs to file this form.
Who Needs to File Form 4797
Form 4797 is typically filed by individuals and businesses that have sold or disposed of property used in a trade or business. Taxpayers who meet any of the following criteria are generally required to file Form 4797:
- Individuals, including sole proprietors, who have sold or exchanged property used for business purposes
- Partnerships and S corporations that have sold or disposed of property used in their trade or business
- Estates and trusts that have sold or exchanged property used in a trade or business
- Individuals or businesses who have experienced an involuntary conversion of property used in a trade or business, such as property that was destroyed, condemned, or stolen
It is important to note that the requirement to file Form 4797 is not exclusive to those who have realized a gain on the sale or disposition of property. Even if the transaction resulted in a loss, taxpayers are still obligated to report it on Form 4797. Reporting losses on the form allows taxpayers to properly adjust their tax liability and potentially claim deductible losses.
Additionally, certain types of property transactions may require the filing of specific sections of Form 4797. For example, if a taxpayer has exchanged property under Section 1031 of the Internal Revenue Code, they may need to complete Section C of Form 4797 to report the like-kind exchange. It is crucial for taxpayers to carefully review the instructions for Form 4797 to determine which sections apply to their specific situation.
It is also worth mentioning that taxpayers with substantial transactions may be required to file multiple Form 4797s. For example, if an individual or business has multiple sales or exchanges of property throughout the year, they may need to file a separate Form 4797 for each applicable transaction.
Failing to file Form 4797 when required can result in penalties and potential audits by the IRS. Therefore, it is important to stay informed about the filing requirements and ensure compliance with tax regulations.
Now that we have explored who needs to file Form 4797, let’s dive into the different sections of the form and what information is required for reporting the sale or disposition of property.
Understanding the Different Sections of Form 4797
Form 4797 consists of several sections, each dedicated to reporting specific types of property transactions. Understanding these sections is essential for accurately completing the form and correctly reporting the sale or disposition of property. The main sections of Form 4797 include:
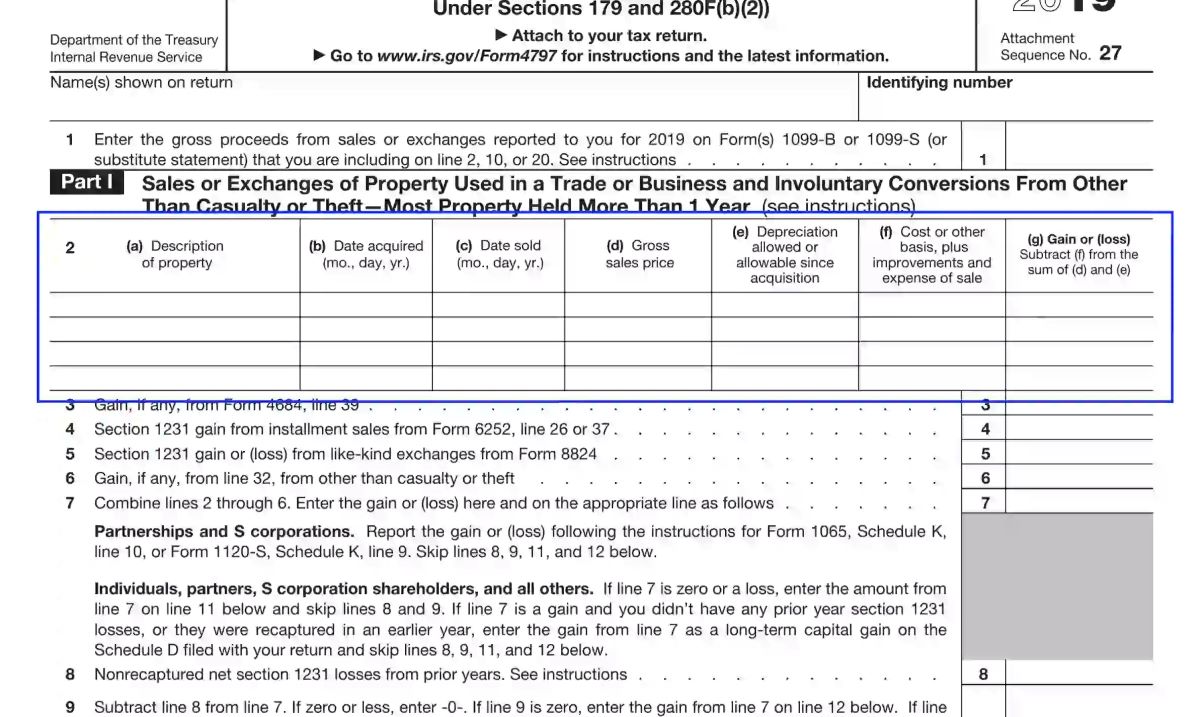
- Part I: Sales or Exchanges of Property
- Part II: Ordinary Gains and Losses
- Part III: 1231 Gains and Losses
- Part IV: Summary
This section is used to report the sale or exchange of property used in a trade or business. Taxpayers must provide details such as the date of the transaction, the description of the property, the sales price, and the adjusted basis of the property. If there are multiple sales or exchanges, separate columns should be used for each transaction.
This section is used to report ordinary gains and losses from the sale, exchange, or other disposition of property that does not qualify as a capital asset. Ordinary gains and losses are typically subject to regular income tax rates.
Part III is used to report gains and losses from the sale, exchange, or involuntary conversion of Section 1231 property. Section 1231 property refers to depreciable business property, such as real estate and certain tangible assets. Gains from Section 1231 property are treated as long-term capital gains, while losses are treated as ordinary losses.
This section is used to summarize the totals from Parts I, II, and III. Taxpayers must calculate their net gain or loss and enter it in this section.
It is important to carefully read the instructions for each section to understand the specific requirements and determine which sections are applicable to your situation. Additionally, taxpayers who have experienced an involuntary conversion of property, such as destruction, condemnation, or theft, may need to complete additional sections of Form 4797 to report these specific transactions.
As with any tax form, accuracy and thoroughness are crucial when completing Form 4797. Any errors or omissions can have potential consequences, such as an incorrect tax liability or an increased chance of being selected for an audit. Therefore, it is helpful to double-check the information entered on the form and seek professional advice if necessary.
Now that we have a better understanding of the different sections of Form 4797, let’s delve into the reporting process for the sale or exchange of property on the form.
Reporting the Sale or Exchange of Property on Form 4797
One of the main purposes of IRS Form 4797 is to report the sale or exchange of property used in a trade or business. This section of the form, Part I, requires taxpayers to provide detailed information about the transaction and accurately calculate the gain or loss associated with it.
Here are the key steps to reporting the sale or exchange of property on Form 4797:
- Enter the relevant information: In Part I, you will need to provide the date of the sale or exchange, a description of the property, and the details of the buyer or transferee. This information helps the IRS determine the nature of the transaction and verify the accuracy of the reported gain or loss.
- Calculate the sales price and adjusted basis: The sales price is the total amount received from the sale or exchange of the property. It includes any cash received, the fair market value of any property exchanged, and any liabilities assumed by the buyer. The adjusted basis, on the other hand, is the original cost of the property plus any improvements or adjustments made over time.
- Calculate the gain or loss: To determine the gain or loss from the sale or exchange, subtract the adjusted basis from the sales price. If the result is positive, you have a gain. If it is negative, you have a loss. This calculation helps determine the amount of taxable income or deductible loss associated with the transaction.
- Report the gain or loss: Once the amount of gain or loss has been calculated, it should be entered in the appropriate column on Form 4797. If you have multiple sales or exchanges, separate columns should be used for each transaction to ensure accurate reporting.
It’s important to note that the reporting requirements may vary depending on the type of property being sold or exchanged. For example, different rules apply to the sale of real estate compared to the sale of depreciable assets like vehicles or machinery. It’s crucial to carefully review the instructions provided with Form 4797 to ensure compliance with the specific reporting requirements for your transaction.
By accurately reporting the sale or exchange of property on Form 4797, you enable the IRS to correctly assess your tax liability. Failing to report these transactions or reporting them incorrectly can lead to penalties, unnecessary audits, or potential legal issues. To ensure accuracy and regulatory compliance, consider consulting with a tax professional or accountant who can provide guidance tailored to your specific situation.
Next, let’s explore the reporting requirements for the disposition of business assets on Form 4797.
Reporting the Disposition of Business Assets on Form 4797
Form 4797 not only captures the sale or exchange of property, but it also provides a means to report the disposition of business assets. Reporting the disposition of business assets on this form is essential for accurately calculating and reporting any gains or losses associated with the transaction.
Here are the key steps to reporting the disposition of business assets on Form 4797:
- Enter the asset information: In the applicable section of Form 4797, provide details about the asset you are disposing of, such as its description, date of disposal, and adjusted basis. This information helps the IRS understand the nature and value of the asset being disposed of.
- Calculate the gain or loss: Subtract the adjusted basis of the asset from the amount realized from the disposition to determine the gain or loss. The amount realized includes any cash received, the fair market value of any property received in exchange, and any liabilities assumed by the buyer.
- Determine the tax treatment: Depending on the nature of the asset and the holding period, the gain or loss may be classified as either ordinary or capital. Generally, assets held for one year or less are considered short-term, while assets held for more than one year are classified as long-term.
- Report the gain or loss: Enter the calculated gain or loss in the appropriate column on Form 4797. If you have multiple dispositions, use separate columns for each transaction to ensure accurate reporting.
It is important to note that the tax treatment of the gain or loss on the disposition of business assets will depend on various factors, including the asset type, holding period, and your business structure. For example, gains on the sale of depreciable assets like equipment or vehicles may be subject to depreciation recapture and taxed as ordinary income.
Additionally, if the asset was used partially for business and partially for personal purposes, you may need to allocate the gain or loss accordingly. It is critical to consult the IRS instructions for Form 4797 and potentially seek guidance from a tax professional to ensure compliance with the tax regulations specific to your situation.
By accurately reporting the disposition of business assets on Form 4797, you provide the necessary information for the IRS to assess your tax liability correctly. Failure to report these transactions or reporting them incorrectly may result in penalties, audits, or potential legal consequences. For complex or significant dispositions, it is advisable to consult with a tax professional who can provide expert advice tailored to your specific circumstances.
Next, let’s delve into the reporting requirements for the sale of depreciable property on Form 4797.
Reporting the Sale of Depreciable Property on Form 4797
Form 4797 plays a crucial role in reporting the sale of depreciable property used in a trade or business. This section of the form allows taxpayers to calculate and report any gains or losses associated with the sale of these assets and determine the tax treatment for their specific situation.
Here are the key steps to reporting the sale of depreciable property on Form 4797:
- Provide asset details: In the applicable section of Form 4797, enter all relevant information pertaining to the depreciable property you have sold. This includes the description of the asset, the date of sale, the adjusted basis, and the total depreciation claimed over the asset’s lifespan.
- Calculate the gain or loss: Subtract the adjusted basis from the amount realized from the sale to determine the gain or loss. The amount realized includes any cash received, the fair market value of any property exchanged, and any liabilities assumed by the buyer.
- Consider depreciation recapture: In the case of depreciable property, special rules apply regarding depreciation recapture. If the amount realized exceeds the asset’s adjusted basis, a portion of the gain may be treated as ordinary income and subject to depreciation recapture, while the remaining amount is treated as a capital gain.
- Determine the tax treatment: Depending on the holding period and the nature of the depreciable property, the gain or loss may be classified as either ordinary or capital. It is important to consult the IRS instructions for Form 4797 to understand the appropriate tax treatment for your specific circumstances.
- Report the gain or loss: Enter the calculated gain or loss in the appropriate column on Form 4797. If you have multiple depreciable property sales, be sure to use separate columns for each transaction to ensure accurate reporting.
It’s worth noting that the tax treatment of gains from the sale of depreciable property can vary depending on the depreciation method used, such as the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS) or the Section 179 deduction. These methods have their specific rules and guidelines for calculating depreciation and recapturing it upon the sale of the asset.
As with other sections of Form 4797, accuracy is essential when reporting the sale of depreciable property. Failing to report these transactions or reporting them incorrectly may lead to penalties, increased tax liabilities, or potential audits. If you have complex depreciable property sales or are unsure about the reporting requirements, it is advisable to consult with a tax professional who can provide guidance tailored to your specific situation.
Now that we have explored the reporting requirements for the sale of depreciable property, let’s move on to discussing special rules and considerations for partnerships and S corporations when filing Form 4797.
Special Rules and Considerations for Partnerships and S Corporations
Partnerships and S Corporations are unique business entities that have special rules and considerations when it comes to reporting the sale or disposition of property on IRS Form 4797. These entities often have multiple owners and follow specific tax regulations. Understanding the nuances for partnerships and S corporations can help ensure accurate reporting and compliance with the tax laws.
Here are some key considerations for partnerships and S corporations when filing Form 4797:
- Partnerships: In a partnership, the sale or disposition of property may result in gain or loss that is allocated to the individual partners. Each partner’s share of the gain or loss, along with any adjustments, should be reported on Schedule K-1, which is then used to complete Form 4797. Partnerships should provide detailed documentation to each partner, clearly indicating their share of the gain or loss and any other relevant information.
- S Corporations: Similarly, S Corporations must allocate the gain or loss from the sale or disposition of property to the individual shareholders. This allocation is reported on Schedule K-1, and each shareholder must use the information provided to complete their individual Form 4797. The S Corporation should ensure timely and accurate reporting of the allocated gain or loss to the shareholders.
- Depreciable property: For partnerships and S Corporations, special considerations arise when it comes to reporting the sale of depreciable property. Any potential depreciation recapture or capital gains or losses must be allocated among the partners or shareholders according to their ownership interests. It is crucial for partnerships and S Corporations to keep reliable records of adjusted basis, depreciation claimed, and any other relevant information related to the depreciable property.
- Multiple assets and transactions: Partnerships and S Corporations often have complex business structures, involving multiple assets and transactions. Each sale or disposition of property must be reported separately on Form 4797. It is essential to carefully document and classify each transaction in order to report them accurately on the form.
Partnerships and S Corporations must also comply with any specific rules or requirements outlined by the IRS for their respective tax status. It is recommended that these entities seek guidance from tax professionals or accountants with expertise in partnership and S Corporation taxation to ensure proper reporting and compliance.
By understanding the special rules and considerations for partnerships and S Corporations when filing Form 4797, these entities can report property transactions correctly, allocate gains or losses accurately, and provide the necessary information to individual partners or shareholders. This promotes compliance with tax regulations and reduces the risk of penalties or audits.
Now that we have covered the special considerations for partnerships and S Corporations, let’s move on to discussing useful tips for completing IRS Form 4797.
Tips for Completing IRS Form 4797
Filing tax forms like IRS Form 4797 can be a complex process. To help simplify the task and ensure accurate reporting, here are some valuable tips to consider when completing Form 4797:
- Organize and gather necessary information: Before filling out the form, gather all relevant documentation related to the sale or disposition of property. This includes details such as dates, descriptions, sales prices, adjusted basis, and any depreciation claimed. Having these records organized and readily available will facilitate the completion of the form.
- Read and understand the instructions: Carefully review the instructions provided with Form 4797. The instructions provide detailed explanations and examples for each section of the form. Understanding the specific requirements for your situation will help ensure accurate reporting and compliance with tax regulations.
- Utilize separate columns for multiple transactions: If you have multiple sales, exchanges, or dispositions of property, use separate columns in the applicable section of Form 4797 for each transaction. This helps avoid confusion and ensures accurate reporting of gains or losses associated with each individual transaction.
- Consider special rules and tax treatment: Be aware of any special rules or specific tax treatments that may apply to your situation. For example, certain types of property, such as depreciable assets, may require different calculations or have unique tax implications. Stay informed and consult with a tax professional if necessary to ensure compliance.
- Double-check calculations: Accurate calculations are crucial when completing Form 4797. Double-check all calculations to ensure the accuracy of gains or losses, depreciation recapture, and adjusted basis. Small errors could result in incorrect tax liability or trigger potential audits.
- Seek professional advice if needed: If you are uncertain about the reporting requirements or find the form too complex, consider consulting a tax professional or accountant with expertise in the specific area. They can provide guidance tailored to your situation, minimize errors, and ensure compliance with tax regulations.
- File the form in a timely manner: Be sure to file Form 4797 by the due date specified by the IRS. Late or incomplete filing may result in penalties or increased scrutiny from tax authorities. Plan ahead and allow sufficient time to complete and submit the form accurately.
Remember, the information provided on Form 4797 is crucial for accurately assessing your tax liability related to the sale or disposition of property. By following these tips and taking a meticulous approach, you can navigate the complexities of Form 4797 and fulfill your tax obligations with confidence.
Now, let’s explore some common errors to avoid when filing Form 4797.
Common Errors to Avoid When Filing Form 4797
Filing tax forms can be a daunting task, and mistakes can lead to compliance issues or potential audits. When completing IRS Form 4797, it is crucial to avoid common errors that may jeopardize the accuracy of your reporting. Here are some common errors to watch out for:
- Inaccurate or incomplete information: Ensure that all information provided on Form 4797 is accurate and complete. Double-check details such as dates, descriptions, sales prices, adjusted basis, and any depreciation claimed. Errors in these areas can lead to miscalculations and misreporting of gains or losses.
- Failure to report all relevant transactions: Be diligent in reporting all sales, exchanges, or dispositions of property on Form 4797. Each transaction should be accurately reported in the applicable section of the form. Failure to report a transaction or omitting it can result in penalties and potential audits.
- Incorrect tax treatment: Understand the appropriate tax treatment for gains or losses associated with different types of property. For example, depreciable assets may have different tax implications compared to real estate or other capital assets. If you are unsure, seek guidance from a tax professional or consult the IRS instructions for Form 4797.
- Not allocating gains or losses properly for partnerships and S corporations: In partnerships and S corporations, it is essential to allocate gains or losses appropriately among the partners or shareholders. Failing to allocate them accurately can lead to discrepancies in individual tax reporting and potential disagreements with the IRS.
- Forgetting depreciation recapture: Depreciation recapture applies to certain types of depreciable property. It is crucial to accurately calculate and report any depreciation recapture associated with the sale or disposition of depreciable assets. Ignoring or miscalculating depreciation recapture can trigger tax liabilities and potential penalties.
- Missed filing deadlines: Ensure that you file Form 4797 by the designated deadline specified by the IRS. Late filing can result in penalties or increased scrutiny from tax authorities. Plan ahead and allow sufficient time to complete and submit the form accurately.
By avoiding these common errors, you enhance the accuracy and integrity of your reporting on Form 4797. Taking the time to review your information, seek professional advice if needed, and adhere to tax regulations will help ensure compliance and avoid potential issues down the line.
Now that we have explored common errors to avoid, let’s conclude our discussion on IRS Form 4797.
Conclusion
IRS Form 4797, the Sales of Business Property, is a crucial tax form for reporting the sale or disposition of property used in a trade or business. By understanding the purpose, requirements, and various sections of Form 4797, individuals and businesses can accurately report gains or losses, calculate depreciation recapture, and determine their tax liability.
In this article, we explored the purpose of Form 4797, who needs to file it, and how to complete the form properly. We discussed the different sections of the form, including reporting the sale or exchange of property, the disposition of business assets, and the sale of depreciable property. We also highlighted special rules and considerations for partnerships and S corporations, as well as provided tips to ensure a smooth filing process and avoid common errors.
When completing Form 4797, it is vital to gather accurate information, carefully follow the instructions, and consider any special rules or tax treatments that apply to your situation. Double-check your calculations, allocate gains or losses correctly for partnerships and S corporations, and meet the filing deadlines to avoid penalties and potential audits.
If you find the process daunting or have complex transactions, don’t hesitate to seek guidance from a tax professional or accountant with expertise in tax law. They can provide tailored advice and ensure compliance with the regulations specific to your circumstances.
Successfully completing and filing Form 4797 helps youw accurately report your tax liability and play your part in maintaining the integrity of the tax system. It also ensures that you can confidently navigate the complex world of Finance and fulfill your financial and legal obligations.
Remember, staying informed and up to date with tax regulations is essential, as laws and requirements may change over time. By staying proactive and understanding your tax responsibilities, you can minimize complications and ensure smooth tax filing procedures in the future.